Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chapter No: 04: Measurement of Power & Power Factor Correction
Загружено:
Chandrakant BhattarИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter No: 04: Measurement of Power & Power Factor Correction
Загружено:
Chandrakant BhattarАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapt er No: 04
M easur ement of power & Power
f act or cor r ect i on
Electric power
The rate which electric energy is transferred by electric circuit.
P = work done per unit time
= QV/t = I*V watts
Where
Q = electric charge in coulombs
t = time in seconds
I = electric current in amps
V = electric potential or Voltage in volts
Power in a Balanced System
The total instantaneous power in a balanced three phase system is constant.
2 cos( ) 2 cos( 120 )
2 cos( 120 )
2 cos( ) 2 cos( 120 )
2 cos( 120 )
cos( ) cos( ) cos( 120 ) cos( 120 )
2
cos( 120 ) co
AN p BN p
CN p
a p b p
c p
a b c AN a BN b CN c
p p
v V t v V t
v V t
i I t i I t
i I t
p p p p v i v i v i
t t t t
p V I
t
= =
= +
= =
= +
= + + = + +
+ +
=
+
( )
Using the above identity and simplifying, =2 t- we obtain
s( 120 )
1
cos cos [cos( ) cos( )]
2
that:
1
3cos
2
cos 2 o os 3 c c s
p p p p
t
A B A B A B
V V I I p
| |
=
|
\ .
+
= + +
= + +
Power in a Balanced System
The important consequences of the instantenous power equation of a balanced three
phase system are:
The instantenous power is not function of time.
The total power behaves similar to DC power.
This result is true whether the load is Y or connected.
T
3 cos
p p
p V I
A
=
he per phase is obtained as .
3
AVERAGE POWE
R
cos
3
p
p p p
p
P V I
p
P
= =
=
Power in a Balanced System
The complex power per phase is S
p
. The total complex power for all phases is S.
p
p
p p p p p
3 cos
1
= cos
3
1
= sin
(Total Instantenous Power)
(Average Power per phase)
(Reactive Pow
3
er per phase)
(Apparent Power per pha
S V I
s
e
)
p p
p p
p p
p p p
p V I
P p V I
Q p V I
S V I
P jQ
-
=
=
=
=
= + =
p p
and refer to magnitude val
C
ues whereas
V and I refer to phasor
omplex power for e
values (Both magn
ach pha
itude a
se
nd phase)
p p
V I
Power in a Balanced System
The complex power per phase is S
p
. The total complex power for all phases is S.
p p p p p
p p p
p p p
Complex power for each phase
Total Complex power for three phas
S V I
S= 3S 3V I
3 3 cos 3 cos
3 3 sin 3 sin
S=3S 3V
e
I 3
a b c p p p L L
a b c p p p L L
P jQ
P jQ
P P P P P V I V I
Q Q Q Q Q V I V I
I
-
-
-
= + =
+ = =
= + + = = =
= + + = = =
= =
2
p
p p L
2
p
Total complex power
Total complex power using
, , and are all rms values, is the load imp
3
line val
edance
3
angl
s ue
e
p
p
L L
L
V I V I
V
Z
Z
P jQ V I
-
=
= + = Z S
Power in a Balanced System
Notice the values of V
p
, V
L
, I
p
, I
L
for different load connections.
2
p 2
p p p
p
p
p L
, , and are all rms values, is the load impe
To
da
3
S=3S 3V I 3
nce
al c
an
3
omplex ower
gle
p
L
p
p
L L
V
V
I Z
Z
P
V
V I
I
jQ
I
-
-
= = =
= + = Z S
V
L
V
L
V
L
V
p
V
p
V
p
I
p
I
p
I
p
V
L
V
p
I
p
V
L
V
L
V
p
V
p
I
p
I
p
Y connected load. connected load.
