Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Matematik Tahun 4
Загружено:
tanwlbmИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Matematik Tahun 4
Загружено:
tanwlbmАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
MATHEMATICS YEAR 4
TOPIC & LEARNING AREA 1 WHOLE NUMBERS 1. Numbers to 100 000
LEARNING OBJECTIVES & LEARNING OUTCOMES
Develop number sense involving numbers of up to 100 000. i. ii Name and write numbers up to 100 000. Determine the place value of digits in any whole number up to 100 000 iii Compare value of numbers to 100 000 iv Round off numbers to the nearest tens, hundreds and thousands. Add numbers to the total of 100 000 i Add any two numbers to four numbers to 100 000 ii Solve addition problems. Subtract numbers from a number less than 100 000 i Subtract one or two numbers from a bigger numbers less than 100 000 ii Solve subtraction problems. Multiply any two numbers with the highest product of 100 000 i Multiply three-digit numbers with a) 100 b) two-digit numbers Multiply four-digit numbers with a) one-digit numbers b) 10 c) two-digit numbers Multiply two-digit numbers with 1 000 Solve multiplication problems.
2. Addition with the highest total of 100 000 3. Subtraction within the range of 100 000
4. Multiplication with the highest product of 100 000
ii
iii iv 5. Division with the
Divide a number less than 100 000 by a two-digit numbers. highest dividend of 100 00 i Divide four-digit numbers by a) one-digit numbers b) 10, 100 and 1 000 c) two-digit numbers Divide five-digit numbers by a) one-digit numbers b) 10, 100 and 1 000 c) two-digit numbers Solve division problems.
ii
iii
6. Mixed operations
Perform mixed operation involving addition and subtraction i Perform mixed operation involving addition and subtraction with numbers less than a) 100 b) 1 000 c) 10 000 ii Solve mixed operation problems
2 FRACTIONS 1. Proper Fractions Name and write proper fractions with denominators up to 10. i ii Name and write proper fractions eith denominators up to 10 Compare the value of two proper fractions with a) the same denominators b) the numerator of 1 and different denominators up to 10.
2. Equivalent fractions Express equivalent fractions for proper fractions. i Express and write equivalent fractions for proper fractions. ii Express equivalent fractions to its simplest form 3. Addition of fractions Add two proper fractions with denominators up to 10 i Add two proper fractions with the same denominator up to 10 to its simplest form. a) with 1 as the numerator for both fractions b) with different numerators ii Add two proper fractions with different denominators up to 10 to its simplest form. a) with 1 as the numerator for both fractions b) with different numerators iii Solve problems involving addition of proper fractions. Subtract proper fractions with denominators up to 10 fractions i Subtract two proper fractions with the same denominator up to 10 to its simplest form. a) with 1 as the numerator for both fractions b) with different numerators Subtract two proper fractions with different denominators up to 10 to its simplest form. a) with 1 as the numerator for both fractions b) with different numerators Solve problems involving subtraction of proper fractions.
4.
Subtraction of
ii
iii
3 DECIMALS 1. Decimal numbers Understand decimal numbers i Name and write decimals with a) one decimal place b) two decimal places ii Recognise the place value of a) tenths b) hundredths c) tenths and hundredths iii Convert fraction to decimals of a) tenths b) hundredths c) tenths and hundredths, and vice versa Add decimals up to two places i Add any two to four decimals of one decimal place involving a) decimals only b) whole numbers and decimals c) mixed decimals ii Add any two to four decimals of two decimal place involving a) decimals only b) whole numbers and decimals c) mixed decimals iii Solve problems involving addition of decimal numbers. Subtract decimals up to two decimals places i Subtract one to two decimals from decimal of one decimal place involving a) decimals only b) mixed decimals c) whole numbers and decimals ( mixed decimals ) ii Subtract one to two decimals of one or two decimal places iii Solve problems involving subtraction of decimals
2. Addition of decimal numbers
3. Subtraction of decimal numbers
4. Multiplication of decimal numbers
Multiply decimals up to two decimal places with a whole number. i Multiply any decimals of one decimal place with a) one-digit number b) 10, 100 and 1000 ii Multiply any decimals of two decimal places with a) one-digit number b) 10, 100 and 1000 iii Solve problems involving multiplication of decimals
5.
