Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
31 (A) The Nervous System
Загружено:
IAS EXAM PORTALИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
31 (A) The Nervous System
Загружено:
IAS EXAM PORTALАвторское право:
www.iasexamportal.
com
IASEXAMPORTAL .COM
www.iasexamportal.com
Multicellular animals must monitor and maintain a constant internal
environment as well as monitor and respond to an external
environment. In many animals, these two functions are coordinated
by two integrated and coordinated organ systems: the nervous
system and the endocrine system. Three basic functions performed
by nervous systems are:1. Receive sensory input from internal and external
environments
2. Integrate the input
3. Respond to stimuli
IASEXAMPORTAL .COM
www.iasexamportal.com
The nervous system monitors and controls almost every organ system
through a series of positive and negative feedback loops.
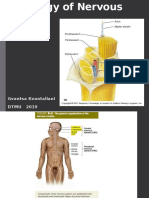
The Central Nervous System (CNS) includes the brain and spinal cord.
The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects the CNS to other parts
of the body, and is composed of nerves (bundles of neurons).
Not all animals have highly specialized nervous systems.
Those with simple systems tend to be either small and very mobile or
large and immobile.
IASEXAMPORTAL .COM
www.iasexamportal.com
Large, mobile animals have highly developed nervous systems: the
evolution of nervous systems must have been an important adaptation
in the evolution of body size and mobility.
IASEXAMPORTAL .COM
www.iasexamportal.com
The vertebrate nervous system is divided into a number of parts. The
central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord. The
peripheral nervous system consists of all body nerves. Motor neuron
pathways are of two types: somatic (skeletal) and autonomic (smooth
muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands).The autonomic system is subdivided
into the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
Peripheral Nervous System
The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) contains only nerves and connects
the brain and spinal cord (CNS) to the rest of the body. The axons and
dendrites are surrounded by a white myelin sheath. Cell bodies are in
the central nervous system (CNS) or ganglia. Ganglia are collections of
nerve cell
IASEXAMPORTAL .COM
www.iasexamportal.com
bodies. Cranial nerves in the PNS take impulses to and from the brain
(CNS). Spinal nerves take impulses to and away from the spinal cord.
There are two major subdivisions of the PNS motor pathways: the
somatic and the autonomic.
The Somatic Nervous System (SNS) includes all nerves controlling the
muscular system and external sensory receptors. External sense organs
(including skin) are receptors. Muscle fibers and gland cells are
effectors.
IASEXAMPORTAL .COM
www.iasexamportal.com
The Autonomic Nervous System is that part of PNS consisting of motor
neurons that control internal organs. It has two subsystems. The
autonomic system controls muscles in the heart, the smooth muscle in
internal organs such as the intestine, bladder, and uterus. The
Sympathetic Nervous System is involved in the fight or flight response.
The Parasympathetic Nervous System is involved in relaxation. Each of
these subsystems operates in the reverse of the other (antagonism).
Both systems innervate the same organs and act in opposition to
maintain homeostasis. For example: when you are scared the
sympathetic system causes your heart to beat faster; the
parasympathetic system reverses this effect.
IASEXAMPORTAL .COM
www.iasexamportal.com
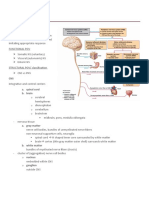
The Central Nervous System (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord.
The CNS is surrounded by bone-skull and vertebrae. Fluid and tissue also
insulate the brain and spinal cord.. The brain is composed of three parts: the
cerebrum (seat of consciousness), the cerebellum, and the medulla
oblongata (these latter two are part of the unconscious brain.
The medulla oblongata is closest to the spinal cord, and is involved with the
regulation of heartbeat, breathing, vasoconstriction (blood pressure), and
reflex centers for vomiting, coughing, sneezing, swallowing, and hiccupping.
The hypothalamus regulates homeostasis. It has regulatory areas for thirst,
hunger, body temperature, water balance, and blood pressure, and links the
Nervous System to the Endocrine System.