3
L p L p
V V I I = =
3
L p L p
V V I I = =
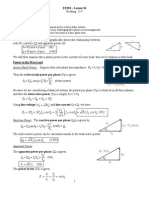
Single versus Three phase systems
Three phase systems uses lesser amount of wire than single phase systems for the
same line voltage V
L
and same power delivered.
a) Single phase system b) Three phase system
2 2
' 2 ' 2
Wire Material for Single phase 2( ) 2 2
(2) 1.33
Wire Material for Three phase 3( ) 3 3
r l r
r l r
= = = =
If same power loss is tolerated in both system, three-phase system use only 75% of
materials of a single-phase system
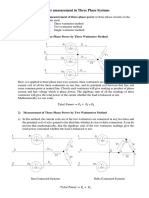
Three Phase Power Measurement
Two-meter method for measuring three-phase power
11
Balanced 3 Balanced 3--phase systems phase systems POWER CALCULATION
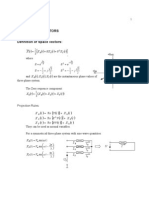
Complex, apparent, active, and reactive
The complex power per phase:
u + u = = sin I jV cos I V
p p p p
*
p p
I V S
p
Phase voltage Phase current
v p
u Z =
p
V V
i p
u Z =
p
I I
(rms) (rms)
p p
jQ P + =
Total complex power:
u Z = =
p p
*
p p
I V 3 3
I V S
For Y connection,
3
V
p
L
V
=
u Z =
L L
I V 3
S
L p
I I =
and
Apparent power is as before, i.e.
S
=
S
12
Balanced 3 Balanced 3--phase systems phase systems POWER CALCULATION
Power measurement using a wattmeter
wattmeter is an instrument used for measuring the average power.
The basic structure
Equivalent Circuit with load
If v(t) = V
m
cos (et + u
v
) and i(t) = I
m
cos (et + u
i
)
then the wattmeter will measure the average power:
Reading on wattmeter ( )
i v
m m
cos
2
I V
P u u =
13
Balanced 3 Balanced 3--phase systems phase systems POWER CALCULATION
Power measurement using a wattmeter
wattmeter is an instrument used for measuring the average power.
14
Balanced 3 Balanced 3--phase systems phase systems POWER CALCULATION
3-phase power measurement using wattmeters: two-wattmeter method
In order to measure average power in 3-phase system ONLY 2
wattmeter's are needed
Reading by wattmeter1,
Reading by wattmeter2,
( ) ) 30 cos( I V cos I V P
o
L L 1 a ab 1
+ u = u =
( ) ) 30 cos( I V cos I V P
o
L L 2 c cb 2
u = u =
ab
V
bc
V
ca
V
o
30
o
30
o
30
cn
V
bn
V
an
V
cb
V
a
I
c
I
u
u
u Z =
Y Y
Z
Z
15
Balanced 3 Balanced 3--phase systems phase systems POWER CALCULATION
Reading by wattmeter1,
Reading by wattmeter2,
( ) ) 30 cos( I V cos I V P
o
L L 1 a ab 1
+ u = u =
( ) ) 30 cos( I V cos I V P
o
L L 2 c cb 2
u = u =
IT CAN BE SHOWN :
) cos( I V 3 P P
L L 2 1
u = +
) sin( I V P P
L L 1 2
u =
This is also true for a A connected load as well
This is also true if the load is unbalanced (ONLY for P1+P2)
Two-wattmeter method CANNOT be used for a 3-phase, 4 wire system UNLESS the
neutral current = 0
P
1
=P
2
resistive load, P
2
> P
1
inductive load, P
2
< P
1
capacitive load
) P P ( 3 Q
1 2 Total
=
2 1 Total
P P P + =
Total
Total
P
Q
tan = u
Two-Wattmeter Power Measurement
cc = current coil
vc = voltage coil
W1 read
1 1
cos
AB A
P V I =
W2 read
2 2
cos
CB C
P V I =
For balanced load with abc phase sequence
1 2
30 and 30
a a
= + =
is the angle between phase current and phase voltage of phase
a
a
Two-Wattmeter Power Measurement(cont.)
1 2
2 cos cos30
3 cos
L L
L L
P P P
V I
V I
= +
=
=
To determine the power factor angle
1 2
2cos cos30
L L
P P V I + =
1 2
( 2sin sin30 )
L L
P P V I =
1 2
1 2
2cos cos30 3
( 2sin sin30 ) tan
L L
L L
P P V I
P P V I
+
= =
1
1 2 1 2
1 2 1 2
tan 3 or tan 3
P P P P
P P P P
| |
= =
|
+ +
\ .
