Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2012: GCE Physics (6PH01) Paper 01 Physics On The Go
Загружено:
Cka DohaИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2012: GCE Physics (6PH01) Paper 01 Physics On The Go
Загружено:
Cka DohaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2012
GCE Physics (6PH01) Paper 01 Physics on the go
Question Number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Answer B B C D B C D A C C
Mark 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Question Number 11*
Answer (QWC Work must be clear and organised in a logical manner using technical wording where appropriate) Plastic: doesnt return to original shape OR stays stretched OR permanently deformed OR stays bent when force/stress removed This is brittle behaviour Breaks/fails/cracks/snaps with little/no plastic deformation OR breaks under stress due to propagation of cracks OR breaks just beyond elastic limit / limit of proportionality Total for question 11
Mark
(1) (1) (1)
(1)
4 4
Question Number 12
Answer Newtons 3rd law: The minimum: Every action has an equal and opposite reaction OR More detail: An object A exerts a force on object B then object B exerts an equal and opposite force on object A Forces act on different bodies OR forces act on the road and the tyre Forces act in opposite directions OR (directions of the) forces are backwards and forwards Forces have same magnitude/size OR both forces are 300 N
Mark
(1)
(1)
(1) (1)
Forces are of same kind OR forces are both are (frictional) contact forces/friction Total for question 12
(1)
5 5
Question Number 13
Answer See: W = mg OR newton unit of force OR newton unit of weight W = 0.98 N or W = 0.1 (kg) x 9.81 (N kg-1 ) = 1 N See: W = Fs OR gpe = Wh OR gpe = mgh OR joule unit of energy Gpe = 0.98 J See: P = W/t or variation OR watt unit of power P = 0.98 W Total for question 13 (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1)
Mark
6 6
Question Number 14 (a)
Answer Line not straight OR gradient not constant Force not proportional to extension OR to obey Hookes Law, force should be proportional to extension Use of area under graph Work done = 2.5 J Example of calculation 0.5 x 15 x 0.33 = 2.48 J OR 1255 squares 2 10-3 J = 2.51 J Elastic (tries to) return to a smaller/original length (So) will be in tension OR applies force /pull Work done stretching the elastic greater OR area under stretching>area under releasing OR the area between the two lines represents the energy (So) energy must be dissipated (in process) OR energy transferred as heat OR energy transferred to internal energy Total for question 14 (1) (1) (1) (1)
Mark
2 2
14 (b)
14 (c) 14 (d)
(1) (1)
(1)
(1)
2 8
Question Number 15(a)(i)
Answer Laminar: at least 2 roughly parallel lines before object Turbulent: lines crossing or showing change in direction of greater than 90o. (Max 1 mark if the laminar flow not shown leading into the turbulent flow.) (1) (1)
Mark
15(a)(ii)
2 marks 1 mark only Laminar flow: No abrupt change in velocity of flow OR no abrupt change in speed or direction of flow (must mention both speed and direction) OR velocity at a point is constant OR flows in layers/flowlines/streamlines OR layers do not mix/cross OR layers are parallel