IASEXAMPORTAL .COM
www.iasexamportal.com
During embryonic development, the brain first forms as a tube, the
anterior end of which enlarges into three hollow swellings that form the
brain, and the posterior of which develops into the spinal cord. Some
parts of the brain have changed little during vertebrate evolutionary
history.
IASEXAMPORTAL .COM
www.iasexamportal.com
The brain stem is the smallest and from an evolutionary viewpoint, the
oldest and most primitive part of the brain. The brain stem is continuous
with the spinal cord, and is composed of the parts of the hindbrain and
midbrain. The medulla oblongata and pons control heart rate,
constriction of blood vessels, digestion and respiration.
The midbrain consists of connections between the hindbrain and
forebrain. Mammals use this part of the brain only for eye reflexes.
IASEXAMPORTAL .COM
www.iasexamportal.com
The cerebellum is the third part of the hindbrain, but it is not considered
part of the brain stem. Functions of the cerebellum include fine motor
coordination and body movement, posture, and balance. This region of
the brain is enlarged in birds and controls muscle action needed for
flight.
IASEXAMPORTAL .COM
www.iasexamportal.com
The forebrain consists of the diencephalon and cerebrum. The thalamus
and hypothalamus are the parts of the diencephalon. The thalamus acts
as a switching center for nerve messages. The hypothalamus is a major
homeostatic center having both nervous and endocrine functions.
The cerebrum, the largest part of the human brain, is divided into left
and right hemispheres connected to each other by the corpus callosum.
The hemispheres are covered by a thin layer of gray matter known as
the cerebral cortex, the most recently evolved region of the vertebrate
brain.
IASEXAMPORTAL .COM
www.iasexamportal.com
The spinal cord runs along the dorsal side of the body and links the brain
to the rest of the body. Vertebrates have their spinal cords encased in a
series of (usually) bony vertebrae that comprise the vertebral column.
The gray matter of the spinal cord consists mostly of cell bodies and
dendrites. The surrounding white matter is made up of bundles of
interneuronal axons (tracts). Some tracts are ascending (carrying
messages to the brain), others are descending (carrying messages from
the brain). The spinal cord is also involved in reflexes that do not
immediately involve the brain.
IASEXAMPORTAL .COM
www.iasexamportal.com
Nervous tissue is composed of two main cell types: neurons and glial
cells. Neurons transmit nerve messages. Glial cells are in direct contact
with neurons and often surround them. The neuron is the functional unit
of the nervous system. Humans have about 100 billion neurons in their
brain alone! While variable in size and shape,
IASEXAMPORTAL .COM
www.iasexamportal.com
The junction between a nerve cell and another cell is called a
synapse. Messages travel within the neuron as an electrical action
potential. The space between two cells is known as the synaptic cleft.
To cross the synaptic cleft requires the actions of neurotransmitters.
Neurotransmitters are stored in small synaptic vessicles clustered at
the tip of the axon. Neurotransmitters tend to be small molecules,
some are even hormones. The neurotransmitters cross the cleft,
binding to receptor molecules on the next cell, prompting
transmission of the message along that cells membrane.
IASEXAMPORTAL .COM
www.iasexamportal.com
Eyes of a crab are quite small but they enable the crab to look all around.
Butterflies have a large eye that seems to be made up of thousands of little
eyes. They can see not only in the front and the sides but the back as well.
Owl can see very well in the night but not during the day
Kite, eagle can see well during the day but not in the night.
The owl has large cornea and a large pupil to allow more light in its eye.
Also it has on its retina a large number of rods and only a few cones.
The day birds on the other hand have more cones and fewer rods.
Louse Braille himself a visually challenged person developed a system for
visually challenged persons and published it in 1821. Braille system has 63
dot pattern or characters.
