Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Tramadol HCL
Загружено:
Cherrylyn FerrerИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Tramadol HCL
Загружено:
Cherrylyn FerrerАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
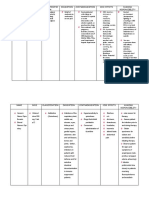
GENERIC/ BRAND NAME & CLASSIFICATION Generic: tramadol hydrochloride Brand: Ultram Classification: central nervous system (cns)
agent; analgesic; narcotic (opiate) agonist
DOSE, STRENGTH & FORMULATION Ordered: 50 mg IVTT Timing: every 6 hours Duration: Other forms: tablets: 50 mg
INDICATION/ MECHANISMS OF DRUG ACTION Indications: Management of moderate to moderately severe pain. Mechanism of action: A centrally acting analgesic not related chemically to opiates. Precise mechanism is not known. Two complimentary mechanisms may be applicable: It may bind to muOpioid receptors and inhibit reuptake or norepinephrine and serotonin. The analgesic effect is only partially antagonized by the antagonist naloxone. Causes significantly less respiratory depression than morphine. In contrast to morphine, tramadol does not cause release of histamine. Produces dependence of mu- opioid type (i.e., like codeine or dextropropoxyphene); however, there is little evidence of abuse.
ADVERSE/ SIDE EFFECTS DRUG INTERACTION CNS: dizziness, vertigo, headache, somnolence, CNS stimulation, anxiety, confusion, incoordination, euphoria, nervousness, sleep disorders, seizures, paresthesia, cognitive dysfunction, hallucinations, tremor, amnesia, concentration difficulty, abnormal gait, migraine, development of drug dependence, speech disorders, depression, increased risk of seizures. GI: Nausea, constipation, vomiting, dyspepsia, dry mouth, diarrhea, abdominal pain, anorexia, flatulence, GI bleeding, hepatitis, stomatitis, dysgeusia, liver failure.
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
RATIONALE
CLIENT TEACHING
Check doctors order. Let the patient verbalize her name.
- To prevent medication error. - To correctly identify the patient so as to prevent error. - So that the patient will not be knowledge deficit about the medication she is taking. - Keeping patient well- hydrated reduces risk of nephrotoxicity. - To indicate patients baseline data and monitor drugs effectiveness. - To establish proper precationary measures and management for possible adverse effects of the drug.
Explain the possible side effects of the drug.
1. Do not perform activities that require mental alertness; drug may cause drowsiness and impair mental or physical performance. Alcohol may intensify drug effects. 2. Report lack of response. Review list of side effects (nausea, dizziness, constipation) that one may experience and report if persistent or intolerable. 3. Advise patient to avoid alcohol while taking tramadol. 4. Urge caregivers to watch patient closely for evidence of suicidal tendencies, especially when therapy starts or dosage changes and to report
Monitor any changes in intake and output of the patient.
Assess patients infection before therapy and regularly thereafter. Be alert for signs and drug interactions like fever and rashes, notify physician immendiately.
Tolerance occurs but is relatively mild; the withdrawal syndrome is not as severe as with other opiates. Rapidly absorbed after PO administration. Food does not affect the rate or extent of absorption.
CV: Vasodilation, syncope, orthostatic hypotension, hypertension, tachycardia, abnormal ECG, myocardial ischemia, palpitations, pulmonary edema/ embolism. Dermatologic: pruritus, sweating, rash, urticaria, vesicles, StevensJohnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis. Body as a whole: asthenia, malaise, allergic reation, accidental injury, weight loss, suicidal tendency. GU: urinary retention/ frequency, menopausal symptoms, dysuria, menstrual disorder. Ophthalmic: miosis, visual disturbances, cataracts. Miscellaneous: anaphylaxis, deafness, tinnitus, hypertonia, dyspnea, serotonin
Assess patients and familys knowledge of drug therapy. Avoid giving tramadol to patients with acute abdominal conditions.