(1)
15(b)(i) 15(b)(ii)
Turbulent flow: Mixing of layers/flowlines/streamlines OR crossing of layers etc. OR contains eddies OR contains vortices/whirlpools OR abrupt/random changes in speed or direction Greater velocity with lower viscosity Lower viscosity So faster flow OR greater velocity Total for question 15
(1) (1) (1) (1)
2 1 2 7
Question Number 16(a)(i)
Answer Use of v = s/t Velocity = 2.1 (m s-1) (No ue) Example of calculation v= = 2.14 m s-1 Use of appropriate equation(s) to calculate velocity Velocity = 4.3 (m s-1) (No ue) (if v = 0 and g = - 9.81 have not been used only award the first mark) Example of calculation v = u + at 0 = u + (-9.81 ms-2) 0.44 s u = 9.81 m s-2 0.44 s = 4.3 m s-1 OR s = ut + at2 0 = (u 0.88 s) + ((-9.81 ms-2) (0.88 s)2) u = 4.3 m s-1 Correct use of Pythagoras/trig function to find the velocity. Magnitude = 4.8 m s-1 Correct use of trig function Angle = 64 (ecf from parts (i) and (ii)) Example of calculation velocity2 = (2.1 m s-1)2 + (4.3 m s-1)2 velocity = 4.8 m s-1 tan of angle = angle = 63.9 (1) (1)
Mark
16(a)(ii)
(1) (1)
16(a)(iii)
(1) (1) (1) (1)
16(b)(i)
Air resistance has not been taken into account OR air resistance acts on the rocket OR friction of the rocket on the stand has not been taken into account OR energy dissipated/transferred due to air resistance (just air resistance does not gain credit) Max 2 Can watch again Can slow down /watch frame by frame/stop at maximum height Too fast for humans to see Does not involve reaction time Can zoom in (to see height reached) Total for question 16
(1)
16(b)(ii)
(1) (1) (1) (1) (1)
2 11
Question Number 17(a)(i)
Answer Upthrust/U Weight/W/mg/gravitational force/force due to gravity (Viscous) drag/fluid resistance/friction/F/D/V (3 correct = 2 marks, 2 correct = 1 mark. All arrows must touch the dot and straight, vertical lines required, no curving around dot, arrows can be of any length)
Mark
17(a)(ii)*
2 marks 0 marks 2 marks 2 marks 1 mark (QWC Work must be clear and organised in a logical manner using technical wording where appropriate) Initially viscous drag = 0 OR viscous drag is very small OR resultant force is downwards OR W > U OR W>U + D Viscous drag increases (Until) forces balanced OR resultant/net force zero OR forces in equilibrium (Therefore) no acceleration (To gain all 4 marks, any letters used to indicate forces must be defined in either parts (a)(i) or (a)(ii)). W = U + D (allow ecf from diagram in part (a)(i)) (1) (1) (1) (1) 4
17(a)(iii)
(1)
Question Number 17(b)(i)
Answer Use of mass = density volume Upthrust = 2.1 105 (N) Example of calculation Mass = 1.0 103 kg m-3 2.1 10-9 m3 = 2.1 10-6 kg Upthrust = 2.1 10-6 kg 9.81 N kg-1 = 2.1 10-5 N State or use viscous drag = W U (F = 3.6 10-5 N) Use of F = 6rv Speed = 2.0 m s-1 (ecf from (b)(i)) (1) Example of calculation F = 5.7 10-5 N 2.1 10-5 N = 3.6 10-5 N v= = = 2.0 m s-1 (1) (1)
Mark
17(b)(ii)
(1)
(1)
17(c)
larger particles have higher terminal/maximum/average velocity OR smaller particles reach terminal velocity quicker MAX 2 Viscous drag varies in proportion to radius (or area in proportion to radius squared) but weight varies in proportion to radius cubed (terminal) velocity proportional to radius squared Total for question 17
