Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
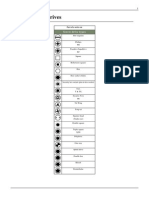
Bolt Head Types
Загружено:
FastMachinistАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Bolt Head Types
Загружено:
FastMachinistАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Document Number: Description:
F-101
Screwdriver Tips and Fastener Sizes
Revision No.: Revision Date: 08-11-10 Sheets: 5
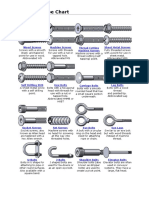
What is a Fastener? A screw or bolt is a shaft with a helical groove or thread formed on its surface and has provisions at one end for turning. A screw or bolt consists of a cylindrical shaft, which in many cases tapers to a point at one end, and with a helical ridge or thread formed on it, and a head at the other end which can be rotated by some means. Its main uses are to hold two or more objects together. The thread is essentially an inclined plane wrapped around the shaft. The thread mates with a complementary helix in the material. The material may be manufactured with the mating helix using a tap, or the screw may create it when first driven in (a self-tapping screw or wood screw). The head is specially shaped to allow a screwdriver or wrench to rotate the screw, driving it in or removing it. The head is of larger diameter than the body of the screw and has no thread so that the screw cannot be driven deeper than the length of the shaft, and to provide compression. Screws can normally be removed and reinserted without reducing their effectiveness. They have greater holding power than nails and permit disassembly and reuse. The vast majority of screws are tightened by clockwise rotation; this is commonly termed as a Right-hand thread. Screws with left-hand threads are used in exceptional cases, when the screw is subject to anticlockwise forces that might undo a right-hand thread. Left-hand screws are used on rotating items such as the left-hand grinding wheel on a bench grinder or the left hand pedal on a bicycle (both looking towards the equipment) or hub nuts on the left side of some automobiles. Fastener Types Fasteners or screws come in a variety styles, head types and drive options. There is a great variety of fasteners available and used throughout all industries and continents. Wood Screws, Sheet Metal Screws, Self-Drilling Screws, Drywall Screws, Machine Screws, Socket Head Cap Screws, Hex Head Screws and Set Screws to name a few. Almost all are available in a variety of head styles. Flat Head, Oval Head, Round Head, Truss Head, Binding, Fillister, Pan Head and Button Head just start the list. Some of them are available
F-101 Screwdriver Tips and Fastener Sizes ARTISAN Hand Tools, Inc. Sheet 1
in Standard or Security configurations, also known as Tamper-Proof or Tamper-Resistant. Most are available in fraction, number and metric sizes and all require some tool to install or remove them. Head Styles
Flat
Oval
Round
Truss
Binding
Pan
Button
Fillister
Socket Head Cap
Low Head Cap
Set (No Head)
Hex
Many screw drives, including Phillips, Torx and Hexagonal, are also manufactured in a Security, (tamper-resistant or tamper-proof), form. These typically have a pin protruding in the center of the screw head, requiring a special tool for installation and removal. In some variants the pin is placed slightly off-center, requiring a correspondingly shaped bit. The slotted screw also comes in a tamper-resistant one-way design with sloped or ramped edges. The screw can be installed by using a standard Slotted driver, but the slopes or ramps require the use of a special tool for removal that prevents the driver from slipping out in the reverse direction. What is the Difference between a Screw and Bolt? A universally accepted distinction between a screw and a bolt does not exist. In common usage the term screw refers to smaller (less than 1/4 inch) threaded fasteners, especially threaded fasteners with tapered shafts used in un-threaded substrates and the term bolt refers to larger threaded fasteners that are designed to be used with nuts or in tapped holes. The term machine screw is commonly used to refer to threaded fasteners that are used with nuts or in tapped holes. The term lag bolt (also known less commonly as a lag screw) is used to refer to larger threaded fasteners with tapered shafts. Various methods of distinguishing bolts and screws exist or have existed. These methods conflict at times and can be confusing. Old SAE and USS standards made a distinction between a bolt and a cap screw based on whether a portion of the shaft was un threaded or not. Cap screws had shafts that were threaded up to the head and bolts had partially threaded shafts. Today a bolt that has a completely threaded shaft might be referred to as a tap bolt.
F-101 Screwdriver Tips and Fastener Sizes
ARTISAN Hand Tools, Inc.
Sheet 2
F-101 Screwdriver Tips and Fastener Sizes
ARTISAN Hand Tools, Inc.
