Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Benefits of Standards in Computing
Загружено:
Uriahs VictorИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Benefits of Standards in Computing
Загружено:
Uriahs VictorАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Uriahs Victor|| VI7070907
Data Communications
Assignment
Computer Systems Engineering || SALCC || 10/30/2012
Uriahs Victor|| VI7070907
Name: Uriahs Victor ID: VI7070907 Course: Computer Systems Engineering Lecturer: K. Harris Due Date: 10/30/2012
Computer Systems Engineering || SALCC || 10/30/2012
Uriahs Victor|| VI7070907 Telegraphy Telegraphy is the long distance transmission of messages without actually distributing it physically by human or animal contact.
Optical Telegraphy
Telegraphy itself has more history than the telegraph itself; some of the first forms of telegraphy were smoke signals where man would use this method to communicate about the movements of the hunt, even today this form of telegraphy is sometimes used as a distress call when someone is lost or needs help. Another form of early telegraphy that is still being used today is the reflecting of light using mirrors, this form of telegraphy was used in the battle of Thermopylae by the Greeks and is used today as a means of signaling ones location. Jungle Telegraph, which is telegraphy where drums are used by tribe members to signal the entire tribe of coming danger is also an early form of telegraphy, the tribe members hit the drums in specific ways to convey different messages. These drums were when hit sometimes hollowed out tree trunks that would give out those warning messages.
Computer Systems Engineering || SALCC || 10/30/2012
Uriahs Victor|| VI7070907 Over the centuries Telegraphy methods became more advanced while still not using any method what so ever of human or animal contact between the sender and the receiver of the message. In 1794 the Semaphore Network was invented in France by French man Claude Chappe and used years after by Napoleon in his wars, semaphores were more precise than previous forms of Telegraphy being able to show 63 different signals, they also used no fuel, but its disadvantage was that when sight got interrupted it was rendered useless, unlike Jungle Telegraph.
. Semaphore Network.
Semaphore is also a flag based alphabet, this new form of Telegraphy was more efficient in communicating since no form of fuel was needed, could be used in low light and was silent. Flag Semaphore has also been updated from flags to lights used by men on ships to signal a coming air craft on landing. In Electronics & Computer Science / Telecommunications Semaphore means; an apparatus for conveying information by means of visual signals, as with movable arms or railway signals, flags etc. therefore the Traffic lights would also be considered as Semaphore.
Computer Systems Engineering || SALCC || 10/30/2012
Uriahs Victor|| VI7070907
Electrical Telegraphy
In the 18th century Telegraphy took a huge leap forward with the invention of electrical telegraphy, the first electrical telegraph was invented by Samuel Soemmering in 1809 using gold wires in water that could send messages around two thousand feet away which were read by determining how much gas was released; an electric current representing each digit of the message would pass through the wire, at the receivers end the wires were covered in acid, that when electrolyzed released steam of hydrogen bubbles next to the associated letter or number. In 1837 British Physicists, William Cooke and Charles Wheatstone partnered together in the invention of the first practical telegraph which worked through electromagnetism called the Five Needle System, it was an alphabetical system with five needles controlled by five separate wires, the needles pointed to the desired letter, the receiver would then note down the letters in the order they came in to make out the message. This Five Needle System was not that easy to operate and to add to its disadvantage was the cost of cabling so it was outshined by the Double Needle System which only had two wires.
Soon enough this Double Needle Telegraph was again made obsolete to a single needle system which used only one wire and the code developed by Samuel Finley Breese Morse, shortened, Samuel Morse, called the Morse Code. Samuel Morse used a solenoid equipped with a marker to record pulses of varying duration on a
Computer Systems Engineering || SALCC || 10/30/2012
Uriahs Victor|| VI7070907 moving strip of paper. This device was called a commutator, it had two keys which made the current flow in opposite directions on the line, the pulses appeared on the paper as dots and dashes that were in a pattern, the different patterns of those dots and dashes were assigned to letters, numbers and punctuation marks. In the early designs of this single-cable-using telegraph machine was slow. The operator on the receiving end would have to watch the needle write and wait for the message to be complete, so soon enough the signal was made audible, by utilizing two different types of stop pins two sounds were made similar to tong and ting. The operator on the receiving end job was made faster but a bit more difficult because they would have to concentrate on listening to the sounds and then writing down the letters, obviously this would be difficult in noisy environments.
