Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Cloxacillin
Загружено:
Roberto Manuel IIИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Cloxacillin
Загружено:
Roberto Manuel IIАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
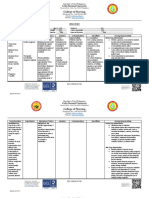
Cloxacillin Brand Name: Cloxapen, Tegopen Classification:anti-infective Dose: 500 mg 1 cup q 6 hours P.
O Mechanism of action: inhibits cell wall synthesis and causes call lysis or death in bacteria that make rigid,cross-linked call wall in several steps. Indications: to treat mild respiratory track infections or localized skin and softtissue infection cause by penicillinase-producing staphylococci. Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to penicillins. Adverse effects: Cloxacillin may cause stomach upset, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting during the first few days as your body adjusts to the medication. If these symptoms persist or become severe, inform your doctor. An allergic reaction may occur while taking Cloxacillin. Symptoms include: - Skin rash; - Itching; - Hives; - Difficulty breathing; Common side effects are: - Diarrhea Less Severe; - Feel Like Throwing Up Less Severe;; - Head Pain Less Severe; - Throwing Up Less Severe Nursing responsibilities: Determine previous exposure and sensitivity to penicillins and cephalosporins and other allergic reactions of any kind before treatment is initiated. Monitor for S&S of anaphylactoid reaction (see Appendix G) or other signs or symptoms of hypersensitivity reaction (see Appendix F) as with other penicillins. Take medication around the clock, do not miss a dose, and continue taking the medication until it is finished. Report to physician the onset of hypersensitivity reaction and superinfections. Check with physician if GI adverse effects (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea) appear. Instruct patient to take the drug with one full glass of water.
Penicillin G Brand Name: Pen G Dose: Pen G NA 4 m units q 8 hours ANSTC(+) Mechanism of action: Inhibits enzymes responsible for cell wall synthesis of susceptible organisms, this creates an osmotically unstable cell wall that swells and bursts from osmotic pressure.
Indications: Penicillin G is reserved for severe infections, or when the oral route is compromised (as in malabsorption syndrome and vomiting), and for some patients requiring prophylactic coverage. Contraindications: Patients with known allergies to penicillin, which is approximately 3% of the population. In patients with renal impairment, dosages should be decreased since excretion of drug is by the renal system. A different formulation should be used in these patients such as penicillin procaine that allows a slow release into the serum from the intramuscular site. Precaution with pregnancy category B, lactation, and hypersensitivity to cephalosporins. Adverse effect: The penicillins are among the least toxic drugs known. They rarely elicit adverse reactions in humans unless present in excessive concentrations. They can disrupt the normal gastrointestinal flora and cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, colitis, and anorexia. At high doses penicillin can have a toxic effect that can cause seizures, platelet dysfunction, hemolytic anemias of an immunologic type, encephalitis, and nephritis. Nursing Responsibilities: Determine previous exposure and sensitivity to penicillins and cephalosporins and other allergic reactions of any kind before treatment is initiated. Monitor for S&S of anaphylactoid reaction (see Appendix G) or other signs or symptoms of hypersensitivity reaction (see Appendix F) as with other penicillins. Take medication around the clock, do not miss a dose, and continue taking the medication until it is finished. Report to physician the onset of hypersensitivity reaction and superinfections. Check with physician if GI adverse effects (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea) appear Ampicillin Brand name: Ampicillin sodium Classification:anti- infective Dose: Mechanism of action: synthetic, broad-spectrum antiobiotic suitable for gram-negative bacteria. Acid resistance, destroyed by penicillinase Indications: Respiratory track infection due to non-penicillinase-producing staphylococci, and streptococci, including streptococcus pneumonia.GI infections due to shigella, salmonella typhosa and other salmonella, e.coli, P.marabilis and entorococci. Contraindication: Hypersensitivity to penicillin Adverese effects: hypersensitivity, nausea and Vomiting, gastritis, stomatitis Nurisng responsibilities List characteristics of signs and symptoms. Note history of sensitivity to the drug
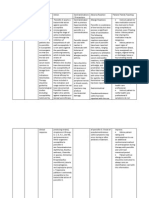
Take 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals; food mat interfere with absorption Instruct the patient not to save pills for future use with family members/friends who have similar condition Take for prescribed number of days even if symptoms subside.
