Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Tissue
Загружено:
Raj KumawatИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Tissue
Загружено:
Raj KumawatАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
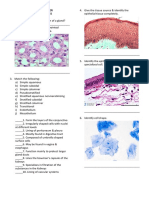
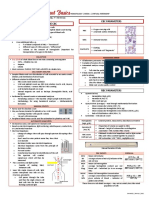
Tissue - a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform certain co mmon functions There are 4 major types
of tissue Epithelial Connective Muscle Nervous 1. Epithelial Tissue General Characteristics: - Found throughout the body, covers all body surfaces both inside and out. - Main glandular tissue. - Attached to underlying connective tissue by noncellular nonliving basement mem brane. - Usually has no vascular tissue - blood supply - Cells reproduce rapidly (rapid healing). - Cells tightly packed together
Functions: Protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, sensory perception Six Specific types of epithelial tissue - categorized based on the shape of the cells and the layers of cells. ( * We won't distinguish glandular epithelium bec ause it is of the cuboidal or columnar type.) A. SIMPLE SQUAMOUS - single layer (simple) of very thin, flattened cells (squamo us). Function: diffusion and filtration. Found in air sacs of lungs, walls of ca pillaries. B. SIMPLE CUBOIDAL - single layer, cube-shaped cells. Function: Secretion and ab sorption. Found: Lining of kidney tubules, ducts of glands, covering surface of ovaries C. SIMPLE COLUMNAR - single layer, elongated cells with their nuclei in about th e same position in each cell (usually near the basement membrane). Protection, s ecretion, absorption. Found in the lining of digestive tract and uterous - contains scatter goblet cells functioning in the secretion of mucus - some columnar cells (involved in absorption) have tiny finger-like processes f rom their free surface called microvilli (increases surface area)
D. STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS - muli-layered, squamous cells. Thicker tisse. Functions in protection. Found lining body cavities like the mouth and outer lay er of skin E. PSEUDOSTRATIFIED COLUMNAR - appear "stratified" but really a single layer wit h nuclei at various levels giving the appearance of layered cells. Usually cilia ted (tiny, hair-like projections for sweeping materials along a surface). Contai ns goblet cells. - Function: secretion and cilia-aided movement - Location: lining air passages like the trachea and tubes of the reproductive s ystem
F. TRANSITIONAL EPITHELIUM - thick, layered cuboidal cells. "Stretchable" tissue , also forms barrier to block diffusion. Found: lining of urinary bladder. 2. Connective Tissue General Characteristics: -Most abundant tissue in your body, found throughout -Binds structures together -Provides support, protection, framework, fills space, stores fat, produces bloo d cells, fights infection, and helps repair tissue. -Composed of more scattered cells with abundant intercellular material ' matrix -Made up of a ground substance (fluid, semi-solid) and fibers -Most has a good blood supply -Cells can reproduce Three common types of cells: 1. mast cells (prevents blood clots) 2. macrophages (phagocytic) and 3. fibroblasts (most abundant, produce fibers) Main types of fibers: -collagenous fibers - thick, made of protein collagen, major structural prot ein in the body, appear in long parallel bundles. Strong, flexible, but not very elastic, also known as white fibers. (bones, ligaments, tendons) - elastic fibers - microfibrils in protein elastin, yellow fibers. Not as st rong, but very elastic (respiratory and vocal cords) CATEGORIES OF CONNECTIVE TISSUE A. LOOSE C.T. or AREOLAR TISSUE - binds skin to underlying organs and organs to organs, space between muscles, throughout body B. ADIPOSE TISSUE - aka FAT, beneath skin, around kidneys and eyeballs, abdomina l membranes. Function: Protective cushion, insulation to preserve body heat, sto res energy, cells are called adipocytes
C. FIBROUS C.T. - dense tissue, closely packed, thick collagenous fibers and fin e network of elastic fibers. Few cells, poor blood supply, thus slow healing. Tendons - connect muscles to bones Ligaments - connect bones to bones
