Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
P5 Sound SHO Light and Optics
Загружено:
Elizabeth AjayiИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
P5 Sound SHO Light and Optics
Загружено:
Elizabeth AjayiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Physics 2-Sound and Simple Harmonic Motion
Sound
Longitudinal waves, not transverse waves
v f = s m v
sound
/ 343 ~
Sound travels faster in solids and liquids than in air.
Speed of sound in solids/liquids is inversely related to its density.
Simple Harmonic Motion
A=Amplitude e=frequency factor t A x cos = e
e A v =
max
2
max
e A a =
T
f
t
t e
2
2 = =
T
f
1
= f = frequency T = period
Spring Pendulum
m
k
= e
L
g
= e (for small angles)
Standing Waves
n
L
n
2
=
Same as rope with both ends fixed
(pipe open at both ends)
n
L
n
4
= (pipe open at one end) # odd n =
n=1 is first harmonic or fundamental frequency
Beat Frequency difference between two frequencies of two different sound waves
Intensity
2
4 r
P
A
P
I = =
t
0
log 10
I
I
= |
2
12
0
10
m
W
I
=
Doppler Effect
S
O
S O
v v
v v
f f
= frequency observed =
O
f =
S
f frequency of source
s o
f f > if, relatively, object and source are moving towards each other
s o
f f < if, relatively, object and source are moving away from each other
Physics 2-Light and Optics
Light
v f =
hc
hf E
photon
= = (not important) s m c / 10 0 . 3
8
= s J h =
34
10 63 . 6
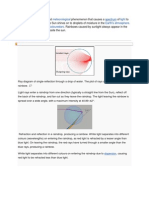
Law of Reflection
Angle of incidence=Angle of reflection
Snells Law of Refraction
2 2 1 1
sin sin u u n n =
v
c
n = Index of Refraction (Frequency of light doesnt change from medium to medium)
1
2
sin
n
n
critical
= u Total Internal Reflection
Optics
Mirrors and Lenses
f d d
i o
1 1 1
= + distance to object =
o
d =
i
d distance to image focal length = f
o
i
o
i
h
h
d
d
m = = magnification = m =
i
h height of image height of object =
o
h
R f
2
1
= = R radius of curvature
Mirror Type d
i
d
o
f
Converging
(Concave)
+ (d
o
>f)
- (d
o
<f)
+ +
Diverging
(Convex)
- + -
Lens Type d
i
d
o
f
Converging + (d
o
>f)
- (d
o
<f)
+ +
Diverging - + -
d
i
>0 real image (and inverted)
d
i
<0 virtual image (and upright)
m>0 upright
m<0 inverted
In-class Problems
Sound
1. The wavelength of a sound wave in air is 1.70m. What is its frequency? (v
sound
=340m/s)
2. A ship on the surface of the water uses sonar to detect a submarine that is below it. If the sonar pulse takes 3s
to return to the ship on the surface, what is the depth of the submarine? (v
sound
=1500m/s in water)
SHO
3. A spring with a 1kg mass attached obeying simple harmonice motion follows the following equation of
motion: . What is the velocity of the mass as it passes through the equilibrium position?
What are the frequency and period of oscillation?
t cm x 5 cos ) 100 ( =
4. A mass on a spring undergoing simple harmonic motion has another mass glued to the original mass while in
motion effectively quadrupling the mass. What is the effect on the period of oscillation?
5. If the length of a pendulum is increased by a factor of 10 and the mass of the bob is doubled, what will be the
effect on the frequency of oscillation?
Standing Waves
6. What is the fundamental frequency of a 0.25m pipe that is open at both ends? (v
sound
=340m/s)
7. After the fundamental frequency, what is the next harmonic of a 0.75m pipe that is open at one end?
(v
sound
=340m/s)
8. If the intensity level of a siren is 80dB at a distance of 10m from a fire truck, what is the intensity level at a
distance of 100m?
Doppler Effect
9. You are moving in a car toward a stationery ambulance with a velocity of 32m/s. Is the frequency of the
ambulances siren you observe higher or lower than the actual emitted frequency? By what percentage is the
frequency you observe different from the actual frequency?
10. A bat is moving with a velocity of 15m/s toward a moth flying directly toward the bat also with a velocity
of 15m/s. If the bat sends out a sound wave of 20kHz, what is the observed frequency (by the bat) of this sound
wave after its reflected off of the moth?
Light and Optics
11. If the angle of incidence of a flashlights beam into a lake is 60, what is the angle of reflection? (n
air
=1,
n
water
=1.33)
12. Light passes from air (n=1) into a glass block (n=1.5). Is the angle of refraction larger or smaller than the
angle of incidence? What is the speed of light in the glass block?
