Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Caed QB1
Загружено:
nandukushiИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Caed QB1
Загружено:
nandukushiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CAED
2.1
PROJECTIONS OF POINTS
(Above HP & Behind VP)
(Above HP & In front of VP)
(Below HP & Behind VP)
(Below HP & In front of VP)
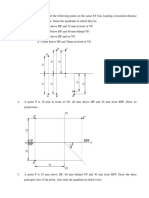
2.1. Draw the projections of a point P in the following positions. i) The point is 25mm above HP and 30mm in front of VP. ii) The point is 25mm above HP and 25mm behind VP. iii) The point is 10mm below HP and 40mm behind VP. iv) The point is in both HP and VP. 2.2. Draw the projections of a point Q in the following positions. i) The point is 20mm above HP and in VP. ii) The point is 30mm in front of VP and in HP. iii) The point is in VP and 35mm below HP. iv) The point is 25mm below HP and 25mm in front of VP. 2.3. Point A is 15mm above HP and 30mm infront of VP. Draw its front, top and right side views. 2.4. Point B is 20mm below HP and 35mm infront VP. Draw its front, top and left side views. 2.5. Point C is 25mm below HP and 15mm in behind VP. Draw its front, top and right side views. 2.6. Point D is 35mm below HP and 25mm in behind VP. Draw its front, top and left side views. 2.7. Point E is 20mm from HP, 15mm from VP and 25mm from RPP (Right Profile Plane) and is in the first quadrant. Draw its projections. 2.8. Point F is 15mm above HP, 30mm in front of VP and 25mm from LPP. Draw its front view, top view and right side view. 2.9. Point G is 20mm above HP, 35mm in front of VP, 25mm from LPP and 60mm from RPP. Draw its front view, top view, right side view and left side view. 2.10. Point H is 25mm below HP, 35mm behind VP and 30mm from RPP. Draw its top view, front view and right side view. 2.11. Point I is 20mm from HP, 25mm from VP and 15mm from LPP and is in the third quadrant. Draw its front, top and side views.
PROJECTIONS OF POINTS
2.2
CAED
2.12. Projections of some points are shown in Fig. 1. Describe clearly, their location. All the dimensions are in mm.
t
10
u' u
35
t' r
18
s'
w
18 20
z' x y'
20
x
25
v v' r' s
Fig. 1
w'
20
x'
2.13. A point lying 20mm below the xy line is the top view of three points P, Q and R. P is 20mm below HP, Q is 35mm above HP and point R is in HP. Draw the projections of these three points and state their positions with reference planes and quadrant in which they lie. 2.14. A point A is 20mm above HP and in the first quadrant. Its shortest distance from the reference xy line is 40mm. Draw the projections of the point and determine its distance from VP. 2.15. Draw the projections of the following points and determine the distance of each point from the reference planes and mention the quadrants in which they lie. i) The front view of the point is 40mm above xy line and its top view is 15mm below the front view. ii) The top view of the point B is 35mm above xy line and front view is 10mm below xy line. iii) The front view of point C is 50mm below xy line and its top view is 10mm above the front view. iv) The front and top views of point D coincide with each other and 30mm above xy line. v) The front view of point E is 30mm above xy line and top view 25mm below xy line. 2.16. The orthographic projections of certain points are shown in Fig. 2. Determine their positions with respect to the planes of projection and state in which quadrant they are situated.
