Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
p149 PDF
Загружено:
Mohammad KeyhaniОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
p149 PDF
Загружено:
Mohammad KeyhaniАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on
Nanostructures (ICNS4)
12-14 March 2012, Kish Island, I.R. Iran
Department of Engineering Sciences, ngstrom Laboratory, Uppsala University, Uppsala 534, SE-751 21, Sweden e Department of Physics, Moi University, Eldoret 1125, Kenya *masoud.karimipour@gmail.com
d
MAG 006
Physical Properties of Magnetic Nd-Fe-B-C Nanoparticles Generated in Distilled Water Using Nd:YAG Laser
S. Seifollahi, H. Dehghanpour* Department of physics, Tafresh University, Tafresh, 39518-79611, Iran *h.dehghanpour@tafreshu.ac.ir
In this work, magnetic nanoparticles were generated by pulsed laser irradiation on the Nd-Fe-B-C magnetic target in Distilled water. Characterization of nanoparticles in terms of size, shape, chemical composition and magnetic properties was carried out by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), energy dispersive X-ray (EDAX), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), magnetic force microscope (MFM). The exposure times were performed on 1, 5 and 10 min. increasing of the exposure time leads to reduce the mean diameter of the nanoparticles, with minimum size of around 3 nm, growth of the nanoparticle number and decreasing of the nanoparticle creation rate. The chemical composition of nanoparticles was similar to the bulk sample. MFM shows that the nanoparticles have the magnetic properties. Keywords: Magnetic nanoparticles; Nd:YAG Laser; Nd -Fe-B-C magnet MAG 007
The influence of Co concentration (x) on the structural, magneto-optical properties of CoxTi1-xO2 films has been investigated. The films were deposited by spray pyrolysis technique on Si(100) substrates at 475C using a hydro-alcoholic solution containing of titanium (iv) isopropoxide and Co(NO3)2 with various Co-doping levels of x=0, 0.003, 0.008, and 0.015. The effect of annealing atmosphere on structural and electronic structure of the films was investigated. X-ray diffraction analysis shows that the films have pure phase of TiO2. Atomic force microscope (AFM) study shows that the annealing does not change significantly the grain size and microstructure of the samples. Room temperature magneto-optical characterization in polar mode shows hysteresis loops for the samples annealed in H2 gas as well as a paramagnetic behaviour for the samples which were annealed in air. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis shows the presence of Co2+ high spin for sample with x=0.008 which annealed in H2. It shows that Co atoms are bounded to oxygen and there is no metallic bound in anatase structure. Therefore, the origin of magnetization could be attributed to the role of oxygen vacancies in anatase thin films. Keywords: Diluted magnetic semiconductors; Grazing incident angle of X-Ray diffraction; Magneto-optical Kerr effect MAG 009
Magnetotransport and Magnetovolume Effects in La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 Nanocrystalline Perovskites Prepared by Mechanical Activation Method
Sh. Tabatabai Yazdi*, Sh. Abareshi, N. Tajabor, M. Rezaee Roknabadi, M. Behdani Department of Physics, Faculty of Sciences, Ferdowsi University, Mashhad 91775-1436, Iran *sh_tabatabai3@yahoo.com
Synthesis of Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles with Adding Yttrium Oxide on Pt-Fe3O4 Nanoparticles
a
Nanocrytalline samples of La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 were synthesized by mechanical activation method in ambient conditions and post sintering at 900 C. The structural, magnetotransport, and magnetovolume properties of the samples were investigated. The results show a metalinsulator transition at TMI = 165 K, a ferro-paramagnetic transition at TC = 160 K and a colossal magnetoresistance (CMR) value of about 40% under the field of 1.5 T around TMI, which are markedly affected by the small grain size (9 nm) of the studied samples. This is attributed to the enhanced intergrain resistivity and spin-polarized tunnelling between neighbouring grains in the present granular samples. Besides, the anomalous behaviour of magnetoresistance, thermal expansion and its coefficient observed around TC of the samples can be explained on the basis of a magnetic two-phase state. Keywords: Manganites; Magnetoresistance; Thermal expansion; Mechanical activation MAG 008
Y-Pt- Fe3O4 nanoparticles were prepared by a simple method. Synthesis of nanoparticles of Fe3O4 was first performed. Then Pt- Fe3O4 nanoparticles were prepared with adding K2PtCl6 in Fe3O4 nanoparticles solvent via reduction of K2PtCl6 in Fe3O4 nanoparticles by NaBH4. For studying the effect of rare earth oxides on Pt- Fe3O4 nanoparticles, Y2O3 was added to the Pt- Fe3O4 solvent. The synthesized nanoparticles were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). These nanoparticles have chemically disordered structures. Susceptibility of prepared nanoparticles was measured by Susceptometer. The hysteresis loop of Y-PtFe3O4 nanoparticles was taken by vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). The asmade nanoparticles have coercivity below 100 Oe and are superparamagnetic in room temperature. Keywords: Y-Pt-Fe3o4 nanoparticles; Magnetic properties; Superparamagnetic; Coersivity; Susceptibility
Room Temperature Magnetization of Co-doped TiO2 Thin Films Prepared by Spray Pyrolysis Technique
M. Karimipoura, b, c*, M. Magetod, e, N. Shahtahmasebia, b, M. Rezaee Roknabada, b, R. Etefagha, b, E. Azhira, b, M. Mwamburie, Z. Topaliand, P. Svedlindhd a Nano Research Centre, Faculty of Basic Science, Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Mashhad, Iran b Department of Physics, Faculty of Basic Science, Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Mashhad, Iran c Department of Physics and Astronomy, Uppsala University, Uppsala 516, SE-75120, Sweden
. ....................................................... .................................................................... .................................................................... .................................................................... ....................................................................