Vitamin B Brand name: vitamin B Polynerv Classification: Vitamins and Minerals(Vitamin B1 in combination with vitamin B6 and/or vitamin B12) Mechanism of action: A coenzyme that stimulate metabolic function and is needed for cell replication, hematopoiesis, and nucleoprotein and myelin synthesis. Indications: Treatment and prevention of vitamin B12 deficiency, and diseases caused by low vitamin B12 levels. Nutritional support in painful neurological manifestations of neuritis & neuropathy eg cervical & shoulderarm syndrome, lumbago, ischialgia & sciatica. Neuropathies caused by disease states Contraindication: Hypersensitivity to Vit B12 Adverse effect: CV: peripheral vascular thrombosis, heart failure. GI: transient diarrhea. Respi: pulmonary edema. Skin: itching, transitory exanthema, urticaria. Nursing responsibilities: 1. determine reticulocyte count, hct, Vit. B 12, iron, folate levels before beginning therapy. 2. Obtain a sensitivity test history before administration 3. Avoid I.V. administration bec. faster systemic elimination will reduce effectiveness of vitamin. 4. Dont give large doses of vitamin B 12 routinely; drug is lost through excretion. 5. Dont mix parenteral preparation in same syringe with other drugs. 6. Protect Vit. B 12 from light. Dont refrigerate or freeze. 7. Monitor patient for for adverse effects.
Вам также может понравиться
- PrednisoloneДокумент2 страницыPrednisoloneKatie McPeekОценок пока нет
- Verapamil HCLДокумент3 страницыVerapamil HCLMae Ann Bueno CastillonОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент7 страницDrug StudyArnel MacabalitaoОценок пока нет
- Nitroglycerin Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыNitroglycerin Drug StudyBeatrizz P GellaОценок пока нет
- Aerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatec Rinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HFAДокумент3 страницыAerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatec Rinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HFAGwyn RosalesОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент4 страницыDrug Studyw dОценок пока нет
- IrbesartanДокумент3 страницыIrbesartanapi-3797941Оценок пока нет
- Lyrica (Pregabalin)Документ2 страницыLyrica (Pregabalin)Laromac RolandОценок пока нет
- Insulin NPHДокумент1 страницаInsulin NPHChristopher LeeОценок пока нет
- Drug Study Table 3Документ5 страницDrug Study Table 3Juliet De GuzmanОценок пока нет
- Sal But AmolДокумент2 страницыSal But AmolKay MirandaОценок пока нет
- Drug Study - AmlodipineДокумент1 страницаDrug Study - AmlodipineDanielle Marie SamblacenoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study (Room 104)Документ4 страницыDrug Study (Room 104)Maeshe Pryll TanamorОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент13 страницDrug StudyAldrin Ian Oraza AlpeОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыDrug StudyMarychen Cabunas100% (1)
- As Pi LetДокумент7 страницAs Pi Letianecunar100% (1)
- Kremil S Drug StudyДокумент1 страницаKremil S Drug StudyDivine LavaОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент5 страницDrug Studyjanelle123 toribioОценок пока нет
- Wesleyan: College of Nursing and Allied Medical SciencesДокумент2 страницыWesleyan: College of Nursing and Allied Medical SciencesShane Aileen AngelesОценок пока нет
- Lui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionДокумент1 страницаLui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionMagdayao Romamea100% (1)
- KaliumДокумент2 страницыKaliumJustine Kaye Iballa HarligaОценок пока нет
- Check The Physician's Observe and Follow The 14 Warn The Mother AboutДокумент2 страницыCheck The Physician's Observe and Follow The 14 Warn The Mother AboutJust nowОценок пока нет
- Darbepoetin AlfaДокумент3 страницыDarbepoetin Alfaapi-3797941Оценок пока нет
- Emergency Room Drug ListДокумент28 страницEmergency Room Drug Listiscariot02Оценок пока нет
- Altretamine: Drug DosageДокумент16 страницAltretamine: Drug DosagePrincess CruzОценок пока нет
- LOSARTAN (ARBs) Drug Study (GERIATRICS)Документ5 страницLOSARTAN (ARBs) Drug Study (GERIATRICS)CHRISTIE MONTANOОценок пока нет
- DioxelДокумент1 страницаDioxelJosselle Sempio CalientaОценок пока нет
- Humulin R, Novolin RДокумент2 страницыHumulin R, Novolin RSheri490100% (2)
- Drug Study - CefradoxilДокумент13 страницDrug Study - CefradoxilJohara G'naid0% (1)
- SeroquelДокумент2 страницыSeroqueldanaОценок пока нет
- Drug Study: Name of Drug Action Indication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilityДокумент4 страницыDrug Study: Name of Drug Action Indication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilityBel CortezОценок пока нет
- Drug Study HydrocodoneДокумент1 страницаDrug Study HydrocodoneYlrenne DyОценок пока нет
