Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
1st Millennium BC
Загружено:
Angel Lhi Dela CruzАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1st Millennium BC
Загружено:
Angel Lhi Dela CruzАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
SUBMITTED BY: ANGEL LHI DELA CRUZ
SUBMITTED TO: MS. ELIZABETH BAYONA
1000 BC- Vulgar fractions used by the Egyptians. However, only unit fractions are used (i.e., those with 1 as the numerator) and interpolation tables are used to approximate the values of the other fractions
first half of 1st millennium BC- Vedic India Yajnavalkya, in his
Shatapatha Brahmana, describes the motions of the sun and the moon, and advances a 95-year cycle to synchronize the motions of the sun and the moon.
8th century BC-The Yajur Veda, one of the four Hindu Vedas, contains the earliest concept of infinity, and states that if you remove a part from infinity or add a part to infinity, still what remains is infinity.
-1000 BC
- first half of 1st millennium BC
-8th century BC
800 BC Baudhayana, author of the Baudhayana Sulba Sutra, a Vedic Sanskrit geometric text, contains quadratic equations, and calculates the square root of two correctly to five decimal places.
early 6th century BC Thales of Miletus has various theorems attributed to him.
600 BC the other Vedic Sulba Sutras (rule of chords in Sanskrit) use Pythagorean triples, contain of a number of geometrical proofs, and approximate at 3.16.
-800 BC
-early 6th century BC
-600 BC
500 BC Indian grammarian Pnini writes the Astadhyayi, which contains the use of metarules, transformations and recursions, originally for the purpose of systematizing the grammar of Sanskrit.
5th century BC Hippocrates of Chios utilizes lunes in an attempt to square the circle.
4th century BC Indian texts use the Sanskrit word Shunya to refer to the concept of void (zero).
370 BC Eudoxus states the method of exhaustion for area determination.
-500 BC
-5th century B
-4th century BC
-370 BC
1st century Heron of Alexandria, the earliest fleeting reference to square roots of negative numbers.
3rd century Ptolemy of Alexandria wrote the Almagest
250 Diophantus uses symbols for unknown numbers in terms of syncopated algebra, and writes Arithmetica, one of the earliest treatises on algebra
1st century
3rd century
250
300 the earliest known use of zero as a decimal digit is introduced by Indian mathematicians
340 Pappus of Alexandria states his hexagon theorem and his centroid theorem
400 the Bakhshali manuscript is written by Jaina mathematicians, which describes a theory of the infinite containing different levels of infinity, shows an understanding of indices, as well as logarithms to base 2, and computes square roots of numbers as large as a million correct to at least 11 decimal places
300
340
400
450 Zu Chongzhi computes to seven decimal places. 500 Aryabhata writes the Aryabhata-Siddhanta, which first introduces the trigonometric functions and methods of calculating their approximate numerical values. It defines the concepts of sine and cosine, and also contains the earliest tables of sine and cosine values (in 3.75-degree intervals from 0 to 90 degrees) 6th century Aryabhata gives accurate calculations for astronomical constants, such as the solar eclipse and lunar eclipse, computes to four decimal places, and obtains whole number solutions to linear equations by a method equivalent to the modern method 550 Hindu mathematicians give zero a numeral representation in the positional notation Indian numeral system
450
500
6th century
550
