Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
How To Spec A Pump
Загружено:
Asa ReidИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
How To Spec A Pump
Загружено:
Asa ReidАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
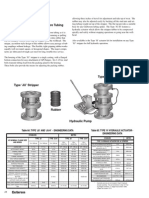
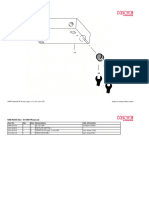
How to Identify and Specify Hydraulic Pumps
REPLACING AN EXISTING PUMP
1. Identify Series, use chart below if necessary.
SERIES P1200 P1500 P2100 P2500 P3700 P3000/3100 P5000/5100 P7500/7600 STUDS No. & Diam. 10 - 1/2" 4 - 1/2" 4 - 9/16 4 -5/8" 8 - 1/2" 4 - 5/8" 4 - 5/8" 8 - 5/8" 7" 5.5" 5.00 6.25" 7.3125" 5.5" 6.25" 8.00" HOUSING HEIGHT HOUSING WIDTH = Gear Width + Thrust Plates: 1/2" 3/4" 3/4 3/4" 1" 3/4" 3/4" 1" THREADED BEARING RETAINER NO NO NO YES YES NO NO NO
2. 3. 4.
Gear Width: Housing Width minus Thrust Plates (see chart above) Shaft Diameter and Configuration (# splines or key size if round) Mounting Flange: Bolt Circle Diameter ________ Pilot Diameter ________ Number Studs _______ Porting: Inlet Outlet Rotation: NPT ________ NPT ________ ODT ________ ODT ________
Pilot Diameter
Housing Height
Housing Width Stud
5.
Split Flange ________ Split Flange ________
Location ________ Location ________
6.
Looking at the shaft end, belly down, inlet on the left = Clockwise Looking at the shaft end, belly down, inlet on the right = Counterclockwise Bi-rotation Pumps usually have equal size ports but still must be plumbed correctly.
Helpful Formulas
PUMP INPUT HORSEPOWER PUMP INPUT TORQUE PUMP OUTPUT FLOW RATE DISPLACEMENT OF PUMP PUMP INPUT SPEED GPM USING PTO HP = GPM x PSI / 1714 / E E = Efficiency T = GPM x PSI x 3.06 / RPM / E D = Displacement GPM = D x RPM x E / 231 D = GPM x 231 / RPM / E RPM = GPM x 231 / D / E GPM = Eng RPM x %PTO x D x E / 231
Вам также может понравиться
- How to Rebuild & Modify Rochester Quadrajet CarburetorsОт EverandHow to Rebuild & Modify Rochester Quadrajet CarburetorsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- ZF8HP RebuildДокумент62 страницыZF8HP RebuildKhristina Stefanova94% (17)
- SS1 Dellorto Carburetor Technical ManualДокумент10 страницSS1 Dellorto Carburetor Technical ManualLSОценок пока нет
- Pgo PMX Sport ServicemanualДокумент116 страницPgo PMX Sport ServicemanualMoppie HofstedeОценок пока нет
- Advanced Hydraulic Course PDFДокумент85 страницAdvanced Hydraulic Course PDFGerman Toledo100% (1)
- DS 7700-22 - 5 Seal Kit For Add-On Spool Valve PSL - PSV 2Документ2 страницыDS 7700-22 - 5 Seal Kit For Add-On Spool Valve PSL - PSV 2Asa Reid100% (1)
- How To Identify and Specify Hydraulic Pumps: Replacing An Existing PumpДокумент1 страницаHow To Identify and Specify Hydraulic Pumps: Replacing An Existing PumpYuriPasenkoОценок пока нет
- Western Main Road Chaguaramas, Trinidad, WIДокумент30 страницWestern Main Road Chaguaramas, Trinidad, WIEdgar Angulo ArizaОценок пока нет
- Fan Pulley Selection GuideДокумент2 страницыFan Pulley Selection GuideSatish MishraОценок пока нет
- Air Conditioning Compressor/Clutch Service ManualДокумент2 страницыAir Conditioning Compressor/Clutch Service ManualromulofcarreraОценок пока нет
- Chrysler: General Notes From Technical Services DepartmentДокумент30 страницChrysler: General Notes From Technical Services DepartmentccbulgariaОценок пока нет
- 25lp5 SD Grundfos DatosДокумент2 страницы25lp5 SD Grundfos DatosArmando AcostaОценок пока нет
- Compressors - Sanden: Compressor IdentificationДокумент41 страницаCompressors - Sanden: Compressor IdentificationIoan Capraru50% (2)
