Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Supertable Urogenital
Загружено:
gjsupИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Supertable Urogenital
Загружено:
gjsupАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
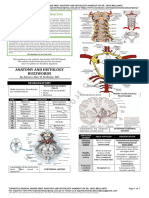
Function Other Notes KIDNEYS metanephroi; ducts are metanephric ducts/ureters.
Are large oval organs situated against dorsal wall of peritoneal cavity (retroperitoneal). Right kidney is more anterior compared to the left. Characteristic bean shape, convex laterally and concave on medial face. Cortex Peripheral part of kidney substance Contains the renal corpuscles & convoluted and looped portions of the kidney tubules Medulla Central part of kidney substance; marked Excretion of wastes The collecting tubules + pelvis + ureter by lines (collecting tubules) which arise by outgrowth from the mesonephric converge to the renal papilla duct Renal Papilla Projection of the substance of the kidney In here is situated the microscopic into the renal pelvis openings of the collecting tubules Renal pyramid Collecting tubules + renal papilla 1 in the cat but 12 in humans Renal pelvis Occupies the renal sinus. Is the expanded Funnel for the urine Renal sinus also contains arteries and beginning of the ureter. veins Ureter White tube from the hilus, turns Passage of wastes In females, the ureters pass dorsal to the posteriorly towards the urinary bladder horns of the uterus In males, they pass dorsal to a white cord (male duct/ductus deferens) which loops over the ureter and disappears dorsal to the bladder Hilus Concavity of the kidney Where the ureter passes out URINARY BLADDER Pear shaped sac at posterior end of peritoneal cavity. Ventral to the rectum in the male, ventral to both rectum & uterus in the female. Covered by a peritoneum continuous with that of the abdominal wall via the median & lateral ligaments Apex/Vertex Free anterior end of the bladder Contains urine Fundus Posterior portion of the bladder Continues posteriorly as the urethra Urethra Narrowed stalk, aka neck of the bladder Passage of urine Rectovesical Pouch Pouch between bladder & rectum (male) Vesicouterine Pouch Pouch between bladder & uterus (female) FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE TRACT Consists of a pair of ovaries and their ducts Ovaries Small oval bodies at the sides of the Each bears little clear vesicles (Graafian peritoneal cavity at the anterior end of follicles) containing an egg/ovum. In the coils of the uterus pregnant females, the ovary also bears little hard lumps, the corpora lutea (represents follicles from which the eggs of the pregnancy were discharged) Mesovarium Mesentery extending forward to the Suspends the ovaries kidney, continuous posteriorly with the
Organ/Structure
Descripton
Oviducts/Mullerian ducts
Uterine/Fallopian tube
Mesosalpinx Horns of uterus
ligament of the uterus Uppermost portion of the oviduct; slender, convoluted tube passing lateral to the ovary and curves over its anterior end Mesentery of the fallopian tube Posterior to fallopian tube; thick walled tube where the uterine tube is found to suddenly widen
Accommodates the microlecithal egg
Supports fallopian tube Place of development of the embryo
Mesometrium
Strong fold of peritoneum supporting the horns
Supports the horns of the uterus
Body of uterus Cervix Vagina
Urogenital canal/urogenital sinus Anal glands
Scrotum
Testis Vaginal sac Tunica vaginalis
Head, body, & tail of the epididymis
Single tube formed by the union of the 2 horns of the uterus in the median line Lower end of the uterus, projects into the Controls the movement of young into the vagina by a fold vagina during the birthing process Tube situated in the median line between Point of entry of the male organ the bladder and rectum. Exits through the ring formed by the pelvic girdle & vertebral column. Common tube formed by the union of the Passage of body fluids and the gonads urethra and the vagina Either side of the rectum close to the Secretes strongly odoriferous secretions, anus presumably of sexual nature MALE REPRODUCTIVE TRACT Where the 2 testes are lodged; divided Contains the testes into 2 compartments by an internal partition Oval, white body inside the scrotum Produces sperm Cavity in which the testis lies; part of the Contains the testis peritoneal cavity Lines the vaginal sac; deflected along the Covering layer of the testis middorsal line of the testis, so a mesorchium is formed between the testis and the wall of the vaginal sac Coiled masses at the anterior end, dorsal Head: receives the invisible efferent surface, and posterior end of the testis ductules from the testis Body: passageway of sperm towards the vas deferens