In 1840 Sir Charles Wheatstone invented the ABC system Telegraph which used a pointer that indicates the one transmitted, it had a hand generator, a pointer and a dial with 30 keys, the device was called a Communicator. It worked by the operator pressing the button for the letter required and winding the generator. The pointer would go around until it reached the key pressed then it disconnected the generator. The generator sent alternating half cycles of current to the line which connected to the receiving communicators pointer, which moved round a letter at a time until it reached the letter being sent. They were capable of up to 15 words per minute and required little operating skill. Telegraphs improved over the years from the Communicator to Multiplex telegraph in 1913, which used multiplexing to transmit eight messages simultaneously (four in each direction) over a single wire. In 1925 Teleprinter Machines came into use enabling a single wire to carry 72 transmissions at the same time (36 in each direction). In 1959 TELEX (TELegraph Exchange) was introduced to the public, it Computer Systems Engineering || SALCC || 10/30/2012
Uriahs Victor|| VI7070907 allowed people a subscription to the Telex Network to dial each other directly. It used telephone like rotary dialing for circuit switching and sent data by Baudot Code.
Computer Systems Engineering || SALCC || 10/30/2012
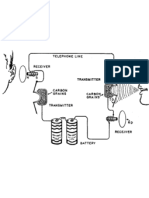
Uriahs Victor|| VI7070907 Telephony Telephony is the technology associated with the electronic transmission of voice, fax or other information between distant parties Before the invention of the first telephone there were already mechanical devices for transmitting spoken words over great distances, some of these mechanical devices were the Speaking Tubes which work by sound transmitting through pipes, strings or other physical media. That was early telephony. In the 1870s, two inventors created devices that could transmit speech electrically, they were Elisha Gray and Alexander Graham Bell. These men quickly tried to get the inventions patented within hours of each other, Alexander Graham Bell ended up patenting his telephone first. Gray however did not give up so easily and started a famous legal battle over the invention of the telephone. Bell turned out victorious in that too. Years before the invention of the first telephone Bell was already looking for ways to improve the telegraph, he began experimenting with electrical signals the telegraph had established as a means of communication approximately 30 years before, on March 10th 1876 Bell first transmitted speech electrically to his assistant Thomas A. Watson, the message was Mr. Watson, come here. I want to see you. After Bell got his invention patented he offered to sell those patents to the chief of a company at the time called Western Union. Western Union was the leading telegraph company at the time, Bell offered to sell the patents at $100,000 and was rejected with the words what use could this company make of an electric toy. Bell took his invention on the road to raise public awareness about the telephone and also in search of financial backers. The first phones installed by Bell were Private Lines that at the time only connected two telephones to each other, Bell established commercial telephone service in 1877, but his invention was mainly used by businessmen because of its cost at the time. Unlike a telegraph the telephone works by sending electric signals whose current responds to air pressure of the original sound in this case human voice. Once the voice passes through the transmitter, it changes into variable electric current. The Computer Systems Engineering || SALCC || 10/30/2012
Uriahs Victor|| VI7070907 modulated current travels through copper wires to the receiver. There it drives electromagnet which makes a diaphragm vibrate reproducing the original sounds. Bells telephone was only able to transmit signals a very short distance, 20 miles at most so variable resistance transmitters that would amplify the original signal had to be developed. In 1877 Thomas Edison financially backed by Western Union the same company turned down Bell years early had intent of breaking Bell Telephone Co. monopoly invented the first carbon microphone that modulated an existing current instead of producing a varying current. The carbon microphone could produce louder and cleaner signals. That same year Edison also invented the loud-speaking receiver, a diaphragm driven by an electromagnet that could transmit voices more clearly. Thanks to the invention of Multiplexing technology, more than one call was able to be handled on one copper wire, Multiplexing helped thin out the growing web of overhead wires that were becoming a nuisance in American Cities. The switchboard in telephony was popular before any signaling system, electronic switches, and dialing pads, it worked by the caller cranking a handle on the phone to call the local switchboard operator who would connect the caller to the other person that they wanted to speak to, the further away the person was the more switchboard stations were needed. One operator would have to contact another operator over an external line until the desired person was reached. In 1889 Almon Stowger invented the automatic switch which connected two parties without the need and aid of an operator. The rotary dial which routes a call via a set of switches activated by a series of pulse signals was developed in 1900 but not installed on a large scale until 1914. When Bells 17 year Patent ran out many independent phone companies sprang up, those companies were able to connect a few hundred homes but could not link to the national system. AT&T refused to link these companies into their network monopoly and bought the companies out when there were on the verge of bankruptcy. As technology improved and the telephone system became immense, calling costs
Computer Systems Engineering || SALCC || 10/30/2012
