Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Biology Terms
Загружено:
Angelica Mae LasamИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Biology Terms
Загружено:
Angelica Mae LasamАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Oxidation is defined as the interaction between oxygen molecules and all the different substances they may contact,
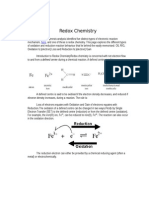
from metal to living tissue. Technically, however, with the discovery of electrons, oxidation came to be more precisely defined as the loss of at least one electron when two or more substances interact. Those substances may or may not include oxygen. (Incidentally, the opposite of oxidation is reduction the addition of at least one electron when substances come into contact with each other.) Sometimes oxidation is not such a bad thing, as in the formation of super-durable anodized aluminum. Other times, oxidation can be destructive, such as the rusting of an automobile or the spoiling of fresh fruit. Reduction- A chemical reaction in which hydrogen is added to, or oxygen is removed from, a compound. Opposite of oxidation.
A reducing agent (also called a reductant or reducer) is the element or compound in a reductionoxidation (redox) reaction that donates an electron to another species; however, since the reducer loses an electron we say it is "oxidized". This means that there must be an "oxidizer"; because if any chemical is an electron donor (reducer), another must be an electron recipient (oxidizer). Thus reducers are "oxidized" and oxidizers are "reduced". An oxidizing agent (also called an oxidant, oxidizer or oxidiser) can be defined as a substance that removes electrons from another reactant in a redox chemical reaction. The oxidizing agent is "reduced" by taking electrons onto itself and the reactant is "oxidized" by having its electrons taken away. Oxygen is the prime example of an oxidizing agent, but it is only one among many. An oxidizing agent (also called an oxidizer or oxidant) is referred to as a chemical compound that readily transfers oxygen atoms or a substance that gains electrons in a redox chemical reaction. The permanganate ion removes electrons from oxalic acid molecules and thereby oxidizes the oxalic acid. Thus, the MnO4- ion acts as an oxidizing agent in this reaction. Oxalic acid, on the other hand, is a reducing agent in this reaction. By giving up electrons, it reduces the MnO4- ion to Mn2+. coenzyme, Any of a number of freely diffusing organic compounds that function as cofactors withenzymes in promoting a variety of metabolic reactions. Coenzymes participate in enzymemediatedcatalysis in stoichiometric (mole-for-mole) amounts, are modified during the reaction, and may require another enzyme-catalyzed reaction to restore them to their original state. coenzyme A nonproteinaceous organic substance that usually contains a vitamin or mineral and combines with a specific protein, the apoenzyme, to form an active enzyme system.
Вам также может понравиться
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsОт EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- Combining Chemicals - Fun Chemistry Book for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksОт EverandCombining Chemicals - Fun Chemistry Book for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksОценок пока нет
- Ethyl Acetate Process and Plant Design PresentationДокумент56 страницEthyl Acetate Process and Plant Design PresentationLee Jian100% (5)
