Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Bio 202 - Exam 1 (Part 1)
Загружено:
GretchenАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Bio 202 - Exam 1 (Part 1)
Загружено:
GretchenАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
BIO 202 - EXAM 1 REVIEW ( PART 1 )
Chapter 19
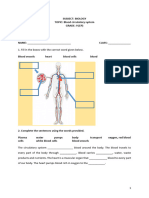
1) Review the relationships amongst blood, interstitial fluid, and lymph.
2) a) b) c) d) e) f)
Blood transports many substances. List six. __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________
3)
Name the four body systems to which blood delivers wastes or chemicals that lead to wastes.
4) a) b) c) d)
List 4 aspects of homeostasis regulated by blood. __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________
5)
Explain how your blood protects you.
6) 7) 8)
Average body temperature is ________________. The pH of blood is _________________. Three hormones that regulate volume and osmotic pressure of blood are __________________, __________________, and ___________________. choices: ADH / aldosterone / ANP / epinephrine / PTH
9) Match the names of the components of plasma with their descriptions. A) Albumins E) Electrolytes F) Fibrinogen G) Globulins _________ Makes up about 92% of plasma _________ Regulatory substances carried in blood _________ Cations and anions carried in plasma _________ Constitutes about 54% of plasma proteins _________ Made by liver; a protein used in clotting _________ Antibody proteins _________ Waste carried to kidneys or sweat glands _________ Food substances carried in blood GAF) Glucose, amino acids, and fats HE) Hormones/enzymes UC) Urea, creatinine W) Water
_________ Of albumin, fibrinogen, and globulin, this is found in the least abundance in plasma
10) 11) 12)
Viruses/bacteria that enter the body as invaders are a) antigens OR b) antibodies? Chemicals made by the body to defend against invaders are a) antigens OR b) antibodies? Immunoglobulins (Igs) produced by plasma cells and found in plasma are a) antigens OR b) antibodies?
13)
Fill in the following blanks with a formed element (leukocytes, erythrocytes, or platelets) a) ________________________ are not truly cells, but cell fragments b) ________________________ are also known as thrombocytes c) ________________________ include neutrophils, lymphocytes, basophils, eosinophils, and monocytes d) ________________________ are also known as white blood cells e) ________________________ make up over 99% of all formed elements
14)
A hematocrit consists of the percentage of centrifuged blood that contains _______________________ blood cells.
15)
Polycythemia occurs when the red blood cell count is ( higher / lower ) than normal. For example, a hematocrit of ( 22 / 40 / 62 ) would indicate polycythemia. Explain why dehydration might lead to polycythemia. Explain also why polycythemia might be dangerous.
16)
Regulation of ( erythrocyte / leukocyte ) number occurs in response to invading microorganisms and antigens.
17)
Blood formation is a process known as ___________________________. All of the different blood cell types arise from _________________________________ cells.
18)
As individuals grow into adulthood, the rate of hemopoiesis ( increases / decreases ). Red bone marrow is then replaced by _____________________________ marrow.
19)
Fill in the blanks in the table to indicate stages in formation of cells. Stem Cell Lymphoid B lymphoblast myeloblast monoblast proerythroblast Myeloid platelet monocyte Precursor Cell Mature Cell T lymphocyte
Which of the following mature cells above passes through a stage as a reticulocyte immediately before the mature stage? ______________________________________
20)
Name several structures where blood formation takes place before birth.
21)
Which type of white blood cells complete their development in lymphoid tissues? ____________________________________________
22)
All other types of blood cells develop totally within myeloid tissue, which is another name for __________________________________________.
23)
Erythropoietin is a hormone made mostly in the _______________________________. This hormone stimulates production of ( RBCs / WBCs / Platelets).
24)
Two types of cytokines that stimulate WBC formation are __________________________________________________ factors (CSFs) and ___________________________ (ILs).