Size depends on whether the animal is pregnant or not. If yes, the horns are greatly enlarged and exhibit a series of swellings, each of which contains an embryo. Mesovarium + mesosalpinx + mesometrium = broad ligament of the uterus in mammals Continues posteriorly as the vagina; the cats uterus is bipartite
Opening of the body of the uterus into the vagina is the external uterine orifice
Head corresponds to the epididymis of lower forms and is derived from the mesonephros
Vas deferens Spermatic cord
Inguinal canal External inguinal rings Internal inguinal rings Prostate gland
Within the spermatic cord White cord found beneath the tissue anterior to the testis; passes forward and enters the peritoneal cavity through the inguinal canal Canal in the peritoneal cavity 2 ends of the inguinal canal
Tail: where the gubernaculum is attached Passageway of sperm Passageway of sperm, seminal fluids, and blood; contains the ductus/vas deferens, blood vessels and nerves Passage of the spermatic cord to the peritoneal cavity External passage of the spermatic cord to the peritoneal cavity Internal passage of the spermatic cord to the peritoneal cavity Contributes to the seminal fluid
Urogenital canal/sinus Cowpers gland/bulbourethral glands
A slight enlargement surrounding the junction of the deferent ducts and urethra Common tube formed by the union of the deferent ducts and urethra Small swellings in the urogenital canal shortly posterior to the prostate gland
Secretes contributions to the seminal fluid, lubricates the urethra
Вам также может понравиться
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- AbdomenДокумент32 страницыAbdomenVirendra K. GajbhiyeОценок пока нет
- Matary GIT Surgery 2013Документ327 страницMatary GIT Surgery 2013Raouf Ra'fat Soliman100% (11)
- EMRCS Abdomin AnatomyДокумент54 страницыEMRCS Abdomin AnatomyShakirОценок пока нет
- Inguinal Hernia 508Документ8 страницInguinal Hernia 508mursyid nasruddinОценок пока нет
- Material Mini NetterДокумент13 страницMaterial Mini NetterVALENTINA ALBORNOZ BASTÍASОценок пока нет
- Open Access Textbook of General Surgery: Hernia JHR BeckerДокумент9 страницOpen Access Textbook of General Surgery: Hernia JHR BeckerusamaОценок пока нет
- Male Genital System - PDFДокумент7 страницMale Genital System - PDFabhishek kaladharanОценок пока нет
- Surgery Cwu ExampleДокумент12 страницSurgery Cwu ExampleDiyana ZatyОценок пока нет
- Case of Inguinal HerniaДокумент3 страницыCase of Inguinal HerniaMustafaОценок пока нет
- Abd&Amp PL Anat D& R AgamДокумент264 страницыAbd&Amp PL Anat D& R Agamrageshrocky123100% (2)
- Anatomy 3.0: Anatomical EmbryologicalДокумент49 страницAnatomy 3.0: Anatomical EmbryologicalShenali SilvaОценок пока нет
- Dr. Madaan Anatomy MCQ 2-2 (Muhadharaty)Документ46 страницDr. Madaan Anatomy MCQ 2-2 (Muhadharaty)Joseph Brima SambaОценок пока нет
- HERNIAДокумент171 страницаHERNIATonyScaria0% (1)
- Hernia FTDДокумент71 страницаHernia FTDEmmanuel Papa AcquahОценок пока нет
- HerniaДокумент47 страницHerniamalathiОценок пока нет
- TBL Abdomen & Ingunal Canal QxsДокумент5 страницTBL Abdomen & Ingunal Canal QxsKAYISIRE EMERYОценок пока нет
- Hernia and LutzДокумент4 страницыHernia and LutzDrew CabigaoОценок пока нет
- MCQs in Applied Basic Sciences For The Primary FRCSДокумент127 страницMCQs in Applied Basic Sciences For The Primary FRCSGiovanni Henry100% (1)
- Hernia 1Документ28 страницHernia 1Aminatulhuda SulaimanОценок пока нет
- Testicular Cancers: Presented By: DR Isha Jaiswal Moderator: DR Madhup Rastogi Date:10 September 2014Документ56 страницTesticular Cancers: Presented By: DR Isha Jaiswal Moderator: DR Madhup Rastogi Date:10 September 2014Ivan VladanovОценок пока нет
- 13 Abdomen Part IДокумент12 страниц13 Abdomen Part IMonique BorresОценок пока нет
- Indicaciones Colgajo Inguinal MusloДокумент10 страницIndicaciones Colgajo Inguinal MusloMATTHEWS1Оценок пока нет
- Inguinal HernioplastyДокумент10 страницInguinal HernioplastyfiansisОценок пока нет
- Lower Limb, Abdomen & Pelvis Questions I MbbsДокумент11 страницLower Limb, Abdomen & Pelvis Questions I MbbsDarshan AcharyaОценок пока нет
- Male Reproductive SystemДокумент121 страницаMale Reproductive SystemProf Lina RamliОценок пока нет
- Hernia and Perianal ConditionsДокумент58 страницHernia and Perianal ConditionsSocial Media workingОценок пока нет
- Block II Review Winter 2023 Abdomen, Pelvis, & Lower Limb: DR Douglas A CotancheДокумент112 страницBlock II Review Winter 2023 Abdomen, Pelvis, & Lower Limb: DR Douglas A CotancheLester Cintron-PerezОценок пока нет
- Anatomy 02Документ90 страницAnatomy 02Puravi SamalОценок пока нет
- 2 - Anatomy Ang Histology Buzzwords Oct 2023 Jamaiyah H. Serad - Hadji OsopДокумент7 страниц2 - Anatomy Ang Histology Buzzwords Oct 2023 Jamaiyah H. Serad - Hadji OsopmikzhiОценок пока нет
- NEET PG 2014 Question Paper With SolutionsДокумент2 472 страницыNEET PG 2014 Question Paper With SolutionsmedpoxОценок пока нет