Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Dual Feeder System Provides Reliable Power
Загружено:
Irfan UllahИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Dual Feeder System Provides Reliable Power
Загружено:
Irfan UllahАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Dual Feeder System
Posted by Ackerley Acton November 29 - 259 views - Filed in Power Systems
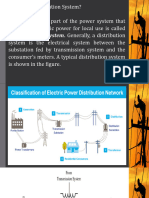
It has been a general practice by distribution utilities to parallel overhead distribution lines/feeders in a common right of way and the same pole as they terminate from a common substation.
The classic standby power system using an engine-generator set. This system protects a facility from prolonged utility company power failures. In some areas, usually metropolitan centers, two utility company power drops can be brought into a facility as a means of providing a source of standby power. As shown in Figure , two separate utility ser-vice drops from separate power-distribution systems are brought into the plant, and an automatic transfer switch changes the load to the backup line in the event of a main-line failure. The dual-feeder system provides an advantage over the auxiliary diesel arrangement in that power transfer from main to
The use of a static transfer switch to transfer the load from the utility company to the on-site generator. standby can be made in a fraction of a second if a static transfer switch is used. Time delays are involved in the diesel generator system that limit its usefulness to power failures lasting more than several minutes. The dual-feeder system of protection is based on the assumption that each of the service drops brought into the facility is routed via different paths. This being the case, the likelihood of a failure on both power lines simultaneously is remote. The dual-feeder system will not, however, protect against areawide power failures, which can occur from time to time.
The dual-feeder system is limited primarily to urban areas. Rural or mountainous regions generally are not equipped for dual redundant utility company operation. Even in urban areas, the cost of bringing a second power line into a facility can be high, particularly if special lines must be installed for the feed. If
two separate utility services are available at or near the site, redundant feeds generally will be less expensive than engine-driven generators of equivalent capacity.
A dual-utility-feeder system with interlocked circuit breakers open. In the event of a loss of either line, the circuit-breaker switches reconfigure the load to place the entire facility on the single remaining ac feed. Switching is performed automatically; manual control is provided in the event of a planned shutdown on one of the lines. Prepared by: zone4info.com Reference: 1. Electric Power Distribution Handbook 2. AC Power System Handbook Article Tags: #Dual Feeder System #parallel power distribution #parallel feeder operation#parallel conductor #parallel generator
Вам также может понравиться
- It Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingОт EverandIt Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingОценок пока нет
- List of Important Pair of Words From CSS Past PapersДокумент23 страницыList of Important Pair of Words From CSS Past PapersIrfan Ullah100% (1)
- Electrical System For High Rise BuildingДокумент47 страницElectrical System For High Rise BuildingMohammad Belal Hossain87% (30)
- Topic: 132 KV Substation Bosan Road Multan: Echnical EportДокумент28 страницTopic: 132 KV Substation Bosan Road Multan: Echnical EportTalha Maqsood87% (15)
- Electrical System For High Rise BuildingДокумент47 страницElectrical System For High Rise Buildingdeskaug1100% (3)
- Distribution System 2Документ12 страницDistribution System 2ismiОценок пока нет
- 1 - Electrical Distribution System ComponentsДокумент22 страницы1 - Electrical Distribution System Components7sn omerОценок пока нет
- Electrical High Rise BuildingДокумент11 страницElectrical High Rise BuildingAstha Goyal100% (1)
- Electrical Distribution Architecture in Water Treatment PlantsДокумент13 страницElectrical Distribution Architecture in Water Treatment PlantsSugeng SumarnoОценок пока нет
- Performance Management SetupsДокумент34 страницыPerformance Management Setupshamdy2001100% (6)
