Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
2014 Essay Final
Загружено:
fazeelm24Исходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
2014 Essay Final
Загружено:
fazeelm24Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
wOHhk fmd iy;sl m;% ^WiiA fm<& jsNd.
h" 2012 wfm%A,A fy;tpg; nghJj; juhju (cah; ju)g; guPl;ir > 2012 [{iy General Certificate of Education Examination (Ad. Level) Examination , July 2012
fN!;sl oHdj II ngsjpftpay; II Physics II
First TermTest
One hour
Section B - Essay
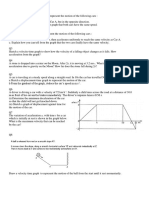
Answer Two questions only A hot air balloon is moving upwards at a constant speed. A camera is accidentally dropped from the balloon at a h height of 92 m as shown below. The camera strikes the ground after 6 s. Ignore the air resistance.
From the instant the camera is dropped, explain the motion of the camera.
Calculate the speed Vi at which the balloon is rising when the camera is dropped
Draw a sketch graph of velocity versus time for the entire motion of the camera. Indicate the initial velocity and the time at which it reaches the ground.
If a jogger , 10 m away from the point P, as shown in the diagram above and running at a constant speed 2 ms-1 sees the camera at the same instant it starts falling from the balloon, will he be able to catch the camera before it strikes the ground. Show your working.
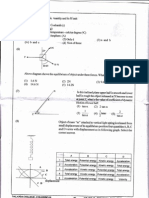
A ball bounces vertically on a hard surface after being thrown vertically up into the air by a boy standing on the ledge of a
building. Just before the ball hits the ground for the first time, it has a velocity of magnitude 15 ms1. Immediately, after bouncing, it has a velocity of magnitude 10 ms1. The graph below shows the velocity of
(02)
A ball bounces vertically on a hard surface after being thrown vertically up into the air by a boy standing on the ledge of a building. Just before the ball hits the ground for the first time, it has a velocity of 15 ms1. Immediately, after bouncing, it has a velocity of magnitude 10 ms1. The graph below shows the velocity of the ball as a function of time from the moment it is thrown upwards into the air until it reaches its maximum height after bouncing once.
(i)
At what velocity does the boy throw the ball into the air? What can be determined by calculating the gradient of the graph during the first two seconds? Determine the gradient of the graph over the first two seconds. State its units. How far below the boys hand does the ball hit the ground? Use an equation of motion to calculate how long it takes, from the time the ball was thrown, for the ball to reach its maximum height after bouncing. What is the position of the ball, measured from the boys hand, when it reaches its maximum height after bouncing?
(ii)
(iii) (iv)
(v)
(vi)
(03)
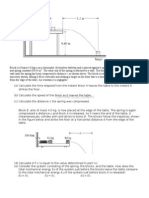
A Holden Commodore travelling at a constant velocity of 30 ms -1 (108 kmh-1) along a straight stretch of road, in a 80 kmh-1 speed limit zone, passes a stationary police car. It takes the police officer 2.0 seconds from the moment the Commodore passes to start the police car moving. The police car accelerates at 5.0 ms 2 to a velocity 40 ms-1 then remains at this constant velocity for another 4.0 s.
(i) How long does it take the police car to reach the speed of 40 ms-1 starting from rest ? (ii) How far has the Holden Commodore travelled during the total time described above? (iii) How far has the police travelled during the total time described above? (iv) On a velocity vs. time graph draw the motion of the Holden Commodore and the police car. Clearly indicate which line represents each vehicle. Label the axes and indicate values. (v) On an acceleration vs. time graph draw the motion of the Holden Commodore and the police car. (vi) On a distance vs. time graph draw the motion of the Holden Commodore and the police car.
