Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
36 37
Загружено:
Krishan Bir SinghИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
36 37
Загружено:
Krishan Bir SinghАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
International Indexed & Refferred Research Journal, October 2012, ISSN 0975-3486, RNI- RAJBAL 2009/30097: VoL IV *ISSUE- 37
Research PaperMathematics
Calculating and Interpreting Reliability Estimates for Achievement Test in Graph Theory - (A modern branch of Mathematics)
October,2012 * Pankit S. Gandhi * Asst. Prof. of Mathematics, Kishinchand Chellaram College, Churchgate, Mumbai A B S T R A C T
A test is a measuring tool or instrument developed to measure the level of attainment of specified instructional objectives. Achievement tests are tests designed to determine how much the learner has learned from specified content via systemic and controlled instruction. They represent a terminal evaluation of the learner's status on the completion of a course of study or training. Instrument reliability is the degree of consistency or dependability with which an instrument measures what it is supposed or designed to measure.The present study aims at analyzing the data (scores) obtained from the achievement tests written by students in the subject of Graph Theory by calculating and interpreting the test - retest and internal consistency reliability estimates. Keywords: Achievement test, Reliability, Graph Theory, Multimedia Package.
Introduction Reliability is the consistency of a measure. In educational testing, reliability refers to the confidence that the test score will be the same across repeated administrations of the test. There are four general classes of reliability estimates, each of which estimates reliability in a different way. They are: i. Inter - Rater or Inter - Observer Reliability ii. Test - Retest Reliability (also called Stability) iii. Parallel - Forms Reliability iv. Internal Consistency Reliability may be estimated through a variety of methods that generally fall into two types: Single-administration and multiple-administration. Multiple-administration methods require that two assessments be administered. In the test-retest method, reliability is estimated as the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient between two administrations of the same measure. Single-administration methods include splithalf and internal consistency. The most common internal consistency measure is Cronbach's alpha, which is usually interpreted as the mean of all possible split-half coefficients. Cronbach's alpha is a generalization of an earlier form of estimating internal consistency, KuderRichardson Formula 20. About Graph Theory Graph theory is an important branch of modern Mathematics that is used throughout the physical, social and artificial sciences. The past few decades have witnessed a spectacular growth of Graph Theory mainly due to its applications in discrete optimization problems and due to the advent of computers. Methodology In this study, the sample consisted of a group of 38 students comprising of S.Y.B.Sc. Mathematics class of a degree college affiliated to Mumbai University. Graph
Theory constitutes two units in the syllabus of Mathematics Paper III (Computational Mathematics) at the Second Year of Bachelor of Science Degree course offered at Mumbai University for students opting for Mathematics at this level. For the purpose of the study a Multimedia package on the first unit of Graph Theory along with an Achievement test was developed by the researcher. The package and the test were validated by experts before being used for the study. Thereafter, the Multimedia package was demonstrated to the students and the same was made available to the students for self study in the computer laboratory of the college. The students were given four sessions of two and a half our each for this self study through the Multimedia package.After the study sessions the achievement test was administered to the students to determine their level of achievement. The test was of one and a half hour duration and comprised of 18 multiple choice questions of 1 mark each and 6 descriptive questions of 2 marks each, thus the total marks of the test summed up to 30. After the achievement test the answer sheets and the question papers were immediately collected back from the students. After two weeks a Retest was administered to the students. The test questions and the time allotted for the retest was exactly the same as the achievement test. The data (scores) obtained was used to find the stability and reliability of the test using SPSS v 17. Calculations In the test-retest method, reliability was estimated as the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient r between the achievement test and retest. The following value was obtained: Pearson product moment correlation coefficient = r = 0.765. Cronbach's
36
RESEARCH ANALYSIS AND EVALUATION
International Indexed & Refferred Research Journal, October 2012, ISSN 0975-3486, RNI- RAJBAL 2009/30097: VoL IV *ISSUE- 37
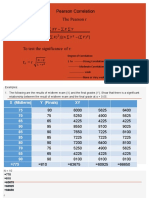
alpha was calculated to determine the internal consistency or average correlation of items in the achievement to gauge its reliability. The following value was obtained: Cronbach's alpha = = 0.810. Findings (Interpretation) The value of r always falls within the range -1 to +1. An r of -1 means a perfect negative correlation and an r of +1 means a perfect positive correlation. An r of 0 means zero correlation. Guilford (1982) offers an interpretation of the value r, as shown in table below. Table 1: Interpretation of Pearson product - moment correlation coefficient (r) Considering Guilford's values, the correlation between achievement test and retest the value of 0.765 can be considered as high, indicating a strong relationship and hence high stability of the achievement test instrument. Value of r Interpretation < 0.2 Slight, almost no relationship. 0.2 - 0.4 Low correlation, definite but small relationship. 0.4 - 0.7 Moderate correlation, substantial relationship. 0.7 - 0.9 High correlation, strong relation ship. 0.9 - 1.0 Very high correlation, very de pendable relationship.