- Book - Dictionary of Terms Used in Petroleum Processing and Refining, D Jones, P. Pujado, S. Treese, Springer, 2015Документ142 страницыBook - Dictionary of Terms Used in Petroleum Processing and Refining, D Jones, P. Pujado, S. Treese, Springer, 2015usebio64Оценок пока нет
- Redox Reactions: Reduction and Oxidation of The ReactantsДокумент43 страницыRedox Reactions: Reduction and Oxidation of The ReactantsNur Atiqah Azmi100% (1)
- History of Oil and Gas in NigeriaДокумент7 страницHistory of Oil and Gas in NigeriaChi Ka100% (1)
- Flash and Fire PointДокумент10 страницFlash and Fire PointYasser AshourОценок пока нет
- IOCL MAthuraДокумент52 страницыIOCL MAthuraUday Bhardwaj100% (3)
- CHE 305 Introduction To VLEДокумент45 страницCHE 305 Introduction To VLEDANICE LUNAОценок пока нет
- Introductiontogastransportation 161222145926 PDFДокумент26 страницIntroductiontogastransportation 161222145926 PDFAl Jawad100% (1)
- Latest Developments in Ammonia Production TechnologyДокумент21 страницаLatest Developments in Ammonia Production TechnologyAnonymous msVFza100% (3)
- Grade 6 Q1 MELCs Unpacked InventoryДокумент6 страницGrade 6 Q1 MELCs Unpacked InventoryKristine Barredo93% (45)
- OxidacionДокумент1 страницаOxidacionPaulaОценок пока нет
- Chemistry 1.11Документ1 страницаChemistry 1.11terran2020Оценок пока нет
- Chemistry 1.11Документ1 страницаChemistry 1.11terran2020Оценок пока нет
- Chemistry 1.11Документ1 страницаChemistry 1.11terran2020Оценок пока нет
- Chemistry 1.11Документ1 страницаChemistry 1.11terran2020Оценок пока нет
- Schneider - Chillers RangeДокумент10 страницSchneider - Chillers RangeerreagaaОценок пока нет
- Chemical Bond Valence: Df8f7rf6f56d5dДокумент91 страницаChemical Bond Valence: Df8f7rf6f56d5dfitradikojerdsswОценок пока нет
- Redox Matkul AnorganikДокумент10 страницRedox Matkul AnorganikAflah Lana Qistina SalsabilaОценок пока нет
- Chemistry IntrodutionДокумент13 страницChemistry IntrodutionlalithaОценок пока нет
- Redox Processes. Eh-pH RelationshipsДокумент13 страницRedox Processes. Eh-pH RelationshipsMozakkir AzadОценок пока нет
- OxidationДокумент5 страницOxidationKudzanai MuchatoraОценок пока нет
- What Are Redox Reactions?: Chemical ReactionДокумент8 страницWhat Are Redox Reactions?: Chemical ReactionReal RuchitОценок пока нет
- Chemical Reaction Oxidation States Electron Transfer Chemical Reactions Oxidation State Electrons Chemical SpeciesДокумент1 страницаChemical Reaction Oxidation States Electron Transfer Chemical Reactions Oxidation State Electrons Chemical SpeciesAlexandra GrigoreОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Project FileДокумент9 страницChemistry Project FileRadhikaОценок пока нет
- Oxidizing and Reducing AgentsДокумент2 страницыOxidizing and Reducing AgentsKenneth D. LigutomОценок пока нет
- Unit I. Electrochemistry: Learning ObjectivesДокумент15 страницUnit I. Electrochemistry: Learning ObjectivesArdenz Emrey LagascaОценок пока нет
- Redox Titration-Study MaterialДокумент21 страницаRedox Titration-Study MaterialUma NathОценок пока нет
- Redox (Reduction-Oxidation, PronunciationДокумент1 страницаRedox (Reduction-Oxidation, PronunciationWlader SalgadoОценок пока нет
- MyДокумент2 страницыMyShourya PratapОценок пока нет
- Oxidizing and Reducing AgentДокумент9 страницOxidizing and Reducing Agentabuzar khalidОценок пока нет
- Oxidation-Reduction ReactionsДокумент8 страницOxidation-Reduction ReactionsShaker MahmoodОценок пока нет
- OXIDATIONДокумент8 страницOXIDATIONAtif RanaОценок пока нет
