Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Arterial Blood Pressure
Загружено:
Examville.com0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
178 просмотров3 страницыFor more FREE Physiology Material visit www.examville.com
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
PDF или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документFor more FREE Physiology Material visit www.examville.com
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
178 просмотров3 страницыArterial Blood Pressure
Загружено:
Examville.comFor more FREE Physiology Material visit www.examville.com
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 3
ARTERIAL BLOOD PRESSURE
It is the pressure exerted by blood on the wall of a blood vessel, especially
pressure in arteries. It is determined by the rate and force of heart beat and
resistance to the flow of blood through vessels.
MEASUREMENT OF BLOOD PRESSURE
Blood pressure is measured by sphygmomanometer. Sphygmomanometer
consists of a rubber cuff attached by a rubber tube to a compressible hand
pump or bulb. Another tube attaches to the cuff and to a column of mercury
or pressure dial.
The cuff is wrapped around the power part of the upper arm and inflated by
squeezing the bulb. The bulb is squeezed until the blood pressure is raised
up to 200 mm Hg till pulse drops. The pulse is felt in two ways (1) by
placing the stethoscope and/ or (2) by placing the fingers over the radial
artery at the wrist. The pressure is slowly lowered by unscrewing the bulb
till the reappearance of the radial pulse.
The pressure at which radial pulse restarts or first sound is heard
corresponds to the systolic pressure. The pressure is lowered further, when
the sound becomes faint or disappears; the pressure recorded on the mercury
column corresponds to the diastolic pressure.
FACTORS AFFECTING ARTERIAL BLOOD PRESSURE
1. AGE - BP increases with age.
2. SEX – In females before menopause, SBP is 5 mm Hg less than that
in males.
3. EXERCISE – BP increases after exercise.
4. GRAVITY – The pressure in any blood vessel below heart level is
increased and that in any blood vessel above heart level is decreased
by the effect of gravity.
5. HEREDITARY – More prone in individuals with family history of
hypertension.
6. POSTURE – Upon sudden standing, DBP increases. It corrects after 1
min. to normal.
7. MEALS – SBP rises after meals.
DETERMINANTS OF ARTERIAL BLOOD PRESSURE
Arterial Blood Pressure – Cardiac output x Peripheral Resistance
Any factor altering the cardiac output or peripheral resistance will cause a
change in arterial blood pressure.
REGULATION OF BLOOD PRESSURE
There are various mechanisms that exist in human body which regulate the
systemic arterial blood pressure.
1. Rapidly acting regulatory mechanisms
2. Intermediate acting regulatory mechanisms
3. Long acting regulatory mechanisms
1. RAPIDLY ACTING REGULATORY MECHANISMS
They help to maintain blood pressure within normal range and prevents
from fluctuating to extreme high or low. They act within seconds of BP
becoming abnormal.
VARIOUS REFLEXES INVOLVED
1. Baroreceptor reflexes
2. Chemoreceptor reflexes
3. CNS Ischaemic response
2. INTERMEDIATE ACTING REGULATORY MECHANISMS
They begin to act within minutes of BP becoming abnormal. They alter
the blood volume and correct any change in BP.
MECHANISMS
1. Capillary fluid shift mechanisms
2. Stress relaxation mechanisms
3. LONG ACTING REGULATORY MECHANISMS
They are slow acting. Act over a period of days to years.
