Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Diesel EmissionReduction
Загружено:
Nguyen NhaИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Diesel EmissionReduction
Загружено:
Nguyen NhaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Fuel News
Diesel Engine Emission Reduction
The purpose of this document is to briefly outline current strategies for reducing diesel engine exhaust emissions. Emission reduction and costs are summarised in a table at the end of this fuel news. Key words- Greenhouse, biodiesel, ethanol, Gaseous Fuels, GTL, NOX, PuriNOX, emulsion, CO,HC, Particulates, soot, Cleanburn Additives, Black smoke , White Smoke, sulphur
1. GREENHOUSE GAS Carbon Dioxide Reduction
A litre of diesel fuel will produce 2.67 kg of carbon dioxide. Because the diesel fuel has been produced from a fossil source of carbon this adds to the carbon dioxide in the biosphere and contributes to the greenhouse effect unless it is removed by some carbon dioxide abatement process (for example -timber plantations). The amount of carbon dioxide produced can be mitigated by adding components that have been produced from a non-fossil source of carbon such as biodiesel or ethanol. Biodiesel is produced by chemical purification of natural hydrocarbon products, for example vegetable oil, tallow, or cooking oil. The process is called esterification and produces a product containing about 10% oxygen. This product has similar properties to diesel and can be used in normal diesel engines. It can be used as a diesel (B100) or as a blend with normal diesel, normally at 20% (B20). Because the biodiesel is made from carbon taken out of the biosphere it adds no new carbon and so does not add to greenhouse gas emissions. Biodiesel is more expensive to produce than normal diesel at current crude prices unless the base stock is a waste material. Cold temperature properties may be an issue. Diesel ethanol blends. Ethanol can be blended with diesel using stabilising additives to produce a diesel fuel. Like biodiesel, ethanol is produced from plants and so is made from carbon taken out of the biosphere and adds no new carbon. The normal ethanol component in a blend is 10%. Ethanol cost more to produce than normal diesel at current crude prices. Both ethanol and biodiesel can reduce diesel carbon dioxide emissions by the approximate proportion in which they are used as substitutes. There can be an increase in fuel consumption proportional to the amount of oxygen present. Gaseous Fuels. Diesel engines can be modified to use gaseous fuels. Gaseous fuels such as Butane, Propane, Natural gas have less carbon and more hydrogen than diesel fuels and so produce less carbon dioxide. However there is an increase in fuel consumption and special tanks are needed to store the gases. The gaseous fuels are cheaper than normal diesel but require expensive modifications to engines and storage. Examples are LPG, CNG (compressed natural gas) and LNG (liquefied natural gas). Gas to Liquid (GTL) Gaseous fuels can be converted to a diesel and petrol equivalent by a gas conversion process. These products have more hydrogen than refined diesel and less carbon so there is a reduction in carbon dioxide emissions. All gaseous fuels and GTL fuels contain very low levels of sulphur and heavy carbon compounds and so reduce other exhaust pollutants. Document: ADF2402.doc Issued: February 10, 2005 Supercedes: February 7, 2002 BP Australia Limited A.C.N. 004 085 616 Page 1 of 5
Ultra Low Sulphur Diesel (ULSD) ULSD is the diesel fuel that meets the Euro 4 fuel specifications. The major benefits of the move to ULSD are provided by the ability to use advanced technology in the engine and the catalyst. These components are often sensitive to sulphur. Vehicle emissions are reduced when ULSD is used with the appropriate Euro 4 fuelled engines the emissions from a Euro 4 vehicle with advanced on-board diagnostics and a particulate trap will dramatically reduce emissions. BP has an ultra low sulphur diesel fuel called BP Eco Ultra. Engine Modifications Engine modifications to improve fuel economy lower exhaust emissions per kilometre, examples are high injection pressure fuel systems.
