Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
C O N T E N T S: Preface Xiii Prologue XV
Загружено:
dongarthОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
C O N T E N T S: Preface Xiii Prologue XV
Загружено:
dongarthАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
C
Co py rig hte dM ate ria l
Preface Prologue xiii xv CHAPTER 1 WHERE TO START Instructions What Do I Need to Know? Instructions for Use Studying and Exams Trivia Sorter 1 1 2 2 2 4 CHAPTER 2 PROTEIN STRUCTURE Amino Acid Structure Interactions Water Hydrophobic Interaction van der Waals Interactions and London Dispersion Forces Hydrogen Bonds Secondary Structure Protein Stability Favorable (Good) Interactions Unfavorable (Bad) Interactions Temperature-Sensitive Mutations Ligand-Binding Specificity Global Conclusion CHAPTER 3 MEMBRANES AND MEMBRANE PROTEINS General Membrane Function Membrane Composition Phospholipid Bilayer Membrane Structure Posttranslational Modification Membrane Fluidity Diffusion in Membranes Movement of Ions and Molecules Across Membranes
v
Copyright 2000 by The McGraw-Hill Companies Retrieved from: www.knovel.com
6 6 8 9 9 11 11 12 15 17 17 19 20 21
22 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 28
vi
Contents
Transport Across Membranes The Nernst Equation
CHAPTER 4 DNA-RNA STRUCTURE DNA Structure DNA Stability RNA Secondary Structure
29 31
35 35 37 38
Co py rig hte dM ate ria l
CHAPTER 5 EXPRESSION OF GENETIC INFORMATION Information Metabolism Directions and Conventions DNA Replication Types of DNA Polymerase Recombination Regulation of Information Metabolism Transcription Regulation of Transcription Translation Use of High-Energy Phosphate Bonds During Translation CHAPTER 6 RECOMBINANT-DNA METHODOLOGY Restriction Analysis Gels and Electrophoresis Blotting Restriction Fragment-Length Polymorphism Cloning Sequencing Mutagenesis Polymerase Chain Reaction CHAPTER 7 ENZYME MECHANISM Active Site Transition State Catalysis Lock and Key Induced Fit Nonproductive Binding Entropy Strain and Distortion 40 40 41 42 45 47 49 53 55 57 60 61 61 65 67 69 70 73 75 76 80 81 81 83 83 83 85 87 88
Copyright 2000 by The McGraw-Hill Companies Retrieved from: www.knovel.com
Contents
vii
Transition-State Stabilization Transition-State Analogs Chemical Catalysis
CHAPTER 8 ENZYME KINETICS S, P, and E (Substrate, Product, Enzyme) Amounts and Concentrations Active Site Assay Velocity Initial Velocity Mechanism Little ks Michaelis-Menten Equation Vmax kcat Km Special Points kcat/Km Rate Accelerations Steady-State Approximation Transformations and Graphs Inhibition Allosterism and Cooperativity The Monod-Wyman-Changeaux Model
88 91 93
95 96 96 97 98 98 100 101 102 103 106 106 107 107 107 108 109 111 112 117 119 123 123 124 125 126 126 128 128 131 132 133 136 137 138
Co py rig hte dM ate ria l
CHAPTER 9 SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION PATHWAYS Signal Transduction Pathways Organization Signals Receptors Soluble Receptors Transmembrane Receptors Enzyme Coupled Receptors G-Protein Coupled Receptors Ion-Channel Coupled Receptors Second Messengers Amplifiers Integrators Inhibitors
Copyright 2000 by The McGraw-Hill Companies Retrieved from: www.knovel.com
viii
Contents
Co py rig hte dM ate ria l
