Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
General Notes On Style and Stylistics
Загружено:
Natalia ZdorenkoИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
General Notes On Style and Stylistics
Загружено:
Natalia ZdorenkoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
General notes on style and stylistics
1. 2. 3. 4.
Object and subject of stylistics Expressive means and stylistic devices Functional styles Meaning from a stylistics point of view
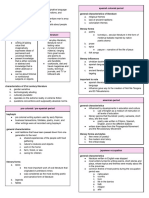
1). The object of stylistics is language because stylistics is the branch of linguistics. Stylistics tasks: 1. The study of the inventory of special language media which by their ontological features secure the desirable effect of the utterance 2. The investigation of certain types of texts which due to the choice and arrangements of language means are distinguished by the pragmatic aspects of the communication The types of text may be called functional style of language. Stylistics branch of linguistics. The subject is the study of language styles, their aims, structure, characteristic feature, the effect of the produce and the study of means and stylistic devices. Stylistic information comprises: 1. Emotive element (state of a speaker) 2. Expressive (attitude) 3. Evaluator 4. Stylistic aspect (what words are used) Additional information is called stylistic. The realization of additional information is always connected with the condition and participants of the word of communication. Stylistic information is information about connotation. The problem of the norm Norm should be regarded as the invariant of the phonemic, morphological, lexical and syntactical patterns circulating in language in action at a given period of time. This invariant embraces all variants. But one of the most characteristic of the norm is its flexibility. Language as system may figuratively be depicted as an employer of language in action. All rules and patterns of language which are connected and classified in words, of grammar, phonetic, lexicology, stylistics first appear in language in action and then they are generalized and framed as rules and patterns of language as a system. 2). All stylistic means can be divided into expressive means and stylistic devices The expressive means of a language are those phonetic, morphological, word-building, lexical, phraseological and syntactical forms which exist in language as a system for the purpose of logical or emotional intensification of the utterance. Expressive means exist on every level of the language. The most powerful are phonetic expressive means: Pitch Stress Possession Whispering A sing-song manner And other ways of using the voice are much more effective than any other means in intensifying an utterance emotionally or logically.
Speaking about morphological e/m we must admit the set of means is very poor: The usage of historical present The usage of shall in the 2nd and 3rd person The usage of demonstrative pronoun with an emphatic meaning Some processes of nominalization At the lexical level there are many words with due to their inner expressiveness constitute a special layer. All kinds of set phrases generally possessed the property of expressiveness. At the syntactical level there are many constructions which when set against synonymous neutral ones will reveal a certain degree of logical or emotional emphasis. Stylistic device is conscious intensification of some typical structural or semantic property of a language unit promote to a generalized status and thus becoming a generative modal. S/d always function in text as markers unities. They always carry some kind of additional information either emotional or logical. Any e/m can be promoted its s/d. 3). A functional style of the language is a system of interrelated language means which serves a definite aim in communication. A functional style appears mainly in the literary standard of a language. In the English literary standard we distinguish the following functional styles: 1. Belles-letters 2. Publicistic style 3. Newspaper style 4. Scientific prose style 5. The style of official documents 6. Colloquial style Style is a literary genre. 4). General meaning: 1. Lexical 2. Grammatical 3. Logical Additional meaning which is called stylistic Stylistic Pragmatic Contextual Additional meaning include: Expressive Emotive Evaluative components. The two aspects of meaning that may be given approximate analysis connotative relation denotative The connotative relation is the relation between sins and the interpreting signs. The denotative relation is the relation between signs and objects. Meaning I stylistics is viewed as a category which is able to acquire meanings imposed on the words by context. Types of meaning: 1. Denotational which informs of the subject of communication 2. Connotational which informs about the participants and condition of communication.
