Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
KLM Embryo CH 5
Загружено:
kamran_zarrarИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
KLM Embryo CH 5
Загружено:
kamran_zarrarАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
KLM CHAPTER 5: ORGANOGENESIS PERIOD
Phases of Development
Growth Morphogenesis Differentiation
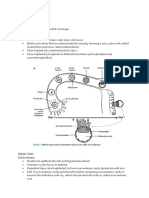
Folding Of The Embryo
Folding occurs both in median and horizontal plane
Cranial Folding: Folding causes formation of foregut Septum Transversum ,Pericadial coelom ,oropharyngeal membrane and heart move ventrally Pericadial coelom moves ventral to heart,septum transversum caudal to heart, Caudal Folding: Caudal Folding caused by elongation of neural tube Formation of Hindgut and Cloaca, Connecting Stalk becomes ventral and Allotois is incorporated Lateral Folding: Formation of lateral folds due to growth of spinal cord and somites. Formation of Midgut Reductionn of Midgut and Umblical Vesicle connection of Omphaloenteric Duct Germ Layer Derivatives: Three Germ Layers Ectoderm , Mesoderm, Endoderm(Derivatives Important) Ectoderm:Complete Nervous System, Glands , Teeth and Dermis related,etc Mesoderm:Skeletal, Muscular, Circulatory, Lymphatic,Reproductive system, etc Endoderm:Epithelial lining of visceral organs,etc
Control Of Development:
Results from genetic plan Development=Growth + Complexity Growth=Mitosis + Extracellular Matrices Complexity= Morphogenesis + Differentiation Changing from pluripotent to specialized by making choices
Choices are made mostly by cues from immediate surrounding instead of cell lineage "Interactions that lead to a change in the course of the development of at least one of interactants are called inductions" Tissue interact by Varying signals in the form of Molecules, Extracellular Matrix or Physical Contact Specificity of a given induction is property of reactivity of molecules rather than that of inductor To Respond to inductor , a cell must have appropriate receptors, transduction pathways and transcription factors Ability to respond is limited, Interactions may fail if interactants are too widely seperated
HIGHLIGHTS OF FOURTH TO EIGHT WEEKS
Fourth Week: 4 to 12 somites, neural tube formation, neuropores close at the end of week, First 2 and then 3 pairs pharyngeal arches visible, Elevation of head, heart pumps blood, Upper limb buds ventrolateral at 26 or 27th day otic pits(internal ear) and lens placode(lenses) visible At end 4th pair of pharyngeal arch and lower limb buds appear Rudiment of CVS system established
LONG TAIL LIKE CAUDAL EMINENCE IS CHARACTERISTIC FEATURE OF END OF FOURTH WEEK
Fifth Week: Changes Minor,Enlargment of head, Face contacts head prominence 2nd pharyngeal arch overgrows forming Cervical sinus over 3rd and 4th Sixth Week: Shows reflexes response to touch Elbow, hand plate , digit rays development Shows spontaneous Movements, twitching of trunk and limb Swellings Auricular Hillocks develop in pharyngeal groove, groove becomes external acoustic meatus(External Auditory Canal) Eyes Obvious, head much larger bent over heart Trunk and Neck begin to straighten Umbilical Herniation Seventh Week: Limbs go considerable change
Notches appear b/w digital rays Ossification of bones starts Eight Week: Digits Seperate SCAPULAR VASCULAR PLEXUS appear and form a CHARACTERISTIC BAND around the neck Purposeful limb movements occur Ossification begins in femur All evidences of caudal eminence disappear DISTINCT HUMAN CHARACTERISTICS head forming half of embryo, neck established , eyelids obvious
