Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Es65 - Properties of Fluids
Загружено:
Annieza Marie Villarin ChavezИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Es65 - Properties of Fluids
Загружено:
Annieza Marie Villarin ChavezАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chavez, Annieza Marie V.
Properties of Fluids
BSCEN-4
ES65 Assignment
MASS DENSITY, (rho) The density of a fluid is its mass per unit of volume.
Units:
English: slugs/ft Metric: gram/cm
SI: kg/m
For an ideal gas, its density can be found from the specific gas constant and ideal gas law:
where: p = absolute pressure of gas in Pa R = gas constant Joule/kg-K T = absolute temperature in Kelvin
SPECIFIC VOLUME, VS Specific volume, Vs, is the volume occupied by a unit mass of fluid.
UNIT WEIGHT or SPECIFIC WEIGHT, Specific weight or unit weight, , is the weight of a unit volume of a fluid.
SPECIFIC GRAVITY Specific gravity, s, is a dimensionless ratio of a fluids density to some standard reference density. For liquids and solids, the reference density is water at 4C (39.2F).
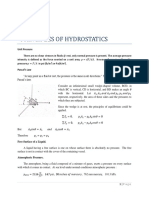
In gases, the standard reference to calculate the specific gravity is the density of air. For water at 4C: = 62.4 lb/ft3 = 9.81 kN/m3 = 1.94 slugs/ft3 s = 1.0 VISCOSITY (Dynamic Viscosity), (MU) Viscosity is the property of a fluid which determines the amount of its resistance to shearing forces. A perfect U fluid would have no viscosity. Area = A
Consider two large, parallel plates at a small distance y apart, the space between them being filled with a fluid. Consider the upper plate to be subject to a force F so as to move with a constant velocity U. The fluid in contact with the upper plate will adhere to it and will move with the same velocity U while the fluid in contact with the fixed plate will have a zero
moving plate V y dy dV
fixed plate
velocity. For small values of U and y, the velocity gradient can be assumed to be a straight line and F varies as A, U and y as:
or but (from the figure)
or
Where the constant of proportionality k is called the dynamic of absolute viscosity denoted as .
Where: = shear stress in lb/ft or Pa 2 = absolute viscosity in lb sec/ft (poises) or Pa-sec y = distance b/n the plates in ft or m U = velocity in ft/s or m/s
KINEMATIC VISCOSITY, (NU) Kinematic viscosity is the ratio of the dynamic viscosity of the fluid, , to its mass density, .
PRESSURES
UNIT PRESSURE OR PRESSURE, p Pressure is the force per unit area exerted by a liquid or gas on a body or surface, with the force acting at right angles to the surface uniformly in all directions.
GAGE PRESSURE (RELATIVE PRESSURE) Gage pressures are pressures above or below the atmosphere and can be measured by pressure gauges or manometers. ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE Atmospheric pressure is the pressure at any one point on the earths surface from the weight of the air above it. Under Normal conditions at sea level: patm = 2166 lb/ft2 = 14.7 psi = 29.9 inches of mercury = 101.325 kPa ABSOLUTE PRESSURE Absolute pressure is the pressure above absolute zero (vacuum).
Note:
Absolute zero is attained if all air is removed. It is the lowest possible pressure attainable. Absolute pressure can never be negative. The smallest gage pressure is equal to the negative of the ambient atmospheric pressure.
Вам также может понравиться
- PleteДокумент47 страницPletediamantechennieОценок пока нет
- Abe 106 - 01Документ6 страницAbe 106 - 01emmanuelОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 2 FluidsДокумент14 страницCHAPTER 2 FluidsIvan JadeОценок пока нет
- Mech 311 Fluid Mechanics Lecture NotesДокумент23 страницыMech 311 Fluid Mechanics Lecture NotesMarcky ReacherОценок пока нет
- 3 Unit PressureДокумент51 страница3 Unit PressureRalph Ian GodoyОценок пока нет
- Chapter Ii - Fluid StaticsДокумент72 страницыChapter Ii - Fluid StaticszetseatberhanuОценок пока нет
- Fluid Mechanics Lecture Cat2 2012Документ10 страницFluid Mechanics Lecture Cat2 2012Jithin Sri100% (1)
- Chapter 3-1Документ16 страницChapter 3-1Mohamed EzzОценок пока нет
- Defining Hydrostatics and Pressure: Figure 1. Pressure Distribution Around A Column of LiquidДокумент10 страницDefining Hydrostatics and Pressure: Figure 1. Pressure Distribution Around A Column of LiquidJohn GaviolaОценок пока нет