Meaning of language unit General Logical Lexical Grammatical Stylistic (pragmatic) Expressive Emotive evaluative
In general linguistics the problem of meaning deals mainly with such aspects of the term as the interrelation between meaning and concept, meaning and sign, meaning and referent. The general tendency is to regard meaning as something fixed at a given period of time. Logical or denotative meaning is the precise meaning of a feature or an idea or phenomenon or an object with the name of which we recognize the whole of the concept. The logical meaning of one word may denote different concepts. It is necessary to distinguish between primary and secondary logical meaning. It is essentially for the stylistics to distinguish between the primary and secondary meaning as some stylistic devices are built on the interplay between them. Pragmatic meaning Stylistics is the domain where meaning assumes paramount importance because it is applied not only to words, word combinations, sentences, but also to the manner of expression into which the matter is cast. In stylistics it is important to discriminate shades of meaning in order to adequately comprehend the idea of a passage or a complete work. Emotive component is connected with the expressive of feelings (pleasure, surprise) Emotive meaning is an intensifying derivative meaning (He looked dreadfully pitiful) The evaluative meaning of phrase or word may be positive negative neutral Stylistic connotation depends on its habitual units in one functional style.
Вам также может понравиться
- STYLISTICSДокумент15 страницSTYLISTICSNikoletta_Zhak83% (12)
- StylisticsДокумент17 страницStylisticsTeodora Alexandra100% (1)
- ABC in Techniques of Stylistics Analysis: A Practical Approach To Descriptive Grammar From Clause To Text StructureДокумент44 страницыABC in Techniques of Stylistics Analysis: A Practical Approach To Descriptive Grammar From Clause To Text StructureShaik R Rahman100% (5)
- Functional Stylistics of The Modern English LanguageДокумент13 страницFunctional Stylistics of The Modern English LanguageLamy MoeОценок пока нет
- Stylistics Module 1Документ6 страницStylistics Module 1Eman Bandoquillo100% (1)
- StylisticsДокумент40 страницStylistics2ygbk750% (2)
- Textual and Reader-Response StylisticsДокумент10 страницTextual and Reader-Response StylisticsDivine ArriesgadoОценок пока нет
- Stylistics and Discourse Analysis Module 2-The Literary Norms DescriptionДокумент6 страницStylistics and Discourse Analysis Module 2-The Literary Norms DescriptionJazlyn CalilungОценок пока нет
- Stylistics Course of Lectures 2020 Final (Repaired)Документ192 страницыStylistics Course of Lectures 2020 Final (Repaired)Mariam SinghiОценок пока нет
- Intro To StylisticsДокумент23 страницыIntro To StylisticsEnas ElsheikhОценок пока нет
- Stylistics 1Документ48 страницStylistics 1Chin Chai100% (1)
- Unit 3 Types of Stylistics IДокумент6 страницUnit 3 Types of Stylistics IEltbechar Bill50% (2)
- Introduction To StylisticsДокумент23 страницыIntroduction To StylisticsGenevieveA.Poso0% (1)
- Module 25 Introduction To StylisticsДокумент31 страницаModule 25 Introduction To Stylisticsshella mae pormento100% (2)
- Stylistics As A Branch of LinguisticsДокумент34 страницыStylistics As A Branch of Linguisticswamanse199283% (6)
- Intro 2 LinguisticsДокумент217 страницIntro 2 LinguisticsHelena LópezОценок пока нет
- An Introduction To LinguisticsДокумент68 страницAn Introduction To LinguisticsFatima Zahraa Darcy100% (2)
- Intro To StylisticsДокумент23 страницыIntro To StylisticsAsterCauliОценок пока нет
- 06 - Branches of StylisticsДокумент38 страниц06 - Branches of StylisticsKashif Iqbal MS Student EarthQuake-Spring 22100% (1)
- Branches of LinguisticsДокумент29 страницBranches of LinguisticsEngr Suleman Memon50% (2)
- Introduction To LinguisticsДокумент3 страницыIntroduction To Linguisticslotissumo100% (6)
- Branches of LinguiticsДокумент9 страницBranches of LinguiticsShanza 2311-FLL/BSENG/F20Оценок пока нет