Division of decimal numbers
Divide decimals up to two decimal places by a whole number. i Divide any decimals of one decimal place with a) one-digit number b) 10 ii Divide decimals of two decimal places by one-digit number iii Divide decimals by a whole number with the dividend value of up to two decimal places iii Solve problems involving division of decimals
4 MONEY 1. Money up to RM10 000 Understand and use vocabulary related to money i ii iii iv v vi Read and write the value of money up to RM10 000 Add money up to RM10 000 Subtract money from up to RM10 000 Multiply money to the highest product of RM10 000 Divide money with divident not more than RM10 000 Perform mixed operation involving addition and subtraction involving money up to RM10 000 vii Round off money to the nearest ringgit viii Solve problems involving of up to RM10 000
5 TIME 1. Reading and writing time Understand, read and write time in hours and minutes i Read time in hours and minutes accoding to the 12-hours system. ii Write time in hours and minutes according to the 12-hours system Construct a simple schedule i Construct, read and extract information from a simple schedule ii Extract information from a calendar iii Solve simple real life problems involving reading the calendar Understand the relationship between units of time i State the relationship between units of time a) 1 day = 24 hours b) 1 year = 365 / 366 days c) 1 decade = 10 years
2. Time schedule
3. Relationship between units of time
ii
Convert a) years to days, and vice versa b) decades to years, and vice versa c) years to months, and vice versa d) hours to day, and vice versa
iii Convert time from a) hours to minutes, and vice versa b) hours and minutes to minutes, and vice versa c) minutes to hours and minutes, and vice versa 4. Basic operations involving time Add, subtract, multiply and divide units of time i Add time involving conversion of units with answers in compound units of : a) hours and minutes b) years and months c) decades and years ii Subtract time involving conversion of units with answers in compound units of : a) hours and minutes b) years and months c) decades and years iii Multiply time involving conversion of units with answers in compound units of : a) hours and minutes b) years and months c) decades and years iv Divide time involving conversion of units with answers in compound units for time duration of : a) hours and minutes b) years and months c) decades and years v Solve problems involving basic operations of time: a) hours and minutes b) years and months c) decades and years Use and apply knowledge of time to find the duration i Read and state the start and end of an event from a schedule ii Calculate the duration of an event from a schedule in a) minutes b) hours c) hours and minutes within a day and two consecutive live days iii Calculate the start or the end of an event from a given duration of time and read the start or end of an event
5. Time duration
6 LENGTH 1. Measuring length Measure lengths using standard units i Read measurement of length using units of milimetre ii Write measurement of length to the nearest scales of tenth division for : a) centimetre b) metre iii Measure and record lengths of objects using units of a) milimetre b) centimetre and milimetre c) metre and centimetre iv Estimate the lengths of objects in a) milimetre b) metre and milimetre c) centimetre and milimetre Understand the relationship between unit of length i State the relationship between centimetre and milimetre ii Convert units of length from a) milimetre to centimetre and vice versa b) compound units to a single unit Add and subtract length i Add units of length, involving conversion of units in: a) milimetre b) metre and milimetre c) centimetre and milimetre ii Subtract units of length involving conversion of units in: a) milimetre b) metre and milimetre c) centimetre and milimetre Multiply and divide length i Multiply units of length involving conversion of units by: a) a one-digit number b) 10, 100, 1000 ii Divide units of length, involving conversion of units by: a) a one-digit number b) 10, 100, 1000 iii Solve problems involving basic operation on length