Cronbach's alpha Internal consistency < 0.5 Unacceptable 0.5 - 0.6 Poor 0.6 - 0.7 Questionable 0.7 - 0.8 Acceptable 0.8 -0.9 Good 0.9 - 1.0 Excellent Table 2: Interpretation of Cronbach's alpha (?) A commonly accepted rule of thumb for describing internal consistency using Cronbach's alpha is as given in the table below .Thus, from the Cronbach's alpha value of 0.810 it can be concluded that the measuring instrument of achievement test was internally consistent. Suggestions The following suggestions are made from the findings of the present study: * Reliability of test instruments should be important considerations for teachers while planning test to measure student achievement. * Educational policy makers should push for qual ity test item writing and insist on reporting reli ability estimates across test instruments to make the prevalent examination system more meaningful.
R E F E R E N C E
[1] Mehrens, W. A., and LehmaN, I. J. (1991) Measurement and Evaluation in Education and Psychology, (4th ed.). Rinehart and Winston Inc: Orlando. [2] Oluwatayo, James Ayodele. (2012). Validity and Reliability Issues in Educational Research, Journal of Educational and Social Research. Vol. 2 (2) May 2012. [3] Cronbach, L. J., & Meehl, P. E. (1955) Construct Validity in Psychological Tests, Psychological Bulletin, 52. [4] Berk, R., (1979). Generalizability of Behavioral Observations: A Clarification of Interobserver Agreement and Interobserver Relability. American Journal of Mental Deficiency, Vol. 83, No. 5. [5] George, D., & Mallery, P. (2003). SPSS for Windows step by step: A simple guide and reference. (4th ed.). Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
RESEARCH ANALYSIS AND EVALUATION
37
Вам также может понравиться
- 'KKS/K Leh (KK VKSJ Ewy KaduДокумент2 страницы'KKS/K Leh (KK VKSJ Ewy KaduKrishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- International Indexed & Referred Research Journal, October, 2012. Issn 0974-2832, Rni-Rajbil 2009/29954 Vol. Iv Issue - 45Документ2 страницыInternational Indexed & Referred Research Journal, October, 2012. Issn 0974-2832, Rni-Rajbil 2009/29954 Vol. Iv Issue - 45Krishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- International Indexed & Referred Research Journal, October, 2012. Issn 0974-2832, Rni-Rajbil 2009/29954 Vol. Iv Issue - 45Документ2 страницыInternational Indexed & Referred Research Journal, October, 2012. Issn 0974-2832, Rni-Rajbil 2009/29954 Vol. Iv Issue - 45Krishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- GR) B) An (Asminti (Nsvid) Til&Kini P (RP/ (Èymi ) : P/I. Kin) Yi P/V) Nbie A (MДокумент2 страницыGR) B) An (Asminti (Nsvid) Til&Kini P (RP/ (Èymi ) : P/I. Kin) Yi P/V) Nbie A (MKrishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- Language Policy of Assam Government in Sixties and Tribal QuestionДокумент2 страницыLanguage Policy of Assam Government in Sixties and Tribal QuestionKrishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- 68 69Документ2 страницы68 69Krishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- Protection of Minority Rights Under Company's Affairs:: Aparajita BhargavaДокумент2 страницыProtection of Minority Rights Under Company's Affairs:: Aparajita BhargavaKrishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- 94-95 RaeДокумент2 страницы94-95 RaeKrishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- October, 2012Документ3 страницыOctober, 2012Krishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- Management Abilities and Skill Set Required For The Hospitality Professionals in IndiaДокумент4 страницыManagement Abilities and Skill Set Required For The Hospitality Professionals in IndiaKrishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- 60 61Документ2 страницы60 61Krishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- 58 59Документ2 страницы58 59Krishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- 70 71Документ2 страницы70 71Krishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- 'KKS/K Leh (KK VKSJ Ewy KaduДокумент2 страницы'KKS/K Leh (KK VKSJ Ewy KaduKrishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- 64 65Документ2 страницы64 65Krishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- 51 53Документ3 страницы51 53Krishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- Peer Pressure Among Adolescents: A Study With Reference To Perceived Parenting StyleДокумент2 страницыPeer Pressure Among Adolescents: A Study With Reference To Perceived Parenting StyleKrishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- 55 57Документ3 страницы55 57Krishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- Basics of Research: Mrs. Kiran Prabha Jain Mrs. Anjali A. JainДокумент2 страницыBasics of Research: Mrs. Kiran Prabha Jain Mrs. Anjali A. JainKrishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- Average Cross-Section ModelsДокумент4 страницыAverage Cross-Section ModelsKrishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- E-Communication Technology The Chain of Development ProcessДокумент2 