- Flotec Pump ManualДокумент24 страницыFlotec Pump ManualdavetheboxОценок пока нет
- Bosch Injector CaracteristicsДокумент14 страницBosch Injector CaracteristicsNelson Augusto97% (31)
- Motores de EngranajeДокумент14 страницMotores de EngranajeValderrama TibaduizaОценок пока нет
- Pump Global Gear Service ManualДокумент41 страницаPump Global Gear Service ManualAddis TesfayeОценок пока нет
- Metaris MH Series Coding EngranajeДокумент81 страницаMetaris MH Series Coding EngranajeJunior Enrique Yataco ArizaОценок пока нет
- Polyol & Tdi PumpsДокумент40 страницPolyol & Tdi Pumpsrozichka100% (1)
- Grundfosliterature 1098 PDFДокумент118 страницGrundfosliterature 1098 PDFRathnayake Rmas100% (1)
- Presentation Coding GPD Diego Gonzalez Ago13Документ42 страницыPresentation Coding GPD Diego Gonzalez Ago13HenryОценок пока нет
- Fork Notes WPДокумент18 страницFork Notes WPdemoracingeduОценок пока нет
- BC501-502 2015Документ119 страницBC501-502 2015CESARALARCON1Оценок пока нет
- Strippers JU y JU HДокумент5 страницStrippers JU y JU HEd CalheОценок пока нет
- Installation Instructions: Fittings and PortsДокумент5 страницInstallation Instructions: Fittings and PortsVictor Lo Dastek UnichipОценок пока нет
- PSI PumpsДокумент12 страницPSI PumpsagiacomuzoОценок пока нет
- Keystone Atuador de Dupla Ação Pneumático PDFДокумент8 страницKeystone Atuador de Dupla Ação Pneumático PDFdiforaОценок пока нет
- Bo Cat Retor Excavadora225BДокумент46 страницBo Cat Retor Excavadora225BLaura MendozaОценок пока нет
- 3DX SchematicДокумент4 страницы3DX Schematicab59510% (1)
- 3656-3756 ML Brochure GouldsДокумент44 страницы3656-3756 ML Brochure Gouldsjulio.esc7Оценок пока нет
- Multistage Vertical Inline Pumps PM1, PM3, PM5 Series: Specifications Information and Repair Parts ManualДокумент12 страницMultistage Vertical Inline Pumps PM1, PM3, PM5 Series: Specifications Information and Repair Parts ManualAnibal QuezadaОценок пока нет
- Bombas BerkeleyДокумент136 страницBombas BerkeleyDaniel Alejandro GuerreroОценок пока нет
- Maintenance and Repair InstructionsДокумент12 страницMaintenance and Repair InstructionsDhananjay NilkuteОценок пока нет
- Pioneer Pump Rental Flyer - IДокумент2 страницыPioneer Pump Rental Flyer - Irhusseinpos4765Оценок пока нет
- Cameron - Type U BOPДокумент38 страницCameron - Type U BOPjeinerdt100% (7)
- Air Amplifier Models Aad 5 Aad 5 C AДокумент20 страницAir Amplifier Models Aad 5 Aad 5 C AOMiD QahqaieОценок пока нет
- Parker (T6, T6CC) Hydraulic Vane PumpsДокумент12 страницParker (T6, T6CC) Hydraulic Vane PumpsEduardo Valladares DuranОценок пока нет
- Catalogo Dragon 250Документ40 страницCatalogo Dragon 250HectorОценок пока нет
- Grader Case 800 Series B VnaftaДокумент20 страницGrader Case 800 Series B VnaftaHarlinton descalziОценок пока нет
- DAKE Press Model 75 H - 907003Документ6 страницDAKE Press Model 75 H - 907003mark_dayОценок пока нет
- 03 Catalog Krisbow9 Air CompressorДокумент8 страниц03 Catalog Krisbow9 Air Compressorrizky8474Оценок пока нет
- TEEL BRONZE ROTARY PUMP Manual & Parts ListДокумент8 страницTEEL BRONZE ROTARY PUMP Manual & Parts ListMoToBunnYОценок пока нет
- Manual Triplex PumpДокумент45 страницManual Triplex PumpSalineñoApasionado100% (1)
- ZF5HP19Документ132 страницыZF5HP19TammyWest100% (2)
- Series 5100Документ12 страницSeries 5100HectorMaldonadoОценок пока нет