25) 26)
_____________________________ accounts for the color of red blood cells. RBCs ( do / do not ) have a nucleus and mitochondria. Explain why this is an advantage for red blood cells specifically.
27)
RBCs are normally shaped like ______________________ discs. What advantage does this shape offer?
28)
The hemoglobin molecule consists of a central protein, which is the protein ( heme / globin ) with four polypeptide chains called ( hemes / globins ).
29)
Each heme contains one _______________________ atom on which a molecule of ( oxygen / carbon dioxide ) can be transported. Each hemoglobin molecule can carry ( 1 / 4 ) oxygen molecules. Remember, almost all oxygen is transported in this manner.
30)
Carbon dioxide has one combining site on hemoglobin; it is the amino acid portion of the ( heme / globin ). About ( 13% / 70% / 97% ) of CO2 is transported in this manner.
31)
Besides O2 and CO2, hemoglobin can also bind to the gas ( nitric / nitrous ) oxide. NO is produced by cells that line the walls of blood vessels. Describe what NO does.
32) 33)
Know the steps of the RBC life cycle (otherwise known as RBC destruction). ___________________________ is a decrease in oxygen in cells; serves as a signal that erythropoiesis is needed (to help provide more oxygen to tissues).
34)
___________________________ is a hormone produced by kidneys when they are hypoxic; stimulates erythropoiesis in the red bone marrow.
35) 36)
___________________________ is a vitamin necessary for normal hemoglobin formation. ___________________________ is a substance produced by the stomach lining and necessary for normal vitamin B12 absorption.
37)
Leukocytes ( have / lack ) hemoglobin, so these cells are known as ( red blood cells / white blood cells ).
38)
WBC count is accounted for by each type of WBC. Such a breakdown of white blood cells is known as a _____________________________ white blood cell count.
39)
Each white blood cell ( has / lacks ) a nucleus. Which type of WBC has a large kidney-shaped nucleus? ( _____________________________ ) Which type of WBC has a nucelus that occupies most of the cell? ( ________________________________) Which WBC is known as a PMN (polymorphonucleocyte) based on the many shapes of its nucleus? ( _____________________________________ )
40)
Which three WBCs are granulocytes? ____________________________, ______________________________, and ____________________________.
41) 42)
What are MHC antigens and how do they affect the success rate of transplants? ______________________________ is the process by which WBCs stick to the capillary wall cells, slow down, stop, and then squeeze out through the vessel wall.
43)
______________________________ are chemicals known as selectins made by injured or inflamed capillary cells stick to chemicals on neutrophils, slowing them down.
44)
______________________________ is the attraction of phagocytes to chemicals such as kinins or CSFs in microbes or in inflamed tissue.
45)
______________________________ is ingestion and disposal of microbes or damaged tissue by neutrophils or macrophages.
46) 47)
______________________________ the largest percentage of WBCs. ______________________________ produce defensins, lysozymes, and oxidants with antibiotic activity.
48)
______________________________ are types of cells that include B cells, T cells, and NK (natural killer) cells.
49)
______________________________ leave the blood, enter tissues, and release heparin, histamine, and serotonin which are all involved in allergic and inflammatory responses.
50)
______________________________ are involved in allergic reactions, combat histamines and provide protection against parasitic worms.
51)
______________________________ form into fixed and wandering macrophages that clean up sites of infection.
52) 53) 54) 55)
______________________________ are important in phagocytosis (two answers). ______________________________ are classified as agranulocytes (two answers). ______________________________ are known as bands in its immature state. B lymphocytes, or B cells, are especially effective against ( bacteria and their toxins / cancer or transplanted cells, viruses, fungi, and some bacteria ).
56)
T lymphocytes, or T cells, are particularly effective against ( bacteria and their toxins / cancer or transplanted cells, viruses, fungi, and some bacteria ).
57)
Natural killer (NK) cells combat a ( few selected / wide variety ) of microbes plus some cancer cells.