c' b c a'
20 45 25 50
x
15
d'
30
35
d b'
Fig. 2
CAED
3.1
PROJECTIONS OF LINES
3.1. A line AB is 60mm long and is inclined at 45 and 25 respectively with HP and VP. Point A is 60mm in front of VP and 25mm above HP. Draw the front view and top view of the line. 3.2. A line PQ is 85mm long and has end P in HP and 25mm in front of VP. It is inclined at 30 to HP and 45 to VP. Draw the projections of the line and find apparent lengths and apparent inclinations. (15) February 2004 3.3. A line AB has its end A, 15mm from HP and 10mm from VP. The end B is 55mm above HP and the line is inclined at 30 to HP. The distance between the end projectors is 50mm. Draw the projections of the line. Determine the true length of the line and its inclination with VP. (15) July 2003 3.4. The left end A of a line AB is 40mm in front of VP and 25mm above HP. The top view of the line is inclined at 30 to VP and the front view of the line is inclined at 45 to the ground. The distance between the projectors is 100mm. Draw the top and front views of the line. Determine the true length and the true inclinations the line makes with VP and HP. 3.5. The top view of a certain line PQ is 60mm long and makes 30 with XY line. Its front view makes 45 with XY line. The end P is 20mm in front of VP and 25mm above HP. Determine its true length, inclination with the reference planes. 3.6. A point P is 40mm above HP and 20mm in front of VP. Another point Q is 20mm above HP and 50mm in front of VP. The top view of the line joining P and Q is inclined at 30 to the XY line. Draw the top and front views of the line. Find i) True length, ii) Traces and iii) Inclinations with the two reference planes. 3.7. The top view of a line PQ, 75mm long, measures 50mm. The end P is 30mm in front of VP and 15mm above HP. The end Q is 15mm in front of VP and above HP. Draw the projections of the line and find its inclinations with HP and VP. (15) March 2001 3.8. A line PQ, measuring 75mm, has one of its ends 40mm in front of VP and 15mm above HP. The other end is 15mm in front of VP and above HP. The top view of the line is 50mm long. Draw the front view of the line and find the inclination of the line PQ with HP and VP. (15) February 2003 3.9. The end A of the line AB is 20mm above HP and 15mm in front of VP. The distance between the ends A and B measured parallel to the reference line is 70mm and the distances measured perpendicular to the reference line, between the ends A and B, in the front view and in the top view are 40mm and 30mm respectively. Draw the projections of the line AB and determine the true length and inclinations of the line with all the three planes. (15) February 2004 3.10. The top view pq of a straight line is 70mm and makes an angle of 60 with XY line. The point Q is 10mm in front of VP and 30mm above HP. The difference between the distances of P and Q above HP is 45mm. Draw the projections. Determine its true length and true inclinations with HP and VP. (15) July 2003 3.11. A line PQ, 90mm long, has end P 10mm above HP and 15mm in front of VP. The top view of the line measures 75mm while its front view is 70mm. Draw the plan and elevation of the line and find its true inclinations with HP and VP. (15) September 2000 3.12. The front view of a line AB, 12.5cm long, is 7.5cm and its top view is 10cm long. Its end B is 3cm from both the principal planes. Draw its projections and find its inclinations with the reference planes. 3.13. Draw the projections of a line AB, 90mm long, its midpoint M being 50mm above HP and 40mm in front of VP. The end A is 20mm above HP and 10mm in front of VP. Find the inclination of the line with VP and HP. (15) February 2002
PROJECTIONS OF LINES
3.2
CAED
3.14. The midpoint of a line AB is 60mm above HP and 50mm in front of VP. The line measures 80mm and is inclined at 30 to HP and 45 to VP. Draw the top, front and left views of the line. Measure the distance between the end projectors parallel to the XY line. (15) August 99 3.15. The front view of a line is 80mm in length and makes 40 with the ground line. Its midpoint C is 60mm in front of VP and 60 mm above HP. Point A is 50mm in front of VP. Draw the top and front views of the line. Determine the true length and true inclinations of the line with the reference planes.