- Types of StylisticsДокумент26 страницTypes of Stylisticsgsunuran75% (4)
- Final Module - Introduction To Stylistics PDFДокумент30 страницFinal Module - Introduction To Stylistics PDFRona Jane Sanchez100% (1)
- Stylistics and Discourse Analysis Syllabus DGPДокумент8 страницStylistics and Discourse Analysis Syllabus DGPJsaiii HiganaОценок пока нет
- Module 7 Stylistics and Discourse AnalysisДокумент41 страницаModule 7 Stylistics and Discourse AnalysisPrincess PortezaОценок пока нет
- Methods of Grammar TeachingДокумент4 страницыMethods of Grammar TeachingJoy Ann MendozaОценок пока нет
- OBE Syllabus - Introduction To Linguistics 1st PartДокумент4 страницыOBE Syllabus - Introduction To Linguistics 1st PartCathy Doodz100% (1)
- 1 Stylistics (2) Master 2Документ47 страниц1 Stylistics (2) Master 2Safa BzdОценок пока нет
- 7 Style and Scope of StylisticsДокумент24 страницы7 Style and Scope of StylisticsAwais Tareq67% (3)
- Handouts RZM, P. 1: Quantity Exhorts Speakers To "Make (Their) Contribution As Informative As Is Required ForДокумент5 страницHandouts RZM, P. 1: Quantity Exhorts Speakers To "Make (Their) Contribution As Informative As Is Required ForAyubkhan Sathikul AmeenОценок пока нет
- Literary Criticism IntroductionДокумент24 страницыLiterary Criticism IntroductionFlorejen Tadiaque100% (1)
- Linguistic Stylistics-Part1 PDFДокумент30 страницLinguistic Stylistics-Part1 PDFMis Lord93% (14)
- Introduction To Stylistics 1Документ15 страницIntroduction To Stylistics 1humayra100% (2)
- Functionalist StylisticsДокумент34 страницыFunctionalist Stylisticsromamarianguadana3156% (9)
- OBE in Language, Culture, and SocietyДокумент11 страницOBE in Language, Culture, and SocietyJerome RamonedaОценок пока нет
- Discourse AnalysisДокумент17 страницDiscourse Analysisimamcahundip100% (3)
- Genre AnalysisДокумент30 страницGenre Analysisvulinhchichi100% (2)
- Gramatical CategoryДокумент10 страницGramatical CategoryAna Karem Kashmir DelgadoОценок пока нет
- What Is StylisticsДокумент30 страницWhat Is StylisticsJauhar Jauharabad100% (4)
- Introduction To Stylistics - WK 1 PDFДокумент52 страницыIntroduction To Stylistics - WK 1 PDFYosra OuertaniОценок пока нет
- Introduction To LinguisticsДокумент40 страницIntroduction To LinguisticsFernandita Gusweni Jayanti0% (1)
- Introduction To SyntaxДокумент12 страницIntroduction To SyntaxAmir SohailОценок пока нет
- Linguistics Micro & Macro Levels PDFДокумент22 страницыLinguistics Micro & Macro Levels PDFMà Ř YãmОценок пока нет
- Stylistics Syllabus Sample OnlyДокумент8 страницStylistics Syllabus Sample OnlyMaria Edna R. Iñigo100% (4)
- Lexical Cohesion: Discourse Analysis - Lecture 4Документ52 страницыLexical Cohesion: Discourse Analysis - Lecture 4Marina TanovićОценок пока нет
- STYLISTICДокумент2 страницыSTYLISTICElizabeth Barruga100% (3)
- Syntax - The Analysis of Sentence StructureДокумент22 страницыSyntax - The Analysis of Sentence StructureHafeed100% (1)
- EL 101 Lang, Culture & SocietyДокумент11 страницEL 101 Lang, Culture & SocietyAquinas Thomas100% (1)
- Stylistics - Lecture 1Документ28 страницStylistics - Lecture 1Елизавета ГармашОценок пока нет
- StylisticsДокумент8 страницStylisticsLucy HarutyunyanОценок пока нет
- Chistovik Shpargalok Po StilistikeДокумент4 страницыChistovik Shpargalok Po StilistikeАнна ГречухаОценок пока нет
- General Notes On Styles and StylisticsДокумент13 страницGeneral Notes On Styles and Stylisticsanna_eniОценок пока нет
- News 1Документ20 страницNews 1yaaaa4202Оценок пока нет
- B68C5 Pedash e StylisticsДокумент40 страницB68C5 Pedash e StylisticsElena MelnykovychОценок пока нет
- General Problems To The Stylistics OutlineДокумент255 страницGeneral Problems To The Stylistics Outlinesarah gaia ruoccoОценок пока нет
- лекции по стилистикеДокумент24 страницылекции по стилистикеKate AndrianovaОценок пока нет
- General Problems To The Stylistics OutlineДокумент255 страницGeneral Problems To The Stylistics OutlineMuhammad Sajid Us Salam67% (3)