13. If an object is placed 6cm in front of a concave mirror (f=2cm), what will be the magnification of the
image? Is it real or virtual, upright or inverted?
14. If an object is placed 6cm from a diverging lens (f=2cm), what is the magnification of the image? Is it real
or virtual, upright or inverted?
15. If an object is placed 6cm from a converging lens (f=4cm), where will the image appear? Will the image be
real or virtual, upright or inverted?
Вам также может понравиться
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- (Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Mit Opencourseware)Документ10 страниц(Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Mit Opencourseware)asitiafОценок пока нет
- Physical Optics, McqsДокумент2 страницыPhysical Optics, McqsNano MohammadОценок пока нет
- KHF 950-990 User ManualДокумент202 страницыKHF 950-990 User ManualmglemОценок пока нет
- Elstest 1pdoubleblindДокумент11 страницElstest 1pdoubleblindHugo AlvarezОценок пока нет
- Physics Practice PaperДокумент18 страницPhysics Practice PaperYooge WohlОценок пока нет
- Practice Midterm 03Документ7 страницPractice Midterm 03Ha ViОценок пока нет
- Unit 03 Wave OpticsДокумент53 страницыUnit 03 Wave OpticsEnglish words BY Utkarsh johriОценок пока нет
- WCNДокумент102 страницыWCNVinaY ChowdaryОценок пока нет
- RainbowДокумент3 страницыRainbowDesy WindyanaОценок пока нет
- Waves NotesДокумент13 страницWaves NotescgozzardОценок пока нет
- ACUSON X300™ Ultrasound System: TransducersДокумент7 страницACUSON X300™ Ultrasound System: TransducersFirОценок пока нет
- Narasaraopeta Engineering College, NarasaraopetДокумент3 страницыNarasaraopeta Engineering College, NarasaraopetneczuberbashaОценок пока нет
- Lecture35 Ch12 CoherenceДокумент25 страницLecture35 Ch12 Coherencepavan457Оценок пока нет
- Inadequacies of Classical MechanicsДокумент10 страницInadequacies of Classical MechanicsvickeyОценок пока нет
- Akg C555LДокумент11 страницAkg C555Lsalecello2113Оценок пока нет
- HOG13010047 - PSP608-PSP901 - TRM Upgrade16E1 To 100 Mbps - Naga Juang-Malintang JaeДокумент1 страницаHOG13010047 - PSP608-PSP901 - TRM Upgrade16E1 To 100 Mbps - Naga Juang-Malintang JaeFred AksoОценок пока нет
- Universidad Nacional de Colombia: Engineering FacultyДокумент3 страницыUniversidad Nacional de Colombia: Engineering Facultypedro1fonzecaОценок пока нет
- Fresnel Zones and Their EffectДокумент3 страницыFresnel Zones and Their EffectDramane BonkoungouОценок пока нет
- Microwave CommДокумент3 страницыMicrowave CommAylie PilobelloОценок пока нет
- Some Applications On The Fields of Laser, PCF and PCF-Sensor by Comsol SoftwareДокумент32 страницыSome Applications On The Fields of Laser, PCF and PCF-Sensor by Comsol SoftwareNadia F Mohammad Al-RoshdeeОценок пока нет
- Sri Vidya College of Engineering & Technology Course Material (Lecture Notes)Документ47 страницSri Vidya College of Engineering & Technology Course Material (Lecture Notes)Kumar RockyОценок пока нет
- Optical Scattering of Gold NanosphereДокумент24 страницыOptical Scattering of Gold NanosphereParas KumarОценок пока нет
- Noise Control Design GuideДокумент44 страницыNoise Control Design Guidejorgeblotta3489Оценок пока нет
- Slinky Wave LabДокумент3 страницыSlinky Wave Labapi-399778797Оценок пока нет
- Cement Evaluation Tool PDFДокумент7 страницCement Evaluation Tool PDFHamed SadeghiОценок пока нет
- Antenna Specifications: Electrical PropertiesДокумент6 страницAntenna Specifications: Electrical PropertiesRobertОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Passive ComponentДокумент72 страницыChapter 2 Passive ComponentAnnan_Faridi_517Оценок пока нет
- Advanced TechnicianДокумент62 страницыAdvanced TechnicianMiles AndrewsОценок пока нет
- The Dual Nature of LightДокумент14 страницThe Dual Nature of LightABHISHEK SAINIОценок пока нет
- Condition Assesement Services Using Ultrasonic & ThermographyДокумент9 страницCondition Assesement Services Using Ultrasonic & ThermographyShahril ShahibullahОценок пока нет