Electrodynamic Wattmeter
What is power factor?
POWER FACTOR is an index which is used to calculate the efficiency level
of electrical usage.
This index is measured from the range of 0 to 1.
The higher the value of the index reflects more efficiency usage of electricity
and vice versa.
KW Real Pow er ( also called Working Pow er, Act ual Pow er or Act ive Pow er)
Thi s i s t he power t hat equi pment such as st ove bur ner, oven and l i ght s
r equi r ed t o per f or m usef ul wor ks.
KVAR React ive Pow er: Thi s i s t he power t hat magnet i c equi pment such as
t r ansf or mer, mot or s and compr essor s r equi r ed t o pr oduce t he magnet i zi ng
f l ux.
KVA Apparent Pow er: It i s t he vect or i al summat i on of React i ve Power (KVAR)
and Real Power (KW)
Power Fact or i s t he r at i o of Wor ki ng Power t o Appar ent Power
Pow er Fact or = KW / KVA
Why we improve power factor?
Eliminating Power Factor Surcharge
Reducing CO2 Emissions
Increased system capacity and reduced system loses in your
electrical system
Increased voltage in your electrical system, resulting in more
efficient motors.
Power Factor Correction
Power factor is particularly important in high-power applications
Inductive loads have a lagging power factor
Capacitive loads have a leading power factor
Many high-power devices are inductive
a typical AC motor has a power factor of 0.9 lagging
the total load on the national grid is 0.8-0.9 lagging
this leads to major efficiencies
power companies therefore penalise industrial users who
introduce a poor power factor
The pr obl em of poor power f act or i s t ackl ed by addi ng
addi t i onal component s t o br i ng t he power f act or back cl oser
t o uni t y
a capaci t or of an appr opr i at e si ze i n par al l el wi t h a l aggi ng
l oad can cancel out t he i nduct i ve el ement
t hi s i s pow er fact or correct ion
a capaci t or can al so be used i n ser i es but t hi s i s l ess
common (si nce t hi s al t er s t he l oad vol t age)
V
L
=840 V (Rms)
Capaci t or s f or pf
Cor r ect i on
I
L
73650
50.68A
3 3 840
Without Pf Correction
L
L
S
I
V
= = =
Measuring Instruments
Definition:
The instruments which are used to measure
electrical quantities are called Electrical
Instruments.
Example: Ammeter
Voltmeter
Energy meter
Вам также может понравиться
- EENG224 Chapter 12 Explores Three Phase CircuitsДокумент15 страницEENG224 Chapter 12 Explores Three Phase Circuitsrmsharma1970Оценок пока нет
- chpt12 2Документ15 страницchpt12 2mksayshiОценок пока нет
- Three-Phase Power Measurement GuideДокумент9 страницThree-Phase Power Measurement GuideVievie Le BluewberrietrufflesОценок пока нет
- To Measure Power in A 3-Phase Circuit With A Balanced Load by One-Wattmeter and Two-Wattmeter Methods and To Estimate The Power From The ResultsДокумент3 страницыTo Measure Power in A 3-Phase Circuit With A Balanced Load by One-Wattmeter and Two-Wattmeter Methods and To Estimate The Power From The ResultsPriyank SamalОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Power Systems PDFДокумент13 страницFundamentals of Power Systems PDFSurender ReddyОценок пока нет
- Lecture1-Review of Power System Networks, Complex Power, and Per UnitsДокумент29 страницLecture1-Review of Power System Networks, Complex Power, and Per Unitsleo232Оценок пока нет
- Complex Power, Reactive Compensation, Three PhaseДокумент31 страницаComplex Power, Reactive Compensation, Three Phaseahmah2009Оценок пока нет
- EEE 357 Circuit Analysis II Lecture 01 Contd.Документ21 страницаEEE 357 Circuit Analysis II Lecture 01 Contd.Shuvodip DasОценок пока нет
- Power System LecturesДокумент422 страницыPower System Lecturessnitin26Оценок пока нет
