Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
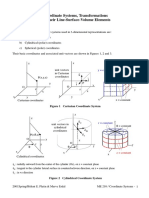
Curvilinear Coordinates
Загружено:
Aji PramonoИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Curvilinear Coordinates
Загружено:
Aji PramonoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
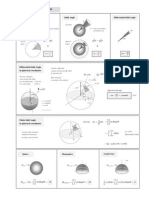
Method I: Trigonometry
cos sin sin sin cos = + + r i j k
r
,
- not constant
1/14/2012 1
Polar angle
Azimuthal angle
,
Spherical Coordinates:
r
x
y
z
A
sinu
sinucos
sinusin
cosu
Consider then imaging that you
decompose it along i, j, k
r
( )
( )
2 2 2
1
1
sin cos
sin sin
cos
cos /
tan /
x r
y r
z r
r x y z
z r
y x
=
=
=
= + +
=
=
1/14/2012 2
Polar angle unit vector
First, draw in x-y plane, then
decompose along i and j
sin cos = + i j
r
x
y
z
i
j
x
y
z
A
2
-sinu
cosu
i
j
cosucos
cosusin
Azimuthal angle unit vector
cos cos sin cos sin = + i j k
1/14/2012 3
r
x
y
z
A
Polar angle unit vector
2
2
sin
sin
sin
'
d dr rd r d
d r drd d
d r d d
d rdrd
= + +
=
=
=
l r
a r
a
Surface in x-y plan
Surface on sphere
d
d
x
y
z
dr
( )
( )
2 2 2
1
1
sin cos
sin sin
cos
cos /
tan /
x r
y r
z r
r x y z
z r
y x
=
=
=
= + +
=
=
Cylindrical Coordinates:
j i
j i r
r k
r k
k r
r k k r
k r k r A
cos sin
sin cos
cos
sin
+ =
+ =
=
=
=
= = =
+ = + =
z r
A A A A
r
x
y
z
i, j, k constant vectors
- not constant
r
,
A
1/14/2012 4
Polar angle; azimuthal angle
Much easier to work out in cylindrical coordinates, as z (k) is fixed
1/14/2012 5
r
x
y
z
k
cos
sin
x r
y r
z z
=
=
=
d dr rd dz
d rdrd dz
d rd dz
= + +
=
=
l r z
a r
Cylindrical Coordinates:
d
dz
dr
Вам также может понравиться
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsОт EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Differential Geometry: Computer Vision #8Документ49 страницDifferential Geometry: Computer Vision #8aerogem618Оценок пока нет
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsОт EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Cylindrical CoordinatesДокумент12 страницCylindrical CoordinatesJyothsna VayyalaОценок пока нет
- Niu Physics PHD Candidacy Exam - Standard Formula SheetДокумент3 страницыNiu Physics PHD Candidacy Exam - Standard Formula SheetMiguel AngelОценок пока нет
- Complex Numbers (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankОт EverandComplex Numbers (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Applied Electromagnetics 7th EditionДокумент20 страницFundamentals of Applied Electromagnetics 7th EditionErayAlbayrakОценок пока нет
- Applications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankОт EverandApplications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankОценок пока нет
- 5A. Triple Integrals in Rectangular and Cylindrical CoordinatesДокумент6 страниц5A. Triple Integrals in Rectangular and Cylindrical CoordinatesadsDgggОценок пока нет
- ECE380 Vector InformationДокумент3 страницыECE380 Vector Informationmikemm5Оценок пока нет
- AE321 Homework SolutionsДокумент13 страницAE321 Homework SolutionsArthur Ding100% (1)
- AE 321 - Solution of Homework #10Документ6 страницAE 321 - Solution of Homework #10Arthur DingОценок пока нет
- Homework Vector SolnДокумент7 страницHomework Vector SolnReemALMousawiОценок пока нет