CHAPTER 11 GLYCOGEN SYNTHESIS AND DEGRADATION Function Location Connections Regulation ATP Yield ATP Cost Molecular Features CHAPTER 12 TCA Cycle TCA CYCLE 147 147 147 148 148 150 150 150 153 153 CHAPTER 13 FAT SYNTHESIS AND DEGRADATION Fatty Acid Synthesis Function Fatty Acid Synthesis Location Fatty Acid Synthesis Connections Fatty Acid Synthesis Regulation Fatty Acid Synthesis ATP Costs (for C16) Fatty Acid Synthesis Equation Elongation and Desaturation Triglyceride and Phospholipid Synthesis 155 156 156 157 157 157 159 160 162
Copyright 2000 by The McGraw-Hill Companies Retrieved from: www.knovel.com
CHAPTER 10 GLYCOLYSIS AND GLUCONEOGENESIS Glycolysis Function Glycolysis Location Glycolysis Connections Glycolysis Regulation Glycolysis ATP Yields Glycolysis Equations Effect of Arsenate Lactate or Pyruvate Gluconeogenesis Function Gluconeogenesis Location Gluconeogenesis Connections Gluconeogenesis Regulation Gluconeogenesis ATP Costs Gluconeogenesis Equations
141 143 143 143 143 144 144 144 145 145 145 145 146 146 146
Contents
ix
Co py rig hte dM ate ria l
CHAPTER 14 ELECTRON TRANSPORT AND OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION Oxidation and Reduction The Electron Transport Chain Connections Regulation P/O Ratios Uncouplers Inhibitors CHAPTER 15 PENTOSE PHOSPHATE PATHWAY Pentose Phosphate Pathway 173 173 174 176 178 178 179 180 183 183 CHAPTER 16 AMINO ACID METABOLISM Nonessential Amino Acid Synthesis Essential Amino Acids Amino Acid Degradation Generalities of Amino Acid Catabolism Products of Amino Acid Degradation CHAPTER 17 INTEGRATION OF ENERGY METABOLISM Integrating Metabolic Pathways ATP Glucose Storage Molecules Metabolic States and Signals Insulin 186 186 187 187 187 188 190 191 192 192 193 194 195
Copyright 2000 by The McGraw-Hill Companies Retrieved from: www.knovel.com
-Oxidation Function -Oxidation Location Carnitine Shuttle -Oxidation Connections -Oxidation Regulation -Oxidation ATP Yield -Oxidation Equation -Oxidation of Unsaturated Fatty Acids -Oxidation of Odd-Chain-Length Fatty Acids
164 164 164 164 164 166 167 168 172
Contents
Co py rig hte dM ate ria l
CHAPTER 18 UREA CYCLE Urea Cycle 225 225 CHAPTER 19 PURINE METABOLISM Purine Synthesis Purine Salvage Deoxynucleotides Purine Degradation 227 227 228 228 229 CHAPTER 20 PYRIMIDINE METABOLISM Pyrimidine Synthesis Pyrimidine Salvage Pyrimidine Degradation 230 230 231 232
Copyright 2000 by The McGraw-Hill Companies Retrieved from: www.knovel.com
Glucagon Epinephrine Secondary Signals Generalities of Metabolism Phosphorylation Glycogen Metabolic Movements of Glycogen Fat Metabolic Movements of Fat Protein Metabolic Movements of Protein Tissue Cooperation Liver Muscle Adipose Brain Connection of Storage Pools Feeding Fasting Starvation Excitement Interorgan Cycles Cori Cycle Alanine Cycle Ketone Bodies
196 197 198 199 202 204 205 207 207 209 209 211 212 212 212 213 213 214 214 217 219 221 221 222 223
Contents
xi
CHAPTER 21 ONE-CARBON METABOLISM One-Carbon Metabolism Oxidation States of Carbon CHAPTER 22 TRACKING CARBONS Glucose to Pyruvate TCA Cycle
233 233 233 236 236 238
Co py rig hte dM ate ria l
CHAPTER 23 ph, pKA, pROBLEMS Proton: H or H3O Acid Base Not All Acids and Bases Are Created Equal log (Ka) pKa Weak Acids Make Strong Bases (and Vice Versa) Who Gets the Proton? Dont Forget Stoichiometry The Sadistic Little p Taking log10(x) Taking log10(x) pH log10 [H ] log10 (Ka) pKa Buffers Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation Titration Curves pIIsoelectric Point The Bicarbonate Buffer Imbalance in Blood pH Acidosis and Alkalosis CHAPTER 24 THERMODYNAMICS AND KINETICS Thermodynamics Free Energy Adding Free-Energy Changes Coupling Free Energies Thermodynamic Cycles G H T S Driving Force 241 242 242 242 243 244 244 245 245 246 247 247 248 248 248 249 250 254 255 257 258 261 261 263 268 268 269 272 273