CAED
4.1
PROJECTIONS OF PLANES
4.1. A hexagonal lamina of sides 25mm has its plane inclined at 50 to HP. One of its sides is on HP and makes an angle of 25 with VP. Draw the projections. 4.2. A regular hexagonal plate of 30mm sides has one corner touching VP and the opposite corner touching HP. The plate is inclined at 60 to HP and 30 to VP. Draw the projections of the plate neglecting its thickness. (20) August 2003 4.3. A regular hexagonal lamina, of sides 30mm, is lying in such a way that one of its sides touches both the reference planes. If the lamina makes an angle of 60 with VP, draw the projections of the lamina. 4.4. A square plate of 40mm sides rests on a corner on HP with one of its diagonals inclined at 30 to HP and 45 to VP. Draw its projections. 4.5. The top view of a circle standing on a point on its rim appears as an ellipse of major axis 50mm and minor axis 30mm with its minor axis inclined at 30 to xy. Draw the projections of the lamina. (15) September 2001 4.6. A circular plate of negligible thickness and 50mm diameter appears as an ellipse in the front view having major axis 50mm and minor axis 30mm. Draw the top view of the plate when the major axis of the ellipse is horizontal. (15) January 2003 4.7. Draw the projections of a circular plate of 50mm diameter resting on HP on a point A on the circumference, with its plane inclined at 45 to HP and the top view of the diameter AB making 30 with VP. 4.8. Draw the top and front views of a circular lamina of diameter 50mm which is resting on the ground such that the surface of the lamina makes 40 to the ground and the diameter through the point on which the lamina rests is inclined at 40 to VP. (15) July 2002 4.9. Determine the true shape of the figure, the top view of which is a regular pentagon of 35mm sides, having one side inclined at 30 to xy line and whose front view is a straight line making an angle of 45 with xy line. 4.10. An isosceles triangular plate has base 50mm long and altitude 70mm. It is placed on HP such that in the front view it is seen as an equilateral triangle of 50mm sides with the side that is parallel to VP inclined at 45 to HP. Draw its top and front views. (15) August 99 4.11. A rectangular lamina of size 60mm x 90mm rests on HP on one of its shorter edges. The lamina is rotated about the edge on which it rests till it appears as a square in the top view. The edge on which the lamina rests is parallel to both HP and VP. Draw its projections and find its inclinations with HP and VP. 4.12. A rectangular plane ABCD of 70mm and 40mm has its shorter side AD on HP and inclined at 30 to VP. Draw the projections of the plane, if the surface is inclined to HP such that the top view appears to be a square of the shorter side. Find the inclination of the plane with HP. 4.13. A rectangular plate, 80mm x 60 mm, is resting on HP. It is tilted about one of its shorter edges, which is parallel to VP in such a way that the front view appears as a square of 60mm sides. Draw the projections of the plate and find its inclination with HP. 4.14. A rectangular plate, 70 x 40 mm has one of its shorter edges in the VP inclined at 40 to HP. Draw its top view if the front view is square of side 40mm. (15) February 2002
PROJECTIONS OF PLANES
4.2
CAED
4.15. A pentagonal lamina of side 30mm is having a side in both HP and VP. The surface of the lamina is inclined at an angle of 60 with HP. Draw the top and front views of the lamina. 4.16. A pentagonal lamina of sides 30mm is resting on a side on HP, which is inclined at 45 to VP and the surface being inclined at 30 to HP. Draw the projections. (15) February 2002, July 2003 4.17. A pentagonal lamina of sides 50mm rests on the ground on one of its sides, which is inclined at 30 to VP. The surface of the lamina is inclined at 45 to HP. Draw the projections of the lamina.
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING DRAWING
6.1
PROJECTIONS OF SOLIDS
