Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Cloud Computing
Загружено:
Nandan KumarИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Cloud Computing
Загружено:
Nandan KumarАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CLOUD COMPUTING-EVOLUTION OR REVOLUTION
WHAT IS CLOUD COMPUTING-LET US SEE..
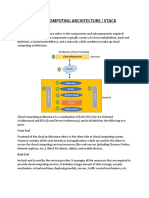
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing as a service rather than a product, whereby shared resources, software, and information are provided to computers and other devices as a metered service over a network (typically the Internet). Cloud computing provides computation, software, data access, and storage resources without requiring cloud users to know the location and other details of the computing infrastructure. End users access cloud based applications through a web browser or a light weight desktop or mobile app while the business software and data are stored on servers at a remote location. Cloud application providers strive to give the same or better service and performance as if the software programs were installed locally on end-user computers.
. Cloud computing is both evolutionary and revolutionary.
Evolutionary because, in many ways, the move to cloud computing is just another stage in the evolution of IT. Weve moved from mainframes to servers to virtual servers and now to the cloudwhich, in many organizations is seen as just a way to outsource non-core functions
Cloud Computing is also revolutionary for the organization. Revolutionary in the sense that theres no longer a need to spend thousands or hundreds of thousands of dollars on hardware to
get a website and/or product running. Rather than building up an IT operations team and a development team, you can let the operations be managed for you by a cloud vendor. Theres cost savings there that havent been available in years past to the small to medium sized business. Socloud computing is both evolutionary and revolutionary. There are many reasons to support the fact that the development of cloud computing has proved to be a evolution and a revolution both In fact,we can say that the evolution of cloud computing has proved to be a revolution in todays world.
Empowerment of end-users of computing resources by putting the provisioning of those resources in their own control, as opposed to the control of a centralized IT service (for example) Agility improves with users' ability to re-provision technological infrastructure resources. Application programming interface (API) accessibility to software that enables machines to interact with cloud software in the same way the user interface facilitates interaction between humans and computers. Cloud computing systems typically use REST-based APIs. Cost is claimed to be reduced and in a public cloud delivery model capital expenditure is converted to operational expenditure This is purported to lower barriers to entry, as infrastructure is typically provided by a third-party and does not need to be purchased for one-time or infrequent intensive computing tasks. Pricing on a utility computing basis is fine-grained with usage-based options and fewer IT skills are required for implementation (in-house).] Device and location independence. enable users to access systems using a web browser regardless of their location or what device they are using (e.g., PC, mobile phone). As infrastructure is off-site (typically provided by a third-party) and accessed via the Internet, users can connect from anywhere Virtualization technology allows servers and storage devices to be shared and utilization be increased. Applications can be easily migrated from one physical server to another. Multi-tenancy enables sharing of resources and costs across a large pool of users thus allowing for: o Centralization of infrastructure in locations with lower costs (such as real estate, electricity, etc.) o Peak-load capacity increases (users need not engineer for highest possible loadlevels) o Utilisation and efficiency improvements for systems that are often only 1020% utilise Reliability is improved if multiple redundant sites are used, which makes well-designed cloud computing suitable for business continuity and disaster recovery.
Scalability and Elasticity via dynamic ("on-demand") provisioning of resources on a fine-grained, self-service basis near real-time, without users having to engineer for peak loads Performance is monitored, and consistent and loosely coupled architectures are constructed using web services as the system interface Security could improve due to centralization of data, increased security-focused resources, etc., but concerns can persist about loss of control over certain sensitive data, and the lack of security for stored kernels. Security is often as good as or better than other traditional systems, in part because providers are able to devote resources to solving security issues that many customers cannot afford. However, the complexity of security is greatly increased when data is distributed over a wider area or greater number of devices and in multi-tenant systems that are being shared by unrelated users. In addition, user access to security audit logs may be difficult or impossible. Private cloud installations are in part motivated by users' desire to retain control over the infrastructure and avoid losing control of information security. Maintenance of cloud computing applications is easier, because they do not need to be installed on each user's computer and can be accessed from different places.