- To know patients and familys knowledge about the drug. - It may mask evidence and disrupt assessment of the abdomen.
concerns at once to prescriber.
syndrome. Drug Interaction: Alcohol/ increase respiratory depression. Anesthetics, general/ increase respiratory depression. Carbamazepine/ decrease tramadol effect R/T increase metabolism. CNS depressants/ Additive CNS depression. Cyclobenzaprine/ increase risk of seizures. Digoxin/ increase risk (rare) of digoxin toxicity. MAO Inhibitors/ increase risk of seizures. Naloxone/ increase risk of seizures if naloxone used for tramadol overdose. Promethazine/ increase risk of seizures. Quinidine/ increase levels of tramadol and decrease levels of M1 R/T inhibition of metabolism. SSRIs/ increase risk
of seizures and increase risk of serotonin syndrome. Tricyclic antidepressants/ increase risk of seizures. Warfarin/ increase PT and INR.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Neuroscience of CompassionДокумент77 страницThe Neuroscience of CompassionAnonymous LXV7PwpОценок пока нет
- Generic NameДокумент2 страницыGeneric NameMichael PalmaОценок пока нет
- CXC CSEC HSB January 2017 P2 PDFДокумент17 страницCXC CSEC HSB January 2017 P2 PDFSayyid Muhammad Aqeed AabidiОценок пока нет
- Chart of Starfinder Playable Races Through Alien Archive 3Документ8 страницChart of Starfinder Playable Races Through Alien Archive 3Thallis ThawanОценок пока нет
- Difflam Drug StudyДокумент1 страницаDifflam Drug StudyDanlee EstandaОценок пока нет
- Knee Examination - OSCE SkillsДокумент3 страницыKnee Examination - OSCE Skillsfranksmith51Оценок пока нет
- Drug Study2Документ8 страницDrug Study2zbestgurlОценок пока нет
- Drug Study Mother TДокумент14 страницDrug Study Mother TEuzelle Jeena ArandaОценок пока нет
- Mental Health - PsychopharmacologyДокумент4 страницыMental Health - PsychopharmacologyRenetria DrakeОценок пока нет
- Carboprost Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыCarboprost Drug StudyAjay SupanОценок пока нет
- Culture, Body, and LanguageДокумент445 страницCulture, Body, and LanguageViktoria Slabkowskaya100% (2)
- Case Study VithoulkasДокумент11 страницCase Study VithoulkasTatiana Savciuc75% (4)
- 2.2 - Powerpoint D - Effects of Exercise On The Cardiovascular SystemДокумент23 страницы2.2 - Powerpoint D - Effects of Exercise On The Cardiovascular SystemAshraf ShaikhОценок пока нет
- Tramadol (Dolcet)Документ1 страницаTramadol (Dolcet)Beverly Ann de LeonОценок пока нет
- Felodipine CefuroximeДокумент3 страницыFelodipine CefuroximecotyboyОценок пока нет
- Nifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyДокумент5 страницNifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyAllyne GavinoОценок пока нет
- Drug TramadolДокумент2 страницыDrug TramadolFlauros Ryu Jabien100% (2)
- Mupirocin Drug StudyДокумент1 страницаMupirocin Drug StudyArthur Christopher Corpuz0% (1)
- Drug Study DemerolДокумент2 страницыDrug Study DemerolKayelyn-Rose CombateОценок пока нет
- QuetiapineДокумент3 страницыQuetiapineMichael KuzbytОценок пока нет
- Drug Study Vit B ComplexДокумент2 страницыDrug Study Vit B Complexbekbekk cabahugОценок пока нет
- Tramadol UltramДокумент2 страницыTramadol UltramatchiekОценок пока нет
- Senokot-S (Senna Concentrate 8.6mg + Docusate Sodium 50mg)Документ2 страницыSenokot-S (Senna Concentrate 8.6mg + Docusate Sodium 50mg)E100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY CLOBETASOL CREAMrevisedДокумент2 страницыDRUG STUDY CLOBETASOL CREAMrevisedswitchlers anneОценок пока нет