- Fluid MechanicsДокумент53 страницыFluid MechanicsNIHAR NAIKОценок пока нет
- Fluid Mechanics: Pressure and Fluid StaticsДокумент35 страницFluid Mechanics: Pressure and Fluid StaticsYusf ari jerjisОценок пока нет
- Properties of FluidsДокумент30 страницProperties of FluidsBojo ManayОценок пока нет
- Fundamental Fluid PropertiesДокумент28 страницFundamental Fluid PropertiesjohnОценок пока нет
- Principles of Hydrostatic PressureДокумент19 страницPrinciples of Hydrostatic PressureCB CañeteОценок пока нет
- Fluid Mechanics and ThermodynamicsДокумент221 страницаFluid Mechanics and ThermodynamicsBurner EmailОценок пока нет
- Fluid Mechanics I CE-407: Pressure MeasurementДокумент23 страницыFluid Mechanics I CE-407: Pressure Measurementtaha zafar100% (1)
- Fluids Handout Bernoilli and Equation of ContinuityДокумент11 страницFluids Handout Bernoilli and Equation of ContinuityShar anilОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ21 страницаChapter 3hailemebrahtuОценок пока нет
- Pressure in Fluids at RestДокумент4 страницыPressure in Fluids at Restkashif55663844Оценок пока нет
- 2 Notes PFDДокумент13 страниц2 Notes PFDtelishalatus077Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Fluid StaticsДокумент13 страницChapter 2 Fluid StaticsguhanОценок пока нет
- Lecture No - 2 PressureДокумент86 страницLecture No - 2 PressureresearchditОценок пока нет
- Hydraulics and Fluid MechanicsДокумент42 страницыHydraulics and Fluid MechanicsAditya SutarОценок пока нет
- Topic 2 - Ecw 211-Fluid StaticsДокумент82 страницыTopic 2 - Ecw 211-Fluid StaticssonghahoonОценок пока нет
- Fluid MechanicsДокумент15 страницFluid MechanicsSheila Mae AsuelaОценок пока нет
- Fluid Statics: Manometers and Pressure MeasurementsДокумент1 страницаFluid Statics: Manometers and Pressure MeasurementssolidwormОценок пока нет
- Lesson No. 2 in ES 65Документ4 страницыLesson No. 2 in ES 65Salahudin H.jamelОценок пока нет
- Lec. 1Документ31 страницаLec. 1Ali. AboudОценок пока нет
- Ce 140 - Hydraulics: By: Paul Rommel R. Valencia, Ce, MameДокумент15 страницCe 140 - Hydraulics: By: Paul Rommel R. Valencia, Ce, MameRochelleОценок пока нет
- 3.) Principles of Hydrostatics PDFДокумент7 страниц3.) Principles of Hydrostatics PDFShan Yi HaiОценок пока нет
- Common Temperature Scales: Basis: Freezing Point of WaterДокумент16 страницCommon Temperature Scales: Basis: Freezing Point of WaterJohnОценок пока нет
- PHY 111aДокумент29 страницPHY 111aCharisse StevensОценок пока нет
- Fluid Mechanics: Hooke'S LawДокумент18 страницFluid Mechanics: Hooke'S Lawsiddhartha2862Оценок пока нет
- Fluid MechanicsДокумент32 страницыFluid MechanicsShristyОценок пока нет
- Fluid Mechanics Notes & Questions PDFДокумент15 страницFluid Mechanics Notes & Questions PDFJatin SinglaОценок пока нет
- Cien 30064 HydraulicsДокумент83 страницыCien 30064 Hydraulicscalebjohnf0512Оценок пока нет
- CHPT 10Документ5 страницCHPT 10sambarta.sanyalОценок пока нет
- Fluid StaticsДокумент40 страницFluid StaticsAbdul AhadОценок пока нет
- 2.1 Fluid StaticsДокумент33 страницы2.1 Fluid StaticsXienlyn BaybayОценок пока нет
- Fluid Properties and Pressure VariationДокумент8 страницFluid Properties and Pressure VariationmurtazaОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics Important DefinitionДокумент33 страницыThermodynamics Important Definitionjaveed136Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 Hydrostatic Pressure and BouyancyДокумент20 страницChapter 6 Hydrostatic Pressure and BouyancyAbba MuhammedОценок пока нет
- O'level Physics PressureДокумент11 страницO'level Physics PressureToretto100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics 2019 2020Документ67 страницFluid Mechanics 2019 2020NikkiОценок пока нет
- Fluid MechanicsДокумент62 страницыFluid Mechanicss.yosores.janchristineОценок пока нет
- Fluid MechanicsДокумент16 страницFluid MechanicsRaju SinghОценок пока нет
- Fluid MechanicsДокумент16 страницFluid MechanicsRaju SinghОценок пока нет
- Part - 2Документ81 страницаPart - 2aryanneet9599Оценок пока нет
- Physics Fluid MechanicsДокумент18 страницPhysics Fluid MechanicsPrajwalОценок пока нет
- Fluid Mechanics (MR 231) Lecture Notes (4) : Coefficient of Volume ExpansionДокумент11 страницFluid Mechanics (MR 231) Lecture Notes (4) : Coefficient of Volume ExpansionAhmedTahaОценок пока нет