2. POLLUTANT REDUCTION
The following pollutants are produced in a diesel engine exhaust, there are different strategies for reducing each one and they are summarised in the followed sections. NOx oxides of nitrogen HC unburnt hydrocarbons C0 carbon monoxide Particulates Black smoke White Smoke Sulphur oxides. Note that diesel fuel substitutes that reduce carbon dioxide emissions also reduce other exhaust pollutants with the exception of oxides of nitrogen. These are reduced by lower combustion temperature.
2.1 NOX Oxides of nitrogen
The high temperatures present in the diesel engine combustion chamber can convert nitrogen from the air into oxides of nitrogen (NOx). NOx production is reduced when combustion temperatures are lowered. This is achieved by:a) adding water to the fuel (PuriNOX) b) circulating inert exhaust gas into the combustion chamber (EGR). c) using exhaust de-NOx catalysts.
PuriNOX
PuriNOX is a process for stabilising water in diesel fuel by using additives to produce an emulsion. The process involves the diesel fuel being put through a special blender with an additive and water to produce a10% water in diesel emulsion that can be used in a diesel engine. Because it is blended on site and requires special blending equipment and an additive it is more expensive than normal diesel, there is a power loss due to the presence of water, however the water component is not taxed at the diesel rate. This technology can be applied to older engines.
EGR Exhaust Gas Recirculation
This is the process of passing part of the exhaust gas into the combustion chamber to reduce temperature and NOX levels. It has the disadvantage that it increases particulate soot levels and so is best used with clean low sulphur diesel fuels. It is a new technology found on later model engines.
Exhaust Catalysts
Exhaust catalysts have been produced that can remove NOx, they are poisoned by diesel fuel sulphur and require fuels with very low sulphur around 10 50 ppm. They can be fitted Document: ADF2402.doc Issued: February 10, 2005 Supercedes: February 7, 2002 BP Australia Limited A.C.N. 004 085 616 Page 2 of 5
to most vehicles but require a very low sulphur fuel. These de-NOx catalysts will enable emissions of smog precursors to diminish, improving urban air quality. Note -Fuels that contain oxygen such as biodiesel and ethanol blends tend to increase NOX production.
2.2 HC Unburnt Hydrocarbons
Unburnt Hydrocarbons are produced when the diesel combustion chamber exhaust valves open before all the fuel has been burnt., Levels are very low for a diesel engine representing less than 0.1% of fuel used. Unburnt Hydrocarbons can be removed or reduced by using a catalytic converter in the exhaust system. Catalytic converters work best with low sulphur (<500ppm) or ultra low sulphur diesel fuel (<50ppm). HC is also be reduced by lowering the density and distillation characteristics of the fuel through refining.
2.3 CO Carbon Monoxide
Carbon Monoxide is produced when carbon molecules are not completely burnt to carbon dioxide when the combustion chamber exhaust valves are opened. Carbon monoxide levels are naturally very low, the low levels produced can be removed using an exhaust catalytic converter as for HC. Exhaust catalytic converters work best with low sulphur (<500ppm) or ultra low sulphur diesel fuel (<50ppm). Using diesel fuel with lower density and distillation properties also reduces carbon monoxide.
2.4 Particulate Matter - Soot
Particulate matter represents compounds with a high carbon content (e.g. aromatics) that have not completely burnt when the combustion chamber is exhausted. These combine with sulphur and water to form particulate matter (soot). There are a number of ways to reduce particulate matter:a) Better Refining reducing sulphur and aromatic content and lowering the distillation final boiling point removes compounds high in carbon and so reduces exhaust particulate. BP Eco Ultra is a good example of this. b) Substitution with alternative fuels biodiesel and ethanol have no sulphur and contain no aromatic compounds. Replacing normal diesel with an alternative fuel reduces sulphur and heavy carbon compounds. c) Alternative processes the gas to liquid process (GTL) converts gas to diesel. GTL diesel has no sulphur and aromatics hence particulates will be reduced. d) Particulate traps these are canisters that sit in the exhaust from the engine and collect particulate matter, at specified intervals they use excess fuel to burn away the particulates. e) Engineering- engine modifications to improve injection spray patterns, remove cool spots in the combustion and preventing the burning of crankcase oil. These changes have been made for modern engines to meet current emission standards. f) Cleanburn additives Adding a metal additive to the diesel fuel reduces the particulate size, examples are manganese, magnesium, iron. Some additives also help to burn off the particulates collected on the exhaust trap, e,g. cerium additives.