a. Direct mechanisms
b. Indirect mechanisms - Involve Renin- Angiotensin system
Aldosterone system
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Algebra Cheat SheetДокумент2 страницыAlgebra Cheat SheetDino97% (72)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Arteries & Circulation (Guyton, Chapter 14-16)Документ21 страницаArteries & Circulation (Guyton, Chapter 14-16)Dianne IgnacioОценок пока нет
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorДокумент15 страниц6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorДокумент15 страниц6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
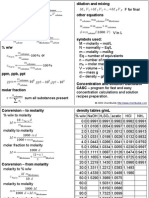
- Concentration Cheat SheetДокумент2 страницыConcentration Cheat Sheetcontact2web50% (2)
- The American Jobs Act (Full Text From The White House)Документ199 страницThe American Jobs Act (Full Text From The White House)Examville.comОценок пока нет
- Basic Math and Pre-Algebra Cheat SheetДокумент34 страницыBasic Math and Pre-Algebra Cheat SheetExamville.com100% (1)
- Amazing Math TricksДокумент22 страницыAmazing Math TricksExamville.comОценок пока нет
- Periodic TableДокумент1 страницаPeriodic TableRoy Cartagena CorderoОценок пока нет
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreДокумент22 страницыOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreYoAmoNYCОценок пока нет
- Chemical Bonding - Important Concepts in Inorganic ChemistryДокумент34 страницыChemical Bonding - Important Concepts in Inorganic ChemistryExamville.comОценок пока нет
- What Are Enzymes - Examville Study GuidesДокумент13 страницWhat Are Enzymes - Examville Study GuidesExamville.comОценок пока нет
- Chemical BondingДокумент33 страницыChemical BondingExamville.comОценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry Review Examville - Com Study AidsДокумент25 страницOrganic Chemistry Review Examville - Com Study AidsExamville.comОценок пока нет
- Global Education Digest UNESCOДокумент154 страницыGlobal Education Digest UNESCOExamville.com100% (1)
- Kinematic Equations - Examville - Com Study Guides SectionДокумент10 страницKinematic Equations - Examville - Com Study Guides SectionExamville.comОценок пока нет
- 100 Best Women Friendly CompaniesДокумент1 страница100 Best Women Friendly CompaniesExamville.com100% (1)
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreДокумент27 страницOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreExamville.comОценок пока нет
- Building Successful Business GrowthДокумент16 страницBuilding Successful Business GrowthExamville.comОценок пока нет
- Business ModelsДокумент42 страницыBusiness ModelsExamville.comОценок пока нет
- Free To Paid UsersДокумент169 страницFree To Paid UsersExamville.comОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Jeopardy - Examville - Com Study Guides SectionДокумент52 страницыChemistry Jeopardy - Examville - Com Study Guides SectionExamville.comОценок пока нет
- Chemistry - Elements, Terminologies and More - Examville - Com Study Guides SectionДокумент47 страницChemistry - Elements, Terminologies and More - Examville - Com Study Guides SectionExamville.comОценок пока нет
- Quick Introduction To Organic Chemistry Examville - Com Study GuidesДокумент27 страницQuick Introduction To Organic Chemistry Examville - Com Study GuidesExamville.comОценок пока нет
- Start Up Customer Development ProcessДокумент28 страницStart Up Customer Development ProcessExamville.comОценок пока нет
- Top Universities in The WorldДокумент6 страницTop Universities in The WorldExamville.com75% (4)
- Triglycerides - Organic Chemistry Notes atДокумент56 страницTriglycerides - Organic Chemistry Notes atExamville.comОценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry Introduction Examville - Com Study Guides SectionДокумент19 страницOrganic Chemistry Introduction Examville - Com Study Guides SectionExamville.comОценок пока нет
- Substrate Control - Organic Chemistry Notes atДокумент39 страницSubstrate Control - Organic Chemistry Notes atExamville.comОценок пока нет