Uriahs Victor|| VI7070907 went down. AT&T pretty much controlled the telephony technology for many years until 1984. Before the 20th century the phone system used twisted copper wires called a loaded system. Copper wires absorbed a large amount of electrical energy produced by the transmitter, distorting the original quality of the sound. Gradually improvements were made to the technology, Radio telephone links created long distance service between countries. Improvements to the copper wire with coaxial cables in the 1940s reduced interference and increased calling capacity for the expanding telephone system. Mobile telephones introduced in the 1940s allowed owners to contact each other using radio frequency and cellular technology which allowed the reuse of frequencies many times in small adjacent areas covered by low powered transmitters. Microwave stations in the 1950s were based off of radar technology and could carry approximately 20,000 phone conversations, this technology is still used today but mostly for broadcasting television signals. Cellular phone technology which is todays most advance form of telephony appeared in the early 1980s. Over the centuries the Telephony has gave birth to other forms such as Internet Telephony. Standards Organizations
International Telecommunications Union (ITU)
The International Telecommunications Union established in 1865 formally called the International Telegraph Union, is the agency of the United Nations which is responsible for the information and communications technologies. Their responsibilities are: Coordinating the shared global use of the radio spectrum. Promoting international cooperation in assigning satellite orbits. Working to improve telecommunication infrastructure. Establishing telecommunication standards.
International Standards Organization
Computer Systems Engineering || SALCC || 10/30/2012
Uriahs Victor|| VI7070907 There are many international standards organizations, the two most established and largest are: International Organization for Standardization (ISO) International Telecommunication Union
The ISO founded in 1947 is the worlds largest developer of voluntary international Standards. Their standards cover aspects of both business and technology. From computers to food safety, agriculture to healthcare.
Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE)
IEEE read as Eye-triple-E is the worlds largest professional association dedicated to advancing technological innovation and excellence for the benefit of humanity. The IEEE was established in 1884 in the age of the Telegraph when electricity was just becoming a major established electrical industry. The IEEE is the result of a merger on January 1st 1963 between the American Institute of Electrical Engineers (AIEE) and the Institute of Radio Engineers (IRE).
Eastern Caribbean Telecommunications Authority (ECTEL) and NTRC
ECTEL was established by the governments of the five Eastern Caribbean States (Commonwealth of Dominica, Grenada, Saint Christopher and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and The Grenadines). Its mission is to promote market liberalization and competition in telecommunications of the contracting states. National Telecommunications Regulatory Commissions (NTRC) is established in each state to implement the work of ECTEL.
St. Lucia Bureau of Standards (SLBS)
The SLBS began its operations formally in April 1991, the Bureau develops and promotes standards for the improvement of local goods and services in order to encourage industrial and economic development, and to ensure the health and safety of consumers as well as safeguarding the environment. Its mission is to advance the island by promoting standardization, quality and metrology.
Computer Systems Engineering || SALCC || 10/30/2012
Uriahs Victor|| VI7070907 Benefits of Standards in Computer Systems Technology
A standard is an agreed, repeatable way of doing something. In computing standards are necessary for ensured understanding and compatibility across the world of computing, creating a computer standard like any other standard is not an easy task so various organizations come up with different types of computing standards so to divide the tremendous task of coming up with standards for the computing world. Some of these organizations include W3C, ISO and IEEE. These organizations come up with various standards including those that somehow relate to computer systems technology. The W3C which stands for World Wide Web Consortium is one of the most important standards organizations, reason being, they develop most web based standards for the World Wide Web which is one of the biggest and most important factors in computer systems technology, the W3C developed standards such as HTML, XML (Extensible Markup Language) and CSS (Cascading Style Sheets). Thanks to Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) standard any document written or coded in this manner will be interpretable by all browsers ensuring a programmer that his webpage will be readable by others, this same document will also be able to be interpreted by browsers that have text-to-speech functions to cater for blind people, thanks to this standard accessibility is assured. When a new technology is developed in computing it is not widely recognized until it has been standardized, by getting that technology standardized it becomes recognized and over rules others that may be similar, this ensures cross compatibility between computer systems and devices that use that technology. This is true in the case of the Bluetooth Standard which ensures that any device with Bluetooth technology can communicate and share data between themselves. By having a technology standardized it also attracts and assures people interested; if a technology is standardized example the USB standard, it slowly but surely becomes more popular in the computing world, this attracts companies to adapt that technology into their
Computer Systems Engineering || SALCC || 10/30/2012
Uriahs Victor|| VI7070907 products because that technology will be one of the top dogs on the market. Though new technologies are always being invented in computing few are standardized, this saves the computing world from miscommunication and incompatibility, by having standards for Computer Systems Technology the computing world becomes organized.