- Coordinate SystemsДокумент4 страницыCoordinate SystemsSundar SkОценок пока нет
- TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS AND FORMULASДокумент4 страницыTRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS AND FORMULASZee Shan100% (1)
- Mathematics N3 Trigonomentry Tutorial Notes PDFДокумент15 страницMathematics N3 Trigonomentry Tutorial Notes PDFKatlego MofommeОценок пока нет
- Triple Integrals in Cylindrical and Spherical CoordinatesДокумент67 страницTriple Integrals in Cylindrical and Spherical CoordinatesJohn Rafael R. CanoosОценок пока нет
- #1 Coordinate Systems: 1.1 Cartesian CoordinatesДокумент8 страниц#1 Coordinate Systems: 1.1 Cartesian CoordinatesShaheer DurraniОценок пока нет
- Choice of Suitable Coordinate System: Curvilinear CoordinatesДокумент15 страницChoice of Suitable Coordinate System: Curvilinear Coordinatespetrified pixelОценок пока нет
- Spherical CoordinatesДокумент1 страницаSpherical CoordinatesLynn KimОценок пока нет
- Matek KepletekДокумент2 страницыMatek KepletekblackjackkОценок пока нет
- Geometry of Radiation: Plane Angle Solid Angle Differential Solid AngleДокумент1 страницаGeometry of Radiation: Plane Angle Solid Angle Differential Solid Angleapi-248972228Оценок пока нет
- Geometry of Radiation: Plane Angle Solid Angle Differential Solid AngleДокумент1 страницаGeometry of Radiation: Plane Angle Solid Angle Differential Solid Angle1anoopishereОценок пока нет
- ECSE 353 FormulasДокумент6 страницECSE 353 FormulasEileen FuОценок пока нет
- Formulario - Teoria ElectromagneticaДокумент5 страницFormulario - Teoria ElectromagneticaErikc GutiérrezОценок пока нет
- Formula Sheet CME 342Документ4 страницыFormula Sheet CME 342Ahmad ElhajОценок пока нет
- CoordinateSystemReview PDFДокумент7 страницCoordinateSystemReview PDFAnandОценок пока нет
- Solid Angle Cheat SheetДокумент1 страницаSolid Angle Cheat SheetRaj BhaktaОценок пока нет
- All CE FormulasДокумент131 страницаAll CE FormulasKathleen LacsonОценок пока нет
- 08 Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates - HandoutДокумент12 страниц08 Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates - HandoutJelor GallegoОценок пока нет
- EMATH 4th Quarter Week 5 ModuleДокумент8 страницEMATH 4th Quarter Week 5 ModuleB - HERRERA, Jhian Carlo G.Оценок пока нет
- Trigonometric Identities Basic Integrals of Elementary FunctionsДокумент4 страницыTrigonometric Identities Basic Integrals of Elementary FunctionsexppurposeexpОценок пока нет
- Maths PMR Form 3 NotesДокумент4 страницыMaths PMR Form 3 NotesAkashahNadiha MarsyaAmnaОценок пока нет
- The Inverse Z-TransformДокумент16 страницThe Inverse Z-TransformMohammad Gulam AhamadОценок пока нет
- Bursa Wolfe TransformationДокумент7 страницBursa Wolfe TransformationGabrielLorenzoBuetaОценок пока нет
- Trigonometric Identities Basic Integrals of Elementary FunctionsДокумент4 страницыTrigonometric Identities Basic Integrals of Elementary FunctionsErnest TiongОценок пока нет
- XI Math Ch3 Trigonometry Chapter Notes AugДокумент11 страницXI Math Ch3 Trigonometry Chapter Notes Augvivekantony0% (1)
- Info Sheet t2 2012Документ4 страницыInfo Sheet t2 2012Luthando PuzaОценок пока нет