- Total Synthesis - Organic Chemistry Notes atДокумент40 страницTotal Synthesis - Organic Chemistry Notes atExamville.comОценок пока нет
- Synthesis - Organic Chemistry Notes atДокумент76 страницSynthesis - Organic Chemistry Notes atExamville.comОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of The LiverДокумент5 страницAnatomy of The LiverAioanei Octavian100% (1)
- Blood PressureДокумент3 страницыBlood PressurephandinhvinhsanОценок пока нет
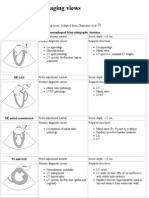
- TEE - Standard Imaging Views - ECHOpediaДокумент3 страницыTEE - Standard Imaging Views - ECHOpediaVishal Prabhu100% (3)
- Heart Disease: Prevention Is Better Than CureДокумент3 страницыHeart Disease: Prevention Is Better Than CureTan Soong WeiОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular SystemДокумент34 страницыCardiovascular Systemkaz92100% (6)
- NCM 107 - Fetal Circulation Final PDFДокумент4 страницыNCM 107 - Fetal Circulation Final PDFAngelica Rose VillegasОценок пока нет
- Ds Week 6 Nrg301 ValenzonaДокумент2 страницыDs Week 6 Nrg301 ValenzonaJoshennaОценок пока нет
- 3D Angiographic Atlas of Neurovascular Anatomy and PathologyДокумент285 страниц3D Angiographic Atlas of Neurovascular Anatomy and PathologyTiago Sequeiros100% (5)
- Peripheral Arterial DiseaseДокумент38 страницPeripheral Arterial DiseaseRessy HastoprajaОценок пока нет
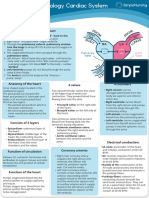
- Anatomy & Physiology Cardiac SystemДокумент1 страницаAnatomy & Physiology Cardiac SystemTori RolandОценок пока нет
- Module Chapter 3Документ31 страницаModule Chapter 3Azween SabtuОценок пока нет
- Lymphatic SystemДокумент7 страницLymphatic SystemAsher Eby VargeeseОценок пока нет
- Circulation Study GuideДокумент3 страницыCirculation Study Guideraanja2Оценок пока нет
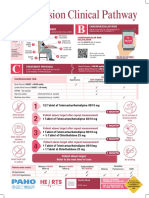
- HEARTS Hypertension Clinical Pathway Editable - ENGДокумент1 страницаHEARTS Hypertension Clinical Pathway Editable - ENGSIANY FIORELLA CHAVEZ MORANОценок пока нет
- Benedict M. Glover (Editor), Pedro Brugada (Editor) - Clinical Handbook of Cardiac Electrophysiology-Springer Nature (2021)Документ230 страницBenedict M. Glover (Editor), Pedro Brugada (Editor) - Clinical Handbook of Cardiac Electrophysiology-Springer Nature (2021)Gabriel CruzОценок пока нет
- Blood VesselsДокумент43 страницыBlood VesselsJessica AcostaОценок пока нет
- Aortic DissectionДокумент5 страницAortic DissectionCosminNGDNОценок пока нет
- Lesson 4 Blood VesselsДокумент14 страницLesson 4 Blood VesselsCarolyn D MayugaОценок пока нет
- Delos Santos - Dawn Athena - Pharma - Mid - CardioДокумент3 страницыDelos Santos - Dawn Athena - Pharma - Mid - CardiovannesafreniereОценок пока нет
- To RememberДокумент2 страницыTo RememberMes KimОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular Failure, Inotropes and Vasopressors: Oxygen DeliveryДокумент4 страницыCardiovascular Failure, Inotropes and Vasopressors: Oxygen DeliveryMarlin Berliannanda TawayОценок пока нет
- Patofisiologi Sistem KardiovaskularДокумент157 страницPatofisiologi Sistem KardiovaskularNyanmaruОценок пока нет
- Laboratory 11Документ8 страницLaboratory 11Jc JardinicoОценок пока нет
- Test Bank Clinically Oriented Anatomy 7th Edition Moore Agur DalleyДокумент19 страницTest Bank Clinically Oriented Anatomy 7th Edition Moore Agur DalleyMichael Burger100% (34)
- Pci To Cto - Copy SssДокумент238 страницPci To Cto - Copy SssSohil3100% (1)
- P ('t':'3', 'I':'668096276') D '' Var B Location Settimeout (Function ( If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') ( B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Документ31 страницаP ('t':'3', 'I':'668096276') D '' Var B Location Settimeout (Function ( If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') ( B.href B.href ) ), 15000)LipatOla123Оценок пока нет
- Adult Primary Intraventricular HemorrhageДокумент16 страницAdult Primary Intraventricular Hemorrhageedi_ikhsan417Оценок пока нет
- Computation of Drips: Marla Aurora JacobaДокумент18 страницComputation of Drips: Marla Aurora JacobaAnne Lorraine Bringas100% (1)
- A High Mean Arterial PressureДокумент8 страницA High Mean Arterial Pressureadek07Оценок пока нет