- CefuroximeДокумент1 страницаCefuroximeRox SanОценок пока нет
- Oraa, Jamie - Drug Study Surgical WardДокумент1 страницаOraa, Jamie - Drug Study Surgical WardJamie LeeОценок пока нет
- Drug Study Cushing's SyndromeДокумент5 страницDrug Study Cushing's SyndromeSelena MarieОценок пока нет
- Drug Study CefuroximeДокумент2 страницыDrug Study CefuroximeDave Michael GeliОценок пока нет
- Cefuroxime Drug Study ChanДокумент5 страницCefuroxime Drug Study Chanczeremar chanОценок пока нет
- DexamethasoneДокумент6 страницDexamethasoneapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug MetronidazoleДокумент1 страницаDrug MetronidazoleSrkocherОценок пока нет
- Timolol MaleateДокумент3 страницыTimolol MaleateAP TOROBXОценок пока нет
- BNP (C)Документ2 страницыBNP (C)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonОценок пока нет
- Pre Gabal in Drug StudyДокумент1 страницаPre Gabal in Drug StudyHailMarieSBarcenasОценок пока нет
- DORMICUMДокумент1 страницаDORMICUMArian Rose100% (1)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationДокумент2 страницыAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAbigail BascoОценок пока нет
- DRUG Kalium Durule (Potasium Chloride)Документ1 страницаDRUG Kalium Durule (Potasium Chloride)rholiboiОценок пока нет
- Drug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToДокумент2 страницыDrug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToSHEILA MAE SACLOTОценок пока нет
- Bicalutamide (Casodex) Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыBicalutamide (Casodex) Drug StudyAtteya Mogote AbdullahОценок пока нет
- ChlorpromazineДокумент2 страницыChlorpromazineFay Dominguez100% (1)
- Drug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolДокумент1 страницаDrug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolmikErlh100% (2)
- LevofloxacinДокумент2 страницыLevofloxacinMuhammad ArsalanОценок пока нет
- UnasynДокумент1 страницаUnasynrachieeeОценок пока нет
- XtendaДокумент2 страницыXtendaAlexis CoronadoОценок пока нет
- MisoprostolДокумент3 страницыMisoprostolMichael Aditya LesmanaОценок пока нет
- Drug Study Ampicillin, CelestamineДокумент5 страницDrug Study Ampicillin, CelestamineLLan Kristine Lazarito100% (1)
- TergecefДокумент2 страницыTergecefianecunar100% (3)
- Drug StudyДокумент1 страницаDrug StudycliffordbuenoОценок пока нет
- MetronidazoleДокумент2 страницыMetronidazoleJm RomancapОценок пока нет
- Drug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameДокумент2 страницыDrug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NamehahahaОценок пока нет
- F. Case Study Thesis-Drug Study (Revised)Документ5 страницF. Case Study Thesis-Drug Study (Revised)Lopirts NiganiОценок пока нет
- Cebu Normal University: Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыCebu Normal University: Drug StudyGwen Marie Taboada100% (1)
- PnssДокумент2 страницыPnssFrances Oscar GaviolaОценок пока нет
- Generic Name: Brand Name: Pletal: Pharmacologic Class: Pharmacokinetics General Indications Contraindications BeforeДокумент2 страницыGeneric Name: Brand Name: Pletal: Pharmacologic Class: Pharmacokinetics General Indications Contraindications Beforeart_mutantОценок пока нет
- Ampicillin PDFДокумент3 страницыAmpicillin PDFandriОценок пока нет