ESTIMATION OF EMBRYONIC AGE:
Estimated by external characteristics, length and mostly crown-rump length Prepared By : Muhammad Kamran http://www.facebook.com/Malik.Naaz
Вам также может понравиться
- Embryogenesis (Week 4-8) & Fetal Period (Week 9-Birth)Документ30 страницEmbryogenesis (Week 4-8) & Fetal Period (Week 9-Birth)مالك مناصرةОценок пока нет
- Embryonic Development of The Cardiovascular and Respiratory System During The First TrimesterДокумент34 страницыEmbryonic Development of The Cardiovascular and Respiratory System During The First TrimesterDennis SukadanaОценок пока нет
- Embryology of Ear & Temporal BoneДокумент37 страницEmbryology of Ear & Temporal BonefitsumalemayehudОценок пока нет
- Pediatric Vestibular Disorders GuideДокумент21 страницаPediatric Vestibular Disorders GuidevipinОценок пока нет
- Embryology ObgДокумент36 страницEmbryology ObgsamrusangaliОценок пока нет
- EMBRYOLOGY OF HEART AND LUNG DEVELOPMENTДокумент7 страницEMBRYOLOGY OF HEART AND LUNG DEVELOPMENTavinash dhameriyaОценок пока нет
- Prenatal Growth of Head and Face: Presented by Amritha. Vasudevan First Year PG Department of OrthodonticsДокумент50 страницPrenatal Growth of Head and Face: Presented by Amritha. Vasudevan First Year PG Department of OrthodonticsReenaChauhanОценок пока нет
- Organogenesis HighlightsДокумент99 страницOrganogenesis HighlightsTimmyОценок пока нет
- Development of The EarДокумент16 страницDevelopment of The Earnapoleon tesfayeОценок пока нет
- Urogenital Development & Associated AnomaliesДокумент114 страницUrogenital Development & Associated AnomaliesvictorОценок пока нет
- Growth and DevelopmentДокумент78 страницGrowth and DevelopmentsukantarautОценок пока нет
- Forms of Embryonic Primordia: Prof. Anthony Obioma NwaoparaДокумент32 страницыForms of Embryonic Primordia: Prof. Anthony Obioma NwaoparamatthewОценок пока нет
- Pre-Natal Growth of Craniofacial Complex: Dr. Munizeh KhanДокумент36 страницPre-Natal Growth of Craniofacial Complex: Dr. Munizeh KhanMohsin Habib100% (1)
- Growth and Development of Cranial and Facial RegionДокумент81 страницаGrowth and Development of Cranial and Facial RegionSwati PawarОценок пока нет
- Early Embryology Week OneДокумент14 страницEarly Embryology Week OnelukesqueОценок пока нет
- 4 Development of The EarДокумент38 страниц4 Development of The EarBryan AtasОценок пока нет
- Organogenesis Key Terms and ProcessesДокумент17 страницOrganogenesis Key Terms and ProcessesEw EwОценок пока нет
- 8 - Derivatives of Germ Layers-Dr - GosaiДокумент35 страниц8 - Derivatives of Germ Layers-Dr - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiОценок пока нет
- DEVELOPMENT OF THE EARДокумент33 страницыDEVELOPMENT OF THE EARMuskan IsmailОценок пока нет
- Development of the Respiratory System and Its AnomaliesДокумент17 страницDevelopment of the Respiratory System and Its AnomaliesmichaelqurtisОценок пока нет
- Branchial ArchesДокумент49 страницBranchial ArchesSherin ThomasОценок пока нет
- Embryonic Folding MBBS - 1stДокумент30 страницEmbryonic Folding MBBS - 1stSubham YadavОценок пока нет
- Embryology of Salivary GlandsДокумент21 страницаEmbryology of Salivary GlandsAssist Professor Dr-Bayad Jaza Mahmud100% (3)
- Embryology Notes - emДокумент18 страницEmbryology Notes - emrigario80% (5)
- Embryology of Appendicular SkeletonДокумент39 страницEmbryology of Appendicular SkeletonMahmoud AbdulahiОценок пока нет
- Development of Face &it's Applied AspectsДокумент95 страницDevelopment of Face &it's Applied AspectsHansa KunduОценок пока нет