5.1. A hexagonal prism of base 40mm side and axis 80mm long has an edge of the base parallel to HP and inclined at 45 to VP. Its axis makes an angle of 60 with HP. Draw three views. (20) February 2002 5.2. Draw the projections of a hexagonal prism of side of base 30mm and axis 60mm long when resting with one of its longest edges on HP. Axis is inclined at 40 to VP. One of the rectangular faces containing the longer edge on which the prism rests is inclined at 30 to HP. 5.3. A right regular pentagonal prism of 30mm side of base and 75mm side is resting on one of its base corners on HP such that the base is inclined at 45 to HP. Two of the base edges containing the standing corner are equally inclined to HP. Draw the projections of the prism, if the axis is inclined at 30 to VP and the base being nearer to the observer. 5.4. A regular pentagonal prism lies with its axis inclined at 60 to HP and 30 to VP. The prism is 80mm long and has a face width of 25mm. One of the corners of the top face is nearer to the observer. Draw the top and front views of the prism. 5.5. A rectangular prism of base 30mm x 40mm and height 50mm stands on one of the longer edges of the base, such that the rectangular face containing the longer edge of the base on which it is standing is inclined at 40 to HP, the top view of the axis being inclined at 30 to xy. Draw the projections of the prism. (20) September 2000 5.6. A cube of 45mm edge is resting on one of its corners on HP with a solid diagonal perpendicular to VP. Draw its top and front views. (20) August 2001 5.7. A hexagonal pyramid of base 30mm side and axis 60mm long is lying on one of its slant edges in HP such that two of its triangular faces containing the slant edge are equally inclined to HP. Draw the projections of the pyramid, when the top view of the axis appears to be inclined to VP at 45 and the base being nearer to the observer than its apex. (20) February 2000 5.8. A hexagonal pyramid of base of sides 30mm long and altitude 60mm is resting on one of its base edges on the ground. This edge makes 30 to the VP and the face containing this edge makes 45 to HP. Draw the projections. (20) February 2002 5.9. Draw the projections of a pentagonal pyramid having side of base 30mm and length of axis 70mm while resting on one of its triangular faces in VP and the edge of the base of that triangular face is at 45 to HP. 5.10. A right regular pentagonal pyramid of 30mm side of base and 72mm height is freely suspended from one of the corners of the base of the pyramid. Draw the projections of the pyramid if the vertical plane containing the axis is inclined to VP by 30 and the base being nearer to the observer, the centre of gravity of the pyramid lies on the axis 18mm from the base. 5.11. A triangular pyramid of height 60mm and base side 40mm long is resting with its apex on HP, such that one of the inclined triangular faces makes an angle of 30 with HP. Draw the top and front views of the pyramid when the top view of the axis makes an angle of 45 with VP.(20) August 2001 5.12. A cylinder, diameter of base 40mm and 70mm high, rests with one of its generators on the ground. The axis is inclined at 60 to VP. Draw its top and front views. 5.13. A right circular cone of base diameter 40mm and axis 60mm long rests on one of the arc points of base circle in HP such that the generator passing through the point is normal to HP and the axis makes an angle of 10 with VP, the apex being nearer to VP. Draw the projections of the solid. (20) February 2000 5.14. A cone of 60mm diameter and 70mm height rests with one of its generators on HP with its axis inclined at 30 to VP. Draw its top, front and right views.
PROJECTIONS OF SOLIDS
5.2
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING DRAWING
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING DRAWING
6.1. 6.2. 6.3. 6.4. 6.5. 6.6. 6.7. 6.8.
6.1
ISOMETRIC PROJECTION
Draw the isometric projection of a hexagon of 40mm sides in horizontal and vertical positions. Draw the isometric projection of a pentagon of 45mm sides in horizontal and vertical positions. Draw the isometric projection of a circle of 80mm diameter in horizontal and vertical positions. Draw the isometric projection of a pentagonal prism of 30mm sides and 70mm height in a vertical position. Draw the isometric view of a hexagonal prism of 30mm sides and length 65mm in the horizontal position. Draw the isometric view of a pentagonal pyramid of 35mm base side and height 85mm. Draw the isometric view of a hexagonal pyramid of 30mm base side and height 75mm. Draw the isometric view of a cylinder of 60mm height and 50mm diameter in the horizontal position. Draw the isometric projection of a cone of 60mm base diameter and height 80mm.
6.9.