58) 59) 60) 61) 62)
Platelets are also known as ______________________________. Your platelets are formed in ______________________________. Platelets are ______________________________. The primary function of platelets is related to ________________________________. List the three mechanisms of hemostasis. __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________
63) 64)
Be able to explain the steps of coagulation with all the factors and enzymes included. What is the difference between an embolus and a thrombus?
65)
Contrast agglutination and coagulation.
66)
Coagulation, or ________________________, involves coagulation factors found in platelets, plasma, or other tissue fluids. The process ( requires / can occur in abscence of ) red blood cells.
67)
Agglutination, or clumping, of erythrocytes is an antigen-_____________ complex that ( does / does not ) require red blood cells because these are sites of __________________ used in the agglutination reaction.
68)
The surface of RBCs contains chemicals that act as ( antigens / antibodies ), also known as ___________________________. Based on these chemicals, blood can be categorized into at least ( 2 / 4 / 24 / 100 ) different blood groups. One of these groups, the ABO group, consists of four possible blood types. Name them: ________, ________, ________, ________.
69)
Explain what causes hemolysis of RBCs in incompatible blood transfusions.
Вам также может понравиться
- 2017 OL Cell Cycle Exam ReviewДокумент3 страницы2017 OL Cell Cycle Exam ReviewAnne Romo50% (8)
- Chapter 8 Transport in Mammals - WorksheetДокумент5 страницChapter 8 Transport in Mammals - Worksheetapi-3728508100% (2)
- Bio WorksheetДокумент2 страницыBio WorksheetCabdi malik XasanОценок пока нет
- Prosthetic Aspects of Dental Implants - IIДокумент73 страницыProsthetic Aspects of Dental Implants - IIKomal TalrejaОценок пока нет
- Ap - BloodДокумент13 страницAp - BloodJustine May Balinggan DelmasОценок пока нет
- Quiz About Cell & Cell OrganellesДокумент6 страницQuiz About Cell & Cell OrganellesJune Emerson ManalangОценок пока нет
- Activity No. Blood: Name: - Rating - DateДокумент4 страницыActivity No. Blood: Name: - Rating - DateJustine May Balinggan DelmasОценок пока нет
- NUMC 101 Module 1 Cardiovascular System Blood Lab ExerciseДокумент10 страницNUMC 101 Module 1 Cardiovascular System Blood Lab ExerciseHannah Vannerie AlanguiОценок пока нет
- Blood PDFДокумент4 страницыBlood PDFJustine May Balinggan DelmasОценок пока нет
- Blood Components Notes-StudentДокумент8 страницBlood Components Notes-Studentapi-655732711Оценок пока нет
- Blood Cells LabДокумент7 страницBlood Cells LabKameron WardОценок пока нет
- Activity BloodДокумент7 страницActivity BloodlumilumiyahОценок пока нет
- Module Chapter 3Документ31 страницаModule Chapter 3Azween SabtuОценок пока нет
- Biology SPMДокумент8 страницBiology SPMMiztaDushanОценок пока нет
- Mitosis & MeiosisДокумент8 страницMitosis & MeiosisamaraadomaОценок пока нет
- 05 Blood NotesДокумент9 страниц05 Blood Noteszeina.abdulal09Оценок пока нет
- Module 13 Answersheet Anatomy 21Документ3 страницыModule 13 Answersheet Anatomy 21Cherold RoldanОценок пока нет
- Anatomía, Sangre, Jhon FuentesДокумент18 страницAnatomía, Sangre, Jhon FuentesMartin FuentesОценок пока нет
- Science 10 Bio WorksheetsДокумент15 страницScience 10 Bio WorksheetsMemmy KidnaОценок пока нет