2.5 Black Smoke
Black smoke is visible particulate and is a transient exhaust emission when the engine is not running as lean. It also indicates poor engine maintenance or filter blockage. Reduction of black smoke uses the same strategy as that used for particulate matter but can also be reduced by engine overhaul or driver training so that the engine is at optimum. Black smoke indicates wasted fuel.
Document: ADF2402.doc Issued: February 10, 2005 Supercedes: February 7, 2002 BP Australia Limited A.C.N. 004 085 616
Page 3 of 5
2.6 White Smoke
White smoke is fuel that has failed to ignite; normally it occurs on cold start. White smoke can be reduced by raising the fuel cetane or by the addition of cetane improving additives.
2.7 Sulphur oxides
Sulphur in the fuel is converted to sulphur oxides when the fuel is burnt. These are corrosive and contribute to particulate emissions. Sulphur emissions can be reduced by removing sulphur during the refining process or substituting with fuels with no sulphur such as biodiesel, ethanol, gaseous fuels, water.
3. SUMMARY
Note costs quoted in the summary are indicative only, the actual costs depend on tax treatment, type of operation and other circumstances. Emission Carbon dioxide Reduction Substitute with biodiesel Substitute with ethanol at 10% Substitute with gas Comments Increases NOx Costs up to 5cpl extra depending on tax Supply of raw material. Reduces other exhaust pollutants Increases NOx Requires blending plant Additive cost up to 5 cpl, Power loss up to10% Power loss and increased fuel consumption up to 30% Capital investment of engine modifications. Gas is cheaper with lower tax rate. Cost of GTL component. Other pollutants are reduced. Require clean fuels with low particulate content Requires blender. additive cost up to 5cpl, neutralised because water component is not taxed. Power loss (10%) leads to increased fuel consumption Cannot be retrofitted Increases engine oil soot levels reduced drain periods Requires very low sulphur diesel <50ppm. Requires refinery investment Cleaner fuels result in cleaner engines and extended oil drain periods Depends on availability of alternative fuel. Can be done locally
Substitute with GTL Engine modifications to reduce fuel consumption PuriNOX
NOx
Exhaust Gas Recirculation DeNOX Catalyst HC and CO Particulate matter Refining to reduce Density, distillation and sulphur and to increase cetane Fuel substitution Engine maintenance
Document: ADF2402.doc Issued: February 10, 2005 Supercedes: February 7, 2002 BP Australia Limited A.C.N. 004 085 616
Page 4 of 5
Exhaust catalyst Metal additives White Smoke Sulphur Oxides Increase Cetane number. Lower sulphur content
Can be retrofitted, requires low sulphur diesel HSE concerns, cost additional 0.1-0.3 cpl, fuel application issues, engine wear and maintenance issues Additional refining costs Additional additive costs Additional refining costs. Requires additional refinery equipment.