- Pravastatin SodiumДокумент3 страницыPravastatin Sodiumapi-3797941Оценок пока нет
- Captopril Drug StudyДокумент1 страницаCaptopril Drug StudyRachel Mae Dente AcedillaОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент11 страницDrug StudyMichelle TamorОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент10 страницDrug Studyjho_26100% (2)
- Mucosta: Tablets 100mgДокумент4 страницыMucosta: Tablets 100mgInukaicchi TakumichiОценок пока нет
- Dolan Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыDolan Drug StudyLian Robbie BautistaОценок пока нет
- College of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementДокумент3 страницыCollege of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementAnika PleñosОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыDrug StudyCen Janber CabrillosОценок пока нет
- Drug Study LevofloxacinДокумент2 страницыDrug Study LevofloxacinDannah BulliandayОценок пока нет
- Drug Study2Документ8 страницDrug Study2zbestgurlОценок пока нет
- Amlodipine BesylateДокумент2 страницыAmlodipine BesylateYakumaОценок пока нет
- Losartan Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыLosartan Drug StudyXerxes DejitoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study FinalДокумент5 страницDrug Study FinalJackie Ann Marie DapatОценок пока нет
- DesyrelДокумент1 страницаDesyrelKatie McPeekОценок пока нет
- Drug Analysis: Malaise, Fatigue, Dizziness, Tremors, AtaxiaДокумент2 страницыDrug Analysis: Malaise, Fatigue, Dizziness, Tremors, AtaxiaFerdinand Sherwin MorataОценок пока нет
- DS (Fenofibrate)Документ5 страницDS (Fenofibrate)Mary April MendezОценок пока нет
- AztreonamДокумент2 страницыAztreonamHannahShaeHayesОценок пока нет
- Tramadol Drug StudyДокумент4 страницыTramadol Drug StudyJust A Nsg StudentОценок пока нет
- ApidraДокумент4 страницыApidraRobert Ivan AgujarОценок пока нет
- Enoxaparin (Lovenox)Документ1 страницаEnoxaparin (Lovenox)EОценок пока нет
- Cerebral Palsy Discharge PlanningДокумент3 страницыCerebral Palsy Discharge Planningjints poterОценок пока нет
- SimethiconeДокумент1 страницаSimethiconeDivine Dela PenaОценок пока нет
- Drugs Study, Nursing, PreoperativeДокумент9 страницDrugs Study, Nursing, PreoperativeKevin Sam AguirreОценок пока нет
- Drugs, Amlodipine, Cefuroxime, Drug StudyДокумент8 страницDrugs, Amlodipine, Cefuroxime, Drug StudyKevin Sam AguirreОценок пока нет
- MetoclopramideДокумент3 страницыMetoclopramideKrizzia CarlosОценок пока нет
- Drug Name Classification and Mechanism of Action Indication/ Dosage/ Route Contraindicatio N Adverse Effects Nursing InterventionsДокумент6 страницDrug Name Classification and Mechanism of Action Indication/ Dosage/ Route Contraindicatio N Adverse Effects Nursing InterventionsVin LandichoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study OrthoДокумент17 страницDrug Study OrthoMc Crister SilangОценок пока нет
- 8copd DrugtabncpДокумент18 страниц8copd DrugtabncpMaristelaMolinaОценок пока нет
- Toxic RelationshipДокумент1 страницаToxic RelationshipwidyasОценок пока нет
- Theories of Learning and Learning MetaphorsДокумент4 страницыTheories of Learning and Learning MetaphorsTrisha Mei Nagal50% (2)
- 5070 s14 QP 11Документ16 страниц5070 s14 QP 11OsamaRahimОценок пока нет
- Decision Making in Perioperative Medicine Clinical Pearls 2021Документ351 страницаDecision Making in Perioperative Medicine Clinical Pearls 2021Dal RdzОценок пока нет
- Eko Serbia A.D. Beograd Rules For The Purchase of Fuel Through AccountsДокумент2 страницыEko Serbia A.D. Beograd Rules For The Purchase of Fuel Through AccountsMarko Perovic PerkeОценок пока нет
- EHEDG Guidelines by Topics 04 2013Документ2 страницыEHEDG Guidelines by Topics 04 2013renzolonardi100% (1)
- Research Activity #2Документ2 страницыResearch Activity #2Shania GualbertoОценок пока нет
- Trillanes V PimentelДокумент2 страницыTrillanes V PimentelKirk LabowskiОценок пока нет
- Ne XT ProtДокумент2 страницыNe XT Protwilliam919Оценок пока нет
- Teleperformance Global Services Private Limited: Full and Final Settlement - December 2023Документ3 страницыTeleperformance Global Services Private Limited: Full and Final Settlement - December 2023vishal.upadhyay9279Оценок пока нет
- Essence Veda Vyasa Smriti PDFДокумент51 страницаEssence Veda Vyasa Smriti PDFmadhav kiranОценок пока нет
- 1Manuscript-BSN-3y2-1A-CEDILLO-222 11111Документ32 страницы1Manuscript-BSN-3y2-1A-CEDILLO-222 11111SHARMAINE ANNE POLICIOSОценок пока нет
- Carbo Hi DratДокумент11 страницCarbo Hi DratILHAM BAGUS DARMA .NОценок пока нет
- InotroposДокумент4 страницыInotroposjuan camiloОценок пока нет
- Textbook of Dental Anatomy, Physiology and Occlusion, 1E (2014) (PDF) (UnitedVRG)Документ382 страницыTextbook of Dental Anatomy, Physiology and Occlusion, 1E (2014) (PDF) (UnitedVRG)Konstantinos Ster90% (20)