Computer Systems Engineering || SALCC || 10/30/2012
Uriahs Victor|| VI7070907 Bibliography
http://www.thefreedictionary.com/semaphore http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Claude_Chappe http://inventors.about.com/od/tstartinventions/a/telegraph.htm http://www.samhallas.co.uk/telhist1/telehist.htm http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Telegraphy http://searchunifiedcommunications.techtarget.com/definition/telegraph http://searchunifiedcommunications.techtarget.com/definition/Telephony http://www.translucency.com/frede/telephone.html http://www.iso.org/iso/home/about.htm http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/International_Telecommunication_Union http://www.ieee.org/about/ieee_history.html http://www.ectel.int/
Computer Systems Engineering || SALCC || 10/30/2012
Вам также может понравиться
- Telecommunication Industrial SkillsДокумент15 страницTelecommunication Industrial SkillsAditya KapoorОценок пока нет
- Wireless World : The Earth With Electronic Waves Around UsОт EverandWireless World : The Earth With Electronic Waves Around UsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Intro Lesson - History of The TelephoneДокумент45 страницIntro Lesson - History of The TelephoneDonn Henry D. PlacidoОценок пока нет
- Basic of TelecommunicationsДокумент25 страницBasic of TelecommunicationsClaren daleОценок пока нет
- Telecommunication Is The Transmission of Messages, Over Significant Distances, For The PurposeДокумент18 страницTelecommunication Is The Transmission of Messages, Over Significant Distances, For The PurposeMayank AgarwalОценок пока нет
- TELECOMMUNICATIONДокумент14 страницTELECOMMUNICATIONMilind Tambe100% (1)
- Telegraphy: Navigation SearchДокумент16 страницTelegraphy: Navigation Searchمحمد زبيدي نور الدينОценок пока нет
- Historical Setting: The Pre-Electromagnetic PastДокумент5 страницHistorical Setting: The Pre-Electromagnetic PastRandy Owen Javier CosmeОценок пока нет
- BSNL Summer Training ReportДокумент47 страницBSNL Summer Training ReportPrashant Kumar100% (1)
- The Radio Amateur's Hand Book: A Complete, Authentic and Informative Work on Wireless Telegraphy and TelephonyОт EverandThe Radio Amateur's Hand Book: A Complete, Authentic and Informative Work on Wireless Telegraphy and TelephonyОценок пока нет
- Evolution of Electronic CommunicationДокумент5 страницEvolution of Electronic CommunicationBalbie RFM100% (1)
- Choose The Best Answer!: Ancient Systems and Optical TelegraphyДокумент4 страницыChoose The Best Answer!: Ancient Systems and Optical TelegraphyAnonymous bpT6mCAoyLОценок пока нет
- FM CommunicationДокумент144 страницыFM CommunicationAhmed Sakr (أحمد صقر)Оценок пока нет
- The Radio Amateur's Hand Book A Complete, Authentic and Informative Work on Wireless Telegraphy and TelephonyОт EverandThe Radio Amateur's Hand Book A Complete, Authentic and Informative Work on Wireless Telegraphy and TelephonyОценок пока нет
- Concepts of TelecomunicationДокумент9 страницConcepts of TelecomunicationSalvador MacuacuaОценок пока нет
- Telecommunications - WikipediaДокумент29 страницTelecommunications - WikipediaSebastian GhermanОценок пока нет
- History of TelecommunicationДокумент21 страницаHistory of Telecommunicationdrnileshkarle5671Оценок пока нет
- Living in The I.T. EraДокумент16 страницLiving in The I.T. EraAira Mae CrespoОценок пока нет
- Mukesh VodafoneДокумент84 страницыMukesh VodafoneRavi Kant VermaОценок пока нет
- History of Communication SystemsДокумент10 страницHistory of Communication SystemsNauman HameedОценок пока нет
- Slayton Tty MuseumДокумент24 страницыSlayton Tty Museumyoung-ThucidОценок пока нет