CARTILAGE (all cartilage cells are called chondrocytes) D. HYALINE CARTILAGE - very fine white (collagenous) fibers. Most common cartila ge. Covers ends of bones and joints, noise, respiratory passages. E. ELASTIC CARTILAGE - more flexible and elastic, external ear and larynx F. FIBROCARTILAGE - very tough, large numerous collagenous fibers. Intervertebra l disks, menisci
G. BONE TISSUE - Osseus tissue. Rigid due to mineral salts. Layers - lamellae, haversian canals, osteocytes H. BLOOD TISSUE - circulates throughout the body 3. Muscle Tissue A. B. C. 4. Skeletal - skeletal muscles - voluntary (striated) Smooth - in hollow organs, stomach - involuntary Cardiac - wall of the heart Nerve Tissue - Found in brain, spinal cord, nerves
A. Neurons - transmit signals B. Neuroglia - protection, support
Вам также может понравиться
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Ana Histology PDFДокумент79 страницAna Histology PDFNagesh NОценок пока нет
- The Mitosis Song Paired Activities Sheet PDFДокумент2 страницыThe Mitosis Song Paired Activities Sheet PDFArshe OmaguingОценок пока нет
- Zoo Sem2 Endoplasmic ReticulumДокумент7 страницZoo Sem2 Endoplasmic ReticulumAnadi ChauhanОценок пока нет
- Answers UNIT 2 Lesson 2.2 Structures of Animal CellsДокумент7 страницAnswers UNIT 2 Lesson 2.2 Structures of Animal CellsKatznjammrОценок пока нет
- Cell The Unit of LifeДокумент5 страницCell The Unit of LifeeloelОценок пока нет
- Optimization of Chromosome Counting Method in Acacia Crassicarpa in Tissue Culture Laboratory PT Arara Abadi R D PerawangДокумент16 страницOptimization of Chromosome Counting Method in Acacia Crassicarpa in Tissue Culture Laboratory PT Arara Abadi R D PerawangMusliadi PasaribuОценок пока нет
- Cell PartsДокумент2 страницыCell PartsZarahbeth Claire G. ArcederaОценок пока нет
- Botany QuizДокумент3 страницыBotany QuizAleczandra QuesadaОценок пока нет
- The Four Primary Tissue Types:: Epithelial (Covering) Connective Tissue (Support) Muscle (Movement) Nervous (Control)Документ33 страницыThe Four Primary Tissue Types:: Epithelial (Covering) Connective Tissue (Support) Muscle (Movement) Nervous (Control)Maira Garcia C.100% (2)
- Histolab Reviewer Epithelial TissuesДокумент2 страницыHistolab Reviewer Epithelial TissuesJustine May S. Colico100% (1)
- Graphic Organizer - Plant TissuesДокумент1 страницаGraphic Organizer - Plant TissuesAningat ChristanОценок пока нет
- Cross-Match TestДокумент2 страницыCross-Match TestSaman HarsОценок пока нет
- Exercise 6 111Документ4 страницыExercise 6 111KathrynGarza10Оценок пока нет
- MCQ Cell & Tissue by Gunjan RawalДокумент13 страницMCQ Cell & Tissue by Gunjan RawalgunjanОценок пока нет
- Hematology Week 1 CBCДокумент4 страницыHematology Week 1 CBCMICHELLE RAPELOОценок пока нет
- Blood 12-6-2018Документ42 страницыBlood 12-6-2018Noor Fatima100% (1)
- Cell-PreparedДокумент33 страницыCell-PreparedFarhanОценок пока нет
- Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Studies On Methanolic Extract of Caryopses of Echinochloa Frumentacea LinkДокумент6 страницAntioxidant and Hepatoprotective Studies On Methanolic Extract of Caryopses of Echinochloa Frumentacea LinkpraneethasruthiОценок пока нет
- Comic StripДокумент2 страницыComic StripSatori TendōОценок пока нет
- BYJU'S Subjective Mock Paper DiscussionДокумент7 страницBYJU'S Subjective Mock Paper DiscussionNaman VatsОценок пока нет
- 1GS Cell PPT 2018Документ73 страницы1GS Cell PPT 2018pixiedustОценок пока нет
- Conducting TissuesДокумент7 страницConducting TissuesDhruv PalОценок пока нет
- Act 3 Animal Cell.Документ8 страницAct 3 Animal Cell.SidОценок пока нет
- Muscle TissueДокумент30 страницMuscle TissueAhwaar Chaudary100% (1)
- Gram StainДокумент3 страницыGram StainAbduladheemОценок пока нет
- Imulfex WB-SP For Leukocyte ReductionДокумент2 страницыImulfex WB-SP For Leukocyte ReductiondatitoxОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 (Cell Organisation)Документ3 страницыChapter 2 (Cell Organisation)Danial AsyraafОценок пока нет
- K.14 Histology of Nasopharynx & PleuraДокумент26 страницK.14 Histology of Nasopharynx & Pleuraenri0% (1)
- Heart HistologyДокумент11 страницHeart HistologyAmanuel MaruОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Evaluation of PlateletsДокумент4 страницыLaboratory Evaluation of Plateletscherry nokiaОценок пока нет