- Embryonic Period 1Документ35 страницEmbryonic Period 1Riya SinghОценок пока нет
- Embryology Summary of Development Part 1 - 2019 - CNS, Axial SK, SK Muscle, SkinДокумент9 страницEmbryology Summary of Development Part 1 - 2019 - CNS, Axial SK, SK Muscle, Skindr.mumtaz09Оценок пока нет
- All About RespiratoryДокумент69 страницAll About RespiratoryMarcellina Awing100% (1)
- Development of Vertebra, Ribs and Skull 2007Документ16 страницDevelopment of Vertebra, Ribs and Skull 2007Qaiser InayatОценок пока нет
- The Third Week of Development: TH THДокумент8 страницThe Third Week of Development: TH THbarbacumlaudeОценок пока нет
- Development of Respiratory SystemДокумент34 страницыDevelopment of Respiratory SystemNatalie HuiОценок пока нет
- Embryology of EarДокумент32 страницыEmbryology of EarAnsuman SahuОценок пока нет
- Pulmonary EmbolismДокумент21 страницаPulmonary EmbolismMadhu Bala100% (2)
- AllantoisДокумент6 страницAllantoisDania IbraheemОценок пока нет
- Development of Face and Oral Cavity 05042014Документ47 страницDevelopment of Face and Oral Cavity 05042014Jamal NaimОценок пока нет
- Embryology Notes emДокумент18 страницEmbryology Notes emLuqman AfifОценок пока нет
- Embryology of Salivary Glands Development (39Документ21 страницаEmbryology of Salivary Glands Development (39Muhammad Ihsan SiregarОценок пока нет
- EMBRYOLOGY 2nd Year Topical Past Papers 2005-22Документ7 страницEMBRYOLOGY 2nd Year Topical Past Papers 2005-22HussnainОценок пока нет
- Gastrulation and Neurulation Processes in Embryonic DevelopmentДокумент74 страницыGastrulation and Neurulation Processes in Embryonic DevelopmentCynthiaОценок пока нет
- Article EmbriologyДокумент6 страницArticle Embriologycestrada10Оценок пока нет
- 72 HR ReviewerДокумент8 страниц72 HR ReviewerAstrid AmadorОценок пока нет
- Early Embryological Development: Oral Histology Dent 206 DR Ashraf ShaweeshДокумент26 страницEarly Embryological Development: Oral Histology Dent 206 DR Ashraf ShaweeshAbod NaserОценок пока нет
- E3. Tadpole TableДокумент6 страницE3. Tadpole Tablepurpleshadow45Оценок пока нет
- 18Документ21 страница18SophiaОценок пока нет
- Growth 1Документ10 страницGrowth 1ng7gmh578qОценок пока нет
- Embryonic Development and OrganogenesisДокумент33 страницыEmbryonic Development and OrganogenesisMariam QaisОценок пока нет
- 3-Embryology of Respiratory SystemДокумент25 страниц3-Embryology of Respiratory SystemNur HikmahОценок пока нет
- 8.folding of EmbryoДокумент26 страниц8.folding of Embryobibi.hansmuddyОценок пока нет
- Third WeekДокумент9 страницThird Weekchandana chandanaОценок пока нет
- Unit 1-High Yield MaterialДокумент18 страницUnit 1-High Yield MaterialMary GradyОценок пока нет
- Weeks 3 - 8Документ32 страницыWeeks 3 - 8Stefan HutsonОценок пока нет
- Endocrine EmbryologyДокумент3 страницыEndocrine Embryologyb.bethel2003Оценок пока нет
- Broncho PneumoniaДокумент46 страницBroncho PneumoniaAfrianzah Sevenfoldism100% (1)
- Acute Respiratory Distres SyndromeДокумент17 страницAcute Respiratory Distres SyndromeLalrinchhani PautuОценок пока нет
- Development of The Respiratory SystemДокумент22 страницыDevelopment of The Respiratory SystemtuhinОценок пока нет
- Anatomi Penginderaan: Ahmad Azwar Habibi Lab Anatomi FK UIN Syarif Hidayatullah JakartaДокумент62 страницыAnatomi Penginderaan: Ahmad Azwar Habibi Lab Anatomi FK UIN Syarif Hidayatullah JakartaIin Widya Sari SiregarОценок пока нет
- Embryology Notes emДокумент32 страницыEmbryology Notes emSavita HanamsagarОценок пока нет