Вам также может понравиться
- Speed, Motion & Acceleration Physics ProblemsДокумент3 страницыSpeed, Motion & Acceleration Physics ProblemsAngeline DangОценок пока нет
- Exercise 2 Term 1 STPMДокумент10 страницExercise 2 Term 1 STPMLiuJiewChuan100% (1)
- Tutorial Chapter 2 Problems SolvedДокумент4 страницыTutorial Chapter 2 Problems SolvedFareez SedakaОценок пока нет
- Tutorial Chapter 2 Problems and SolutionsДокумент4 страницыTutorial Chapter 2 Problems and SolutionsbatrisyaОценок пока нет
- Hewitt Chapter 3 Free Fall Note OutlineДокумент5 страницHewitt Chapter 3 Free Fall Note OutlineAsmaa AkraicheОценок пока нет
- HomeworkДокумент3 страницыHomeworkZaki SahakОценок пока нет
- Mech. & Dynamics Tut. 2Документ4 страницыMech. & Dynamics Tut. 2Conrod Wayne SmithОценок пока нет
- Physics Tute 3Документ2 страницыPhysics Tute 3Pevin De silvaОценок пока нет
- 11th Worksheet 23-24Документ9 страниц11th Worksheet 23-24Harsh RanaОценок пока нет
- University Physics Chapter2Документ9 страницUniversity Physics Chapter2Karlo OrnietaОценок пока нет
- (25382) 17. H Projectile Motion QuestionsДокумент8 страниц(25382) 17. H Projectile Motion QuestionsDEEPJYOTI DEKAОценок пока нет
- Kinematics ReviewДокумент2 страницыKinematics ReviewJacqueline MayugaОценок пока нет
- BHVBVCCVVДокумент7 страницBHVBVCCVVLucho BenottoОценок пока нет
- Motion One Dimension-01 (Worksheet)Документ4 страницыMotion One Dimension-01 (Worksheet)Krishna Khanna 11 S6Оценок пока нет
- Free Fall Acceleration & ProjectileДокумент2 страницыFree Fall Acceleration & ProjectilejakelakerОценок пока нет
- Session 1: Kinematics QuestionsДокумент2 страницыSession 1: Kinematics Questionsapi-3804363100% (1)
- DP Physics Kinematic Practice ProblemsДокумент6 страницDP Physics Kinematic Practice Problemsmkhonza octaviaОценок пока нет
- Topic 2 KinematicsДокумент12 страницTopic 2 Kinematicsjiawei leeОценок пока нет
- 1.1.2 Dynamics 00-10Документ5 страниц1.1.2 Dynamics 00-10Murray PhysicsОценок пока нет
- Projectile Motion QuiZДокумент7 страницProjectile Motion QuiZyashsodhaniОценок пока нет
- Newton 2Документ4 страницыNewton 2Tsedeke YeteshaОценок пока нет
- Worksheet - Projectile Motion 2Документ5 страницWorksheet - Projectile Motion 2mjdaihmohammedОценок пока нет
- Kinematics WorksheetДокумент4 страницыKinematics Worksheetkee4292100% (1)
- Analyzing Motion GraphsДокумент7 страницAnalyzing Motion GraphsMohd Sabri NorОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Kinematic RevisionДокумент7 страницChapter 2 Kinematic RevisionJohnson116Оценок пока нет
- 12 UKin TestДокумент7 страниц12 UKin TestNicko MendozaОценок пока нет
- 07-Kin PS 2Документ2 страницы07-Kin PS 2Menkent Santisteban BarcelonОценок пока нет
- 1.2.2 Equations 00-10Документ6 страниц1.2.2 Equations 00-10Murray PhysicsОценок пока нет
- Latihan Linear MotionДокумент3 страницыLatihan Linear MotionLily Suhany MahmoodОценок пока нет
- Assignment 2.1 MotionДокумент7 страницAssignment 2.1 Motionpanghua tanОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 KinematicsДокумент5 страницChapter 2 KinematicsCecilia GomesОценок пока нет
- Speed Acceleration TestДокумент8 страницSpeed Acceleration Testapi-233777623Оценок пока нет
- PHYA10 - Physics I (Physical Sciences) Practical Worksheet #01Документ2 страницыPHYA10 - Physics I (Physical Sciences) Practical Worksheet #01Sabine MohamadОценок пока нет
- Quiz On ProjectileДокумент21 страницаQuiz On ProjectileMary Ann TeodoroОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 3Документ4 страницыTutorial 3伟铭Оценок пока нет
- Class 11 Motion in 1DДокумент1 страницаClass 11 Motion in 1DShantanu Ashima GaurОценок пока нет
- 1-D Kinematics Test ReviewДокумент2 страницы1-D Kinematics Test ReviewKaitlynОценок пока нет
- Phy (Ans p1) Kinematic (As) SДокумент6 страницPhy (Ans p1) Kinematic (As) SPrincess KimОценок пока нет
- PPA6 EOC CH 02 MacДокумент13 страницPPA6 EOC CH 02 Macdevonna.wolfeОценок пока нет
- Extra Exercise Chapter One: System of Units: - BT, Where T Refers To Time. What AreДокумент5 страницExtra Exercise Chapter One: System of Units: - BT, Where T Refers To Time. What AreAina AdamОценок пока нет
- Assignment 7Документ2 страницыAssignment 7Vinayak ParasharОценок пока нет
- Kinematics - QuestionsДокумент48 страницKinematics - QuestionsMohamud JamaОценок пока нет
- Term 1: Mechanics and Thermodynamics: Chapter 2: KinematicsДокумент3 страницыTerm 1: Mechanics and Thermodynamics: Chapter 2: KinematicshanabeeОценок пока нет
- Kinematics Aki Ola QuestionsДокумент21 страницаKinematics Aki Ola QuestionsjohnОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 02 PDFДокумент3 страницыWorksheet 02 PDFVijay BhaskarОценок пока нет