- Tryout Consent Form - 2014 - Sign and ReturnДокумент2 страницыTryout Consent Form - 2014 - Sign and ReturnSanjeevan BaraОценок пока нет
- DAMPNESSДокумент21 страницаDAMPNESSChukwu SolomonОценок пока нет
- Lab CompilationДокумент11 страницLab CompilationJanita SiddiquiОценок пока нет
- Qualitative Tests Organic NotesДокумент5 страницQualitative Tests Organic NotesAdorned. pearlОценок пока нет
- Sociology/Marriage PresentationДокумент31 страницаSociology/Marriage PresentationDoofSadОценок пока нет
- Learning Guide No 5Документ19 страницLearning Guide No 5Menal JemalОценок пока нет
- Written Assignment Unit 4 Health ScienceДокумент6 страницWritten Assignment Unit 4 Health SciencesafsdaОценок пока нет
- Case Study LenovoДокумент10 страницCase Study LenovoGOHAR GHAFFARОценок пока нет
- T W H O Q L (Whoqol) - Bref: Skrócona Wersja Ankiety Oceniającej Jakość ŻyciaДокумент6 страницT W H O Q L (Whoqol) - Bref: Skrócona Wersja Ankiety Oceniającej Jakość ŻyciaPiotrОценок пока нет
- DET Tronics: Unitized UV/IR Flame Detector U7652Документ2 страницыDET Tronics: Unitized UV/IR Flame Detector U7652Julio Andres Garcia PabolaОценок пока нет
- Industrial Visit ReportДокумент8 страницIndustrial Visit ReportAnuragBoraОценок пока нет
- Pescatarian Mediterranean Diet Cookbook 2 - Adele TylerДокумент98 страницPescatarian Mediterranean Diet Cookbook 2 - Adele Tylerrabino_rojoОценок пока нет
- Transformers: Z Z Z S S Z S SДокумент17 страницTransformers: Z Z Z S S Z S SSreenivasaraoDharmavarapu100% (1)
- 2nd Term Study Guide 4th Grade Feb 2024 Cambridge ObjectivesДокумент8 страниц2nd Term Study Guide 4th Grade Feb 2024 Cambridge Objectivessofi.cardenas1968Оценок пока нет
- Fawad Hussain, Feedback On Industrial Visit To Sahiwal Coal Power PlantДокумент2 страницыFawad Hussain, Feedback On Industrial Visit To Sahiwal Coal Power PlantSyed Fawad MarwatОценок пока нет
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityОт EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (32)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDОт EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedОт EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (82)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)От EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Рейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionОт EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (404)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsОт EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsОценок пока нет
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaОт EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceОт EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (51)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeОт EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeРейтинг: 2 из 5 звезд2/5 (1)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsОт EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (4)
- The Twentysomething Treatment: A Revolutionary Remedy for an Uncertain AgeОт EverandThe Twentysomething Treatment: A Revolutionary Remedy for an Uncertain AgeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossОт EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (6)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (42)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.От EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (110)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesОт EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (1412)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsОт EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Critical Thinking: How to Effectively Reason, Understand Irrationality, and Make Better DecisionsОт EverandCritical Thinking: How to Effectively Reason, Understand Irrationality, and Make Better DecisionsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (39)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeОт EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (254)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsОт EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (170)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryОт EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (46)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlОт EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (60)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsОт EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsОценок пока нет
- Hearts of Darkness: Serial Killers, The Behavioral Science Unit, and My Life as a Woman in the FBIОт EverandHearts of Darkness: Serial Killers, The Behavioral Science Unit, and My Life as a Woman in the FBIРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (20)