- Power System Fault AnalysisДокумент26 страницPower System Fault AnalysisadnanОценок пока нет
- Three Phase NetworksДокумент12 страницThree Phase NetworksA-Jay N. GalizaОценок пока нет
- 2 - 209 - ACPower3PhaseAC Power - 7may2014Документ23 страницы2 - 209 - ACPower3PhaseAC Power - 7may2014gazpeitia1Оценок пока нет
- 3 Phase PowerДокумент6 страниц3 Phase PowerRonieboy Baliber CairoОценок пока нет
- Ee220 Expt1Документ10 страницEe220 Expt1pkn.11ee56Оценок пока нет
- A.... Wattmeters & Measurement of PowerДокумент22 страницыA.... Wattmeters & Measurement of PowerTajammul HussainОценок пока нет
- Review of Basic Concepts - Professor J R Lucas 2.1 Single Phase PowerДокумент9 страницReview of Basic Concepts - Professor J R Lucas 2.1 Single Phase PowerNormanSulimaОценок пока нет
- BEEE Experiment Power FactorДокумент13 страницBEEE Experiment Power FactorRahul SankaranОценок пока нет
- 3 Phase GeneratorsДокумент9 страниц3 Phase GeneratorsAndrew CroninОценок пока нет
- Review of Chapter 2 Matlab Examples (Part IIДокумент7 страницReview of Chapter 2 Matlab Examples (Part IIkaren dejoОценок пока нет
- EE301 Lesson 36 Three Phase PowerДокумент24 страницыEE301 Lesson 36 Three Phase PowerBayu MeNunggu SaYapnyaОценок пока нет
- Active Filters With Control Based On The P-Q TheoryДокумент8 страницActive Filters With Control Based On The P-Q TheoryradhathotaОценок пока нет
- Syllabus:: Electrical Dept. Electrical Power III Dr. Omar AlazzawiДокумент97 страницSyllabus:: Electrical Dept. Electrical Power III Dr. Omar AlazzawiAkram KhasheaОценок пока нет
- 3 Phase Lecture NoteДокумент20 страниц3 Phase Lecture NoteMompati LetsweletseОценок пока нет
- 3 Phase CKTДокумент10 страниц3 Phase CKTpranayreddy12Оценок пока нет
- Balanced 3-Phase Circuits: Please Turn OFF Mobile Phones!Документ26 страницBalanced 3-Phase Circuits: Please Turn OFF Mobile Phones!sidiqbalОценок пока нет
- Base (Reference) PaperДокумент7 страницBase (Reference) Papermphaniteja2012Оценок пока нет
- Lab # 11Документ4 страницыLab # 11Dadu DaduОценок пока нет
- Notes On Power System Load Flow Analysis Using An Excel WorkbookДокумент20 страницNotes On Power System Load Flow Analysis Using An Excel WorkbookkittuОценок пока нет
- ECE 495/595 Introduction to More Three Phase Power SystemsДокумент63 страницыECE 495/595 Introduction to More Three Phase Power SystemsNathan HenryОценок пока нет
- Psa I 17ee62Документ20 страницPsa I 17ee62Shreyas KanabaragiОценок пока нет
- Newton Raphson & JacobiДокумент21 страницаNewton Raphson & Jacobimadhes14Оценок пока нет
- L Power Factor Correction and Harmonic FilteringДокумент26 страницL Power Factor Correction and Harmonic FilteringHammadZamanОценок пока нет
- Review PSC KCL and KVLДокумент40 страницReview PSC KCL and KVLmmnldzОценок пока нет
- Three Phase CircuitsДокумент25 страницThree Phase CircuitsAbhishek meenaОценок пока нет
- EE 368 Lecture Notes-2011Документ84 страницыEE 368 Lecture Notes-2011frimponge100% (3)
- Lec2 Power SystemДокумент37 страницLec2 Power SystemparthОценок пока нет
- Simulation of Three-Phase Bridge Rectifier Using MATLAB/ SIMULINK For Harmonic MitigationДокумент5 страницSimulation of Three-Phase Bridge Rectifier Using MATLAB/ SIMULINK For Harmonic MitigationIJMERОценок пока нет
- Section 1. Definitions and Per Unit System: V T V TDTДокумент7 страницSection 1. Definitions and Per Unit System: V T V TDTpepemirasОценок пока нет
- Review of Reactive Power AC CircuitsДокумент30 страницReview of Reactive Power AC CircuitsAbdulyunus AmirОценок пока нет
- THREE PHASE POWER FACTOR CORRECTIONДокумент9 страницTHREE PHASE POWER FACTOR CORRECTIONuama87Оценок пока нет