Вам также может понравиться
- CC DocumentДокумент13 страницCC Documentgopikrishnan1234Оценок пока нет
- AN Assignment ON "Cloud Computing" "Master of Computer Application" Session 2012-2015Документ8 страницAN Assignment ON "Cloud Computing" "Master of Computer Application" Session 2012-2015ravindersehgalОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing DraftДокумент14 страницCloud Computing Draftakhil829208Оценок пока нет
- Overview of Cloud Computing TechnologyДокумент3 страницыOverview of Cloud Computing Technologyzubair90Оценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing: Cloud Computing Is A Technology That Uses The Internet and Central Remote Servers To Maintain Data andДокумент11 страницCloud Computing: Cloud Computing Is A Technology That Uses The Internet and Central Remote Servers To Maintain Data androhan7801Оценок пока нет
- Presentation On Cloud ComputingДокумент21 страницаPresentation On Cloud ComputingPraveen Kumar PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing: Presentation ByДокумент20 страницCloud Computing: Presentation Bymahesh_mallidiОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing and Virtualization: Streamlining Your IT InfrastructureОт EverandCloud Computing and Virtualization: Streamlining Your IT InfrastructureОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing: Cloud Computing Is The Delivery of Computing As A Service Rather Than A Product, WherebyДокумент15 страницCloud Computing: Cloud Computing Is The Delivery of Computing As A Service Rather Than A Product, WherebyShashank GuptaОценок пока нет
- Proxy Re Encryptions (Pre) Based Deduplication Scheme On Encrypted Big Data For Cloud AbstractДокумент31 страницаProxy Re Encryptions (Pre) Based Deduplication Scheme On Encrypted Big Data For Cloud AbstractsantoshОценок пока нет
- According To The IEEE Computer Society Cloud Computing IsДокумент6 страницAccording To The IEEE Computer Society Cloud Computing IsaaryavamanОценок пока нет
- ReportДокумент17 страницReportsaurabh128Оценок пока нет
- Attribute-Based Access Control With Constant-Size Ciphertext in Cloud ComputingДокумент14 страницAttribute-Based Access Control With Constant-Size Ciphertext in Cloud ComputingGateway ManagerОценок пока нет
- Characteristics of CloudДокумент2 страницыCharacteristics of CloudSukhjinder Singh GillОценок пока нет
- Ict PDFДокумент13 страницIct PDFMuzayyab MaLikОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing AUДокумент11 страницCloud Computing AUTHANGA DURAIОценок пока нет
- "Cloud Computing": Made By: Aayush Chopra 09itmg1001cseДокумент23 страницы"Cloud Computing": Made By: Aayush Chopra 09itmg1001cseAbhimanyu NarwalОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing Unit-1 PDFДокумент27 страницCloud Computing Unit-1 PDFSaif KhanОценок пока нет
- Topic:Cloud Computing Name:Aksa Kalsoom Submitted To:Sir Amir Taj Semester:7 ROLL# 11PWBCS0276 Section:BДокумент6 страницTopic:Cloud Computing Name:Aksa Kalsoom Submitted To:Sir Amir Taj Semester:7 ROLL# 11PWBCS0276 Section:BlailaaabidОценок пока нет
- Introduction To CCДокумент11 страницIntroduction To CCHAFIZ AMEENUDDINОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing: Ahmed Ibrahem Muhammed Biomedical Informatics Diploma 2011/2012Документ8 страницCloud Computing: Ahmed Ibrahem Muhammed Biomedical Informatics Diploma 2011/2012aibrahemmОценок пока нет
- Unit 1Документ13 страницUnit 1Bnod MsraОценок пока нет
- Implementation of Cloud Based Query Solver System For Educational Institutes Featuring OntologyДокумент7 страницImplementation of Cloud Based Query Solver System For Educational Institutes Featuring OntologyIjarcet JournalОценок пока нет
- Ijett V21P256Документ8 страницIjett V21P256Bharath KumarОценок пока нет
- A Study of Cloud Computing MethodologyДокумент5 страницA Study of Cloud Computing MethodologyR Dharshini SreeОценок пока нет
- Synopsis On CLOUD COMPUTING by Prashant GuptaДокумент6 страницSynopsis On CLOUD COMPUTING by Prashant GuptaPrashant GuptaОценок пока нет