Copyright 2000 by The McGraw-Hill Companies Retrieved from: www.knovel.com
xii
Contents
Co py rig hte dM ate ria l
Appendix Glossary Index 284 287 319
Copyright 2000 by The McGraw-Hill Companies Retrieved from: www.knovel.com
Kinetics Velocity Transition State Theory Rate Constants Rate Constants and Mechanism
275 275 276 277 283
Вам также может понравиться
- On FramingДокумент6 страницOn Framingbibrons100% (1)
- Amino Acids: Structure and Function of Proteins and Their Constituent Amino AcidsДокумент31 страницаAmino Acids: Structure and Function of Proteins and Their Constituent Amino AcidsNate Vojtik100% (4)
- Enzymes & Biological CatalysisДокумент64 страницыEnzymes & Biological Catalysisjoer13Оценок пока нет
- Lipid BiosynthesisДокумент67 страницLipid Biosynthesissaraniya100% (3)
- Polymer Lectures 08 GivenДокумент35 страницPolymer Lectures 08 GivenHussam Suhail SaleemОценок пока нет
- Aquatic Chemistry: Chemical Equilibria and Rates in Natural WatersДокумент7 страницAquatic Chemistry: Chemical Equilibria and Rates in Natural WatersShriram NandagopalОценок пока нет
- Index: Index Terms Links AДокумент25 страницIndex: Index Terms Links AbibronsОценок пока нет
- Chemical Ligation: Tools for Biomolecule Synthesis and ModificationОт EverandChemical Ligation: Tools for Biomolecule Synthesis and ModificationLuca D. D'AndreaОценок пока нет
- Key Suggestions For MBBS StudentsДокумент14 страницKey Suggestions For MBBS Studentsnihadabj2003Оценок пока нет
- Enzyme KineticsДокумент10 страницEnzyme Kineticskedirwoliy100% (1)
- Lecture 26: Enzyme Mechanism: Serine Proteases: Biochemistry I Fall Term, 2004Документ5 страницLecture 26: Enzyme Mechanism: Serine Proteases: Biochemistry I Fall Term, 2004Louis FortunatoОценок пока нет
- Lecture in Biochemistry: Prof. Dr. Karl-Heinz Van Pée Technische Universität Dresden Solo 9 - 22 September 2016Документ252 страницыLecture in Biochemistry: Prof. Dr. Karl-Heinz Van Pée Technische Universität Dresden Solo 9 - 22 September 2016bellaseba3_916194545Оценок пока нет
- Pplication of HromatographyДокумент20 страницPplication of HromatographyHarinesh JayОценок пока нет
- 013101367X TocДокумент6 страниц013101367X TocIrham Hikmawan RamadhanОценок пока нет
- Biological Membranes & TransportДокумент58 страницBiological Membranes & TransportShimmering MoonОценок пока нет
- Kreb's Cycle and ETCДокумент27 страницKreb's Cycle and ETCAmayika Tripathy0% (1)
- Aloe Vera Crosslink CAДокумент11 страницAloe Vera Crosslink CAuntia_sariОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2 Enzyme KineticsДокумент31 страницаLecture 2 Enzyme KineticsCarinaJongLeeОценок пока нет
- Biomaterials ReviewДокумент8 страницBiomaterials ReviewJosevi Jiménez MerinoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Microbial MetabolismДокумент9 страницChapter 4 Microbial MetabolismMohamidin MamalapatОценок пока нет
- RtyuДокумент13 страницRtyuspetОценок пока нет
- Untitled 0Документ46 страницUntitled 0Agam Duma Kalista WibowoОценок пока нет
- Bruice ContentsДокумент15 страницBruice ContentsArivoli UlakoliОценок пока нет
- Kreb Cycle Part 1 PDH ComplexДокумент25 страницKreb Cycle Part 1 PDH ComplexHaze MОценок пока нет