(1)
(1) (1) (1)
3 15
Question Number 18(a)
Answer Use of F = kx k = 32 (N m-1) Example of calculation = 32.0 N m-1 k= (1) (1)
Mark
18(b)(i)
Use of F = kx OR F = ma F = 4.1 (N) (ecf) Example of calculation F = 31.97 N m-1 0.127 m F = 4.06 N OR F = 0.4 kg x (9.81 m s-2 +0.4 m s-2) F = 4.08 N Max 2 Can be answered using a description: Resultant force = force of spring on mass - weight Substitution of resultant force into F = ma OR Could be answered using a calculation e.g. F = 4.06 N 3.9 N a = 0.16 N OR clear substitution of any force into this equation. 0.4 m s-2 Use of v = u + at v = 0.8 m s-1 (allow ecf) Example of calculation v = 0 + (0.4 x 2) = 0.8 m s-1
(1) (1)
18(b)(ii)
(1) (1)
(1) (1) (1) (1)
18(b)(iii)
18(b)(iv) 18(b)(v)
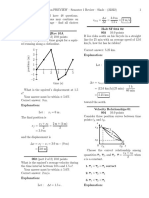
Graph correct shape i.e. 1 region of acceleration, 1 region of deceleration Constant velocity between Use of area under graph to find distance OR use of appropriate equations of motion Distance = 4.0 m (correct answer only) Example of calculation Area = ( 2 s 0.8 m s-1 ) + ( 3 s 0.8 m s-1 ) + ( 2 s 0.8 m s-1 ) Area = 4.0 m Spring extended beyond static extension OR extension increased at start (So) resultant force upwards Total for question 18
(1) (1) (1) (1)
18(b)(vi)
(1) (1)
2 14
Вам также может понравиться
- 1A Force MSДокумент69 страниц1A Force MSShuvashis BiswasОценок пока нет
- Statics & Resolving Forces 2 MSДокумент8 страницStatics & Resolving Forces 2 MSelsieОценок пока нет
- Jan 11 MSДокумент9 страницJan 11 MSshangardeziОценок пока нет
- Ias-Physics Student Text Book Answer.Документ14 страницIas-Physics Student Text Book Answer.mayaОценок пока нет
- Jee Main 2017 Question Paper Solutions Physics 2nd AprilДокумент22 страницыJee Main 2017 Question Paper Solutions Physics 2nd AprilAmit SharmaОценок пока нет
- EdUnit 5 Answers (1995-2006) Excel PhysicsДокумент141 страницаEdUnit 5 Answers (1995-2006) Excel PhysicsAravinth Pushparaj100% (2)
- Edexcel A Level Bk2 Physics Answers FINAL PDFДокумент39 страницEdexcel A Level Bk2 Physics Answers FINAL PDFNasrin SultanaОценок пока нет
- PhysicsДокумент13 страницPhysicsbrandonllsОценок пока нет
- MS Jan 2006 Paper - 5 & 6Документ21 страницаMS Jan 2006 Paper - 5 & 6Parbon AcharjeeОценок пока нет
- Physics I - Final - Fall 2006 Answer Key: Part A-1 - 48 Points (12 × 4) - There Is Partial Credit For Some QuestionsДокумент5 страницPhysics I - Final - Fall 2006 Answer Key: Part A-1 - 48 Points (12 × 4) - There Is Partial Credit For Some QuestionsAndrian BesliuОценок пока нет
- Answers To Oscillations QuestionsДокумент27 страницAnswers To Oscillations QuestionsMimran1994Оценок пока нет
- 6731 - 01 - Rms - 20060 JanДокумент13 страниц6731 - 01 - Rms - 20060 JanAhmed HussienОценок пока нет
- 1.2 Forces MSДокумент7 страниц1.2 Forces MSTara NaОценок пока нет
- Toaz - Info Cape Physics Unit 1 p2 Mark Schemes 2022 2007 PRДокумент171 страницаToaz - Info Cape Physics Unit 1 p2 Mark Schemes 2022 2007 PRNirvan RampersadОценок пока нет
- Projectiles 2 MSДокумент6 страницProjectiles 2 MSelsieОценок пока нет
- 7 Solutions 2014 With MaterialsДокумент54 страницы7 Solutions 2014 With Materialsapi-248740887Оценок пока нет