6.10. Draw the isometric projection of a frustum of cone whose top diameter is 30mm and bottom diameter is 50mm and height of frustum being 40mm. 6.11. The frustum of a square pyramid of sides 40mm and 20mm and height 60mm rests on the centre of the top of a square block of side 60mm and height 20mm. the base edges of the frustum of pyramid are parallel to the top edges of the square block. Draw the isometric projection of the combination of the solids. (20) July 2003 6.12. A square pyramid of base side 40mm and height 70mm rests symmetrically on a cube of edge 50mm which itself is placed on a cylinder of diameter 80mm and thickness 30mm. Draw the isometric projection of the solids if the axes of the three solids are in a common line. (20) August 2002 6.13. A regular pentagonal prism of base edge 30mm and axis 60mm is mounted centrally over a cylindrical block of 80mm diameter and 25mm thick. Draw the isometric projection of the combined solids. 6.14. A sphere of diameter 40mm rests centrally on the top smaller end of frustum of a hexagonal pyramid. The frustum of the pyramid has 25mm sides at the top, 40mm sides at the base and is 80mm high. Draw the isometric projection of the combination of the solids. (20) March 2005 6.15. A sphere of 25mm diameter is placed centrally on a cylindrical block of base diameter 40mm and 25mm thick, which is in turn placed on a hexagonal prism of base side 30mm and axis 70mm long, when they are coaxial. Draw the isometric projection of the combined solids. (20) January 2004 6.16. A cylinder of 20mm diameter and height 25mm is placed vertically at the centre of the rectangular face of a hexagonal prism of 25mm sides and axis 60mm. Draw the isometric projection of the combination of solids. (20) March 2005 6.17. A cylindrical slab of 50mm diameter and 20mm thickness is resting on the ground and on top of this cylinder a cube of 30mm is resting coaxially. On top of this cube rests a square pyramid of side 20mm and height 40mm coaxially. Draw the isometric projection of the solids. (20) February 2003
6.18. A hemispherical vessel of diameter 90mm is placed centrally over a cylinder of diameter 60mm and height 75mm which in turn kept centrally over a square prism of base side 80mm and height 20mm. Draw the isometric projection of the combination of solids. (20) February 2002 6.19. Draw the isometric projection the combination of solids shown in Fig. 1. 6.20. Draw the isometric projection the combination of solids shown in Fig. 2. 6.21. Draw the isometric projection of the paperweight with a spherical knob at the top, the front view of which is shown in Fig. 3. All dimensions are in mm (20) August 2001
70
60 25 40 25
22
25
10 R
32 63
80
60 75 70
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
6.22. Draw the isometric projection of the object shown in Fig. 4, using the isometric scale. All dimensions are in mm. 6.23. Draw the isometric projection of the combination of the solids shown in Fig. 5. All dimensions are in mm. (20) July 2003
S 50 Hexagonal pyramid of base 30mm 60 20 30 50mm SQ 25 45 70 75 20 75mm 30mm 15 SQ60 30mm
R 20mm, SPHERE
10mm 60
Cylinder of dia 30
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Fig. 6
Fig. 7
6.24. Fig. 6 shows the front view of three solids, a cylinder, a square prism and a cut sphere placed one above the other with their axes coaxial. The dimensions shown are in mm. Draw the isometric projection of the combination of solids. (20) February 2000 6.25. Draw the isometric projection of the combination of solids shown in Fig. 7. (20) January 2004
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING DRAWING
7.1
DEVELOPMENT OF SURFACES
7.1. Draw the development of a cylinder of diameter 40mm cut by a section plane perpendicular to VP and making an angle of 50 with HP and passing through a point in the axis 20mm below the top surface. 7.2. A pipe made of half circular and half square shape is cut as shown in Fig. 1. Draw the development of the lateral surface of the object. All the dimensions are in mm. 7.3. Draw the development of the lateral surface of the frustum of the cone shown in Fig. 3. 7.4. Draw the development of the lateral surface of part P of the cone shown in Fig. 2.
60 30
30
100
45
45
40 P
70
30 45 45
10 Fig. 1
20 Fig. 2
10
50 Fig. 3
7.5. A frustum of a pentagonal pyramid, base side 40mm and top surfacee side 20mm and height 50mm, is resting on HP on its smaller base, with one of its base sides parallel to VP. Draw the projections of the frustum and develop the lateral surface of the frustum. 7.6. A string is wound around the lateral surface of a pentagonal pyramid, base side 50mm and axis 80mm long, starting from one of its base corners and ending at the same corner. Determine the minimum length of the string and show it in the projections of the pyramid. 7.7. A hexagonal pyramid, base side 30mm and axis 70mm long, is resting with its base on HP and an edge of base is inclined at 40 to XY. It is cut by an inclined plane perpendicular to VP and inclined at 40 to HP and passing through a point on the axis 30mm from the apex. Draw the development of the lateral surface of the bottom portion of the pyramid. 7.8. A frustum of hexagonal pyramid, bottom base edge 40mm and top surface edge 25mm, is resting on its base on the HP with one of the base edges perpendicular to VP. Draw its projections and development of lateral surface of the frustum.