- Lec Week10Документ4 страницыLec Week10Haripriya RadhakrishnanОценок пока нет
- Advanced Higher Maths: Formulae: Essential Trigonometric IdentitiesДокумент5 страницAdvanced Higher Maths: Formulae: Essential Trigonometric IdentitiesknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- Complex Numbers-Class NotesДокумент5 страницComplex Numbers-Class NotesSwapnendu SikdarОценок пока нет
- Algebra and Functions GuideДокумент1 страницаAlgebra and Functions GuideNaqibullah MohammadОценок пока нет
- 6.641 Electromagnetic Fields, Forces, and Motion: Mit OpencoursewareДокумент8 страниц6.641 Electromagnetic Fields, Forces, and Motion: Mit OpencoursewareAhmed AiadОценок пока нет
- Tutorial v1Документ5 страницTutorial v1Ram KumarОценок пока нет
- TrigonometruyДокумент3 страницыTrigonometruyRitu SharmaОценок пока нет
- Rotational Motion 2009 7Документ85 страницRotational Motion 2009 7Julian BermudezОценок пока нет
- FORMULAE Formulas for Algebra, Calculus, Statistics, Geometry and TrigonometryДокумент3 страницыFORMULAE Formulas for Algebra, Calculus, Statistics, Geometry and TrigonometryKama AzizОценок пока нет
- 2010 01 12 3DBeam CDT6Документ65 страниц2010 01 12 3DBeam CDT6r1c4rd0f3rОценок пока нет
- 13-Surface Integrals - Part 2Документ10 страниц13-Surface Integrals - Part 2Mohd Afiq AminОценок пока нет
- Mathematics For Physics PDFДокумент5 страницMathematics For Physics PDFReddyvari Venugopal100% (1)
- Ah FormulaeДокумент5 страницAh FormulaeVijay RajuОценок пока нет
- Trigonometry Review: Opp Hyp Hyp Opp Adj Hyp Hyp Adj Opp Opp Adj AdjДокумент6 страницTrigonometry Review: Opp Hyp Hyp Opp Adj Hyp Hyp Adj Opp Opp Adj Adjkoulis19920% (1)
- Complex Mappings 2Документ43 страницыComplex Mappings 2Akash PОценок пока нет
- Engineering Electrodynamics MidtermДокумент36 страницEngineering Electrodynamics MidtermSrinivas PrasadОценок пока нет
- Integral Calculus 15 16 20Документ6 страницIntegral Calculus 15 16 20Sharmaine FajutaganaОценок пока нет
- Triple SubstitutionДокумент4 страницыTriple SubstitutionTinaОценок пока нет
- BAHIR DAR UNIVERSITY FACULITY OF CIVIL AND WATER RESOURCE ENGINERRIG DEPARTMENT OF STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING FINITE ELEMENT METHEOD OF ANALYSIS ASSIGNMENT 1Документ6 страницBAHIR DAR UNIVERSITY FACULITY OF CIVIL AND WATER RESOURCE ENGINERRIG DEPARTMENT OF STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING FINITE ELEMENT METHEOD OF ANALYSIS ASSIGNMENT 1Mesfin FikreaОценок пока нет
- 3A. Double Integrals in Rectangular CoordinatesДокумент8 страниц3A. Double Integrals in Rectangular Coordinatesjuan perez lunaОценок пока нет
- C Programming Lesson On One-Dimensional ArraysДокумент3 страницыC Programming Lesson On One-Dimensional Arraysroyce542Оценок пока нет
- Petrophysics in Horizontal WellsДокумент13 страницPetrophysics in Horizontal WellsusuarioОценок пока нет
- Resonance: Resonance Describes The Phenomenon of Increased Amplitude That Occurs WhenДокумент10 страницResonance: Resonance Describes The Phenomenon of Increased Amplitude That Occurs WhenLijukrishnanОценок пока нет
- Tutsheet 5Документ2 страницыTutsheet 5vishnuОценок пока нет
- IC Training Matrix Template Sample 11623Документ5 страницIC Training Matrix Template Sample 11623Nithin MathaiОценок пока нет