IASEXAMPORTAL .COM
www.iasexamportal.com
Online Coaching for IAS Exams
http://iasexamportal.com/civilservices/courses/
Books for IAS Exams
http://iasexamportal.com/civilservices/books
Contact Us at:
http://iasexamportal.com/civilservices/contact-us
IASEXAMPORTAL .COM
Вам также может понравиться
- Solar Power in IndiaДокумент9 страницSolar Power in IndiaIAS EXAM PORTAL100% (1)
- Nuclear Power in IndiaДокумент10 страницNuclear Power in IndiaIAS EXAM PORTAL100% (1)
- Old NCERT PDF For IAS UPSC ExamsДокумент1 страницаOld NCERT PDF For IAS UPSC ExamsIAS EXAM PORTALОценок пока нет
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorДокумент15 страниц6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Green Development InitiativeДокумент7 страницGreen Development InitiativeIAS EXAM PORTALОценок пока нет
- 6 (B) Vijayanagar EmpireДокумент4 страницы6 (B) Vijayanagar EmpireIAS EXAM PORTALОценок пока нет
- 10 (A) Nature and Causes For The Rise of National MovementДокумент21 страница10 (A) Nature and Causes For The Rise of National MovementIAS EXAM PORTALОценок пока нет
- 1 (C) Historical Background & Origin of Indian ConstitutionДокумент5 страниц1 (C) Historical Background & Origin of Indian ConstitutionIAS EXAM PORTALОценок пока нет
- 3 (B) Gupta & Post-Gupta PeriodДокумент7 страниц3 (B) Gupta & Post-Gupta PeriodIAS EXAM PORTALОценок пока нет
- 9 (A) The Beginning of The Gandhian EraДокумент16 страниц9 (A) The Beginning of The Gandhian EraIAS EXAM PORTALОценок пока нет
- SSC CGL Numerical Aptitude Concepts of GeometryДокумент10 страницSSC CGL Numerical Aptitude Concepts of GeometryIAS EXAM PORTALОценок пока нет
- SSC CGL Numerical Aptitude Basic AlgebraДокумент11 страницSSC CGL Numerical Aptitude Basic AlgebraIAS EXAM PORTALОценок пока нет
- Online Coaching SSC CGL Tier 1 Reasoning Blood RelationsДокумент9 страницOnline Coaching SSC CGL Tier 1 Reasoning Blood RelationsIAS EXAM PORTALОценок пока нет
- SSC Online Coaching CGL Tier 1 Numercial Aptitude Ratio ProportionДокумент9 страницSSC Online Coaching CGL Tier 1 Numercial Aptitude Ratio ProportionIAS EXAM PORTALОценок пока нет
- SSC CGL Reasoning Sitting ArrangementsДокумент5 страницSSC CGL Reasoning Sitting ArrangementsIAS EXAM PORTALОценок пока нет
- SSC CGL Numerical Aptitude Time and DistanceДокумент5 страницSSC CGL Numerical Aptitude Time and DistanceIAS EXAM PORTALОценок пока нет
- SSC Online Coaching CGL Tier 1 Numercial Aptitude Alligation MixtureДокумент9 страницSSC Online Coaching CGL Tier 1 Numercial Aptitude Alligation MixtureIAS EXAM PORTALОценок пока нет
- Hindi Online Coaching SSC CGL Tier 1 Demo ChaptersДокумент13 страницHindi Online Coaching SSC CGL Tier 1 Demo ChaptersIAS EXAM PORTALОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Chapter 8 - Nervous ReviewerДокумент18 страницChapter 8 - Nervous Reviewerchristian anchetaОценок пока нет
- KMF 1023 Cognitive Psychology: Case Study (20%) - 3 Students in A GroupДокумент8 страницKMF 1023 Cognitive Psychology: Case Study (20%) - 3 Students in A GroupAnonymous lrLmuJОценок пока нет
- Phrenology and PhysiognomyДокумент10 страницPhrenology and PhysiognomyMuhammad HassanОценок пока нет