страницыE-Communication Technology The Chain of Development ProcessKrishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- 45 46Документ2 страницы45 46Krishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- 43 45Документ3 страницы43 45Krishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- Mass Transport of Visco-Elastic Electrodes: Hardeep Singh TejaДокумент3 страницыMass Transport of Visco-Elastic Electrodes: Hardeep Singh TejaKrishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- 37 38Документ2 страницы37 38Krishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- 38 39Документ2 страницы38 39Krishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- Separation of Judiciary From Executive: Mrs - Deepika BhatnagarДокумент2 страницыSeparation of Judiciary From Executive: Mrs - Deepika BhatnagarKrishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- 39 40Документ2 страницы39 40Krishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- ASSAM Movement and Its Impact On Tribal: Dulen BassumataryДокумент2 страницыASSAM Movement and Its Impact On Tribal: Dulen BassumataryKrishan Bir SinghОценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Pearson RДокумент15 страницPearson RJa VilleОценок пока нет
- Independence TestДокумент10 страницIndependence TestRaffayОценок пока нет
- Chapter5 1 Sample TestДокумент38 страницChapter5 1 Sample TestQUYỀN TRẦN NGỌC VĨNHОценок пока нет
- TOEIC Answer SheetДокумент1 страницаTOEIC Answer SheetKhờ Ngu ĐầnОценок пока нет
- Hardness Conversion TableДокумент2 страницыHardness Conversion TableUmesh SakhareliyaОценок пока нет
- Unit 3Документ28 страницUnit 3JuanОценок пока нет
- Model PembelajaranДокумент6 страницModel Pembelajaranabu aОценок пока нет
- Junior Engineer Trainee Mechanical MCQ PreviewДокумент94 страницыJunior Engineer Trainee Mechanical MCQ PreviewmailbkraoОценок пока нет
- BUAN6359 - Spring2022 Exam2 PracticeДокумент13 страницBUAN6359 - Spring2022 Exam2 PracticeRutuja PabaleОценок пока нет
- Assignment #2Документ2 страницыAssignment #2Robin PabustanОценок пока нет
- Score your ACT English practice test with this keyДокумент1 страницаScore your ACT English practice test with this keyfathalla englishОценок пока нет
- ANOVA MCQ (Free PDF) - Objective Question Answer For ANOVA Quiz - Download Now!Документ10 страницANOVA MCQ (Free PDF) - Objective Question Answer For ANOVA Quiz - Download Now!jayant bansalОценок пока нет
- Statistics and Probability: Quarter 4 - Module 2 Null and Alternative Hypotheses and Test StatisticsДокумент16 страницStatistics and Probability: Quarter 4 - Module 2 Null and Alternative Hypotheses and Test StatisticsSonnel Calma100% (2)
- 8 Ypothesis Esting: October 31 - November 7, 2020Документ31 страница8 Ypothesis Esting: October 31 - November 7, 2020BENITEZ JOEL R.0% (1)
- Chi-Square Tests for Chapter 10 ReviewДокумент5 страницChi-Square Tests for Chapter 10 ReviewFerekkanОценок пока нет
- Iit Jee Advance Sample PapersДокумент4 страницыIit Jee Advance Sample PapersRruchi ShrimalliОценок пока нет
- UPSC Civil Services Preliminary Exam 2022 Answer KeyДокумент1 страницаUPSC Civil Services Preliminary Exam 2022 Answer KeyMOUNIKA KUNCHAPUОценок пока нет
- Bio Statistics PG CD MДокумент23 страницыBio Statistics PG CD McrneeteshОценок пока нет
- It8076 Software TestingДокумент2 страницыIt8076 Software Testingdassdass22Оценок пока нет
- Statistics & Probability Performance TaskДокумент2 страницыStatistics & Probability Performance TaskEeNihc DPОценок пока нет
- CLG Project ReportДокумент13 страницCLG Project Reportruchi sharmaОценок пока нет
- Anesthesiology: 2017 ABA Exams ReportДокумент24 страницыAnesthesiology: 2017 ABA Exams ReportMuath AlzghlellatОценок пока нет
- Non-Parametric Techniques: Mann-Whitney Test Wilcoxon Signed Rank TestДокумент31 страницаNon-Parametric Techniques: Mann-Whitney Test Wilcoxon Signed Rank TestRahul JajuОценок пока нет
- Eleven Plus Exams 3-D Non Verbal Reasoning (Composite Shapes) Paper 1 - Multiple Choice For CEM (Durham University)Документ6 страницEleven Plus Exams 3-D Non Verbal Reasoning (Composite Shapes) Paper 1 - Multiple Choice For CEM (Durham University)duskydope100% (1)
- UPSC NDA Exam 2008-II General Ability Solved PaperДокумент12 страницUPSC NDA Exam 2008-II General Ability Solved PaperDebashish Mukherjee100% (1)
- Introduction To Hypothesis TestingДокумент17 страницIntroduction To Hypothesis TestingMaimai PanaОценок пока нет
- Capr-I En229Документ13 страницCapr-I En229Anonymous WglGv0GОценок пока нет
- Real Statistics Examples ANOVA 1Документ282 страницыReal Statistics Examples ANOVA 1Nazakat HussainОценок пока нет
- Analisis Psikometri Intelligenz Structur Test (IST) Pada MahasiswaДокумент11 страницAnalisis Psikometri Intelligenz Structur Test (IST) Pada Mahasiswa269 - Ahmad Rizha Al HakimОценок пока нет
- The Population Frequencies Are Equal To The Expected Frequencies. The Null Hypothesis Is FalseДокумент3 страницыThe Population Frequencies Are Equal To The Expected Frequencies. The Null Hypothesis Is FalseAbbegail CalinaoОценок пока нет