- Biology G9 Extended Programme Worksheet1-1Документ3 страницыBiology G9 Extended Programme Worksheet1-1liamlouis982Оценок пока нет
- Module Chapter 3Документ32 страницыModule Chapter 3Miz MiaОценок пока нет
- BIO 202 Blood Lab 22S PDFДокумент2 страницыBIO 202 Blood Lab 22S PDFTraci GardnerОценок пока нет
- CSEC Science - Blood Circulatory System WorksheetДокумент2 страницыCSEC Science - Blood Circulatory System WorksheetC ROBERTSОценок пока нет
- Blood Basics: 1. What Makes Up The Blood in Our Bodies?Документ2 страницыBlood Basics: 1. What Makes Up The Blood in Our Bodies?Jessica StewartОценок пока нет
- MD II Material Pentru 24.03.2020Документ5 страницMD II Material Pentru 24.03.2020Irina Panciu StefanОценок пока нет
- Week 4 Homework - 231005 - 204804Документ36 страницWeek 4 Homework - 231005 - 204804dongolsaleenОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1 - Module 1 - Circulatory SystemДокумент27 страницLesson 1 - Module 1 - Circulatory SystemPapiОценок пока нет
- Circulatory System HandoutДокумент4 страницыCirculatory System HandoutshearmureighОценок пока нет
- Activity 4 Anatomy and PhysiologyДокумент4 страницыActivity 4 Anatomy and PhysiologySarah Jane MaganteОценок пока нет
- Cell Cycle and Division: 11.1 ChromosomesДокумент10 страницCell Cycle and Division: 11.1 ChromosomesEstee ChowОценок пока нет
- Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and TissuesДокумент2 страницыEssentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and TissuesDonna AlejoОценок пока нет
- Cell - The Unit of Life Line-By-Line NcertДокумент14 страницCell - The Unit of Life Line-By-Line Ncertchandumenswear3Оценок пока нет
- Cell Cycle, Mitosis WorksheetДокумент3 страницыCell Cycle, Mitosis Worksheetrosellevalerio2014Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Fill in The BlankДокумент10 страницChapter 3 Fill in The BlankArlanosaurusОценок пока нет
- Heart, Blood Vessesls and Blood WorksheetДокумент4 страницыHeart, Blood Vessesls and Blood WorksheetJoanne MullengerОценок пока нет
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis WorksheetДокумент3 страницыCell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheetjulia.dukeОценок пока нет
- Immunity/Immunology: Objective: Describe The Defensive Functions Possessed by Mammalian BloodДокумент5 страницImmunity/Immunology: Objective: Describe The Defensive Functions Possessed by Mammalian BloodSabina Parvin100% (1)
- Blood Cells and CirculationДокумент1 страницаBlood Cells and CirculationmachukirОценок пока нет
- Immune System REVISION AnswersДокумент22 страницыImmune System REVISION Answersinder191100% (1)
- Biology (3rd Half) Aqa Higher (2019)Документ873 страницыBiology (3rd Half) Aqa Higher (2019)quatumjrОценок пока нет
- Transport in Humans: 8.1 The Human Transport SystemДокумент11 страницTransport in Humans: 8.1 The Human Transport SystemPhylliscccОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry AtfДокумент26 страницBiochemistry AtfDanielchowdary GarapatiОценок пока нет
- BacteriaДокумент5 страницBacteriaShin RyuОценок пока нет
- 3j Cuci - The Circulatory System WorksheetДокумент6 страниц3j Cuci - The Circulatory System Worksheetcharmaine nwankwoОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology/Lymphatic System Chapter 10-ObjectivesДокумент9 страницAnatomy and Physiology/Lymphatic System Chapter 10-ObjectivesJustine May Balinggan DelmasОценок пока нет