- Redox Reactions: What Is A Redox Reaction?Документ2 страницыRedox Reactions: What Is A Redox Reaction?izzati03Оценок пока нет
- Chemistry For Engineers: CHEM 114Документ22 страницыChemistry For Engineers: CHEM 114Ivyy Joyce BuanОценок пока нет
- Chemistry For Engineers: CHEM 114Документ22 страницыChemistry For Engineers: CHEM 114Ivyy Joyce BuanОценок пока нет
- Redox ReaxДокумент2 страницыRedox ReaxKristine Celaya AlbinoОценок пока нет
- Chem Notes Redox ReactionsДокумент2 страницыChem Notes Redox Reactionsyifec22390Оценок пока нет
- Oxidation and Reduction in Organic Chemistry AssignmentДокумент9 страницOxidation and Reduction in Organic Chemistry AssignmentAmanuel TarekegnОценок пока нет
- RedoksДокумент33 страницыRedokssanty_vanftowsОценок пока нет
- 9.1 Oxidation and Reduction 9.1.1 Definitions: Oxidation and Reduction Take Place Together at The Same Time in The SameДокумент22 страницы9.1 Oxidation and Reduction 9.1.1 Definitions: Oxidation and Reduction Take Place Together at The Same Time in The SameJaimin SuraniОценок пока нет
- L14 - Reduction and OxidationДокумент50 страницL14 - Reduction and OxidationNur AishahОценок пока нет
- Orca Share Media1679932480278 7046147521763878353Документ13 страницOrca Share Media1679932480278 7046147521763878353Endelyn Salva SajorgaОценок пока нет
- Enzymes Gen BioДокумент11 страницEnzymes Gen BioLyanna HidalgoОценок пока нет
- Chemistry and Electricity:: ElectrochemistryДокумент5 страницChemistry and Electricity:: ElectrochemistrySuleman TariqОценок пока нет
- Redox TitrationДокумент24 страницыRedox TitrationNamrata patelОценок пока нет
- Redox MCQ Sheet For Jee MainДокумент10 страницRedox MCQ Sheet For Jee MainAbhay VishwakarmaОценок пока нет
- Class XI Redox Reactions NotesДокумент5 страницClass XI Redox Reactions NoteseasaОценок пока нет
- G - 004 - Chemical - Reactions IGCSE Chem CDДокумент1 страницаG - 004 - Chemical - Reactions IGCSE Chem CDPrincess KimОценок пока нет
- Redox Reaction: Oxidation and Reduction in Terms of Oxygen TransferДокумент28 страницRedox Reaction: Oxidation and Reduction in Terms of Oxygen TransferfaridОценок пока нет
- Genera Biology 1 (Chemical Reaction)Документ3 страницыGenera Biology 1 (Chemical Reaction)Jean DaclesОценок пока нет
- Experiment 2c Introduction, Objective, ProcedureДокумент3 страницыExperiment 2c Introduction, Objective, ProcedureHisfan NaziefОценок пока нет
- List of Definitions Chemistry MДокумент8 страницList of Definitions Chemistry Mlucky Dino54Оценок пока нет
- Redox Reactions - Shobhit NirwanДокумент12 страницRedox Reactions - Shobhit NirwanAadarsh PandeyОценок пока нет
- Lidza - OxidationДокумент3 страницыLidza - OxidationKudzanai MuchatoraОценок пока нет
- Redox Reaction: Home Work Ch. 4.4, P. 109-114 Oxidation Number Ch. 19.1 19.7 19.8 19.9Документ34 страницыRedox Reaction: Home Work Ch. 4.4, P. 109-114 Oxidation Number Ch. 19.1 19.7 19.8 19.9Sam LoveОценок пока нет
- ElectrochemistryДокумент23 страницыElectrochemistryVignesh VbОценок пока нет
- Redox Reactions NotesДокумент4 страницыRedox Reactions Notesarjunrkumar2024Оценок пока нет
- Hsslive Xi Chem Notes Anil CH 8. REDOX REACTIONSДокумент6 страницHsslive Xi Chem Notes Anil CH 8. REDOX REACTIONSKrishnendu NairОценок пока нет
- Applications of Redox Reaction in ElectrochemistryДокумент3 страницыApplications of Redox Reaction in ElectrochemistryStaniaОценок пока нет
- A Metal Bar Containing Iron Acquires Dark Orange ColorДокумент1 страницаA Metal Bar Containing Iron Acquires Dark Orange ColorPedroPasmayОценок пока нет