- Stylistic- практ. заняття №1Документ4 страницыStylistic- практ. заняття №1Христина МарчукОценок пока нет
- Written Report of EXCEPT The TRUTHДокумент7 страницWritten Report of EXCEPT The TRUTHBethel Montemayor67% (3)
- Amorous Heian Heroes The Irogonomi As AДокумент5 страницAmorous Heian Heroes The Irogonomi As AhelenamxОценок пока нет
- Brahman AsДокумент2 страницыBrahman Asvrohit308Оценок пока нет
- I Cried For You Chords by Katie Meluatabs at Ultimate Guitar ArchiveДокумент2 страницыI Cried For You Chords by Katie Meluatabs at Ultimate Guitar ArchiveIván EscobarОценок пока нет
- BlossomДокумент27 страницBlossomNatacha Kamdem50% (2)
- A Brief History of American Literature and TheirДокумент10 страницA Brief History of American Literature and TheirToppeee toppeeeОценок пока нет
- CI Poems About DeathДокумент8 страницCI Poems About DeathKelsey CooperОценок пока нет
- 6 The Crown As Corporation by Frederick Maitland 1901Документ14 страниц6 The Crown As Corporation by Frederick Maitland 1901trustkonanОценок пока нет
- 21st CL 12Документ4 страницы21st CL 12Lia PalmaОценок пока нет
- Works of Rizal While in USTДокумент9 страницWorks of Rizal While in USTKarlo Antonio100% (2)
- 7 Key Concepts PosterДокумент1 страница7 Key Concepts PosterJerome Reyes ArellanoОценок пока нет
- English GR 2Документ14 страницEnglish GR 2Jovancy PaulrajОценок пока нет
- Creative WritingДокумент28 страницCreative WritingKina Mangumpit100% (1)
- Module 3 Creative NonfictionДокумент37 страницModule 3 Creative Nonfictionelmer rivero0% (1)
- Https WWW - Shmoop.com Study-Guides Poetry Church-Going Summary Stanza-1Документ4 страницыHttps WWW - Shmoop.com Study-Guides Poetry Church-Going Summary Stanza-1Ritankar RoyОценок пока нет
- The Restoration of Iban IUR' Motive Into Iban Pop SongДокумент5 страницThe Restoration of Iban IUR' Motive Into Iban Pop SongInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Contemporary Philippine Ars From The RegionДокумент4 страницыContemporary Philippine Ars From The RegionLeah Jean VillegasОценок пока нет
- 1 5Документ22 страницы1 5rafael g. manriqueОценок пока нет
- Karthavirya Dvadasha Nama StotramДокумент2 страницыKarthavirya Dvadasha Nama Stotrammlalithssk0% (1)
- Rahat Indori - Poems - : Classic Poetry SeriesДокумент16 страницRahat Indori - Poems - : Classic Poetry SeriesSHASHANK SINGH RATHOREОценок пока нет
- Jayanta Mahapatra PoemsДокумент13 страницJayanta Mahapatra PoemsAastha SuranaОценок пока нет
- BlackoutДокумент2 страницыBlackoutapi-280476563Оценок пока нет
- The Divine LoopholeДокумент8 страницThe Divine LoopholeShrestha Ghosh Mullick0% (1)
- Gen Ed FilipinoДокумент3 страницыGen Ed FilipinoBOBOKOОценок пока нет
- Stetkevych Al-Sharif Al-Radi JAL PDFДокумент31 страницаStetkevych Al-Sharif Al-Radi JAL PDFSuzanne StetkevychОценок пока нет
- Spring 2015 CatalogДокумент108 страницSpring 2015 CatalogsoulofОценок пока нет
- Ela Standards 2nd GradeДокумент5 страницEla Standards 2nd Gradeapi-444071223Оценок пока нет
- Teaching Literature in The Mother Language: S A D XviiДокумент7 страницTeaching Literature in The Mother Language: S A D XviiJamia SanicoОценок пока нет
- Mishima, Yukio - Acts of Worship (Kodansha, 1989) PDFДокумент219 страницMishima, Yukio - Acts of Worship (Kodansha, 1989) PDFMohaimin Riaz100% (2)
- Hispanic and European Studies Program-Universitat Pompeu Fabra 2011Документ6 страницHispanic and European Studies Program-Universitat Pompeu Fabra 2011Gina FreyreОценок пока нет
- Summary: The Laws of Human Nature: by Robert Greene: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandSummary: The Laws of Human Nature: by Robert Greene: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (30)
- The Stoic Mindset: Living the Ten Principles of StoicismОт EverandThe Stoic Mindset: Living the Ten Principles of StoicismРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (12)