- Preface: Information TransmissionДокумент71 страницаPreface: Information Transmissiondeshmukhneha679Оценок пока нет
- ELECTROДокумент4 страницыELECTROSam’s BackupОценок пока нет
- 5.2 Building TelecommunicationДокумент15 страниц5.2 Building TelecommunicationJohn Rhey Almojallas BenedictoОценок пока нет
- History of CommunicationДокумент106 страницHistory of CommunicationJohn Andrew ConsultaОценок пока нет
- A Brief History of TelecommunicationsДокумент2 страницыA Brief History of TelecommunicationsvanОценок пока нет
- History of TelephoneДокумент11 страницHistory of TelephoneRose Ann ManalaysayОценок пока нет
- Find Sources: - : An Old TelephoneДокумент6 страницFind Sources: - : An Old Telephonenarpat kumarОценок пока нет
- "Since Its Invention in 1876 The Telephone: Morse, Samuel Finley Breese (1791-1872), AmericanДокумент7 страниц"Since Its Invention in 1876 The Telephone: Morse, Samuel Finley Breese (1791-1872), AmericanSorin CosminОценок пока нет
- History: Telecommunication IsДокумент9 страницHistory: Telecommunication IsswathipalaniswamyОценок пока нет
- History: Telecommunication IsДокумент9 страницHistory: Telecommunication IsswathipalaniswamyОценок пока нет
- Dasar TelekomunikasiДокумент44 страницыDasar TelekomunikasimuhammadthaufiqhОценок пока нет
- Evolution of Microwave CommunicationsДокумент27 страницEvolution of Microwave CommunicationsStephany Bryan Diez Itao67% (3)
- FFDFДокумент26 страницFFDFSoumava PaulОценок пока нет
- Mil PresentationДокумент14 страницMil PresentationMaricel BeranaОценок пока нет
- TelecommunicationДокумент6 страницTelecommunicationkarthiveera100% (1)
- TelecommunicationsДокумент23 страницыTelecommunicationsnigel989Оценок пока нет
- To Study The Customer Satisfaction in AirtelДокумент77 страницTo Study The Customer Satisfaction in AirtelSami Zama0% (1)
- Background of Telecommunication Service Provider Sector: Early Era of TelecomДокумент54 страницыBackground of Telecommunication Service Provider Sector: Early Era of TelecomTanya GogiaОценок пока нет
- Industrial AgeДокумент22 страницыIndustrial AgeElyse CameroОценок пока нет
- Telephone System in BuildingsДокумент15 страницTelephone System in BuildingsJonica Mae JomadiaoОценок пока нет
- Communications Within A Company Speaking TubesДокумент7 страницCommunications Within A Company Speaking TubesNehlee Joie GuandeОценок пока нет
- Telecom Industry: Telecom History Since 1842 Till Now .."Документ38 страницTelecom Industry: Telecom History Since 1842 Till Now .."alok19886Оценок пока нет
- History of Telecommunications-2013-1Документ26 страницHistory of Telecommunications-2013-1Eric Newton100% (3)
- l0 Q&A Main-ImportantДокумент19 страницl0 Q&A Main-ImportantcddewanОценок пока нет
- Customer Acquisition and Retention at Bharti AirtelДокумент84 страницыCustomer Acquisition and Retention at Bharti AirtelAnonymous H6vlwbОценок пока нет
- History of Mobile and Wireless CommunicationДокумент7 страницHistory of Mobile and Wireless CommunicationMaria IramОценок пока нет
- TelecommunicationДокумент9 страницTelecommunicationNanee DevaОценок пока нет
- Some Features: Who Created The Phone?Документ5 страницSome Features: Who Created The Phone?monica utrerasОценок пока нет
- Wired Communication 1Документ39 страницWired Communication 1Ley Martinez FaylognaОценок пока нет
- Overview of Fiber Optic Communication: Dr. Irneza KEE4843 (Opto-Electronics) 0 - Intro 1Документ17 страницOverview of Fiber Optic Communication: Dr. Irneza KEE4843 (Opto-Electronics) 0 - Intro 1Afiqah RazmanОценок пока нет
- Electrical Telegraph: o o o oДокумент9 страницElectrical Telegraph: o o o oAnonymous JOOQkGbwoRОценок пока нет
- History of Telecom & ElectronicsДокумент90 страницHistory of Telecom & ElectronicsRajuraji100% (1)