For further information, please call the BP Lubricants and Fuel Technical Helpline 1300 139 700 local call or visit www.bp.com.au/fuelnews
Document: ADF2402.doc Issued: February 10, 2005 Supercedes: February 7, 2002 BP Australia Limited A.C.N. 004 085 616
Page 5 of 5
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- 3.2.P.2.3 Manufacturing Process Development (92 Págs) PDFДокумент92 страницы3.2.P.2.3 Manufacturing Process Development (92 Págs) PDFaldoОценок пока нет
- Calculation of Heat and Mass BalanceДокумент18 страницCalculation of Heat and Mass BalanceJitendra Bhatia100% (3)
- Damage Analysis of Catalyst Tube of Reformer FurnaceДокумент9 страницDamage Analysis of Catalyst Tube of Reformer FurnaceAnonymous xmSWrWbUKGОценок пока нет
- APPENDIX B Filler Metal Comparison Chart ABS-AWSДокумент3 страницыAPPENDIX B Filler Metal Comparison Chart ABS-AWSplkv100% (1)
- AkzoNobel - Colloidal Silica For Adhesives BrochureДокумент6 страницAkzoNobel - Colloidal Silica For Adhesives BrochureCarlos GuerreroОценок пока нет
- XII Chemistry CH#11 Notes (Sir Nasim Zulfiqar)Документ9 страницXII Chemistry CH#11 Notes (Sir Nasim Zulfiqar)salmanОценок пока нет
- Internship Format1Документ44 страницыInternship Format1Prajwal ChavanОценок пока нет
- SHELL AND TUBE HEAT EXCHANGER DESIGNДокумент60 страницSHELL AND TUBE HEAT EXCHANGER DESIGNniaaparamita100% (1)
- Bio Process Problem 1Документ1 страницаBio Process Problem 1AshenafiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 2Документ41 страницаChapter 3 2jerrica thomasОценок пока нет
- Equipment for Drilling Fluid Laboratory TestingДокумент14 страницEquipment for Drilling Fluid Laboratory TestingAlok SinghОценок пока нет
- PDF Cecil BrochureДокумент20 страницPDF Cecil Brochurechiralic100% (1)
- Tempcore ProcessДокумент4 страницыTempcore Processvikassolanki2010Оценок пока нет
- 1 PBДокумент12 страниц1 PBLela MaelaОценок пока нет
- Unit 10 Biota and EnvironmentДокумент0 страницUnit 10 Biota and Environmentwww.bhawesh.com.npОценок пока нет
- Characterization of InclusionsДокумент8 страницCharacterization of Inclusionsmahdisajjadi100% (1)
- Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons Practice WorksheetДокумент2 страницыProtons, Neutrons, and Electrons Practice WorksheetRedHoeBeerОценок пока нет
- T04: Mass Balance in Non Reacting System (Introduction Tu Multi Unit) A. Sugar Factory Activity (6 Min)Документ2 страницыT04: Mass Balance in Non Reacting System (Introduction Tu Multi Unit) A. Sugar Factory Activity (6 Min)Dewi Mawaddatus SholekhahОценок пока нет
- Compressed Air SystemДокумент29 страницCompressed Air Systemsk sajidОценок пока нет
- Nickel CobaltДокумент8 страницNickel CobaltSunnyОценок пока нет
- Ch11 CastingProcessesДокумент102 страницыCh11 CastingProcessesFahmi PrayogiОценок пока нет
- Water Cycle Questions AnwarДокумент4 страницыWater Cycle Questions Anwarapi-124758305Оценок пока нет
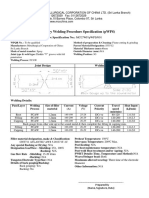
- WPS MCC 001 PDFДокумент1 страницаWPS MCC 001 PDFNuwan RanaweeraОценок пока нет
- Microporous and Mesoporous Materials: Sean M.W. Wilson, Vida A. Gabriel, F.Handan TezelДокумент11 страницMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials: Sean M.W. Wilson, Vida A. Gabriel, F.Handan TezelEcОценок пока нет
- Pamphlet 152 - Edition 4 - April 2018Документ29 страницPamphlet 152 - Edition 4 - April 2018acidoanimalОценок пока нет
- PWS&PQRДокумент1 страницаPWS&PQRkuppiliramaОценок пока нет
- HSC 2016 March ChemistryДокумент3 страницыHSC 2016 March ChemistryRohit GhereОценок пока нет
- 04 - Spektroskopi UV-Vis - 3Документ16 страниц04 - Spektroskopi UV-Vis - 3muktadi-amri-8721Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Structure, Properties and Behavior of MatterДокумент49 страницChapter 2 Structure, Properties and Behavior of Matteraxeman1nОценок пока нет
- Edicto - Thermodynamics Lab - Heat FusionДокумент2 страницыEdicto - Thermodynamics Lab - Heat FusionEdicto, Beatrice CarolineОценок пока нет