NOTE
Abstract Book |INST| Sharif University of Technology|
149
MAG
Z. Golsanamloua*, M. M Golzana, A. Hassanzadehb Department of Physics, University of Urmia, 165, Iran b Department of Chemistry, University of Urmia, 165, Iran *zahra.golsanamlou@gmail.com
Вам также может понравиться
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- فايل الگوی خلاصه مقاله کنگرهДокумент1 страницаفايل الگوی خلاصه مقاله کنگرهMohammad KeyhaniОценок пока нет
- p26 27 PDFДокумент2 страницыp26 27 PDFMohammad KeyhaniОценок пока нет
- pAPP230 PDFДокумент1 страницаpAPP230 PDFMohammad KeyhaniОценок пока нет
- p20 PDFДокумент1 страницаp20 PDFMohammad KeyhaniОценок пока нет
- pMOD069 PDFДокумент1 страницаpMOD069 PDFMohammad KeyhaniОценок пока нет
- p25 PDFДокумент1 страницаp25 PDFMohammad KeyhaniОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Ferro SchneiderДокумент30 страницFerro Schneidervoravuth srisomboonsuk100% (1)
- LQuiz (TOV1) # 15 (Eng)Документ5 страницLQuiz (TOV1) # 15 (Eng)PkrОценок пока нет
- Engineering MechanicsДокумент2 страницыEngineering MechanicsVenkat SiddhardhaОценок пока нет
- 1976 US Standard Atmosphere Model: The Atmospheric EnvironmentДокумент9 страниц1976 US Standard Atmosphere Model: The Atmospheric EnvironmentIeva MisiunaiteОценок пока нет
- Encapsulados Ensayos E2 C2 F1Документ4 страницыEncapsulados Ensayos E2 C2 F1fgdfgdfОценок пока нет
- Assign Chap 8Документ3 страницыAssign Chap 8nishedhОценок пока нет
- Nuclear Reaction ReviewДокумент3 страницыNuclear Reaction ReviewSeyi Martins ObandoОценок пока нет
- Using Labview To Measure Temperature With A ThermistorДокумент18 страницUsing Labview To Measure Temperature With A ThermistorjdaudpotoОценок пока нет
- Governor ApparatusДокумент14 страницGovernor ApparatusHimanshu Kulshrestha100% (1)
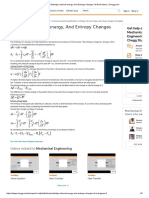
- Definition of Enthalpy, Internal-Energy, and Entropy Changes of Real GasesДокумент1 страницаDefinition of Enthalpy, Internal-Energy, and Entropy Changes of Real Gasesprashant_cool_4_u100% (1)
- Mse WallДокумент4 страницыMse WallEngr AtaUllahОценок пока нет
- 3 Surface Roughness SymbolsДокумент7 страниц3 Surface Roughness SymbolsAMIRHUSAIN MOMINОценок пока нет
- Course On Structural StabilityДокумент3 страницыCourse On Structural StabilityVenkatesh ReddyОценок пока нет
- Areas Between Curves.: X X A or X 0. There Are Two Enclosed Pieces ( A X 0Документ35 страницAreas Between Curves.: X X A or X 0. There Are Two Enclosed Pieces ( A X 0jhonna valdezОценок пока нет
- Physics Apparent WeightДокумент1 страницаPhysics Apparent WeightMarc Daniel LaurinaОценок пока нет
- Accelerator Physics I - BeckДокумент35 страницAccelerator Physics I - BeckJuan Antonio Valls FerrerОценок пока нет
- Chapter 20-1 - 已合并 PDFДокумент116 страницChapter 20-1 - 已合并 PDF林昀宣Оценок пока нет
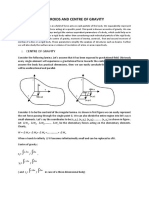
- Centroids and Centre of GravityДокумент31 страницаCentroids and Centre of Gravitysakshm guptaОценок пока нет
- EXP5Документ8 страницEXP5Yassi CurtisОценок пока нет
- Physics Investigatory Project: Hariyana Vidya Mandir Salt Lake, KolkataДокумент15 страницPhysics Investigatory Project: Hariyana Vidya Mandir Salt Lake, KolkataIndrani BhattacharyaОценок пока нет
- WEEK 4 Potential EnergyДокумент72 страницыWEEK 4 Potential EnergyJun De FontanozaОценок пока нет
- BCT-Syllabus-1st-Year-1st-Part (1) - UnknownДокумент22 страницыBCT-Syllabus-1st-Year-1st-Part (1) - Unknownishanpokhrel16Оценок пока нет
- Flow Sensor Technical Guide BookДокумент20 страницFlow Sensor Technical Guide Books12originalОценок пока нет
- Vector Group Test of TransformerДокумент4 страницыVector Group Test of TransformerHamayoun Murtaza100% (2)
- EDC - Unit I FinalДокумент172 страницыEDC - Unit I FinalDr Umapathy100% (1)
- Grade 11 Physics Module4Документ81 страницаGrade 11 Physics Module4JohnRenzoMolinarОценок пока нет
- Carnot Engine TheoremДокумент4 страницыCarnot Engine TheoremMisc BagОценок пока нет
- Weston 2018Документ7 страницWeston 2018Kartick TarafderОценок пока нет
- Transducer: Controller (Control Theory)Документ5 страницTransducer: Controller (Control Theory)Farrukh JamilОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 - Hydrostatic Forces On Submerged SurfacesДокумент17 страницChapter 3 - Hydrostatic Forces On Submerged SurfacesGSaurav DahalОценок пока нет