- Three Phase System: Prepared by Mr. Lim Cheng Siong Faculty of Electrical Engineering Universiti Teknologi MalaysiaДокумент46 страницThree Phase System: Prepared by Mr. Lim Cheng Siong Faculty of Electrical Engineering Universiti Teknologi MalaysiaKenneth ChawОценок пока нет
- Three-Phase Power Factor CorrectionДокумент9 страницThree-Phase Power Factor CorrectionUnknownОценок пока нет
- Lab No.4: TASK 4.1Документ2 страницыLab No.4: TASK 4.1Danish AslamОценок пока нет
- Symmetrical Components v2Документ32 страницыSymmetrical Components v2Carlos RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Lab Sheets IM2-EEL1196 Tri2 1314Документ11 страницLab Sheets IM2-EEL1196 Tri2 1314RumeshОценок пока нет
- Space Vector Definition and Projection RulesДокумент19 страницSpace Vector Definition and Projection RulesGovor CristianОценок пока нет
- System RepresentationДокумент31 страницаSystem Representationaldy otomasiОценок пока нет
- EE301Topic35 PDFДокумент9 страницEE301Topic35 PDFNaren VmdОценок пока нет
- System RepresentationДокумент31 страницаSystem RepresentationFebian TomyОценок пока нет
- Symmetrical ComponentsДокумент32 страницыSymmetrical ComponentsReza SiavoshiОценок пока нет
- Exp3 Star-Delta ConnectionДокумент9 страницExp3 Star-Delta Connectionpijechad0% (2)
- Three Phase Power MeasurementsДокумент2 страницыThree Phase Power MeasurementsTharindu NuwanОценок пока нет
- Ps Course - Elee3260 - Uoit - Lec 2Документ64 страницыPs Course - Elee3260 - Uoit - Lec 2ksajjОценок пока нет
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetОт EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetОценок пока нет
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorОт EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorОценок пока нет
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetОт EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetРейтинг: 2 из 5 звезд2/5 (1)
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetОт EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetОценок пока нет
- Tap Changing of Transformer 2. Using Capacitor or Capacotor Bank For Power Factor Correction 3. Using Synchronous Condensor 4. 4.phase AdvancerДокумент1 страницаTap Changing of Transformer 2. Using Capacitor or Capacotor Bank For Power Factor Correction 3. Using Synchronous Condensor 4. 4.phase AdvancerChandrakant BhattarОценок пока нет
- Power Quality Issues and ControlДокумент1 страницаPower Quality Issues and ControlChandrakant BhattarОценок пока нет
- Power Quality Issues and ControlДокумент1 страницаPower Quality Issues and ControlChandrakant BhattarОценок пока нет
- The SSSC Is One of The Most Recent FACTS Devices ForДокумент1 страницаThe SSSC Is One of The Most Recent FACTS Devices ForBiswajit MohapatraОценок пока нет
- AbcdДокумент1 страницаAbcdChandrakant BhattarОценок пока нет
- The SSSC Is One of The Most Recent FACTS Devices ForДокумент1 страницаThe SSSC Is One of The Most Recent FACTS Devices ForBiswajit MohapatraОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент1 страницаUntitledChandrakant BhattarОценок пока нет
- Transformer Winding Resistance Testing of Fundamental ImportanceДокумент1 страницаTransformer Winding Resistance Testing of Fundamental ImportanceChandrakant BhattarОценок пока нет
- Active Filter2Документ8 страницActive Filter2khansidreesОценок пока нет
- AbstractДокумент1 страницаAbstractChandrakant BhattarОценок пока нет
- Power Quality Improvement Using DVRДокумент1 страницаPower Quality Improvement Using DVRChandrakant BhattarОценок пока нет
- Lucas Nuelle Stand Motor AsincronДокумент18 страницLucas Nuelle Stand Motor AsincronStelistuSuperОценок пока нет