- Stoicism The Art of Happiness: How the Stoic Philosophy Works, Living a Good Life, Finding Calm and Managing Your Emotions in a Turbulent World. New VersionОт EverandStoicism The Art of Happiness: How the Stoic Philosophy Works, Living a Good Life, Finding Calm and Managing Your Emotions in a Turbulent World. New VersionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (51)
- The Emperor's Handbook: A New Translation of The MeditationsОт EverandThe Emperor's Handbook: A New Translation of The MeditationsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (10)
- The Secret Teachings Of All Ages: AN ENCYCLOPEDIC OUTLINE OF MASONIC, HERMETIC, QABBALISTIC AND ROSICRUCIAN SYMBOLICAL PHILOSOPHYОт EverandThe Secret Teachings Of All Ages: AN ENCYCLOPEDIC OUTLINE OF MASONIC, HERMETIC, QABBALISTIC AND ROSICRUCIAN SYMBOLICAL PHILOSOPHYРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (4)
- Stoicism: How to Use Stoic Philosophy to Find Inner Peace and HappinessОт EverandStoicism: How to Use Stoic Philosophy to Find Inner Peace and HappinessРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (86)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldОт EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (64)
- How States Think: The Rationality of Foreign PolicyОт EverandHow States Think: The Rationality of Foreign PolicyРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (7)
- The Authoritarian Moment: How the Left Weaponized America's Institutions Against DissentОт EverandThe Authoritarian Moment: How the Left Weaponized America's Institutions Against DissentРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (17)
- The Story of Philosophy: The Lives and Opinions of the Greater PhilosophersОт EverandThe Story of Philosophy: The Lives and Opinions of the Greater PhilosophersОценок пока нет
- Stonewalled: My Fight for Truth Against the Forces of Obstruction, Intimidation, and Harassment in Obama's WashingtonОт EverandStonewalled: My Fight for Truth Against the Forces of Obstruction, Intimidation, and Harassment in Obama's WashingtonРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (21)
- This Is It: and Other Essays on Zen and Spiritual ExperienceОт EverandThis Is It: and Other Essays on Zen and Spiritual ExperienceРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (94)
- It's Easier Than You Think: The Buddhist Way to HappinessОт EverandIt's Easier Than You Think: The Buddhist Way to HappinessРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (60)
- There Is a God: How the World's Most Notorious Atheist Changed His MindОт EverandThere Is a God: How the World's Most Notorious Atheist Changed His MindРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (71)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosОт Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (207)
- Body Language: Decode Human Behaviour and How to Analyze People with Persuasion Skills, NLP, Active Listening, Manipulation, and Mind Control Techniques to Read People Like a Book.От EverandBody Language: Decode Human Behaviour and How to Analyze People with Persuasion Skills, NLP, Active Listening, Manipulation, and Mind Control Techniques to Read People Like a Book.Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (81)
- Surrounded by Idiots: The Four Types of Human Behavior and How to Effectively Communicate with Each in Business (and in Life) (The Surrounded by Idiots Series) by Thomas Erikson: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandSurrounded by Idiots: The Four Types of Human Behavior and How to Effectively Communicate with Each in Business (and in Life) (The Surrounded by Idiots Series) by Thomas Erikson: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- The Courage to Be Disliked: How to Free Yourself, Change Your Life, and Achieve Real HappinessОт EverandThe Courage to Be Disliked: How to Free Yourself, Change Your Life, and Achieve Real HappinessРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (1603)