- 15 - Rendi Nofitasari RobiansahДокумент3 страницы15 - Rendi Nofitasari RobiansahRendi Nofitasari RОценок пока нет
- Manual of Seamanship PDFДокумент807 страницManual of Seamanship PDFSaad88% (8)
- Ch13 (Man)Документ44 страницыCh13 (Man)kevin echiverriОценок пока нет
- 01 - Quality Improvement in The Modern Business Environment - Montgomery Ch01Документ75 страниц01 - Quality Improvement in The Modern Business Environment - Montgomery Ch01Ollyvia Faliani MuchlisОценок пока нет
- Egyptian Gods and GoddessesДокумент5 страницEgyptian Gods and GoddessesJessie May BonillaОценок пока нет
- Dax CowartДокумент26 страницDax CowartAyu Anisa GultomОценок пока нет
- LWB Manual PDFДокумент1 страницаLWB Manual PDFKhalid ZgheirОценок пока нет
- Tribunal Judgment On QLASSIC in MalaysiaДокумент14 страницTribunal Judgment On QLASSIC in Malaysiatechiong ganОценок пока нет
- Reading 53 Pricing and Valuation of Futures ContractsДокумент3 страницыReading 53 Pricing and Valuation of Futures ContractsNeerajОценок пока нет
- Traditions and Encounters 3Rd Edition Bentley Test Bank Full Chapter PDFДокумент49 страницTraditions and Encounters 3Rd Edition Bentley Test Bank Full Chapter PDFsinhhanhi7rp100% (7)
- Petersen S 4 Wheel Off Road December 2015Документ248 страницPetersen S 4 Wheel Off Road December 20154lexx100% (1)
- Pearbudget: (Easy Budgeting For Everyone)Документ62 страницыPearbudget: (Easy Budgeting For Everyone)iPakistan100% (3)
- Summarydoc Module 2 LJGWДокумент14 страницSummarydoc Module 2 LJGWKashish ChhabraОценок пока нет
- TrerwtsdsДокумент167 страницTrerwtsdsvinicius gomes duarteОценок пока нет
- Power Sector Assets v. CIR GR 198146 8 Aug 2017Документ19 страницPower Sector Assets v. CIR GR 198146 8 Aug 2017John Ludwig Bardoquillo PormentoОценок пока нет
- Soal Asking and Giving OpinionДокумент2 страницыSoal Asking and Giving OpinionfitriaОценок пока нет
- Tales From The SSRДокумент48 страницTales From The SSRBrad GlasmanОценок пока нет
- Mastery Problem (L04, 5, 6), 27: 2,500 500 0 200 100 1,300 1,500 (Expense) 2,000 0 200 100 1,300 1,000Документ2 страницыMastery Problem (L04, 5, 6), 27: 2,500 500 0 200 100 1,300 1,500 (Expense) 2,000 0 200 100 1,300 1,000Paulina OlivaresОценок пока нет
- Attendance 2.0 Present 2.1 Absent With ApologyДокумент3 страницыAttendance 2.0 Present 2.1 Absent With ApologyPaul NumbeОценок пока нет
- Rothkopf, in Prase of Cultural ImperialismДокумент17 страницRothkopf, in Prase of Cultural Imperialismmystery1871Оценок пока нет
- Carollo Motion To StayДокумент7 страницCarollo Motion To Stayal_crespoОценок пока нет
- Boone Pickens' Leadership PlanДокумент2 страницыBoone Pickens' Leadership PlanElvie PradoОценок пока нет
- Aud Prob Compilation 1Документ31 страницаAud Prob Compilation 1Chammy TeyОценок пока нет
- Case Study FutureForm CitizenMДокумент3 страницыCase Study FutureForm CitizenMOrçun Cavit AlpОценок пока нет
- 2.Hp2.Eou Test U7 PreinterДокумент6 страниц2.Hp2.Eou Test U7 PreinterMinh Trí NgôОценок пока нет
- (Digest) Marcos II V CAДокумент7 страниц(Digest) Marcos II V CAGuiller C. MagsumbolОценок пока нет
- The Kurdistan Worker's Party (PKK) in London-Countering Overseas Terrorist Financing andДокумент28 страницThe Kurdistan Worker's Party (PKK) in London-Countering Overseas Terrorist Financing andrıdvan bahadırОценок пока нет
- Udom Selection 2013Документ145 страницUdom Selection 2013Kellen Hayden100% (1)
- ID-MSHKKT46-KT-2 E-PolicyДокумент4 страницыID-MSHKKT46-KT-2 E-Policymeilll130935Оценок пока нет
- Unit 3: This Study Resource WasДокумент9 страницUnit 3: This Study Resource WasAnanda Siti fatimah100% (2)
- Solutions-Debraj-Ray-1 Dev EcoДокумент62 страницыSolutions-Debraj-Ray-1 Dev EcoDiksha89% (9)