Вам также может понравиться
- Caed Question Bank10!8!17Документ17 страницCaed Question Bank10!8!17Shubh PatiyatОценок пока нет
- First Sem Engineering Graphics Question BankДокумент11 страницFirst Sem Engineering Graphics Question BankPRIYA RAJIОценок пока нет
- GE6152 Engineering GraphicsДокумент13 страницGE6152 Engineering GraphicspsvnccОценок пока нет
- Question BankДокумент12 страницQuestion BankBalaChandarОценок пока нет
- Questions of LifeДокумент17 страницQuestions of Lifesiddarth kocheriОценок пока нет
- AssignmentДокумент23 страницыAssignmentjessie026Оценок пока нет
- Engineering GraphicsДокумент15 страницEngineering GraphicsvpsraviОценок пока нет
- Projection of LinesДокумент2 страницыProjection of LinesanandandmeenaОценок пока нет
- 6 1Документ5 страниц6 1S.C. HaneeshОценок пока нет
- Eg QBДокумент13 страницEg QBHarini RameshОценок пока нет
- 20ME0301-Engineering GraphicsДокумент7 страниц20ME0301-Engineering GraphicsBk TechinteluguОценок пока нет
- SELVAM COLLEGE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING GRAPHICS DOCUMENTДокумент13 страницSELVAM COLLEGE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING GRAPHICS DOCUMENTRichard S DavidsonОценок пока нет
- RazizДокумент48 страницRazizChandramohan GОценок пока нет
- Engg. Drawing QuestionsДокумент9 страницEngg. Drawing QuestionsdearsaswatОценок пока нет
- EG Question BankДокумент9 страницEG Question BankdiduthegreatОценок пока нет
- Engg Graphics - UNIT-II Questions & AnswersДокумент10 страницEngg Graphics - UNIT-II Questions & AnswersS A ABDUL SUKKURОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент10 страницUntitledSuyog ChaudhariОценок пока нет
- GE8152 EG Consolidated Question BankДокумент13 страницGE8152 EG Consolidated Question BankGnaneswaran NarayananОценок пока нет
- Question Bank Engineering Graphics (GE6152) : Unit-I Plane Curves & Free Hand SketchingДокумент14 страницQuestion Bank Engineering Graphics (GE6152) : Unit-I Plane Curves & Free Hand Sketchingnandhu20Оценок пока нет
- A Line ABДокумент5 страницA Line ABnabalsinghОценок пока нет
- Engineering Graphics Assignment with Projections of Points, Lines, Pentagon, and Circular LaminaДокумент1 страницаEngineering Graphics Assignment with Projections of Points, Lines, Pentagon, and Circular Laminakumar kmОценок пока нет
- EG Question Bank PDFДокумент22 страницыEG Question Bank PDFManish DVОценок пока нет
- Anna University Engineering Graphics Question BankДокумент11 страницAnna University Engineering Graphics Question BankRajkumarОценок пока нет
- AssignmentДокумент14 страницAssignmentAdel AwadОценок пока нет
- GEC 1101 - Engineering Graphics: Tutorial-Module - 3 Projection of Straight Lines and PlanesДокумент3 страницыGEC 1101 - Engineering Graphics: Tutorial-Module - 3 Projection of Straight Lines and PlanesG. RajeshОценок пока нет
- Caed Manual-Apr2823Документ45 страницCaed Manual-Apr2823Aditya KulkarniОценок пока нет
- Ellipses, parabolas, hyperbolas & engineering graphics questionsДокумент6 страницEllipses, parabolas, hyperbolas & engineering graphics questionsDamo Daran GОценок пока нет
- GE6152 EngineeringGraphicsquestionbankДокумент11 страницGE6152 EngineeringGraphicsquestionbankNatarajan AgoramОценок пока нет
- Kings: Department of Mechanical EngineeringДокумент11 страницKings: Department of Mechanical Engineeringrammit2007Оценок пока нет
- Unit II Projection of Points and Straight Lines Planes Important SumsДокумент3 страницыUnit II Projection of Points and Straight Lines Planes Important SumsrajeshОценок пока нет