- Assignment No.:01: Course Title: Cloud Computing Submitted By: Sabera Sultana (1803003)Документ11 страницAssignment No.:01: Course Title: Cloud Computing Submitted By: Sabera Sultana (1803003)MD Monowar Ul IslamОценок пока нет
- Azure FundamentalsДокумент38 страницAzure Fundamentalsumakant bhardwajОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing - PrashantДокумент6 страницCloud Computing - PrashantSachin MauryaОценок пока нет
- Introduction About CloudДокумент6 страницIntroduction About CloudMula RamaniОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing: A Paper Presentation ONДокумент8 страницCloud Computing: A Paper Presentation ONGonella NagamallikaОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing Unit2Документ37 страницCloud Computing Unit2Bella SОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing Is The On-Demand Availability ofДокумент8 страницCloud Computing Is The On-Demand Availability ofVovОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing: Age of InternetДокумент6 страницCloud Computing: Age of InternetAlmore Cato IIОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingОт EverandCloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingОценок пока нет
- Problem Definition: Implementing Digital Signature With RSA To The Data On CloudДокумент22 страницыProblem Definition: Implementing Digital Signature With RSA To The Data On CloudHamid HaqaniОценок пока нет
- Report Cloud ComputingДокумент15 страницReport Cloud ComputingsaneshsivanОценок пока нет
- DocumentДокумент14 страницDocumentAyush PatelОценок пока нет
- Module1 NotesДокумент7 страницModule1 NotesHik HjkkОценок пока нет
- Assignment On Benefits of Cloud ComputingДокумент8 страницAssignment On Benefits of Cloud ComputingMonir HossainОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Cloud ComputingДокумент13 страницIntroduction To Cloud ComputingGopinath MuthusamyОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing DocumentationДокумент11 страницCloud Computing DocumentationSailaja MannemОценок пока нет
- Seminar Report On Cloud Computing.Документ25 страницSeminar Report On Cloud Computing.Rahul Kumar SinghОценок пока нет
- What Is Cloud ComputingДокумент17 страницWhat Is Cloud ComputingVictor ImarhiagbeОценок пока нет
- Abstract of Cloud ComputingДокумент6 страницAbstract of Cloud ComputingJanaki JanuОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing Research PaperДокумент11 страницCloud Computing Research PaperPracheta BansalОценок пока нет
- Unit 5 Cloud ComputingДокумент12 страницUnit 5 Cloud ComputingvibhamanojОценок пока нет
- FALLSEM2022-23 CSE3035 ETH VL2022230103255 Reference Material I 20-07-2022 IntroductionДокумент12 страницFALLSEM2022-23 CSE3035 ETH VL2022230103255 Reference Material I 20-07-2022 IntroductionAditi SudhirОценок пока нет
- Virtualizing The Private Cloud For Maximum Resource UtilizationДокумент5 страницVirtualizing The Private Cloud For Maximum Resource UtilizationIjarcet JournalОценок пока нет
- Cloud: Get All The Support And Guidance You Need To Be A Success At Using The CLOUDОт EverandCloud: Get All The Support And Guidance You Need To Be A Success At Using The CLOUDОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing IntroductionДокумент16 страницCloud Computing IntroductionVicОценок пока нет
- Cloud ComputingДокумент21 страницаCloud ComputingAndara KaryaОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing 2Документ12 страницCloud Computing 2madhu08nangelОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing: (A Computing Platform For Next-Generation Internet)Документ7 страницCloud Computing: (A Computing Platform For Next-Generation Internet)Srini VasuluОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Cloud ComputingДокумент19 страницIntroduction To Cloud ComputingManisha GuptaОценок пока нет
- Cloud ComputingДокумент15 страницCloud ComputingSanjana MehtaОценок пока нет
- An Assignment On Cloud ComputingДокумент5 страницAn Assignment On Cloud ComputingMD Monowar Ul IslamОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing Section-1: Prepared by Manish Kumar Aery. IET Bhaddal Technical Campus, RoparДокумент16 страницCloud Computing Section-1: Prepared by Manish Kumar Aery. IET Bhaddal Technical Campus, Roparjuanestudia12Оценок пока нет