- G481 Module 2 Forces in Action Questions MSДокумент7 страницG481 Module 2 Forces in Action Questions MSAmberОценок пока нет
- Density, Viscosity & Drag 1 MSДокумент8 страницDensity, Viscosity & Drag 1 MSaayanzubair12125Оценок пока нет
- Chapter2 AnswersДокумент6 страницChapter2 AnswersanirudhОценок пока нет
- PHY Exam 1Документ8 страницPHY Exam 1Samantha GornickОценок пока нет
- Mark Scheme Practice Mechanics 1110Документ26 страницMark Scheme Practice Mechanics 1110XhanAfaqОценок пока нет
- Frictional Torque On A Rotating Disc: Carl E MunganДокумент5 страницFrictional Torque On A Rotating Disc: Carl E MunganSeethaОценок пока нет
- Answer PHYSIC STPM Trial Sem 1 2013Документ6 страницAnswer PHYSIC STPM Trial Sem 1 2013Zuraini ArshadОценок пока нет
- General Physics ReviewerДокумент8 страницGeneral Physics ReviewerXyrell Claude Monta100% (1)
- Final Exam Review 1-SolutionsДокумент16 страницFinal Exam Review 1-Solutionsdavidchoikekekek100% (1)
- H2 Physics J2 CT1 2013 Paper 2 SolutionsДокумент10 страницH2 Physics J2 CT1 2013 Paper 2 SolutionsMichael LeungОценок пока нет
- 2010 H2 Physics Paper 3 Soln - Updated For StudentsДокумент8 страниц2010 H2 Physics Paper 3 Soln - Updated For Studentslaslover100% (1)
- F GMM/R: 6735 Unit Test Phy5Документ5 страницF GMM/R: 6735 Unit Test Phy5muxadeyОценок пока нет
- Markscheme Phys Yr 10 P 4 Ms Mid yДокумент9 страницMarkscheme Phys Yr 10 P 4 Ms Mid yAhmed FathyОценок пока нет
- JC2 (05/06) Physics Common Test 2006 Suggested Answers: Paper 1Документ13 страницJC2 (05/06) Physics Common Test 2006 Suggested Answers: Paper 1wangks1980Оценок пока нет
- Practicetest 7 SLNДокумент11 страницPracticetest 7 SLNNigel CastilloОценок пока нет
- Solution Assignment 1: (Fall 2013) : Question # 1Документ72 страницыSolution Assignment 1: (Fall 2013) : Question # 1Ayaan JuttОценок пока нет
- Memorandum May/June 2011 Examination: Module Code: Phy1501Документ5 страницMemorandum May/June 2011 Examination: Module Code: Phy1501Gogo SongaОценок пока нет
- CLS Aipmt 14 15 XI Phy Study Package 4 SET 2 Chapter 14Документ54 страницыCLS Aipmt 14 15 XI Phy Study Package 4 SET 2 Chapter 14rupa biswas93% (86)
- Refraction & Superposition AnswerДокумент6 страницRefraction & Superposition Answergrace_ng_45Оценок пока нет
- Mit ExamДокумент11 страницMit ExamAli RostamiОценок пока нет
- 11 12 H2 J1 CT P2solnДокумент8 страниц11 12 H2 J1 CT P2solnMichael LeungОценок пока нет
- Online Review AnswersДокумент15 страницOnline Review AnswersdebshistoryfairОценок пока нет
- 7540 02 Rms 20070314Документ12 страниц7540 02 Rms 20070314shahidqaviОценок пока нет
- RPMT 2011 Question Paper SolutionsДокумент28 страницRPMT 2011 Question Paper SolutionsRohit Mehta100% (1)
- Unit 5 Physics Oscillations AnswersДокумент26 страницUnit 5 Physics Oscillations Answersareyouthere92100% (1)
- Physics Final ProblemsДокумент17 страницPhysics Final ProblemsCheldon BigDaddy Banks100% (1)
- Yr 11 Physics Half Yearly 2011Документ13 страницYr 11 Physics Half Yearly 2011David FengОценок пока нет
- AGS AS Physics MC and SA Answers Term 2 2012: Answers / Explanatory Notes Marks AvailableДокумент6 страницAGS AS Physics MC and SA Answers Term 2 2012: Answers / Explanatory Notes Marks AvailableGeneralBrainsОценок пока нет