- Kinematics Test W SolutionsДокумент5 страницKinematics Test W SolutionsNicholas ChevalierОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 2 Kinematics in One Dimension: H KM 95 H. KM 65Документ2 страницыTutorial 2 Kinematics in One Dimension: H KM 95 H. KM 65Fareez SedakaОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 1Документ4 страницыTutorial 1Mirnal MungraОценок пока нет
- Nota Padat ForceДокумент22 страницыNota Padat Forcejesunathan44@yahoo.comОценок пока нет
- ODU Mechanics Questions o Level A Level PhysicsДокумент40 страницODU Mechanics Questions o Level A Level Physicsduncon100% (1)
- H2 Kinematics Tutorial 2015Документ9 страницH2 Kinematics Tutorial 2015Ronnie QuekОценок пока нет
- Projectile Motion and Kinematics QuestionsДокумент12 страницProjectile Motion and Kinematics QuestionsManish GoyalОценок пока нет
- 71EEE 1stLE MC1Документ12 страниц71EEE 1stLE MC1Gabriel LizaresОценок пока нет
- Physics Homework Chapter 2: Review Example 2.5Документ2 страницыPhysics Homework Chapter 2: Review Example 2.5甯敬芸Оценок пока нет
- Kinematics Review Physics 11Документ2 страницыKinematics Review Physics 11Raymond NguyenОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 ExercisesДокумент4 страницыUnit 1 Exercises张书Оценок пока нет
- Kinematics MC PracticeДокумент17 страницKinematics MC Practicescientific1576Оценок пока нет
- Determine frequency using sonometerДокумент10 страницDetermine frequency using sonometerfazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- Relevant Mathematics For A/L Physics: 1.symbolsДокумент7 страницRelevant Mathematics For A/L Physics: 1.symbolsfazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- Phy-13-Eng-1 - 2019 MARCH FINALДокумент11 страницPhy-13-Eng-1 - 2019 MARCH FINALfazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- Thermal PhysicsДокумент7 страницThermal Physicsfazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- Mechanics: M.M.Fazeel B.SC M.SC PGDEДокумент4 страницыMechanics: M.M.Fazeel B.SC M.SC PGDEfazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- Mechanics: M.M.Fazeel B.SC M.SC PGDEДокумент4 страницыMechanics: M.M.Fazeel B.SC M.SC PGDEfazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- Determine frequency using sonometerДокумент10 страницDetermine frequency using sonometerfazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- Waves and OscillationsДокумент4 страницыWaves and Oscillationsfazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- Mechanics QuestДокумент17 страницMechanics Questfazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- Measurements and InstrumentsДокумент10 страницMeasurements and Instrumentsfazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- D EM Y: Units and DimensionsДокумент5 страницD EM Y: Units and Dimensionsfazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- D EM Y: Units and DimensionsДокумент5 страницD EM Y: Units and Dimensionsfazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- Physics 11 - Work, Power, Energy WorksheetДокумент4 страницыPhysics 11 - Work, Power, Energy Worksheetfazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- Chemi - Doc1 2Документ5 страницChemi - Doc1 2Mohamemd Fazeel Mohammed AsifОценок пока нет
- 2008 w08 QP 1Документ20 страниц2008 w08 QP 1fazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- 2014 Essay FinalДокумент3 страницы2014 Essay Finalfazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- Img 0001Документ1 страницаImg 0001fazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- 14 - Current ElectricityДокумент9 страниц14 - Current Electricityfazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- Analyzing an encrypted documentДокумент1 страницаAnalyzing an encrypted documentfazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- 2014 Essay FinalДокумент3 страницы2014 Essay Finalfazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- Physics Marking Guide 11Документ21 страницаPhysics Marking Guide 11fazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- Tute 01 PhysicsДокумент1 страницаTute 01 Physicsfazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- Img 0008Документ1 страницаImg 0008fazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- Grade 12 Final QPДокумент8 страницGrade 12 Final QPfazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- Tute 01 PhysicsДокумент2 страницыTute 01 Physicsfazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- Reaction between two cubes on a horizontal plane with applied forceДокумент1 страницаReaction between two cubes on a horizontal plane with applied forcefazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- MCQ 2009Документ55 страницMCQ 2009fazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- 09 - OscillationsДокумент11 страниц09 - Oscillationsfazeelm24Оценок пока нет
- AP B 9webrev FluidsДокумент5 страницAP B 9webrev Fluidsfazeelm24Оценок пока нет