- Electrical-engineering-portal-substation-dc-auxiliary-supplyДокумент6 страницElectrical-engineering-portal-substation-dc-auxiliary-supplyWang MariusОценок пока нет
- Impacts of Substation Transformer Backfeed at High PV PenetrationsДокумент5 страницImpacts of Substation Transformer Backfeed at High PV PenetrationssulemankhalidОценок пока нет
- Orbit 60 Series System Datasheet 137M5182 PDFДокумент35 страницOrbit 60 Series System Datasheet 137M5182 PDFJuan Antonio MarinОценок пока нет
- Per Bay Cost Model For Electrical SubstationsДокумент23 страницыPer Bay Cost Model For Electrical Substationswilliamb285Оценок пока нет
- Basic SubstationДокумент13 страницBasic SubstationevilcomputerОценок пока нет
- Electrical System For High Rise Building PDFДокумент47 страницElectrical System For High Rise Building PDFShanaia Bual100% (2)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionОт EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Electrical System Design For High Rise BuildingДокумент12 страницElectrical System Design For High Rise Buildingbookbok100% (5)
- Investigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsОт EverandInvestigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsОценок пока нет
- Marine power and energy management control systemsДокумент51 страницаMarine power and energy management control systemssj_hecklers67% (3)
- Electrical System Design For High Rise BuildingДокумент12 страницElectrical System Design For High Rise BuildingArun BavaОценок пока нет
- Iec Ieee 60780-323 - 2016Документ36 страницIec Ieee 60780-323 - 2016Tamara Silvana Cárcamo100% (1)
- Methods for Increasing the Quality and Reliability of Power System Using FACTS DevicesОт EverandMethods for Increasing the Quality and Reliability of Power System Using FACTS DevicesОценок пока нет
- Hysys Dynamics PDFДокумент549 страницHysys Dynamics PDFminh nguyenОценок пока нет
- Project ReportДокумент34 страницыProject ReportSumit Sharma75% (4)
- Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) Between Two Low-Voltage Utility SuppliesДокумент4 страницыAutomatic Transfer Switch (ATS) Between Two Low-Voltage Utility SuppliesMohamedAhmedFawzyОценок пока нет
- Load Management SystemДокумент4 страницыLoad Management SystemGuruprit Singh SohalОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2 - Basic Power Distribution Arrangements in MinesДокумент17 страницLecture 2 - Basic Power Distribution Arrangements in MinesAmar RathodОценок пока нет
- Critical-Power Automatic Transfer Systems - Design and ApplicationДокумент18 страницCritical-Power Automatic Transfer Systems - Design and ApplicationRazvan Mares100% (1)
- Automatic Transfer Switch ATS Between Two Low-Voltage Utility SuppliesДокумент4 страницыAutomatic Transfer Switch ATS Between Two Low-Voltage Utility SuppliesSebastianCicognaОценок пока нет
- IPS Chap-1Документ17 страницIPS Chap-1justjhakkas7525Оценок пока нет
- Eee2 SLM1Документ20 страницEee2 SLM1Perez Trisha Mae D.Оценок пока нет
- Power Marine ManagementДокумент4 страницыPower Marine ManagementSyby SibelОценок пока нет
- Critically Evaluating The Electrical Installation and Protection Systems and Standards in High-Rise BuildingДокумент47 страницCritically Evaluating The Electrical Installation and Protection Systems and Standards in High-Rise Buildingmuhammad jamalОценок пока нет
- Station Service System: A. GeneralДокумент5 страницStation Service System: A. GeneralmbarabasОценок пока нет
- Electrical Distribution: Second Class Installation Distribution SystemsДокумент4 страницыElectrical Distribution: Second Class Installation Distribution SystemsJerry CañeroОценок пока нет
- Reliability Considerations in Simple Paralleling ApplicationsДокумент8 страницReliability Considerations in Simple Paralleling Applications3efooОценок пока нет
- Distribution Substations For Electrical Engineers - BeginnersДокумент14 страницDistribution Substations For Electrical Engineers - BeginnersPrashant RajputОценок пока нет
- Substation DC Auxiliary Supply Battery and Charger ApplicationsДокумент6 страницSubstation DC Auxiliary Supply Battery and Charger ApplicationsRoberto AlissonОценок пока нет
- Critical Power System Reliability & The Art of Ground Fault ProtectionДокумент9 страницCritical Power System Reliability & The Art of Ground Fault Protectionhhh81sg4120Оценок пока нет