- MS G484 Jan11Документ9 страницMS G484 Jan11samy9387Оценок пока нет
- Physics PacketДокумент17 страницPhysics PacketAdarsh BhattОценок пока нет
- Preparatory Guide Physics PDFДокумент260 страницPreparatory Guide Physics PDFHasan NawazОценок пока нет
- Olympiad Paper 1 October 2010 SolutionsДокумент5 страницOlympiad Paper 1 October 2010 SolutionsKarn KumarОценок пока нет
- IAS Physics Student Book 1 (2018) AnswersДокумент32 страницыIAS Physics Student Book 1 (2018) AnswersGazar77% (56)
- Practice Final ExamДокумент7 страницPractice Final ExamChetanya SinglaОценок пока нет
- IAS Physics SB1 AnswersДокумент32 страницыIAS Physics SB1 AnswersManmayee RoutОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5Документ4 страницыChapter 5Aadar NОценок пока нет
- Physics 1 NotesДокумент68 страницPhysics 1 NotesMikhael Glen Lataza100% (1)
- PH2130C 2006 Exam PaperaДокумент7 страницPH2130C 2006 Exam PaperabbteenagerОценок пока нет
- Harcourt Education LTD Catalyst 1 AДокумент125 страницHarcourt Education LTD Catalyst 1 AJoeОценок пока нет
- Sample: Year 8 Mathematics Scheme of WorkДокумент1 страницаSample: Year 8 Mathematics Scheme of WorkCka DohaОценок пока нет
- Unit BДокумент142 страницыUnit BCka DohaОценок пока нет
- Iprimary Awd Maths Iss1 PDFДокумент30 страницIprimary Awd Maths Iss1 PDFCka DohaОценок пока нет
- WPH03 01 Que 20180113 2Документ16 страницWPH03 01 Que 20180113 2Cka DohaОценок пока нет
- WCH03 01 Que 20180124Документ16 страницWCH03 01 Que 20180124Cka DohaОценок пока нет
- 4PH0 1P Que 20140515Документ28 страниц4PH0 1P Que 20140515ramexistsОценок пока нет
- Physics GCE SampleДокумент49 страницPhysics GCE Samplesaif-100% (1)
- Physics A: Unit 2: Approved Specimen Question PaperДокумент13 страницPhysics A: Unit 2: Approved Specimen Question PaperCka DohaОценок пока нет
- 2015 Phy 1pДокумент32 страницы2015 Phy 1pkosala naveen wijekulasuriyaОценок пока нет
- 83 Revision Questions For IGCSE Questions-1Документ5 страниц83 Revision Questions For IGCSE Questions-1Zalnoon Mohamed100% (1)
- How To Get An A in English-Parents VersionДокумент45 страницHow To Get An A in English-Parents VersionsmithmccaulskyОценок пока нет
- c4 A Mark SchemeДокумент16 страницc4 A Mark SchemeCka DohaОценок пока нет
- Physics A: Unit 2: Approved Specimen Question PaperДокумент13 страницPhysics A: Unit 2: Approved Specimen Question PaperCka DohaОценок пока нет
- Stats June 2010 1HДокумент24 страницыStats June 2010 1HCka DohaОценок пока нет
- New Physics SAM PaperДокумент69 страницNew Physics SAM PaperCka DohaОценок пока нет
- New Physics SAM PaperДокумент69 страницNew Physics SAM PaperCka DohaОценок пока нет
- IGCSE Physics Paper 4420 2H Que 20101109Документ36 страницIGCSE Physics Paper 4420 2H Que 20101109zorba_oОценок пока нет
- 6PH08 01 Que 20120307Документ16 страниц6PH08 01 Que 20120307Rashwan ZahirОценок пока нет
- EC2sh LДокумент4 страницыEC2sh LzamdivaОценок пока нет
- Artikel Penelitian Annisa Humairah IbrahimДокумент15 страницArtikel Penelitian Annisa Humairah Ibrahimisma nurhandayaniОценок пока нет
- CEPF640/CEBF640 CEFF640: N-Channel Enhancement Mode Field Effect Transistor FeaturesДокумент4 страницыCEPF640/CEBF640 CEFF640: N-Channel Enhancement Mode Field Effect Transistor FeaturesAngel FaneitezОценок пока нет