- (Common To All Branches of Engineering) : (20A03101T) Engineering DrawingДокумент3 страницы(Common To All Branches of Engineering) : (20A03101T) Engineering Drawingramu vasaОценок пока нет
- Question Bank Engg Graphics 1Документ15 страницQuestion Bank Engg Graphics 1yuvashreesharmiОценок пока нет
- Engineering Drawing Tutorial SheetsДокумент23 страницыEngineering Drawing Tutorial SheetsManoj Paudel100% (2)
- Tutorial – Lettering & Dimensioning PracticeДокумент20 страницTutorial – Lettering & Dimensioning PracticeSubramanian ManivelОценок пока нет
- Ge6152 Engineering Graphics Reg2013 QBДокумент16 страницGe6152 Engineering Graphics Reg2013 QBKarthik GanesanОценок пока нет
- Drawing Class 1Документ1 страницаDrawing Class 1Kiran MОценок пока нет
- Caed QB-2022Документ9 страницCaed QB-2022kalyanivishal777Оценок пока нет
- Engineering DRG I 2072Документ21 страницаEngineering DRG I 2072santoОценок пока нет
- Eg 2Документ8 страницEg 2Adhi ThyanОценок пока нет
- I B.Tech Question Unit2Документ11 страницI B.Tech Question Unit2Drkumar SwamyОценок пока нет
- Engg. Drawing - Lab MannualДокумент16 страницEngg. Drawing - Lab Mannualanandsohan916Оценок пока нет
- Engineering GraphicsДокумент32 страницыEngineering GraphicsL1-36 Abhisaranya koyyalamudiОценок пока нет
- Engineering Drawing 1: Department of Mechanical EngineeringДокумент29 страницEngineering Drawing 1: Department of Mechanical EngineeringSujal AdhikariОценок пока нет
- Engineering Drawing Sheet Problems 2019-20 First SemdocxДокумент5 страницEngineering Drawing Sheet Problems 2019-20 First SemdocxRohan DharpawarОценок пока нет
- Engineering Graphics Question BankДокумент10 страницEngineering Graphics Question BankAmey ChaudhariОценок пока нет
- Projection of Straight LinesДокумент63 страницыProjection of Straight LinesYash Fifa0% (1)
- Updated EG Assignment Sheet and AutoCAD ExercisesДокумент13 страницUpdated EG Assignment Sheet and AutoCAD Exercisesdevanshurajpoot1Оценок пока нет
- Engineering Graphics Question Bank 2021-22Документ15 страницEngineering Graphics Question Bank 2021-22asjadpathan0770Оценок пока нет
- Practice Questions - I - EGДокумент2 страницыPractice Questions - I - EGDhanus DhanuОценок пока нет
- Engineering Graphics Question BankДокумент10 страницEngineering Graphics Question BankDevil GameОценок пока нет
- Anna University QuestionsДокумент20 страницAnna University QuestionsMurugan PonnusamyОценок пока нет
- Dr.NGP Institute of Technology Engineering Graphics Question BankДокумент18 страницDr.NGP Institute of Technology Engineering Graphics Question BankPraveen MathiОценок пока нет
- Engineering Graphics Question Bank on Plane Curves, Freehand Sketching and ProjectionsДокумент15 страницEngineering Graphics Question Bank on Plane Curves, Freehand Sketching and ProjectionsimamuddeenОценок пока нет
- Ed Assignments 2021Документ9 страницEd Assignments 2021avscoolguy123Оценок пока нет
- Graphics Assignment LINESДокумент2 страницыGraphics Assignment LINESAbdul NazarОценок пока нет
- Qus PaperДокумент6 страницQus PaperBalamurugan KarnanОценок пока нет
- CSEC Mathematics June 1999 P2Документ10 страницCSEC Mathematics June 1999 P2zarzsultan12Оценок пока нет
- CBSE Class 10 Applications of Trigonometry (13) - 1Документ1 страницаCBSE Class 10 Applications of Trigonometry (13) - 1Vaibhave SОценок пока нет