- Fluids Exams - 042111Документ4 страницыFluids Exams - 042111Rhomel John PadernillaОценок пока нет
- Pressure: Force Area Perpendicular Gauge PressureДокумент6 страницPressure: Force Area Perpendicular Gauge PressureSyed Rameez MohiuddinОценок пока нет
- Fluid MechanicsДокумент98 страницFluid MechanicsoperationmanagerОценок пока нет
- CE 521 - Reaction Paper On Introduction To Principles of HydrostaticsДокумент8 страницCE 521 - Reaction Paper On Introduction To Principles of HydrostaticsHipolito RarangolОценок пока нет
- 02 - Fluid Statics PDFДокумент33 страницы02 - Fluid Statics PDFJoan LaksmitaОценок пока нет
- فلود 3Документ19 страницفلود 3عبدالله خيريОценок пока нет
- Fluid MechanicsДокумент45 страницFluid MechanicsCholwe Essau MbilimaОценок пока нет
- Fisdas Pert 8 - 9 FluidaДокумент14 страницFisdas Pert 8 - 9 FluidaAuliaОценок пока нет
- Topics 10-2 Relationship Between Pressure and DensityДокумент4 страницыTopics 10-2 Relationship Between Pressure and DensityHinata CosaОценок пока нет
- Aerospace MaterialsДокумент68 страницAerospace MaterialsAykut Üçtepe100% (1)
- ZXMP S200 Commissioning Guide - R1.1Документ47 страницZXMP S200 Commissioning Guide - R1.1Achmad Abdil MansyuriОценок пока нет
- 545 ELP-ES-2011 - Catálogo de DisipadoresДокумент24 страницы545 ELP-ES-2011 - Catálogo de DisipadoresrichkidОценок пока нет
- Export Dataset To PDF in ASP NetДокумент2 страницыExport Dataset To PDF in ASP NetWilliamОценок пока нет
- Acidizing TreatmentsДокумент93 страницыAcidizing TreatmentsPeña Lucia100% (2)
- Watertight Doors On Ships: Types, Maintenance & SOLAS RegulationsДокумент16 страницWatertight Doors On Ships: Types, Maintenance & SOLAS Regulationsgeorgesaguna100% (1)
- ThanksДокумент17 страницThankssselvanjhcОценок пока нет
- AY 2015-16cvbbnjДокумент245 страницAY 2015-16cvbbnjSyed Abdul AzizОценок пока нет
- Update Notifikasi Depkes FEB 18Документ6 страницUpdate Notifikasi Depkes FEB 18pratistanadia_912023Оценок пока нет
- CENG6206 Soil Dynamics ExerciseProblemДокумент4 страницыCENG6206 Soil Dynamics ExerciseProblemFekadu Wub100% (1)
- Toshiba 42pw33q - S Ch. Pw33 SchematicsДокумент18 страницToshiba 42pw33q - S Ch. Pw33 SchematicstodorloncarskiОценок пока нет
- Final Thesis DATAДокумент60 страницFinal Thesis DATAdahaletushar75Оценок пока нет
- ThaiREC Checklist-Barge Inspection Questionnaire GasДокумент18 страницThaiREC Checklist-Barge Inspection Questionnaire Gasเปีย วันชัย สวนทอง100% (1)
- Presented By:: Rafi Sheikh Sheeraz Malik Syed Ahmed Ali Umair Ali Waqar AmeenДокумент34 страницыPresented By:: Rafi Sheikh Sheeraz Malik Syed Ahmed Ali Umair Ali Waqar AmeenSyed Ahmed AliОценок пока нет
- Technical LetteringДокумент12 страницTechnical LetteringMaverick Timbol50% (2)
- DP1100Документ3 страницыDP1100tunradotОценок пока нет
- FM-200 Alpha Series SystemsДокумент6 страницFM-200 Alpha Series SystemsGurusumiОценок пока нет
- Sample Electrical LayoutДокумент1 страницаSample Electrical LayoutBentesais Bente UnoОценок пока нет
- Sop For LP Pump (R1)Документ6 страницSop For LP Pump (R1)SonratОценок пока нет
- Career Cluster SurveyДокумент6 страницCareer Cluster Surveydaaiyahnaim100% (1)
- Debug 1214Документ2 страницыDebug 1214Faizah Ayulia NawitaОценок пока нет
- Earned Schedule - Walt LipkeДокумент27 страницEarned Schedule - Walt LipkeKatie BensonОценок пока нет
- Amplitude Shift KeyingДокумент3 страницыAmplitude Shift KeyingPurnendh ParuchuriОценок пока нет
- Cable TrenchДокумент57 страницCable TrenchHari Krishna AaryanОценок пока нет
- Persuasive Speech Outline Spring 2016Документ2 страницыPersuasive Speech Outline Spring 2016api-311467409Оценок пока нет
- AÇO - DIN17100 St52-3Документ1 страницаAÇO - DIN17100 St52-3Paulo Henrique NascimentoОценок пока нет
- British Columbia Institut of TechnologyДокумент2 страницыBritish Columbia Institut of Technologyrobertofca2266Оценок пока нет
- Brickwork ApparatusДокумент4 страницыBrickwork ApparatusRoslie AbdullahОценок пока нет
- 02-Engine Mechanical System PDFДокумент129 страниц02-Engine Mechanical System PDFSigit Indrawan100% (1)
- HEKO Products and Services: Elements For Bucket ElevatorsДокумент36 страницHEKO Products and Services: Elements For Bucket ElevatorsShariq KhanОценок пока нет