- Enzyme TechnologyДокумент47 страницEnzyme TechnologyCharulata BhattacharyaОценок пока нет
- Denaturation and Renaturation of Ribonuclease - Unit4 A - Lecture - Unit 4Документ18 страницDenaturation and Renaturation of Ribonuclease - Unit4 A - Lecture - Unit 4raghuvanshiparnika4Оценок пока нет
- Characterization of Poly(viny1 Alcohol) PolymersДокумент11 страницCharacterization of Poly(viny1 Alcohol) PolymersChristhy Vanessa Ruiz MadroñeroОценок пока нет
- Test Bank For Biochemistry 5th EditionДокумент40 страницTest Bank For Biochemistry 5th EditionkhuyenhenryzwoowОценок пока нет
- CarmegliptinДокумент12 страницCarmegliptinQuân MinhОценок пока нет
- Effect of Fouling On The Capacity and BreakthroughДокумент11 страницEffect of Fouling On The Capacity and BreakthroughJordan Hiles-BrownОценок пока нет
- Zhou 2018Документ32 страницыZhou 2018Koreab KoeenОценок пока нет
- Organo Cat Alys IsДокумент15 страницOrgano Cat Alys IsrajendickОценок пока нет
- Polylactic Acid Synthesis With PolymerizationДокумент9 страницPolylactic Acid Synthesis With PolymerizationnierzaОценок пока нет
- Catalytic Antibodies and Enzyme DynamicsДокумент15 страницCatalytic Antibodies and Enzyme DynamicsSmritisikha DebasishОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry Metabolic Pathways OverviewДокумент32 страницыBiochemistry Metabolic Pathways OverviewSanjana VasistОценок пока нет
- The Organic Chemistry of Enzyme-Catalysed ReactionsДокумент63 страницыThe Organic Chemistry of Enzyme-Catalysed ReactionskunwarskОценок пока нет
- Immobilized Enzyme Systems TechniquesДокумент25 страницImmobilized Enzyme Systems Techniquessanyukta sinhaОценок пока нет
- Metabolism Learning ObjectivesДокумент3 страницыMetabolism Learning ObjectivesJoe DerryОценок пока нет
- Cellular respiration pathways and regulationДокумент9 страницCellular respiration pathways and regulationYousif KashatОценок пока нет
- Bioquimica - 8mayo LípidosДокумент38 страницBioquimica - 8mayo LípidosLidia Escutia GuadarramaОценок пока нет
- Multivalency: Concepts, Research and ApplicationsОт EverandMultivalency: Concepts, Research and ApplicationsJurriaan HuskensОценок пока нет
- Aluminio Modificado HpamДокумент11 страницAluminio Modificado HpamximenaesgОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8 Biochemistry and Clinical Pathology Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20Документ41 страницаChapter 8 Biochemistry and Clinical Pathology Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20prat.medbooksОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ83 страницыChapter 1CharleneKronstedtОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics of Multi-Stage Self-Assembly of pH-Sensitive Gradient Copolymers in Aqueous SolutionsДокумент34 страницыThermodynamics of Multi-Stage Self-Assembly of pH-Sensitive Gradient Copolymers in Aqueous SolutionsRafael PiresОценок пока нет
- Biological Chemistry: Enzyme Kinetics Part 1Документ30 страницBiological Chemistry: Enzyme Kinetics Part 1Mohammed shaffiqueОценок пока нет
- KeperawatanДокумент7 страницKeperawatanYOHANA KEDANGОценок пока нет
- ContinueДокумент3 страницыContinueJúÑi ØrОценок пока нет
- 1.1 Chemical Composition of CellДокумент22 страницы1.1 Chemical Composition of CellSergej ElekОценок пока нет
- Enzyme Technology - CHAPLIN PDFДокумент316 страницEnzyme Technology - CHAPLIN PDFSharan Gayathrinathan100% (1)
- Last Lecture SlidesДокумент19 страницLast Lecture SlidesCena904Оценок пока нет