Sheet 3
F-101 Screwdriver Tips and Fastener Sizes
ARTISAN Hand Tools, Inc.
Sheet 4
F-101 Screwdriver Tips and Fastener Sizes
ARTISAN Hand Tools, Inc.
Sheet 5
Вам также может понравиться
- Assignment 1Документ5 страницAssignment 1Ameer HamzaОценок пока нет
- 105 FastenersДокумент7 страниц105 Fastenerssuri1989Оценок пока нет
- EASA Chapter 05Документ20 страницEASA Chapter 05Abdul Qadeer KhanОценок пока нет
- Nut and Bolts: Trem PaperДокумент15 страницNut and Bolts: Trem Papershams0% (1)
- Nail (Fastener) : Cam Dowels ConformatДокумент9 страницNail (Fastener) : Cam Dowels Conformatsheshe_19Оценок пока нет
- Screw FastenersДокумент7 страницScrew FastenersKristian MarajОценок пока нет
- أنواع المسامير والكوبلنجДокумент16 страницأنواع المسامير والكوبلنجOmar AlharthiОценок пока нет
- Screwdriver: Tool ScrewsДокумент4 страницыScrewdriver: Tool Screwscotton byОценок пока нет
- Aircraft HardwareДокумент26 страницAircraft Hardwaregueting_overОценок пока нет
- Bolt and ThreadsДокумент5 страницBolt and Threadssmg26thmayОценок пока нет
- All About ScrewsДокумент19 страницAll About Screwsbkpaul3107100% (1)
- Module 6-5 Fasteners Pt3 PresentationДокумент44 страницыModule 6-5 Fasteners Pt3 Presentationabdullahqureshi789456Оценок пока нет
- Adp 6Документ3 страницыAdp 6mohd_azhar_51Оценок пока нет
- A Wrench or Spanner Is A Tool Used To Provide Grip and Mechanical Advantage in Applying Torque To Turn ObjectsДокумент8 страницA Wrench or Spanner Is A Tool Used To Provide Grip and Mechanical Advantage in Applying Torque To Turn ObjectshabtshОценок пока нет
- Basic Hand Tools GuideДокумент33 страницыBasic Hand Tools GuideNan OoОценок пока нет
- Screw Drive Styles ExplainedДокумент3 страницыScrew Drive Styles ExplainedSadia afrinОценок пока нет
- Bolt (Fastener) - WikipediaДокумент3 страницыBolt (Fastener) - WikipediaaravindОценок пока нет
- 14 Different Types of Screwdriver Explained in Detail Notes PDFДокумент15 страниц14 Different Types of Screwdriver Explained in Detail Notes PDFPankaj ShahОценок пока нет
- Using Shop ToolsДокумент14 страницUsing Shop Toolsgillian marbebe100% (1)
- What Are Some General Safety Tips To Know When Using Screwdrivers?Документ5 страницWhat Are Some General Safety Tips To Know When Using Screwdrivers?surafel AyeleОценок пока нет
- Engineering Drawing - Fastening Devices Research PaperДокумент16 страницEngineering Drawing - Fastening Devices Research PaperMalik ForbesОценок пока нет
- Nut (Hardware) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент6 страницNut (Hardware) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediashivarwatОценок пока нет
- Tools & Equipment Info Sheet 2Документ19 страницTools & Equipment Info Sheet 2anleyedemeОценок пока нет
- Screw Drive HeadsДокумент6 страницScrew Drive Headskennedykioko01Оценок пока нет
- Introduction To The Different Types of Screw HeadsДокумент17 страницIntroduction To The Different Types of Screw HeadsventsymОценок пока нет
- U.S. Quarter Coin Fastener Helical Nut: ScrewДокумент6 страницU.S. Quarter Coin Fastener Helical Nut: ScrewRonalyn FloresОценок пока нет
- FastenersДокумент28 страницFastenersthulasi_krishnaОценок пока нет
- Fastners PDFДокумент26 страницFastners PDFபிரேம் ஆனந்த்Оценок пока нет
- Screw - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент28 страницScrew - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaJoseph GonsalvesОценок пока нет
- What Is Screw Different Types of Screw Explained in Detail Notes PDFДокумент16 страницWhat Is Screw Different Types of Screw Explained in Detail Notes PDFPankaj ShahОценок пока нет
- 1 Pipe WrenchДокумент16 страниц1 Pipe Wrenchkent john ballartaОценок пока нет
- List of Screw DrivesДокумент18 страницList of Screw Drivespoutsasmplemare100% (2)
- screw driverДокумент44 страницыscrew driverIDTR JamshedpurОценок пока нет
- Information Sheet 2.1-2docxДокумент8 страницInformation Sheet 2.1-2docxErnesto CabuyadaoОценок пока нет
- Hand ToolsДокумент44 страницыHand Toolsmarlito100% (1)
- Screw DetailsДокумент21 страницаScrew DetailsHans HamiltonОценок пока нет
- Types of Screwdriver and Their Uses (With Pictures)Документ7 страницTypes of Screwdriver and Their Uses (With Pictures)Iman SadeghiОценок пока нет
- Hand Tools and Bench Work GuideДокумент26 страницHand Tools and Bench Work GuideRozy MacaseroОценок пока нет
- Aircraft Hardware FastenersДокумент36 страницAircraft Hardware FastenersUmar HasanОценок пока нет
- 20 Types of Screws ExplainedДокумент17 страниц20 Types of Screws ExplainedYatta FunОценок пока нет
- Engine Room Tools Part 2Документ51 страницаEngine Room Tools Part 2raotalhaОценок пока нет
- Types of bolts, screws, nuts and their usesДокумент4 страницыTypes of bolts, screws, nuts and their usesNakanakanaknakОценок пока нет
- Starting Woodturning A Beginners GuideДокумент15 страницStarting Woodturning A Beginners GuideSameh_Abd_Aziz75% (4)
- Pojedini Tipovi VijakaДокумент4 страницыPojedini Tipovi Vijakaserzo75Оценок пока нет
- Fastener Type Chart: Wood Screws Machine Screws Thread Cutting Machine Screws Sheet Metal ScrewsДокумент4 страницыFastener Type Chart: Wood Screws Machine Screws Thread Cutting Machine Screws Sheet Metal Screwslemuel bacsaОценок пока нет
- Bolts Vs Screws - Difference Between Bolts and ScrewsДокумент4 страницыBolts Vs Screws - Difference Between Bolts and ScrewsRamzi BEN AHMEDОценок пока нет
- PDF 2Документ14 страницPDF 2deepu8011653276Оценок пока нет
- TYPES OF PIN AND COMMONLY USEDДокумент3 страницыTYPES OF PIN AND COMMONLY USEDdevmarineacademyОценок пока нет
- Types of Screws and Bolts: Fasteners With A Tapered Shank (Self-Threading Screws)Документ8 страницTypes of Screws and Bolts: Fasteners With A Tapered Shank (Self-Threading Screws)Saiful AmreeОценок пока нет
- Types of FastenersДокумент16 страницTypes of FastenersWDS GroupОценок пока нет
- Mechanical Fasteners - Part IIДокумент24 страницыMechanical Fasteners - Part IIsaded05Оценок пока нет
- Fasteners and HardwareДокумент42 страницыFasteners and HardwareAyman MousaОценок пока нет
- Washers and TypesДокумент9 страницWashers and TypesRamu PavanОценок пока нет
- PJJ Mechanical FastenerДокумент14 страницPJJ Mechanical FastenerAdib RizqullohОценок пока нет
- Free Hand Skech Book - 579Документ22 страницыFree Hand Skech Book - 579mpatilboy25Оценок пока нет
- 42 Different Types of Wrenches Explained in Detail Notes PDFДокумент24 страницы42 Different Types of Wrenches Explained in Detail Notes PDFMuhammad ZainОценок пока нет
- Module 6-5 Fasteners Pt7 (3) PresentationДокумент15 страницModule 6-5 Fasteners Pt7 (3) Presentationabdullahqureshi789456Оценок пока нет
- CP3 - Free Hand SketchДокумент181 страницаCP3 - Free Hand SketchHrishikesh deshpandeОценок пока нет
- Spare Parts List For Drive Unit Digga Pd6 - Pd7Документ5 страницSpare Parts List For Drive Unit Digga Pd6 - Pd7NOVIKOVОценок пока нет
- Carraro 26.22Документ9 страницCarraro 26.22Mindaugas MonkevičiusОценок пока нет