2. Relationship between units of length
3. Basic operation involving length
7 MASS 1. Measuring Mass Measure mass using standard units i ii Measure of masses using units of kilogram and gram Read measurement of masses to the nearest scales division of kilograms and grams iii Estimate the masses of objects using kilograms and grams 2. Relationship between units of mass Understans the relationship between units of mass i Convert units of mass from a) kilograms to grams b) kilograms and grams to grams c) kilograms and grams to kilograms Add and subtract involving units of mass. i Add mass involving units of mass in: a) kilograms b) grams c) kilograms and grams ii Subtract mass involving unis of mass in: a) kilograms b) grams c) kilograms and grams Multiply and divide units of mass iii Multiply mass involving conversion of units with a) a one-digit number b) 10, 100, 1000 iv Divide mass involving conversion of units a) a one-digit number b) 10, 100, 1000 v Solve problems involving basic operations with mass
3. Basic operations involving mass
8 VOLUME OF LIQUID 1. Measuring volume of liquid Measure and compare volume of liquid using standard units i ii Read measurement of volume of liquid in litres and mililitres Write measurement of volume of liquid to the nearest scales of tenth division for a) litre b) mililitre iii Measure and record the volume of liquid in litres and mililitres iv Estimate the volume of liquid in litres and mililitres
2. Relationship between units of volume of liquid
Understand the relationship between units of volume of liquid i Convert units of volume from: a) litres to mililitres b) mililitres to litres c) litres and mililitres to litres d) litres and mililitres to mililitres Add and subtract units of volume i Add volume of liquid involving conversion of units in: a) litre b) mililitre c) litre and mililitre ii Subtract volume of liquid involving conversion of units in: a) litre b) mililitre c) litre and mililitre Multiply and divide units of volume i Multiply volume of liquid involving conversion of units in: a) one-digit number b) 10, 100, 1000 ii Divide volume of liquid involving conversion of units by: a) one-digit number b) 10, 100, 1000 iii Solve problems involving volume of liquids
3. Basic operation involving volume of liquid
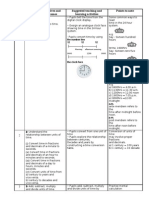
9 SHAPE AND SPACE 1. Two-Dimensional shapes Understand the perimeter of a two-dimensional shape i Identify the sides of a a) square b) rectangle c) triangle Measure and resord the perimeter of a a) square b) rectangle c) triangle
ii
Understand the area of a two-dimensional shape i Identify the dimension of a a) square b) rectangle ii Compare with unit squares the size of a a) square b) rectangle iii Measure and record the dimensional of squares and rectangles
Find the area and perimeter two-dimensional shapes i ii 2. Three-Dimensional Understand the volume for cubes and cuboids Shapes i ii Identify the dimensions of cubes and cuboids Compare with a unit cube a) Cuboid b) Cube iii Measure and record the dimension of cubes and cuboids Find the volume for cubes and cuboids i ii 10 DATA HANDLING 1. Pictograph Use a pictograph to read and display data i Describe a pictograph featuring a) the picture used to represent data, b) the title of the graph c) what the axes represent d) what one unit of picture represent ii Extract and interpret information from pictographs iii Construct pictographs to illustrate given information iv Solve a given problem by organising and interpreting numerical data in pictographs Use bar graph to read and display data i Describe a bar graph featuring a) the title of the graph b) what the axes represent ii Extract and interpret information from bar graphs iii Construct bar graphs to illustrate given information iv Solve a given problem by organising and interpreting numerical data in bar graphs Calculate the volume of cubes and cuboids Solve problems involving of cubes and cuboids Calculate the area of squares and rectangles Solve problems involving perimeter and area of twodimensional shape