- Kinetics of Polymer Degradation InvolvinДокумент5 страницKinetics of Polymer Degradation InvolvinFrancesca TeocoliОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Biochemistry Text SummaryДокумент18 страницChapter 5 Biochemistry Text SummaryKyle BroflovskiОценок пока нет
- Enzymes Speed Up Cellular ReactionsДокумент54 страницыEnzymes Speed Up Cellular ReactionsCesar Augusto Airampo Macedo100% (1)
- 2012 Transport in OrganismДокумент22 страницы2012 Transport in OrganismGeorgios PlethoОценок пока нет
- Dokumen - Tips Downloadable-Printable PDFДокумент91 страницаDokumen - Tips Downloadable-Printable PDFhalimaton syuhada'Оценок пока нет
- NScELEC3 WEEK 14 LESSONДокумент6 страницNScELEC3 WEEK 14 LESSONAlyssa Jane AbellonОценок пока нет
- Stryer Biochem10e Lectureslides Ch17Документ91 страницаStryer Biochem10e Lectureslides Ch17will011225Оценок пока нет
- Protein (Structures and Functions)Документ46 страницProtein (Structures and Functions)Dian AgustiarОценок пока нет
- Michael R. Caplan Et Al - Control of Self-Assembling Oligopeptide Matrix Formation Through Systematic Variation of Amino Acid SequenceДокумент9 страницMichael R. Caplan Et Al - Control of Self-Assembling Oligopeptide Matrix Formation Through Systematic Variation of Amino Acid SequenceMdo3Оценок пока нет
- Appendix: Functional GroupsДокумент3 страницыAppendix: Functional GroupsbibronsОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry: Basic Concepts inДокумент3 страницыBiochemistry: Basic Concepts inbibronsОценок пока нет
- Apdx04Документ10 страницApdx04bibronsОценок пока нет
- TocДокумент16 страницTocbibronsОценок пока нет
- IndxДокумент27 страницIndxbibronsОценок пока нет
- PrefДокумент1 страницаPrefbibronsОценок пока нет
- GlosДокумент32 страницыGlosbibronsОценок пока нет
- Apdx05Документ1 страницаApdx05bibronsОценок пока нет
- Aerofoils Appendix C OnlineДокумент1 страницаAerofoils Appendix C OnlinebibronsОценок пока нет
- IndxДокумент27 страницIndxbibronsОценок пока нет
- Conversion chart for linear, area, volume, density and other unitsДокумент2 страницыConversion chart for linear, area, volume, density and other unitsbibrons100% (1)
- LosДокумент9 страницLosbibronsОценок пока нет
- RefsДокумент9 страницRefsbibronsОценок пока нет
- Apdx05Документ1 страницаApdx05bibronsОценок пока нет
- Conversion chart for linear, area, volume, density and other unitsДокумент2 страницыConversion chart for linear, area, volume, density and other unitsbibrons100% (1)
- Aerofoils Appendix C OnlineДокумент1 страницаAerofoils Appendix C OnlinebibronsОценок пока нет
- Aircraft Design: Ajoy Kumar KunduДокумент2 страницыAircraft Design: Ajoy Kumar Kundubibrons0% (1)
- Appendices I-IVДокумент9 страницAppendices I-IVOlavGОценок пока нет
- 00a ISMFRONTДокумент1 страница00a ISMFRONTİbrahim Anıl BalkanОценок пока нет
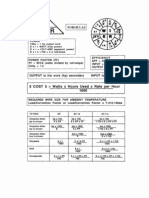
- Electrical Formulas and Calculations - E-Book - (2005) National Electrical CodeДокумент14 страницElectrical Formulas and Calculations - E-Book - (2005) National Electrical Codemagdy473Оценок пока нет
- FHB-Grading and DrainageДокумент5 страницFHB-Grading and DrainagebibronsОценок пока нет
- Performance Standards (Amendments)Документ18 страницPerformance Standards (Amendments)bibronsОценок пока нет
- Wall Brace Construction 64Документ3 страницыWall Brace Construction 64bibronsОценок пока нет
- Wall Bracing OhioДокумент1 страницаWall Bracing OhiobibronsОценок пока нет