- Assessment of Adult ADHDДокумент24 страницыAssessment of Adult ADHDPsydoc100% (4)
- Santrock Section 3 InfancyДокумент21 страницаSantrock Section 3 InfancyAssumpta Minette Burgos100% (5)
- Histology of Nervous TissueДокумент40 страницHistology of Nervous TissueSHARON MARIA SUNNYОценок пока нет
- The Cannibals of Candyland PDFДокумент98 страницThe Cannibals of Candyland PDFLuis Castro100% (1)
- Instant Download Ebook PDF Brain and Behavior A Cognitive Neuroscience Perspective Canadian Edition PDF ScribdДокумент25 страницInstant Download Ebook PDF Brain and Behavior A Cognitive Neuroscience Perspective Canadian Edition PDF Scribdmyrtis.donaldson459100% (39)
- Lecture 5Документ22 страницыLecture 5SudhanshuОценок пока нет
- The Pathology of Boredom (Heron, 1956)Документ6 страницThe Pathology of Boredom (Heron, 1956)Lidia FilipОценок пока нет
- Dreams PresentationДокумент9 страницDreams Presentationapi-235827245Оценок пока нет
- Pe and Health Module 1Документ6 страницPe and Health Module 1Cielo DimayugaОценок пока нет
- Your Body Speaks Your MindДокумент54 страницыYour Body Speaks Your MindSatinder Bhalla100% (2)
- Bobath & Brunnstrom ApproachesДокумент40 страницBobath & Brunnstrom ApproachesManiu EmeseОценок пока нет
- An Introduction To The Philosophy of Psychology (Daniel Weiskopf Fred Adams) (Z-Library)Документ168 страницAn Introduction To The Philosophy of Psychology (Daniel Weiskopf Fred Adams) (Z-Library)Salomon BarbosaОценок пока нет
- Brain ExercisesДокумент19 страницBrain ExercisesgodolfintorentОценок пока нет
- Carlson - Vision-Topik 9 PDFДокумент40 страницCarlson - Vision-Topik 9 PDFPutri Unka Maryona AnugrahОценок пока нет
- Manly P. Hall - Spinal Column & The KundaliniДокумент48 страницManly P. Hall - Spinal Column & The KundaliniBret Trismegistus100% (31)
- Neurotransmitter - Prof. RondangДокумент35 страницNeurotransmitter - Prof. RondangYoga WitularОценок пока нет
- Article SummaryДокумент4 страницыArticle Summaryapi-260817278Оценок пока нет
- From Broca and Wernicke To The Neuromodulation EraДокумент10 страницFrom Broca and Wernicke To The Neuromodulation EraMarcela MacedoОценок пока нет
- Nervous System: Chapter TestДокумент4 страницыNervous System: Chapter TestJunior SencionОценок пока нет
- Topical Approach To Lifespan Development 8th Edition Santrock Test BankДокумент50 страницTopical Approach To Lifespan Development 8th Edition Santrock Test Banksorrancemaneuverpmvll100% (32)
- Cerebrovascular Disease: Cva & TbiДокумент19 страницCerebrovascular Disease: Cva & TbiKC MutiaОценок пока нет
- 1 BhatnagarandSoodДокумент8 страниц1 BhatnagarandSoodRicardo TischlerОценок пока нет
- Eccles, John - How The Self Controls Its BrainДокумент114 страницEccles, John - How The Self Controls Its Braintempullybone100% (6)
- مراجعة ساينس لغات رابعة ابتدائي ترم اول 2023 بالاجابات اعداد مسترДокумент18 страницمراجعة ساينس لغات رابعة ابتدائي ترم اول 2023 بالاجابات اعداد مسترSamwilОценок пока нет
- Physical Development InfantsДокумент36 страницPhysical Development InfantsChrisel Joy Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- 3 Nervous SystemДокумент33 страницы3 Nervous SystemSusan ZhaoОценок пока нет
- Aumann 1996Документ12 страницAumann 1996M4shroomОценок пока нет