- Wksheets BloodДокумент3 страницыWksheets BloodPUNCHОценок пока нет
- Science 6 - 3RD Periodical ExamДокумент4 страницыScience 6 - 3RD Periodical ExamSheree EguiaОценок пока нет
- BIOLOGY TUTORIAL QUESTIONS Prep-1Документ15 страницBIOLOGY TUTORIAL QUESTIONS Prep-1ikoabasiubohОценок пока нет
- Immune System InquiryДокумент2 страницыImmune System InquiryStudentCarolina OrtizОценок пока нет
- S8 - End-of-Unit 1 TestДокумент2 страницыS8 - End-of-Unit 1 TestaloonaothmanОценок пока нет
- Set 2 Cell Biology Grades 4 5 PDFДокумент18 страницSet 2 Cell Biology Grades 4 5 PDFAbir OmarОценок пока нет
- Circulatory SystemДокумент3 страницыCirculatory SystemPatrickОценок пока нет
- Memmlers The Human Body in Health and Disease 11th Edition Cohen Test BankДокумент5 страницMemmlers The Human Body in Health and Disease 11th Edition Cohen Test Banklomentnoulez2iОценок пока нет
- b2 OrganisationДокумент112 страницb2 OrganisationsavinbusinesswomanОценок пока нет
- Practice TestДокумент5 страницPractice Testcarmen sandiegoОценок пока нет
- Quiz 2 (Blood Group) Form 3 ScienceДокумент2 страницыQuiz 2 (Blood Group) Form 3 Sciencechristina teoОценок пока нет
- LONG TEST IN SCIENCE 9-Set AДокумент2 страницыLONG TEST IN SCIENCE 9-Set AJezha Mae VertudazoОценок пока нет
- Plant Kingdom Unit TestДокумент7 страницPlant Kingdom Unit TestrileysandersjakeОценок пока нет
- 1819 Level I Science Basic Question CH 1 Sec 2 PDFДокумент7 страниц1819 Level I Science Basic Question CH 1 Sec 2 PDFCanioОценок пока нет
- Animal Systems Review 202401Документ10 страницAnimal Systems Review 202401NoelleОценок пока нет
- A Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisОт EverandA Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisОценок пока нет
- Chapter 13 Learning Objectives - Spinal Cord and Spinal NervesДокумент2 страницыChapter 13 Learning Objectives - Spinal Cord and Spinal NervesGretchen100% (1)
- Chapter 23 Respiratory System - Study GuideДокумент5 страницChapter 23 Respiratory System - Study GuideGretchenОценок пока нет
- Labeling Bones - Bio 201Документ16 страницLabeling Bones - Bio 201Gretchen100% (1)
- Chapter 12 (Nervous System) Learning ObjectivesДокумент2 страницыChapter 12 (Nervous System) Learning ObjectivesGretchenОценок пока нет
- Bio 201 - Bone Practical Part 1 (Axial Skeleton)Документ5 страницBio 201 - Bone Practical Part 1 (Axial Skeleton)Gretchen100% (1)
- Bio 201 - Bone Practical (Part 2)Документ7 страницBio 201 - Bone Practical (Part 2)GretchenОценок пока нет
- Bio 202 - Exam 1 (Part 3)Документ5 страницBio 202 - Exam 1 (Part 3)GretchenОценок пока нет
- Bio 202 - Exam 1 (Part 2)Документ6 страницBio 202 - Exam 1 (Part 2)GretchenОценок пока нет
- Bio 201 - Tissue Practical (Powerpoint)Документ53 страницыBio 201 - Tissue Practical (Powerpoint)GretchenОценок пока нет
- Dirac Equation Explained at A Very Elementary LevelДокумент16 страницDirac Equation Explained at A Very Elementary Levelsid_senadheera100% (2)
- The Prediction of Travel Behaviour Using The Theory of Planned BehaviourДокумент16 страницThe Prediction of Travel Behaviour Using The Theory of Planned Behaviourhaneena kadeejaОценок пока нет
- Group5 (Legit) - Brain Base-Curriculum-InnovationsДокумент6 страницGroup5 (Legit) - Brain Base-Curriculum-InnovationsTiffany InocenteОценок пока нет