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- 4e Friction Questions PDFДокумент16 страниц4e Friction Questions PDFSara Maged50% (2)
- (Tamas I. Gombosi) Physics of The Space EnvironmenДокумент357 страниц(Tamas I. Gombosi) Physics of The Space Environmenbrky100% (1)
- Core BooksДокумент16 страницCore BooksEng RitОценок пока нет
- Kozyrev Aether Time and TorsionДокумент8 страницKozyrev Aether Time and Torsionjjuulliisseess100% (2)
- 2 Naïve and Scientific RealismДокумент5 страниц2 Naïve and Scientific RealismValentin MateiОценок пока нет
- Philosophers' Perspectives on Self-IdentityДокумент31 страницаPhilosophers' Perspectives on Self-IdentityMarshall Teach86% (28)
- Physics II ProblemsДокумент1 страницаPhysics II ProblemsBOSS BOSSОценок пока нет
- Prism of Lyra - EbookДокумент4 страницыPrism of Lyra - Ebookdouglasray2150100% (1)
- Astronomy Lesson PlanДокумент5 страницAstronomy Lesson PlanWilliam BaileyОценок пока нет
- Moment HomeworkДокумент6 страницMoment Homeworkapi-200073732Оценок пока нет
- Retrograde Planets & Past ConnectionsДокумент4 страницыRetrograde Planets & Past Connectionsnmremala100% (1)
- Why Is There Something Rather Than NothingДокумент2 страницыWhy Is There Something Rather Than NothingnaasifmalequeОценок пока нет
- GravityДокумент5 страницGravityRatriОценок пока нет
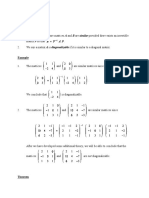
- Diagonal MatrixДокумент7 страницDiagonal MatrixMuzaFarОценок пока нет
- Il'enkov's Interpretation of Spinoza's Concept of the IdealДокумент20 страницIl'enkov's Interpretation of Spinoza's Concept of the IdealAnonymous IfL830HBjFОценок пока нет
- Dewar's Guide To DebatingДокумент13 страницDewar's Guide To DebatingEd Luna100% (1)
- LongevityДокумент3 страницыLongevitykannansesОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Astronomy PDFДокумент61 страницаIntroduction To Astronomy PDFReynaldo AldamarОценок пока нет
- Planetary Dysphoria and Environmental Disaster in Sebald's Nach der NaturДокумент7 страницPlanetary Dysphoria and Environmental Disaster in Sebald's Nach der Naturtantalus11Оценок пока нет
- The Antigod PDFДокумент1 000 страницThe Antigod PDFTeodor CimpocaОценок пока нет
- 1 - Analytical Planetary Solution VSOP2000 (Moisson & Bretagnon, 2001)Документ9 страниц1 - Analytical Planetary Solution VSOP2000 (Moisson & Bretagnon, 2001)LurzizareОценок пока нет
- (Classic Texts in The Sciences) Bernhard Riemann (Auth.), Jürgen Jost (Eds.) - On The Hypotheses Which Lie at The Bases of Geometry (2016, Birkhäuser Basel) PDFДокумент181 страница(Classic Texts in The Sciences) Bernhard Riemann (Auth.), Jürgen Jost (Eds.) - On The Hypotheses Which Lie at The Bases of Geometry (2016, Birkhäuser Basel) PDFayan849Оценок пока нет
- Antippa 2000Документ18 страницAntippa 2000cineva123456Оценок пока нет
- Sir Isaac Newton's Laws of MotionДокумент21 страницаSir Isaac Newton's Laws of MotionGabutin, Jan MarieОценок пока нет
- Anh 1Документ3 страницыAnh 1Khiem Nguyen ThaiОценок пока нет
- "My People Love Me!": The Standoff in Libya: by Douglas NoblehorseДокумент3 страницы"My People Love Me!": The Standoff in Libya: by Douglas NoblehorseAnonymous pgWs18GDG1Оценок пока нет
- Penny Seator - Morinus MethodДокумент17 страницPenny Seator - Morinus MethodJohnette Ricchetti100% (2)
- Energy BasicsДокумент8 страницEnergy BasicsCarol McLeodОценок пока нет
- Universal Wavefunction - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент2 страницыUniversal Wavefunction - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaafterragnarokОценок пока нет
- The Process of Creation by DR Israr AhmedДокумент41 страницаThe Process of Creation by DR Israr AhmedKhilafatMedia100% (1)