2. Bar Graph
Вам также может понравиться
- Bird - Higher Engineering Mathematics - 5e - Solutions ManualДокумент640 страницBird - Higher Engineering Mathematics - 5e - Solutions Manualeta93% (44)
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 5От EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 5Оценок пока нет
- 10.1007 - 978 1 4020 9340 1Документ396 страниц10.1007 - 978 1 4020 9340 1xinfeng HE100% (1)
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 6От EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 6Оценок пока нет
- CBC - RAC (PACU-CRE) Servicing NC IIIДокумент139 страницCBC - RAC (PACU-CRE) Servicing NC IIIrayОценок пока нет
- MSCFE 620 Group SubmissionДокумент9 страницMSCFE 620 Group SubmissionGauravОценок пока нет
- Yearly Plan Year 3Документ8 страницYearly Plan Year 3Shima OmarОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Year 4: Cikgu Osman B. SaidДокумент10 страницMathematics Year 4: Cikgu Osman B. SaidFaridah AbdullahОценок пока нет
- Rancangan Tahunan MatematikДокумент19 страницRancangan Tahunan MatematikHailmi OthmanОценок пока нет
- Yearly Plan MathsДокумент8 страницYearly Plan MathsTasaratha Rajan AnamalaiОценок пока нет
- Week Topic / Learning Area Learning Objective / Learning Outcomes Suggested Activities 1 Whole NumbersДокумент11 страницWeek Topic / Learning Area Learning Objective / Learning Outcomes Suggested Activities 1 Whole NumbersGane GanesanОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year 5) 2010: WE EK Topic / Learning Areas Learning Objectives / Learning Outcome RemarksДокумент10 страницMathematics Yearly Plan (Year 5) 2010: WE EK Topic / Learning Areas Learning Objectives / Learning Outcome RemarksMoorsyidee MokhtaruddinОценок пока нет
- Rancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 5 2012 MS Excell Shared by AzyДокумент13 страницRancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 5 2012 MS Excell Shared by AzyTravis MonroeОценок пока нет
- RPT Mat Year 6Документ6 страницRPT Mat Year 6Kayalvile Vijaya KumarОценок пока нет
- YEARLY MATHEMATICS PLAN FOR YEAR 6 STUDENTSДокумент6 страницYEARLY MATHEMATICS PLAN FOR YEAR 6 STUDENTSMohd RedzuanОценок пока нет
- RPT MT Y5 2012Документ9 страницRPT MT Y5 2012Ani HaniОценок пока нет
- NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNДокумент6 страницNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNor AishahОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year Six) : 1. Whole NumbersДокумент3 страницыMathematics Yearly Plan (Year Six) : 1. Whole NumbersRamziah BongsuОценок пока нет
- RPT Math Tahun 4 2013Документ11 страницRPT Math Tahun 4 2013Preloved BoutiqeuОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year Six) : 1. Whole NumbersДокумент3 страницыMathematics Yearly Plan (Year Six) : 1. Whole NumbersAdemizan AhadОценок пока нет
- Rpt&Plan-j Math Year 4Документ27 страницRpt&Plan-j Math Year 4Kee SekKhaiОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year 6Документ4 страницыMathematics Yearly Plan (Year 6Faridah Binti KamaludinОценок пока нет
- Rancangan Tahunan Matematik Tahun 5 2013Документ8 страницRancangan Tahunan Matematik Tahun 5 2013Nurulnaim OmarОценок пока нет
- Year 5 Mathematics Yearly Plan OverviewДокумент19 страницYear 5 Mathematics Yearly Plan Overviewranj19869Оценок пока нет