- Measurements and InstrumentationДокумент73 страницыMeasurements and Instrumentationgop_santriyaОценок пока нет
- Oc and SC Tests On A Single-Phase Transformer: Experiment No. 1Документ5 страницOc and SC Tests On A Single-Phase Transformer: Experiment No. 1Abuturab MohammadiОценок пока нет
- Ac 3 PhaseДокумент27 страницAc 3 PhaseTanishk SharmaОценок пока нет
- Polyphase Circuits Problems and SolutionsДокумент3 страницыPolyphase Circuits Problems and SolutionsJohn Eduard Felix BetuinОценок пока нет
- Basic Electrical LabДокумент32 страницыBasic Electrical Labsrinu247Оценок пока нет
- 通用电气ge Discovery Mr750 3.0t 磁共振成像系统8kw 3.0t Mns AmДокумент8 страниц通用电气ge Discovery Mr750 3.0t 磁共振成像系统8kw 3.0t Mns Amservice iyadMedicalОценок пока нет
- II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April - 2012 Electrical Circuit Analysis - IiДокумент8 страницII B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April - 2012 Electrical Circuit Analysis - IiViswa ChaitanyaОценок пока нет
- Preboard EeДокумент6 страницPreboard EeJohn Raymond LumanlanОценок пока нет
- Electrical QuestionsДокумент60 страницElectrical Questionskorayal72Оценок пока нет
- EEE374 Lab Manual: Electrical Measurements and InstrumentationДокумент179 страницEEE374 Lab Manual: Electrical Measurements and InstrumentationAmnaОценок пока нет
- Three Phase Power MeasurementsДокумент2 страницыThree Phase Power MeasurementsTharindu NuwanОценок пока нет
- Grundfos Pump Selection GuideДокумент11 страницGrundfos Pump Selection Guide8bgbcОценок пока нет
- CAMSCOДокумент12 страницCAMSCOraulОценок пока нет
- Electrical Measurement: Measurement Is The Process by Which One Can Convert Physical ParametersДокумент16 страницElectrical Measurement: Measurement Is The Process by Which One Can Convert Physical ParametersDereje DeribОценок пока нет
- Experiment No:-02: Electrical SymbolsДокумент6 страницExperiment No:-02: Electrical SymbolsAdesh Bhortakke100% (2)
- Mathematical EconomicsДокумент4 страницыMathematical EconomicsSayyid JifriОценок пока нет
- Questions BankДокумент12 страницQuestions BankshekhadaaОценок пока нет
- List of EquipmentsДокумент73 страницыList of EquipmentsalibankerОценок пока нет
- STL 10aДокумент55 страницSTL 10aCharlie FullerОценок пока нет
- RAW WATER PUMP TEST REPORTДокумент5 страницRAW WATER PUMP TEST REPORTMohammad AtaullahОценок пока нет
- Engineering Utilities 1 Module 2Документ13 страницEngineering Utilities 1 Module 2harabassОценок пока нет
- Transformer: D DT M .T M FДокумент10 страницTransformer: D DT M .T M Fyogananda12345Оценок пока нет
- Operation Manual For Electrical EquipmentДокумент86 страницOperation Manual For Electrical EquipmentGunawan sitinjakОценок пока нет
- Specification For GeneratorДокумент45 страницSpecification For GeneratorMohd Nasir Md BakhirОценок пока нет
- Transformers, Kapp, 1908 PDFДокумент386 страницTransformers, Kapp, 1908 PDFJuan Carlos Vega100% (2)
- Measure Electrical Power with Clamp Meters and Power MetersДокумент5 страницMeasure Electrical Power with Clamp Meters and Power Metersche syakirОценок пока нет
- Measure Electrical Instruments CharacteristicsДокумент76 страницMeasure Electrical Instruments CharacteristicsAbhijeet Singh 1112Оценок пока нет
- Course Name: Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation Course Code: MC1307 Course Instructor-Princy RandhawaДокумент191 страницаCourse Name: Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation Course Code: MC1307 Course Instructor-Princy RandhawanoushadОценок пока нет
- A.... Wattmeters & Measurement of PowerДокумент22 страницыA.... Wattmeters & Measurement of PowerTajammul HussainОценок пока нет