- Bronchioles Then Divide Into Three TypesДокумент3 страницыBronchioles Then Divide Into Three TypesJeremy EvansОценок пока нет
- Supple Students of Batch I and JДокумент1 страницаSupple Students of Batch I and Jkamran_zarrarОценок пока нет
- Handmade ArtДокумент31 страницаHandmade Artkamran_zarrarОценок пока нет
- Cell InjuryДокумент8 страницCell Injurykamran_zarrarОценок пока нет
- AIOU (Extension in Admission Date)Документ1 страницаAIOU (Extension in Admission Date)kamran_zarrarОценок пока нет
- Behavioral Sciences MCQДокумент10 страницBehavioral Sciences MCQMuhammad Bilal50% (4)
- Allama Iqbal Medical College Lahore Open Merit List 2013Документ28 страницAllama Iqbal Medical College Lahore Open Merit List 2013Shawn ParkerОценок пока нет
- Class Lectures 2014Документ297 страницClass Lectures 2014kamran_zarrarОценок пока нет
- Mbbs Sendup TeamДокумент2 страницыMbbs Sendup Teamkamran_zarrarОценок пока нет
- MedCom's MCQs CH 16Документ4 страницыMedCom's MCQs CH 16kamran_zarrarОценок пока нет
- Nets Certificate: Microsoft Certified System Engineer (Mcs2003)Документ2 страницыNets Certificate: Microsoft Certified System Engineer (Mcs2003)kamran_zarrarОценок пока нет
- GKMC DG Khan Merit List 2014-15Документ10 страницGKMC DG Khan Merit List 2014-15kamran_zarrarОценок пока нет
- Allama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore - Pathology Dept 2 Term Paper - 3 Year 2014 Each Question Carries 5 MarksДокумент1 страницаAllama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore - Pathology Dept 2 Term Paper - 3 Year 2014 Each Question Carries 5 Markskamran_zarrarОценок пока нет
- Medsolutions PharmacologyДокумент123 страницыMedsolutions Pharmacologykamran_zarrarОценок пока нет
- Allama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore - Pathology Dept 2 Term Paper - 3 Year 2014 Each Question Carries 5 MarksДокумент1 страницаAllama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore - Pathology Dept 2 Term Paper - 3 Year 2014 Each Question Carries 5 Markskamran_zarrarОценок пока нет
- Med-Solutions Pathology & MicrobiologyДокумент181 страницаMed-Solutions Pathology & Microbiologykamran_zarrar100% (1)
- Med-Com's Imp EmbryoДокумент7 страницMed-Com's Imp Embryokamran_zarrarОценок пока нет
- Med-Solutions Forensic MedicineДокумент140 страницMed-Solutions Forensic Medicinekamran_zarrar100% (3)
- MedCom's MCQs CH 15Документ3 страницыMedCom's MCQs CH 15kamran_zarrarОценок пока нет
- KLM Embryo CH 5Документ3 страницыKLM Embryo CH 5kamran_zarrarОценок пока нет
- MedCom's MCQs CH 14Документ4 страницыMedCom's MCQs CH 14kamran_zarrarОценок пока нет
- Med-Com's CH 14 MCQsДокумент4 страницыMed-Com's CH 14 MCQskamran_zarrarОценок пока нет
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorДокумент15 страниц6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Clinical Embryology (CH 1-7) (KLM) : TrisomyДокумент4 страницыClinical Embryology (CH 1-7) (KLM) : Trisomykamran_zarrarОценок пока нет
- Med-Com's CH 14 MCQsДокумент4 страницыMed-Com's CH 14 MCQskamran_zarrarОценок пока нет
- Med-Com Imp LowerДокумент12 страницMed-Com Imp Lowerkamran_zarrarОценок пока нет
- Med-Com's Clinical ReviewДокумент7 страницMed-Com's Clinical Reviewkamran_zarrarОценок пока нет
- KLM Chapter 6Документ4 страницыKLM Chapter 6Ceo MedComОценок пока нет
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorДокумент15 страниц6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorДокумент15 страниц6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorДокумент15 страниц6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Bacto PeptoneДокумент1 страницаBacto PeptonedobtОценок пока нет