- YEARLY PLAN - MATHEMATICS YEAR 4Документ13 страницYEARLY PLAN - MATHEMATICS YEAR 4Fauzia AngelОценок пока нет
- Yearly Scheme of Work Year 4 2013Документ15 страницYearly Scheme of Work Year 4 2013muhdmudzakkirОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year 4)Документ9 страницMathematics Yearly Plan (Year 4)Mhreal PetronasОценок пока нет
- Maths Plan for Numbers up to 7 Digits & FractionsДокумент7 страницMaths Plan for Numbers up to 7 Digits & FractionsAnna NintehОценок пока нет
- RPT Matematik Tahun 4Документ11 страницRPT Matematik Tahun 4mees-samaОценок пока нет
- RPT Mathematics Year 4Документ9 страницRPT Mathematics Year 4YoNz AliaTiОценок пока нет
- Math curriculum for year 3 studentsДокумент8 страницMath curriculum for year 3 studentsyuslinaaОценок пока нет
- Year3 Mat HSPДокумент8 страницYear3 Mat HSPShazwani HamzahОценок пока нет
- MATHEMATICS YEARLY PLAN FOR YEAR SIXДокумент10 страницMATHEMATICS YEARLY PLAN FOR YEAR SIXnaim8889Оценок пока нет
- MT Yearly Plan Year 1 6Документ6 страницMT Yearly Plan Year 1 6abusufian80Оценок пока нет
- RPT & Plan-J Math Year 4Документ27 страницRPT & Plan-J Math Year 4Syafiah EppieОценок пока нет
- Rancangan Tahunan Matematik Tahun 5 - 2012Документ8 страницRancangan Tahunan Matematik Tahun 5 - 2012mrdan100% (1)
- Curriculum Specifications Mathematics For Year 3 Yearly Plan 2005Документ8 страницCurriculum Specifications Mathematics For Year 3 Yearly Plan 2005Khaulah Al-HumayyraОценок пока нет
- Rancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 6 - 2013 - BiДокумент10 страницRancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 6 - 2013 - BimrdanОценок пока нет
- RPT & Plan-J Math Year 5 2012Документ26 страницRPT & Plan-J Math Year 5 2012sapuanazianОценок пока нет
- Maths Year 3Документ0 страницMaths Year 3SOlero MAniskuОценок пока нет
- Rancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 6 2013 BiДокумент10 страницRancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 6 2013 BiNajwa NurОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Yearly Plan 2014 Year 5 Week Topic / Learning Area Learning Objectives / Learning OutcomesДокумент8 страницMathematics Yearly Plan 2014 Year 5 Week Topic / Learning Area Learning Objectives / Learning OutcomesMohd ZahariОценок пока нет
- Curriculum Specifications Mathematics For Year 3 Yearly Plan 2005Документ8 страницCurriculum Specifications Mathematics For Year 3 Yearly Plan 2005Muhamad IrhamОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year 5) : Week Topic / Learning Areas Learning Objectives / Learning Outcome RemarksДокумент8 страницMathematics Yearly Plan (Year 5) : Week Topic / Learning Areas Learning Objectives / Learning Outcome RemarksMhreal PetronasОценок пока нет
- Learning Outcome Years 5Документ6 страницLearning Outcome Years 5Ardent HatredОценок пока нет
- Yearly Plan Mathematic Year 6Документ8 страницYearly Plan Mathematic Year 6Rosni OthmanОценок пока нет
- RPT & Plan-J Math Year 5 2010Документ20 страницRPT & Plan-J Math Year 5 2010Zoe KooОценок пока нет
- Yearly Plan Mathematics Year 6 2013 Topic/ Learning Area Objectives/ Learning Out Comes RemarksДокумент2 страницыYearly Plan Mathematics Year 6 2013 Topic/ Learning Area Objectives/ Learning Out Comes RemarksNor AishahОценок пока нет
- RPT: Mathematics Year 5Документ20 страницRPT: Mathematics Year 5man_zero1984Оценок пока нет
- Mathematics Yearly Plan Y4Документ14 страницMathematics Yearly Plan Y4skppasirОценок пока нет
- Week Topic / Learning Area Learning Objective / Learning Outcomes Suggested Activities 1 Whole NumbersДокумент10 страницWeek Topic / Learning Area Learning Objective / Learning Outcomes Suggested Activities 1 Whole NumbersAlana QuinnОценок пока нет
- Matematik Tahun 2Документ6 страницMatematik Tahun 2Azmin OsmanОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Yearly Plan Y5Документ12 страницMathematics Yearly Plan Y5skppasir0% (1)