- Ions and SaltsДокумент2 страницыIons and Saltsmansi bavliyaОценок пока нет
- Unit 4 Electrochemical EnergyДокумент49 страницUnit 4 Electrochemical EnergyRitchel Conde BoholОценок пока нет
- CH 6,7 NotesДокумент18 страницCH 6,7 NotesAishi GuptaОценок пока нет
- #1 Soal Diskusi RedoksДокумент8 страниц#1 Soal Diskusi RedoksAlfi FadhilaОценок пока нет
- Redox Reactions: Classical Idea of Redox ReactionДокумент10 страницRedox Reactions: Classical Idea of Redox ReactionRohan ThomasОценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry and Redox ReactionДокумент2 страницыElectrochemistry and Redox ReactionJeremy De CastroОценок пока нет
- Redox Reactions & ElectrochemistryДокумент14 страницRedox Reactions & Electrochemistryajaysharma19686191Оценок пока нет
- MGP1-P4068MS001-F14-0004 - 003 - Valve Sizing Calculations - RemovedДокумент19 страницMGP1-P4068MS001-F14-0004 - 003 - Valve Sizing Calculations - RemovedA siddiquiОценок пока нет
- Manual (Simulation)Документ17 страницManual (Simulation)Asad RazaОценок пока нет
- Sci Worksheet W3 Act 2Документ5 страницSci Worksheet W3 Act 2Mae GuerreroОценок пока нет
- Internal Stage by Stage Balances (W4)Документ21 страницаInternal Stage by Stage Balances (W4)Tle SupawidОценок пока нет
- Uop Pacol Dehydrogenation Process: Peter R. PujadóДокумент10 страницUop Pacol Dehydrogenation Process: Peter R. PujadóBharavi K S100% (1)
- Assignment 2 (Energy Efficiency in Boilers) 2017-2018Документ2 страницыAssignment 2 (Energy Efficiency in Boilers) 2017-2018A.HassanОценок пока нет
- Soxhlet Apparatus: AIM: To Understand The Construction and Working of A Soxhlet ApparatusДокумент4 страницыSoxhlet Apparatus: AIM: To Understand The Construction and Working of A Soxhlet ApparatusARATHI PMPMОценок пока нет
- Chm271 - Chapter 2 Thermochemistry - UpdatedДокумент68 страницChm271 - Chapter 2 Thermochemistry - UpdatedNurfarhanah AsyknОценок пока нет
- MeetingДокумент16 страницMeetingwikimax155Оценок пока нет
- W4V28 - Gas Logistics - IFP - TOTAL MOOCДокумент4 страницыW4V28 - Gas Logistics - IFP - TOTAL MOOCRebekah PetersonОценок пока нет
- LNG As A Marine Fuel - Possibilities and Problems: Jerzy HerdzikДокумент8 страницLNG As A Marine Fuel - Possibilities and Problems: Jerzy HerdzikKeyboardMan1960Оценок пока нет
- The Story of ULSD Optimisation at The Chevron Pembroke RefineryДокумент11 страницThe Story of ULSD Optimisation at The Chevron Pembroke RefineryLindsey BondОценок пока нет
- Assignment-1 (Water Technology)Документ2 страницыAssignment-1 (Water Technology)Mohit LuniaОценок пока нет
- Unit Iv Control of Emission From Si and Ci EnginesДокумент30 страницUnit Iv Control of Emission From Si and Ci Enginesrahulmnm007Оценок пока нет
- Chemical Thermodynamics 2Документ33 страницыChemical Thermodynamics 2Gliezl ImperialОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 2Документ3 страницыWorksheet 2Pratyusha MitraОценок пока нет
- Hydrate Formation Sour Gas - CampbellДокумент5 страницHydrate Formation Sour Gas - CampbellthunderОценок пока нет
- This Study Resource Was: ProblemДокумент2 страницыThis Study Resource Was: ProblemKyle Labastilla100% (1)
- First Aid For Accident With HFC/HCFCДокумент2 страницыFirst Aid For Accident With HFC/HCFCSrini VasanОценок пока нет
- 13.09 Stream A AxensДокумент27 страниц13.09 Stream A AxensJorge Ariel QuipildorОценок пока нет
- Chem12 C1102 SWBSДокумент5 страницChem12 C1102 SWBSAhmad asaОценок пока нет