- Mini Fragment Implants and InstrumentsДокумент13 страницMini Fragment Implants and InstrumentsMarc KleinОценок пока нет
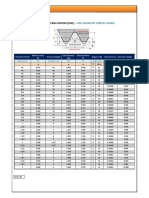
- UNC, UNF, & UNEF Thread ANSI B1,1 PDFДокумент4 страницыUNC, UNF, & UNEF Thread ANSI B1,1 PDFLuRobertОценок пока нет
- HQ TC 006Документ18 страницHQ TC 006ratneshsrivastava7Оценок пока нет
- Formulario geométrico engranesДокумент2 страницыFormulario geométrico engranesLuis Eduardo Rodriguez GarrafaОценок пока нет
- Transmission P T oДокумент1 страницаTransmission P T oGuyue be0% (1)
- PDF Din 976 - CompressДокумент7 страницPDF Din 976 - CompresskrisОценок пока нет
- Fasteners Guide: Thread BasicsДокумент28 страницFasteners Guide: Thread BasicsLaritza Marquez CristanchoОценок пока нет
- MU06 Rosca Americana Grossa Unc Tecem PDFДокумент1 страницаMU06 Rosca Americana Grossa Unc Tecem PDFJnr SktОценок пока нет
- Power Transmission: Components Used To Transmit Power: Gears, Belt, Clutch and BrakesДокумент17 страницPower Transmission: Components Used To Transmit Power: Gears, Belt, Clutch and Brakesrip111176Оценок пока нет
- TR 4050Документ14 страницTR 4050Fabian Hernandez HernandezОценок пока нет
- Tronzadora de Metal Dewalt) 687641-EДокумент4 страницыTronzadora de Metal Dewalt) 687641-EManuel HernandezОценок пока нет
- Trapezoidal ThreadsДокумент5 страницTrapezoidal ThreadsSaraswantoОценок пока нет
- PulleyДокумент6 страницPulleySanthosh PothulaОценок пока нет
- Helicoil Metric Inserts - Aerocpace Standard Interchangeability ListДокумент2 страницыHelicoil Metric Inserts - Aerocpace Standard Interchangeability Listja_mufc_scribd100% (1)
- Design and Selection Of: Robert P. Phlllips Specialty Tools Division RockfordДокумент14 страницDesign and Selection Of: Robert P. Phlllips Specialty Tools Division RockfordPrabhat SharmaОценок пока нет
- D&E Excel Bom: WBS: Nv15-Ot660 DCN:45529Документ2 страницыD&E Excel Bom: WBS: Nv15-Ot660 DCN:45529Dhenil ManubatОценок пока нет
- Agma-918-A93 Examples For Calculationg Geometrical Factors For Spur An Helical Gears PDFДокумент49 страницAgma-918-A93 Examples For Calculationg Geometrical Factors For Spur An Helical Gears PDFMariorosales MendezОценок пока нет
- PDF - Self Recorded - Lect-7 Unit - 3 Gear Trains - Problems On Epicyclic Gear TrainДокумент15 страницPDF - Self Recorded - Lect-7 Unit - 3 Gear Trains - Problems On Epicyclic Gear TrainNikhil JadhavОценок пока нет
- Inventory levels and stock transfers of tools and fittingsДокумент1 626 страницInventory levels and stock transfers of tools and fittingsAbdul BasheerОценок пока нет
- GF 400 2017Документ351 страницаGF 400 2017ArlanОценок пока нет
- KORLOYTESTDEHAYEДокумент36 страницKORLOYTESTDEHAYEnicodehayeОценок пока нет
- FT 200Документ36 страницFT 200api-242597694Оценок пока нет
- 2nd Chapter Notes Mechanical Engineering DiplomaДокумент7 страниц2nd Chapter Notes Mechanical Engineering DiplomaUsmanОценок пока нет
- 3.125 11ns THread SpecificationДокумент4 страницы3.125 11ns THread SpecificationvijaygalaxyОценок пока нет
- AGCO Beauvais Engineering: Fasteners: Metallurgical RequirementsДокумент5 страницAGCO Beauvais Engineering: Fasteners: Metallurgical RequirementsRafa Lopez PuigdollersОценок пока нет
- Theory of Gears r3Документ53 страницыTheory of Gears r3gamini ranaweeraОценок пока нет
- Southbend Shaper V2 Parts ListДокумент6 страницSouthbend Shaper V2 Parts ListStephen HowardОценок пока нет
- Simple MachinesДокумент13 страницSimple Machinespetunia1008554Оценок пока нет