- Human Body System WorksheetДокумент2 страницыHuman Body System WorksheetRPh Krishna Chandra JagritОценок пока нет
- Artigo RolfingДокумент8 страницArtigo RolfingIsis CalioОценок пока нет
- Dumbar y El LenguajeДокумент21 страницаDumbar y El LenguajeAdalid VelascoОценок пока нет
- Klubsybear Additional Recalls: Hematology A.karyolysisДокумент2 страницыKlubsybear Additional Recalls: Hematology A.karyolysisMartin ClydeОценок пока нет
- AppendicitisДокумент11 страницAppendicitisbobtagubaОценок пока нет
- Potato Poisoning: Understanding Solanine ToxicityДокумент13 страницPotato Poisoning: Understanding Solanine ToxicityDaz Jones100% (2)
- Tetralogy of FallotДокумент3 страницыTetralogy of FallotKamal FauzeОценок пока нет
- Heme Degradation and Jaundice: Molecular Biochemistry IIДокумент40 страницHeme Degradation and Jaundice: Molecular Biochemistry IInarasaiyanhariharanОценок пока нет
- (BOTAFUN) Plant Cell Cycle ControlДокумент3 страницы(BOTAFUN) Plant Cell Cycle ControlBen Joshua MancileОценок пока нет
- Diaphragmatic HerniaДокумент8 страницDiaphragmatic HerniaAnonymous 9xHTwHYОценок пока нет
- Biology Revision Essay Questions and Answers For Secondary Kusoma - Co - .KeДокумент48 страницBiology Revision Essay Questions and Answers For Secondary Kusoma - Co - .Kestevewanji0% (1)
- AP Bio LabsДокумент9 страницAP Bio Labsjustindong100% (1)
- Angliski Kniga VezbiДокумент6 страницAngliski Kniga VezbiMartina JovevskaОценок пока нет
- ETIOLOGY of Cell InjuryДокумент77 страницETIOLOGY of Cell InjurybesthachakrapaniОценок пока нет
- Physical Exam of the Eye: Structures, Findings, DiagnosesДокумент16 страницPhysical Exam of the Eye: Structures, Findings, DiagnosesriveliОценок пока нет
- Underground Clinical Vignettes BiochemistryДокумент128 страницUnderground Clinical Vignettes Biochemistrymartha2112Оценок пока нет
- OkinagaДокумент8 страницOkinagaMOULIANNA8949Оценок пока нет
- Pilates Advanced MatworkДокумент74 страницыPilates Advanced MatworkPooja Jugdar Deshmukh100% (2)
- Mizuho Vascular (Transcranial) DopplerДокумент4 страницыMizuho Vascular (Transcranial) DopplersigmakarsaОценок пока нет
- Toxicokinetics & ToxicodynamicsДокумент31 страницаToxicokinetics & ToxicodynamicsWahyudin AhmadОценок пока нет
- 15 Healing Miracles EX735 SCENAR Book StoriesДокумент11 страниц15 Healing Miracles EX735 SCENAR Book StoriesBacean Aurel Ioan100% (5)
- Geoffrey Gadd, Sarah C. Watkinson, Paul S. Dyer Fungi in The Environment PDFДокумент407 страницGeoffrey Gadd, Sarah C. Watkinson, Paul S. Dyer Fungi in The Environment PDFStefan Stef100% (1)
- A Monster Calls - ExtractДокумент2 страницыA Monster Calls - ExtractJo PatrickОценок пока нет
- THYMUS PPT Final 7marДокумент15 страницTHYMUS PPT Final 7marRajesh UgalmugleОценок пока нет
- Bernadette Gardner - Going Deep PDFДокумент123 страницыBernadette Gardner - Going Deep PDFRysham AyshathОценок пока нет
- Embriologi Alat Kelamin (Deferensiasi SexДокумент19 страницEmbriologi Alat Kelamin (Deferensiasi SexAdi Putra GhifariОценок пока нет
- Sleep Disorders in Children and Adolescents: Understanding Causes and Treatment OptionsДокумент50 страницSleep Disorders in Children and Adolescents: Understanding Causes and Treatment OptionsCitra Sukri Sugesti100% (1)
- ESMO Epidemiology Classification and Clinical Presentation of NETs A European PerspectiveДокумент39 страницESMO Epidemiology Classification and Clinical Presentation of NETs A European PerspectiveMario MutuleanuОценок пока нет
- jm800328v PDFДокумент9 страницjm800328v PDFVINODОценок пока нет