- Three Dimensional Geometry 1. Central Idea of 3D 7. Distance of A Point P From Coordinate AxesДокумент7 страницThree Dimensional Geometry 1. Central Idea of 3D 7. Distance of A Point P From Coordinate Axesmanju priyaОценок пока нет
- 30-Question Math Sample PaperДокумент3 страницы30-Question Math Sample PaperAbhay SinghОценок пока нет
- Fifth Grade Geometry Vocabulary: W D A Acute AngleДокумент5 страницFifth Grade Geometry Vocabulary: W D A Acute Anglebry christianОценок пока нет
- IB 04 Straight Lines (11 16)Документ3 страницыIB 04 Straight Lines (11 16)eamcetmaterials100% (1)
- Answers To Coursebook Exercises: 5 ShapesДокумент7 страницAnswers To Coursebook Exercises: 5 ShapesLina AmrОценок пока нет
- Vector FM (Practice)Документ6 страницVector FM (Practice)Muhammad FurrukhОценок пока нет
- Cyclic Quadrilateral TheoremsДокумент4 страницыCyclic Quadrilateral Theoremsbuurning100% (1)
- Similarity and congruency formulaДокумент9 страницSimilarity and congruency formulaJorifОценок пока нет
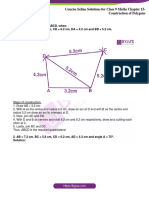
- Concise Selina Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 15 Construction of PolygonsДокумент31 страницаConcise Selina Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 15 Construction of Polygonsbhaskar51178Оценок пока нет
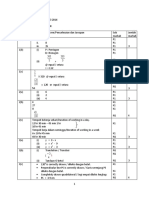
- Mathematics 8: Quarter 3-Week 5 Module 3: Solving Corresponding Parts of Congruent TrianglesДокумент10 страницMathematics 8: Quarter 3-Week 5 Module 3: Solving Corresponding Parts of Congruent TrianglesGelina TibayanОценок пока нет
- Congruence of TrianglesДокумент17 страницCongruence of TrianglesSanduniОценок пока нет
- CO Math10 Q2 Module3Документ18 страницCO Math10 Q2 Module3Teacher ApolОценок пока нет
- Vector 2Документ4 страницыVector 2Hugo Zuidweg RedondoОценок пока нет
- QuestionBank Projection of SolidsДокумент4 страницыQuestionBank Projection of SolidsAmritanshu AmritОценок пока нет
- Lesson Planning Sheet BisectorsДокумент1 страницаLesson Planning Sheet BisectorsJonathan RobinsonОценок пока нет
- Mathematics-Form 3-Chapter 1, 2, 3 & 4 by KelvinДокумент10 страницMathematics-Form 3-Chapter 1, 2, 3 & 4 by KelvinKelvin33% (3)
- Conic Section - (Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola)Документ40 страницConic Section - (Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola)Manas PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Brocard's TheoremДокумент7 страницBrocard's TheoremskОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5-MathsДокумент13 страницChapter 5-MathsChitturi SushanthОценок пока нет
- (BAUN) DLP Math5 - Visualizing & Describing Solid FiguresДокумент14 страниц(BAUN) DLP Math5 - Visualizing & Describing Solid FiguresHannah Jane Baun100% (3)
- 2U CSSA Geometry and LinearДокумент3 страницы2U CSSA Geometry and LinearGrace HuangОценок пока нет
- Linear Function - Maths in FocusДокумент47 страницLinear Function - Maths in FocusRicha Ng100% (1)
- Straight LinesДокумент4 страницыStraight Linesblue_l1Оценок пока нет
- Lesson 10 - Spherical TrigonometryДокумент12 страницLesson 10 - Spherical TrigonometryEd Vill100% (1)
- Solution:: 6-6 Trapezoids and KitesДокумент33 страницыSolution:: 6-6 Trapezoids and KitesShiv MohanОценок пока нет
- Geometry Flashcards PDFДокумент59 страницGeometry Flashcards PDFsekharsamyОценок пока нет
- MM PT3 Pahang AnsДокумент5 страницMM PT3 Pahang Ansahchin5Оценок пока нет
- Hyperbolic GeometryДокумент35 страницHyperbolic GeometryFrancisco Gurrola100% (1)