- Sibeko Et Al. 2020Документ16 страницSibeko Et Al. 2020Adeniji OlagokeОценок пока нет
- RPMДокумент35 страницRPMnisfyОценок пока нет
- Letters of Travell by George SandДокумент332 страницыLetters of Travell by George SandRocío Medina100% (2)
- Napoleons Letter To The Jews 1799Документ2 страницыNapoleons Letter To The Jews 1799larsОценок пока нет
- Plant-Biochemistry-by-Heldt - 2005 - Pages-302-516-79-86 PDFДокумент8 страницPlant-Biochemistry-by-Heldt - 2005 - Pages-302-516-79-86 PDF24 ChannelОценок пока нет
- Two Dimensional Flow of Water Through SoilДокумент28 страницTwo Dimensional Flow of Water Through SoilMinilik Tikur SewОценок пока нет
- Superhero Photoshop Lesson PlanДокумент4 страницыSuperhero Photoshop Lesson Planapi-243788225Оценок пока нет
- LGBT in Malaysia: Social Welfare SystemДокумент24 страницыLGBT in Malaysia: Social Welfare SystemMuhammad Syazwan Ahmad Fauzi100% (1)
- Digital Culture and The Practices of ArtДокумент31 страницаDigital Culture and The Practices of ArtLívia NonatoОценок пока нет
- Marimba ReferenceДокумент320 страницMarimba Referenceapi-3752991Оценок пока нет
- KULT Divinity Lost - Scenario - An Echo From The Past (28-29)Документ2 страницыKULT Divinity Lost - Scenario - An Echo From The Past (28-29)Charly SpartanОценок пока нет
- A Study of Cognitive Human Factors in Mascot DesignДокумент16 страницA Study of Cognitive Human Factors in Mascot DesignAhmadОценок пока нет
- 2017 Ecatalogue Howtim Exit SignДокумент38 страниц2017 Ecatalogue Howtim Exit SignSatish Phakade-PawarОценок пока нет
- THE THIRD TEST - No AnswersДокумент11 страницTHE THIRD TEST - No Answersdniela .fdrsairОценок пока нет
- Dua e Mujeer Arabic English Transliteration PDFДокумент280 страницDua e Mujeer Arabic English Transliteration PDFAli Araib100% (2)
- Pengaruh Suhu Pengeringan Terhadap Karakteristik Kimia Dan Aktivitas Antioksidan Bubuk Kulit Buah Naga MerahДокумент9 страницPengaruh Suhu Pengeringan Terhadap Karakteristik Kimia Dan Aktivitas Antioksidan Bubuk Kulit Buah Naga MerahDika CodОценок пока нет
- Lesson On Inferring Tone and MoodДокумент32 страницыLesson On Inferring Tone and MoodAngel PabilloОценок пока нет
- MoncadaДокумент3 страницыMoncadaKimiko SyОценок пока нет
- Literature Is An Important Component of A Total Language Arts Program at All Grade Levels Because of The Many Benefits It OffersДокумент1 страницаLiterature Is An Important Component of A Total Language Arts Program at All Grade Levels Because of The Many Benefits It Offersbersam05Оценок пока нет
- Member, National Gender Resource Pool Philippine Commission On WomenДокумент66 страницMember, National Gender Resource Pool Philippine Commission On WomenMonika LangngagОценок пока нет
- Faqs Harvest Moon BTNДокумент245 страницFaqs Harvest Moon BTNMurloc NightcrawlerОценок пока нет
- Part 1: Hôm nay bạn mặc gì?Документ5 страницPart 1: Hôm nay bạn mặc gì?NamОценок пока нет
- The Dallas Post 07-24-2011Документ16 страницThe Dallas Post 07-24-2011The Times LeaderОценок пока нет
- First Aid EssentialsДокумент5 страницFirst Aid EssentialsQueen ValleОценок пока нет
- Libro de Social Studies PDFДокумент76 страницLibro de Social Studies PDFNoheОценок пока нет
- Modern America Study Guide With Answers 2020 21Документ2 страницыModern America Study Guide With Answers 2020 21maria smithОценок пока нет