- RPT MT THN4Документ14 страницRPT MT THN4hafidie83Оценок пока нет
- RPT MT THN4Документ14 страницRPT MT THN4Sk Saujana Impian DuaОценок пока нет
- RPT MT THN4Документ14 страницRPT MT THN4startecerОценок пока нет
- RPT MT THN2Документ9 страницRPT MT THN2Hasnawati BachoОценок пока нет
- RT Mat T3Документ8 страницRT Mat T3Candace ClayОценок пока нет
- Year 3 Maths Plan 2012Документ9 страницYear 3 Maths Plan 2012Maryah Yahya AzlimdnorОценок пока нет
- Rancangan Tahunan Matematik Tahun 6 - 2012Документ6 страницRancangan Tahunan Matematik Tahun 6 - 2012mrdanОценок пока нет
- Week Learning Objectives and Learning Outcomes Suggested Teaching and Learning Activities Points To NoteДокумент6 страницWeek Learning Objectives and Learning Outcomes Suggested Teaching and Learning Activities Points To NoteTan J IngОценок пока нет
- Math Syllabus 2Документ6 страницMath Syllabus 2api-172189277Оценок пока нет
- 1-6 Practice - AДокумент2 страницы1-6 Practice - AStanleyОценок пока нет
- Revised Curriculum M.ed f3Документ502 страницыRevised Curriculum M.ed f3Darshan BhandariОценок пока нет
- Csci 2021 Fall 2010 Quiz 1 (100 Points) : NameДокумент6 страницCsci 2021 Fall 2010 Quiz 1 (100 Points) : NameulairaiОценок пока нет
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogДокумент5 страницMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogRolan Cuevas DoriaОценок пока нет
- Assignment 2: Quantum OperatorsДокумент3 страницыAssignment 2: Quantum OperatorsSan D'Оценок пока нет
- Routine and Non-Routine Problem Solving StrategiesДокумент14 страницRoutine and Non-Routine Problem Solving StrategieselizaldeОценок пока нет
- Projeto Final Joao-Vitor-RomanoДокумент87 страницProjeto Final Joao-Vitor-RomanoGuilherme Ferreira LimaОценок пока нет
- 1011202222101PM-Class 5 Revision Worksheet For First Term Examination - MathsДокумент7 страниц1011202222101PM-Class 5 Revision Worksheet For First Term Examination - Mathsak dОценок пока нет
- Hessian MatrixДокумент4 страницыHessian MatrixRofaelEmilОценок пока нет
- Komodo 2022 DragonДокумент10 страницKomodo 2022 DragonAdi GunawanОценок пока нет
- Hash FunctionsДокумент119 страницHash FunctionsSibusiso Gama100% (1)
- UkkonenДокумент14 страницUkkonenValentinОценок пока нет
- Linear Inequalities V2Документ20 страницLinear Inequalities V2Nicole ConcepcionОценок пока нет
- Equations of Order One: Differential Equations Module 2AДокумент5 страницEquations of Order One: Differential Equations Module 2AJuvilee RicoОценок пока нет
- Visualising The Distribution of PrimesДокумент35 страницVisualising The Distribution of PrimesrosicomusОценок пока нет
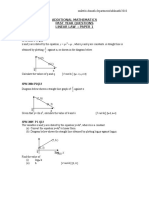
- Linear Law p1Документ2 страницыLinear Law p1Salmizam Izam100% (1)
- S&S Primary Order Form 2018 PDFДокумент8 страницS&S Primary Order Form 2018 PDFYoo MamaОценок пока нет
- 121 1 MATHS PP1 QnsДокумент6 страниц121 1 MATHS PP1 QnsnasraОценок пока нет
- Psa - 2 Units 201-20-Important Questions 1Документ3 страницыPsa - 2 Units 201-20-Important Questions 1Kunte Vikas Rao0% (1)
- Hull WhiteДокумент2 страницыHull WhiteJavierma BedoyaОценок пока нет
- Autocad 2014 PDF DXF Reference Enu 98Документ1 страницаAutocad 2014 PDF DXF Reference Enu 98GERMAN RPОценок пока нет
- Differential Geometry For Physicists - Lecture4 - Manuel HohmannДокумент9 страницDifferential Geometry For Physicists - Lecture4 - Manuel HohmannSalim DávilaОценок пока нет
- Blank Design Square ShellДокумент9 страницBlank Design Square ShellSumairОценок пока нет
- Problems in Uncertainty With Solutions Physics 1Документ13 страницProblems in Uncertainty With Solutions Physics 1asОценок пока нет
- (Discrete Mathematical Structure) : Total Pages:6Документ6 страниц(Discrete Mathematical Structure) : Total Pages:6Prs SorenОценок пока нет
- BooksДокумент2 страницыBooksDavid PattyОценок пока нет