- Ascorbic AcidДокумент2 страницыAscorbic AcidJaymark Lambino100% (1)
- SilgramДокумент6 страницSilgramJacqueline SweetОценок пока нет
- Document DRUG 4Документ4 страницыDocument DRUG 4Linda AdamsonОценок пока нет
- Cefazolin Sodium AncefДокумент1 страницаCefazolin Sodium AncefKristi WrayОценок пока нет
- CEFOXITINДокумент30 страницCEFOXITINJaessa FelicianoОценок пока нет
- MetronidazoleДокумент2 страницыMetronidazolehauteanicoleОценок пока нет
- OxacillinДокумент2 страницыOxacillinSatinderSinghОценок пока нет
- Ketorolac Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыKetorolac Drug StudyRic VelascoОценок пока нет
- Atracurium BesylateДокумент3 страницыAtracurium BesylateAP TOROBXОценок пока нет
- DRUGSTUDY TramadolДокумент3 страницыDRUGSTUDY TramadolMicaela Andrea CieloОценок пока нет
- DiarryДокумент10 страницDiarryVan Ryan CondenoОценок пока нет
- TRAMADOL Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыTRAMADOL Drug Studygersalia.christiennikkiОценок пока нет
- Navy Radiowave (Bioeffects) Brief 1971Документ14 страницNavy Radiowave (Bioeffects) Brief 1971Center for Electrosmog Prevention100% (1)
- Spinal Cord Injury NotesДокумент13 страницSpinal Cord Injury Notescorememories10Оценок пока нет
- Ethanol Injection Method Liposomes PDFДокумент2 страницыEthanol Injection Method Liposomes PDFElizabeth100% (1)
- Object and Space PerceptionДокумент10 страницObject and Space PerceptionadriricaldeОценок пока нет
- Mohan Ram STS 1982 by HTTPДокумент7 страницMohan Ram STS 1982 by HTTPmurciano207100% (2)
- Yeast and FermentationДокумент6 страницYeast and FermentationMilito GilbertoОценок пока нет
- Mark Scheme: Double Award Science BiologyДокумент9 страницMark Scheme: Double Award Science BiologyDaniel LoughreyОценок пока нет
- 242-Article Text-810-1-10-20220110Документ15 страниц242-Article Text-810-1-10-20220110Cans UwuОценок пока нет
- KaoshikiiДокумент24 страницыKaoshikiiapi-238078813Оценок пока нет
- CVДокумент1 страницаCVapi-377129715Оценок пока нет
- Brilinta (Ticagrelor) Tablets, For Oral UseДокумент2 страницыBrilinta (Ticagrelor) Tablets, For Oral UsePonpimol Odee BongkeawОценок пока нет
- AB BC : Part AДокумент39 страницAB BC : Part AApoorva GuptaОценок пока нет
- 07 Lecture 1Документ111 страниц07 Lecture 1Obieda NaseefОценок пока нет
- Urinary Tract InfectionДокумент7 страницUrinary Tract InfectionCaressie BiscoОценок пока нет
- Interpretation of Cardiac Enzymes:: Test: SGOTДокумент4 страницыInterpretation of Cardiac Enzymes:: Test: SGOTMohammed AbdouОценок пока нет
- Stomatitis: An Overview: Protecting The Oral Cavity During Cancer TreatmentДокумент4 страницыStomatitis: An Overview: Protecting The Oral Cavity During Cancer TreatmentLenna IkawatiОценок пока нет
- Poster Sessions PDFДокумент105 страницPoster Sessions PDFAllenMarkLibradoОценок пока нет
- Extraction of Urea From Human UrineДокумент21 страницаExtraction of Urea From Human UrineJustine Daquioag100% (1)
- 6 MonocytopoiesisДокумент8 страниц6 MonocytopoiesisVannisa Dwi NovianaОценок пока нет
- CPR 10Документ3 страницыCPR 10melodia gandezaОценок пока нет
- Experiment 1 Cell BioДокумент7 страницExperiment 1 Cell BioWinserng 永森Оценок пока нет
- B I N G oДокумент52 страницыB I N G oJay Andrea Vea Dayuday-IsraelОценок пока нет
- Clayton & Willihnganz: Basic Pharmacology For Nurses, 17th EditionДокумент4 страницыClayton & Willihnganz: Basic Pharmacology For Nurses, 17th EditionabsianoОценок пока нет