- Global Environment Unit 2Документ13 страницGlobal Environment Unit 2Se SathyaОценок пока нет
- Slidex StrepДокумент9 страницSlidex StrepLizeth Daniela RojasОценок пока нет
- General Wireless Design Considerations 1 PDFДокумент0 страницGeneral Wireless Design Considerations 1 PDFDurga TejaОценок пока нет
- Esthetics and Shade Communication: A Practical Approach: Clinical ApplicationДокумент21 страницаEsthetics and Shade Communication: A Practical Approach: Clinical Applicationcatalin_adinaОценок пока нет
- BNB SB0114Документ4 страницыBNB SB0114graziana100% (2)
- B11 - Overload Relays (Ref) ENДокумент20 страницB11 - Overload Relays (Ref) ENAhmed AbazaОценок пока нет
- Quick Start Guide For The Remote Access Dial-In Multiport Ethernet ModemДокумент16 страницQuick Start Guide For The Remote Access Dial-In Multiport Ethernet ModemdilipОценок пока нет
- STAN Statistika 12 PDFДокумент25 страницSTAN Statistika 12 PDFPembelajaran Jarak JauhОценок пока нет
- Type of TrucksДокумент8 страницType of TrucksYojhan VelezОценок пока нет
- Renal New Growth - NCM 103 - or CaseДокумент19 страницRenal New Growth - NCM 103 - or CasePat EnriquezОценок пока нет
- StringTokenizer in JavaДокумент11 страницStringTokenizer in JavaNeha saxena Neha saxenaОценок пока нет
- LEM 91-161 Fla E 0612Документ13 страницLEM 91-161 Fla E 0612Julen IturriozОценок пока нет
- Strength of Materials: 2. Assume Missing Data, If Any, SuitablyДокумент2 страницыStrength of Materials: 2. Assume Missing Data, If Any, SuitablynvnrevОценок пока нет
- Parasites in Reptile PDFДокумент21 страницаParasites in Reptile PDFRamadhani SyafitriОценок пока нет
- B-701 Boysen Permacoat Flat Latex2Документ7 страницB-701 Boysen Permacoat Flat Latex2ircvpandoОценок пока нет
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding - Surgical ManagementДокумент14 страницAbnormal Uterine Bleeding - Surgical ManagementNikhil DevОценок пока нет
- PE4 ExamДокумент3 страницыPE4 ExamEugene ColotОценок пока нет
- TP260SR Tier 3 TC002-1037Документ1 страницаTP260SR Tier 3 TC002-1037Jorge GalarceОценок пока нет
- Government Schemes: Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers' WelfareДокумент29 страницGovernment Schemes: Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers' WelfareDushyant MudgalОценок пока нет
- Marcelo - GarciaДокумент6 страницMarcelo - GarciaNancy FernandezОценок пока нет
- Rig 166 Data SheetДокумент2 страницыRig 166 Data SheetEstuardo OlanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 Introduction To Thermodynamics PDFДокумент17 страницChapter 6 Introduction To Thermodynamics PDFSaurav PaulОценок пока нет
- 9trffi&hpr.! Ni-: Use E EДокумент2 страницы9trffi&hpr.! Ni-: Use E ERafi ZulfiОценок пока нет
- Part 7 Mean Field TheoryДокумент40 страницPart 7 Mean Field TheoryOmegaUserОценок пока нет
- Final Tana Beles - pdf2222Документ72 страницыFinal Tana Beles - pdf2222Tiruneh Yeneneh100% (1)
- MHFU Hunter RankДокумент5 страницMHFU Hunter RankGustin PrayogoОценок пока нет
- Anaerobic Degradation of Palm Oil Mill Ef Uent (POME)Документ8 страницAnaerobic Degradation of Palm Oil Mill Ef Uent (POME)HusainiОценок пока нет
- C P P P: Rain'S Etrophysical Ocket ALДокумент54 страницыC P P P: Rain'S Etrophysical Ocket ALviya7100% (4)