- Lecture 3 - Utility Company Power and Mine Power System EquipmentДокумент15 страницLecture 3 - Utility Company Power and Mine Power System EquipmentAmar Rathod0% (1)
- HVDC Unit-IДокумент16 страницHVDC Unit-ISreenivas Reddy BodimallaОценок пока нет
- Power Evacuation and Grid Interconnection DesignДокумент20 страницPower Evacuation and Grid Interconnection Designmani0723Оценок пока нет
- Applying a Single Pole Protection Scheme to a Double-Circuit 230kV Transmission LineДокумент38 страницApplying a Single Pole Protection Scheme to a Double-Circuit 230kV Transmission LineMiguel CbОценок пока нет
- AC Auxiliary Systems in Power Substations DesignДокумент13 страницAC Auxiliary Systems in Power Substations DesignAleksandarОценок пока нет
- SreenuДокумент36 страницSreenumuskaansОценок пока нет
- 3 Designs of DC Distribution Systems in Power Substations PDFДокумент8 страниц3 Designs of DC Distribution Systems in Power Substations PDFRobert GalarzaОценок пока нет
- A6 Power DistributionДокумент16 страницA6 Power DistributionGOD MОценок пока нет
- q2 Distribution SystemsДокумент3 страницыq2 Distribution SystemsenginearswebОценок пока нет
- Computer Aided Power System AnalysisДокумент323 страницыComputer Aided Power System AnalysisCaribОценок пока нет
- Aamir: M. Sohail Khan & Sufyan Saleem Dept, of Electrical Engineering Bahaudian Zakariya University Multan, PakistanДокумент32 страницыAamir: M. Sohail Khan & Sufyan Saleem Dept, of Electrical Engineering Bahaudian Zakariya University Multan, PakistanSanthosh KumarОценок пока нет
- More GeneratorsДокумент2 страницыMore GeneratorsKarthikeyan GunaОценок пока нет
- DC Micro Grid SystemДокумент5 страницDC Micro Grid SystemAnurag BilthareОценок пока нет
- Chapter6 PDFДокумент38 страницChapter6 PDFJaved LakanwalОценок пока нет
- Balance or Blackout enДокумент2 страницыBalance or Blackout entefamdОценок пока нет
- Power System - Basic Structure and Functioning - EE Power SchoolДокумент9 страницPower System - Basic Structure and Functioning - EE Power Schoolmuhammad_sarwar_27Оценок пока нет
- UNIT-2 Introduction To Facts: Need For Transmission Networks InterconnectionsДокумент13 страницUNIT-2 Introduction To Facts: Need For Transmission Networks Interconnectionspadma kalyan RelaОценок пока нет
- 7 Trans SystemДокумент7 страниц7 Trans SystemAhmedОценок пока нет
- Ssali Sub StationДокумент8 страницSsali Sub StationBUKENYA BEEE-2026Оценок пока нет
- Electrical System Design in the PhilippinesДокумент9 страницElectrical System Design in the Philippinesdyesaendaya06Оценок пока нет
- Electrical Distribution System Arrangements ExplainedДокумент12 страницElectrical Distribution System Arrangements ExplainedWendi HaryadiОценок пока нет
- EPS 7 - Power DistributionДокумент24 страницыEPS 7 - Power DistributionPuvan ThanОценок пока нет
- Chapter Ten: Distribution SystemДокумент16 страницChapter Ten: Distribution SystemBonnie SantosОценок пока нет
- Phiosophy and Operation of Check Zone ProtectionДокумент2 страницыPhiosophy and Operation of Check Zone ProtectionIrfan UllahОценок пока нет
- 9 DIFFERENCES BETWEEN MANAGER and LEADERSДокумент2 страницы9 DIFFERENCES BETWEEN MANAGER and LEADERSIrfan UllahОценок пока нет
- Characteristic or Intrinsic Impedence of The LineДокумент10 страницCharacteristic or Intrinsic Impedence of The LineIrfan UllahОценок пока нет
- Spring 2017 - ENG301 - 2Документ3 страницыSpring 2017 - ENG301 - 2Irfan UllahОценок пока нет
- NTS FormДокумент1 страницаNTS FormIrfan UllahОценок пока нет
- Gat CurriculumДокумент8 страницGat CurriculumIrfan UllahОценок пока нет
- Conditional Sentences Unit 39-ConditionalsДокумент4 страницыConditional Sentences Unit 39-ConditionalsIrfan UllahОценок пока нет
- Have or Get - 2Документ2 страницыHave or Get - 2Irfan UllahОценок пока нет
- Personality InformationДокумент6 страницPersonality InformationIrfan UllahОценок пока нет
- WingleДокумент7 страницWingleIrfan UllahОценок пока нет
- How To Complain in EnglishДокумент3 страницыHow To Complain in EnglishIrfan UllahОценок пока нет
- Conditional Sentences Complete All TypesДокумент17 страницConditional Sentences Complete All TypesIrfan UllahОценок пока нет
- NTS FormДокумент1 страницаNTS FormIrfan UllahОценок пока нет
- Energy Vs MWДокумент21 страницаEnergy Vs MWIrfan UllahОценок пока нет
- The Terrorist Prince Murtaza Bhutto 18 QistsДокумент18 страницThe Terrorist Prince Murtaza Bhutto 18 QistsIrfan UllahОценок пока нет