- TNPSC GROUP I PRELIM EXAM SOLUTIONSДокумент18 страницTNPSC GROUP I PRELIM EXAM SOLUTIONSMONNISH G. MB11564Оценок пока нет
- Error MsgsДокумент162 страницыError Msgsapi-19417993Оценок пока нет
- Singapore IGF Parallax Betwn Science & GitaДокумент116 страницSingapore IGF Parallax Betwn Science & GitasathviksraoОценок пока нет
- SME QA Answering Directions General PDFДокумент20 страницSME QA Answering Directions General PDFSagan AlamОценок пока нет
- Complete - Quarter 3 - Science 7 - Weeks 1 - 8Документ42 страницыComplete - Quarter 3 - Science 7 - Weeks 1 - 8alyzamarie deramos100% (1)
- Visit TutorialДокумент83 страницыVisit Tutorialfab1991Оценок пока нет
- คำอธิบายกระบวนวิชาДокумент12 страницคำอธิบายกระบวนวิชาCuga SaharathОценок пока нет
- R Program Record 2023Документ12 страницR Program Record 2023Niveditha NisanamОценок пока нет
- PHYSICS Engineering (BTech/BE) 1st First Year Notes, Books, Ebook - Free PDF DownloadДокумент205 страницPHYSICS Engineering (BTech/BE) 1st First Year Notes, Books, Ebook - Free PDF DownloadVinnie Singh100% (2)
- The Estimation of Pi Using Monte Carlo Technique With Interactive AnimationsДокумент7 страницThe Estimation of Pi Using Monte Carlo Technique With Interactive AnimationsMunjiba NiloopherОценок пока нет
- Q-Learning Based Link Adaptation in 5GДокумент6 страницQ-Learning Based Link Adaptation in 5Gkalyank1Оценок пока нет
- Golden Ratio PropertiesДокумент6 страницGolden Ratio Propertiesneiljain421Оценок пока нет
- Structural Design of Multi-Storeyed Building by U H VaryaniДокумент5 страницStructural Design of Multi-Storeyed Building by U H VaryanidineshОценок пока нет
- Further Pure Mathematics FP1 - Mock - MsДокумент4 страницыFurther Pure Mathematics FP1 - Mock - Mswa030waОценок пока нет
- Measuring and Modeling The Fatigue Performance of Elastomers For Applications With Complex Loading RequirementsДокумент24 страницыMeasuring and Modeling The Fatigue Performance of Elastomers For Applications With Complex Loading RequirementssanthoshnlОценок пока нет
- INFERENTIAL STATISTICS: Hypothesis Testing: Learning ObjectivesДокумент5 страницINFERENTIAL STATISTICS: Hypothesis Testing: Learning Objectiveslynette cantosОценок пока нет
- DLL Quarter 4 Week 6 MATHEMATICS 3Документ4 страницыDLL Quarter 4 Week 6 MATHEMATICS 3Cherry ursuaОценок пока нет
- D 2718 - 00 Rdi3mtgtmda - PDFДокумент6 страницD 2718 - 00 Rdi3mtgtmda - PDFRufo CascoОценок пока нет
- Textbook of Heat Transfer - S. P. Sukhatme PDFДокумент122 страницыTextbook of Heat Transfer - S. P. Sukhatme PDFVineet Mathew50% (6)
- Interacción Tabique PórticoДокумент225 страницInteracción Tabique Pórticodalex_tauro93Оценок пока нет
- Checkpoint 2016 - P2Документ15 страницCheckpoint 2016 - P2seetОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 Linkage, Recombination, and Eukaryotic Gene MappingДокумент20 страницChapter 7 Linkage, Recombination, and Eukaryotic Gene MappingSiamHashan100% (1)
- Problem 12-53: A T A V TДокумент57 страницProblem 12-53: A T A V Tadam johnsonОценок пока нет
- PPTДокумент18 страницPPTSaipreethiОценок пока нет
- Mix Design PresentationДокумент313 страницMix Design Presentationbsk109Оценок пока нет