- WPT - Spring Set Brake Air ReleaseДокумент5 страницWPT - Spring Set Brake Air ReleaseSilver AngelОценок пока нет
- PumpeДокумент14 страницPumpeMaximus MaxisОценок пока нет
- Manual MoynoДокумент34 страницыManual Moynocarlangas77Оценок пока нет
- Pump Repair ManualДокумент17 страницPump Repair ManualSergiSerrano100% (1)
- User'S Manual: MSA Multi Spring ActuatorДокумент92 страницыUser'S Manual: MSA Multi Spring ActuatorspbhavnaОценок пока нет
- Williams V Dual Seal Plunger 12-2012 PDFДокумент12 страницWilliams V Dual Seal Plunger 12-2012 PDFDucVikingОценок пока нет
- 2300 Series ManualДокумент24 страницы2300 Series ManualJuprayОценок пока нет
- PGP030 031 SeriesДокумент28 страницPGP030 031 SeriesWesame ShnodaОценок пока нет
- Plymouth and Chrysler-built cars Complete Owner's Handbook of Repair and MaintenanceОт EverandPlymouth and Chrysler-built cars Complete Owner's Handbook of Repair and MaintenanceОценок пока нет
- The Book of the Singer Junior - Written by an Owner-Driver for Owners and Prospective Owners of the Car - Including the 1931 SupplementОт EverandThe Book of the Singer Junior - Written by an Owner-Driver for Owners and Prospective Owners of the Car - Including the 1931 SupplementОценок пока нет
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiОт EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiОценок пока нет
- Bladder AccumulatorsДокумент2 страницыBladder AccumulatorsAsa ReidОценок пока нет
- 2022 Versiona AFPCatalog May2022 Web-48-49Документ2 страницы2022 Versiona AFPCatalog May2022 Web-48-49Asa ReidОценок пока нет
- User's Guide - BTL6-AE500 - B50 - M - E2 - E28 KA - LA - DE - EN - FR - IT - ESДокумент13 страницUser's Guide - BTL6-AE500 - B50 - M - E2 - E28 KA - LA - DE - EN - FR - IT - ESAsa ReidОценок пока нет
- BGT Series Fdhb500ukv2.0 1306Документ11 страницBGT Series Fdhb500ukv2.0 1306Asa ReidОценок пока нет
- SL3 - E4 UNF - Phase OutДокумент2 страницыSL3 - E4 UNF - Phase OutAsa ReidОценок пока нет
- B7845PLVC en PDFДокумент345 страницB7845PLVC en PDFAsa ReidОценок пока нет
- Proportional Directional Spool Valves Type PSL, PSV, PSM, Size 5Документ166 страницProportional Directional Spool Valves Type PSL, PSV, PSM, Size 5Asa ReidОценок пока нет
- B ATEX enДокумент14 страницB ATEX enAsa ReidОценок пока нет
- 2022 Versiona AFPCatalog May2022 Web-26-27Документ2 страницы2022 Versiona AFPCatalog May2022 Web-26-27Asa ReidОценок пока нет
- B1008Документ616 страницB1008Asa ReidОценок пока нет
- 4300 - Catalog - Industrial Tube Fittings PDFДокумент512 страниц4300 - Catalog - Industrial Tube Fittings PDFAsa ReidОценок пока нет
- DS 7700-31 - 5 Seal Kit For Conn - Block PSL - PSV 3Документ2 страницыDS 7700-31 - 5 Seal Kit For Conn - Block PSL - PSV 3Asa ReidОценок пока нет
- Proportional Amplifier Type EV22K5: Product DocumentationДокумент21 страницаProportional Amplifier Type EV22K5: Product DocumentationAsa ReidОценок пока нет
- B - 22 - 2011-En (Size 3 and 5 and 7)Документ11 страницB - 22 - 2011-En (Size 3 and 5 and 7)Asa ReidОценок пока нет
- Proportional Amplifier Type EV2S: Product DocumentationДокумент29 страницProportional Amplifier Type EV2S: Product DocumentationAsa ReidОценок пока нет
- D7918-En (LHT)Документ15 страницD7918-En (LHT)Asa ReidОценок пока нет
- Product Specifications: EatonДокумент1 страницаProduct Specifications: EatonAsa ReidОценок пока нет
- Nca 33Документ89 страницNca 33Asa ReidОценок пока нет
- IQAN Studios Datasheet HY33 8399 UKДокумент8 страницIQAN Studios Datasheet HY33 8399 UKAsa ReidОценок пока нет