- How To Choose A TransformerДокумент6 страницHow To Choose A TransformerIrfan UllahОценок пока нет
- Big Large and GreatДокумент1 страницаBig Large and GreatIrfan UllahОценок пока нет
- Steps To Ensure Effective Substation GroundingДокумент7 страницSteps To Ensure Effective Substation GroundingIrfan UllahОценок пока нет
- Operating and Financial DataДокумент14 страницOperating and Financial DataIrfan UllahОценок пока нет
- Organization: A Message From The Chairman Main Activities History Organi Office LocationДокумент2 страницыOrganization: A Message From The Chairman Main Activities History Organi Office LocationIrfan UllahОценок пока нет
- P&i 174Документ97 страницP&i 174Irfan UllahОценок пока нет
- Test 4Документ3 страницыTest 4Irfan UllahОценок пока нет
- Research & Info ActivitiesДокумент4 страницыResearch & Info ActivitiesIrfan UllahОценок пока нет
- Office Location: A Message From The Chairman Main Activities History Organi Office LocationДокумент3 страницыOffice Location: A Message From The Chairman Main Activities History Organi Office LocationIrfan UllahОценок пока нет
- Fun EnglishДокумент34 страницыFun Englishsniju100% (3)
- Int'l CooperationДокумент2 страницыInt'l CooperationIrfan UllahОценок пока нет
- MM0706 Edition 5Документ20 страницMM0706 Edition 5Irfan UllahОценок пока нет
- Electrical Important McqsДокумент1 страницаElectrical Important McqsIrfan UllahОценок пока нет
- Electronics Plus Telecom Paper Without AnswersДокумент43 страницыElectronics Plus Telecom Paper Without AnswersIrfan UllahОценок пока нет
- Encode or Decode File As MIME Base64 (RFC 1341)Документ17 страницEncode or Decode File As MIME Base64 (RFC 1341)Predrag DamnjanovićОценок пока нет
- Cisco Unified SIP Proxy: Data SheetДокумент14 страницCisco Unified SIP Proxy: Data SheetmandeepmailsОценок пока нет
- CBCT2203-Basic Concepts of Information TechnologyДокумент12 страницCBCT2203-Basic Concepts of Information TechnologySimon RajОценок пока нет
- Ecfl 30Документ4 страницыEcfl 30Jozsef MolnarОценок пока нет
- Obj 1997paper 2Документ15 страницObj 1997paper 2Uday KakkarОценок пока нет
- Sap fb50 Tutorial Step by Step GL Account PostingДокумент12 страницSap fb50 Tutorial Step by Step GL Account Postingsaeedawais47Оценок пока нет
- Eventdesigneree PDFДокумент19 страницEventdesigneree PDFMohamed Amin MessaoudОценок пока нет
- Uppen 12000 Power Amplifier SpecificationДокумент2 страницыUppen 12000 Power Amplifier SpecificationAlexandra SanduОценок пока нет
- Wire SharkДокумент4 страницыWire SharkIggyОценок пока нет
- Current Trends and Issues in ITДокумент30 страницCurrent Trends and Issues in ITPol50% (2)
- BambuДокумент5 страницBambuAditya Widya PranataОценок пока нет
- Class C Operation: Resonant FrequencyДокумент4 страницыClass C Operation: Resonant FrequencynerminaОценок пока нет
- Atitudine LSM9DS0 SensorДокумент74 страницыAtitudine LSM9DS0 SensorquebornОценок пока нет
- PLC Trainer Simulates Automation ControlsДокумент2 страницыPLC Trainer Simulates Automation Controlssyed mohammad ali shahОценок пока нет
- Flare Dec+JanДокумент87 страницFlare Dec+Janfarooq_flareОценок пока нет
- Cares Technical Approval TA1-A 5050: AnconДокумент14 страницCares Technical Approval TA1-A 5050: AnconFederico.IoriОценок пока нет
- Original Pump Disposables: Flexibility and Accuracy For All B. Braun PumpsДокумент2 страницыOriginal Pump Disposables: Flexibility and Accuracy For All B. Braun Pumpsmas agung chandraОценок пока нет
- R ManualДокумент48 страницR Manualvolterbtc00Оценок пока нет
- Bantu Migration - Ancient History Encyclopedia PDFДокумент10 страницBantu Migration - Ancient History Encyclopedia PDFEmelda MimieОценок пока нет
- Block Chain: BY Mohamed Safwan A Kavin Manoj C M Cse Ii Year Gce, SalemДокумент21 страницаBlock Chain: BY Mohamed Safwan A Kavin Manoj C M Cse Ii Year Gce, SalemMohamed safwanОценок пока нет
- Caterpillar 420F2 PDFДокумент10 страницCaterpillar 420F2 PDFRicardo RodriguezОценок пока нет
- 890-399 GSM Manual Rev2.1-1Документ24 страницы890-399 GSM Manual Rev2.1-1SandroОценок пока нет
- PanKnob ManualДокумент8 страницPanKnob ManualJohnОценок пока нет
- Steertek NXTДокумент2 страницыSteertek NXTJosé rosasОценок пока нет
- pg138 Axi EthernetДокумент176 страницpg138 Axi EthernetSovi SoviОценок пока нет
- Technical ProgramScheduleДокумент6 страницTechnical ProgramScheduleBiswajitRoyОценок пока нет