- Decentralized Access Control With Anonymous Authentication of Data Stored in CloudsДокумент47 страницDecentralized Access Control With Anonymous Authentication of Data Stored in CloudsShiva KrishnaОценок пока нет
- Cloud ComputingДокумент7 страницCloud ComputingViệt Dũng Trần NguyễnОценок пока нет
- 05 - Activity - 1Документ5 страниц05 - Activity - 1DATU AL-ANSARI UKOОценок пока нет
- Operating System Interview Questions and AnswersДокумент8 страницOperating System Interview Questions and AnswersSunil Wesley100% (1)
- RobotStudio - Operating Manual - ABB RoboticsДокумент536 страницRobotStudio - Operating Manual - ABB RoboticsPrabhu100% (1)
- Module 1 - Operating-System ServicesДокумент78 страницModule 1 - Operating-System ServicesKailashОценок пока нет
- jGRASP TutorialДокумент11 страницjGRASP TutorialDaVid Silence KawlniОценок пока нет
- Docker Commands Cheat SheetДокумент2 страницыDocker Commands Cheat SheetVikram ReddyОценок пока нет
- Rotor-Cuda 1.0.7 TutorialДокумент17 страницRotor-Cuda 1.0.7 TutorialLoïc TernisienОценок пока нет
- Web Application Firewall WAF GatewayДокумент2 страницыWeb Application Firewall WAF Gatewayarafat shabaniОценок пока нет
- Calypso 16 AIMS-InterfaceДокумент16 страницCalypso 16 AIMS-InterfaceDragu StelianОценок пока нет
- Selecting Development ApproachДокумент10 страницSelecting Development ApproachSoroosh RahimianОценок пока нет
- Register Assistant User Manual Release v5.1 © 2010-2018 Mentor Graphics CorporationДокумент274 страницыRegister Assistant User Manual Release v5.1 © 2010-2018 Mentor Graphics Corporationdupipi100% (1)
- Bca 4 Sem Database Management Systems 79726 Dec 2022Документ2 страницыBca 4 Sem Database Management Systems 79726 Dec 2022fafasadОценок пока нет
- Module of JAVA Training in Indore at SSi EducationДокумент3 страницыModule of JAVA Training in Indore at SSi Educationssiedu_semОценок пока нет
- iDRAC8 With Lifecycle Controller Version 2.75.75.75: Release NotesДокумент17 страницiDRAC8 With Lifecycle Controller Version 2.75.75.75: Release NotesANthonyОценок пока нет
- Oracle Cash Management Bank Statement Upload WebadiДокумент14 страницOracle Cash Management Bank Statement Upload WebadiPradeep MenochaОценок пока нет
- 20090403 - pcs (p) Bài tập C#Документ5 страниц20090403 - pcs (p) Bài tập C#Sato Kenta 健太Оценок пока нет
- Introduction To Power BI Slide DeckДокумент265 страницIntroduction To Power BI Slide DeckAchamyeleh TamiruОценок пока нет
- From Simplex To Duplex ModeДокумент28 страницFrom Simplex To Duplex ModetrippinfelixОценок пока нет
- File RusakДокумент404 страницыFile RusakKala IrengОценок пока нет
- IN 951 AdministratorGuide en PDFДокумент649 страницIN 951 AdministratorGuide en PDFVenkatesh NarisettyОценок пока нет
- HDDFaulty c0t0d0 OutputДокумент12 страницHDDFaulty c0t0d0 OutputrejnanОценок пока нет
- Object-Oriented Analysis and Design With Applications: Unit Iii Chapter 5: NotationДокумент24 страницыObject-Oriented Analysis and Design With Applications: Unit Iii Chapter 5: NotationAli JamaОценок пока нет
- Latest QTP/uft Interview QuestionsДокумент8 страницLatest QTP/uft Interview Questionsjamesmikky0% (1)
- EcoBank Training Manual-V1-11-DEC-2015 PDFДокумент126 страницEcoBank Training Manual-V1-11-DEC-2015 PDFMohamed Musthafa100% (1)
- HAHAДокумент4 страницыHAHAnutwoОценок пока нет
- Setup TDA Step by Step GuideДокумент14 страницSetup TDA Step by Step GuideMuhammad AyoubОценок пока нет
- SF EC Position Management en PDFДокумент174 страницыSF EC Position Management en PDFFelipe JohnstoneОценок пока нет
- How To Become An HLA Guru in Ashort TimeДокумент39 страницHow To Become An HLA Guru in Ashort Timeephrem32Оценок пока нет
- Garcia Marquez, Gabriel - Memorias de Mis Putas TristesДокумент4 страницыGarcia Marquez, Gabriel - Memorias de Mis Putas Tristesadolfo adolfoОценок пока нет
- System Monitoring Using Solution ManagerДокумент27 страницSystem Monitoring Using Solution ManagerAlexanderОценок пока нет