Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
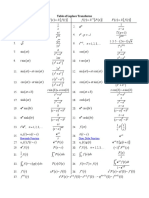
Trigonometry Formula Guide GG27
Загружено:
KennethMathОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Trigonometry Formula Guide GG27
Загружено:
KennethMathАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Formulas For Triangles #27 of Gottschalks Gestalts
A Series Illustrating Innovative Forms of the Organization & Exposition of Mathematics by Walter Gottschalk
Infinite Vistas Press PVD RI 2001 GG27-1 (23)
2001 Walter Gottschalk
500 Angell St #414 Providence RI 02906 permission is granted without charge to reproduce & distribute this item at cost for educational purposes; attribution requested; no warranty of infallibility is posited
GG27-2
laws governing side / angle relationships of triangles
D consider any triangle with vertices / angles A, B, C, with opposite sides a, b, c, with circumradius R; then the following laws hold:
D law of sines a b c = = = 2R sin A sin B sin C
GG27-3
D law of cosines a 2 = b 2 + c 2 - 2 b c cos A b 2 = c 2 + a 2 - 2 c a cos B c 2 = a 2 + b 2 - 2 a b cos C
D variations on the law of cosines a2 = b 2 + c 2 - 2 b c cos A A = ( b + c)2 - 4 b c cos 2 2 A = ( b - c)2 + 4 b c sin 2 2 & cyclicly
GG27-4
D law of cosines - projection a = b cos C + c cos B b = c cos A + a cos C c = a cos B + b cos A
D variations on the law of cosines - projection a sin B a sin C tan A = = c - a cos B b - a cos C & cyclicly
GG27-5
D law of tangents a-b 2 = a + b tan 1 ( A + B)
2
tan ( A - B)
b-c 2 = b + c tan 1 (B + C)
2
tan (B - C)
c-a 2 = c + a tan 1 (C + A )
2
tan (C - A )
D law of cotangents (a + b) cot ( A + B) = (a - b) cot ( A - B)
2 2 1 1
( b + c) cot (B + C) = ( b - c) cot (B - C)
2 2
(c + a ) cot (C + A ) = (c - a ) cot (C - A )
2 2
GG27-6
D law of secants a sec (B + C) = ( b + c) sec (B - C)
2 2 1 1
b sec (C + A ) = (c + a ) sec (C - A )
2 2
c sec ( A + B) = (a + b) sec ( A - B)
2 2
D law of cosecants a csc (B + C) = ( b - c) csc (B - C)
2 2 1 1
b csc (C + A ) = (c - a ) csc (C - A ) 2 2 c csc ( A + B) = (a - b) csc ( A - B)
2 2 1 1
GG27-7
D Mollweide' s equations which are slight variations of the law of secants & the law of cosecants 1 sin A a 2 = b + c cos 1 (B - C) 2 1 sin B b 2 = c + a cos 1 (C - A ) 2 1 sin C c 2 = a + b cos 1 ( A - B) 2
GG27-8
1 cos A a 2 = b - c sin 1 (B - C) 2 1 cos B b 2 = c - a sin 1 (C - A ) 2 1 cos C c 2 = a - b sin 1 ( A - B) 2
GG27-9
formulas for the trig fcns of the angles of a triangle ito the sides D the 6 basic trig fcns of the 3 angles of a triangle with vertices / angles A, B, C, with opposite sides a, b, c, with semiperimeter s are given ito the sides by 18 formulas of which the first 3 are listed below, the remaining 15 then being easy consequences: 2 s (s - a ) (s - b) (s - c) bc
sin A =
b2 + c2 - a 2 cos A = 2bc s (s - a ) (s - b) (s - c) b2 + c2 - a 2
tan A = 4
GG27-10
D also note the formulas 2 s (s - a ) 1 + cos A = bc & cyclicly 1 - cos A = & cyclicly 2 (s - b) (s - c) bc
GG27-11
formulas for the trig fcns of the half - angles of a triangle ito the sides D the 6 basic trig fcns of the 3 half - angles of a triangle with vertices / angles A, B, C, with opposite sides a, b, c, with semiperimeter s are given ito the sides by 18 formulas of which the first 3 are listed below, the remaining 15 then being easy consequences: A (s - b) (s - c) sin = bc 2 s (s - a ) A = bc 2 A (s - b) (s - c) = 2 s (s - a )
cos
tan
GG27-12
formulas for the area of a triangle D consider any triangle with vertices / angles A, B, C, with opposite sides a, b, c, with altitudes h a , h b , h c to sides a, b, c, with semiperimeter s, with circumradius R, with inradius r, with exradii ra , rb , rc to sides a, b, c; then the area K of the triangle is given by the following formulas:
GG27-13
1 K = a ha 2 K=
& cyclicly
1 b c sin A & cyclicly 2 & cyclicly
1 sin B sin C K = a2 sin A 2 1 sin B sin C K = a2 2 sin (B + C)
& cyclicly
K = 2 R 2 sin A sin B sin C A B C K = 4 R s sin sin sin 2 2 2 K = 4 R r cos A B C cos cos 2 2 2
K = s 2 tan
A B C tan tan 2 2 2
GG27-14
K = s (s - a ) tan
A 2
& cyclically
K = s (s - a ) (s - b) (s - c) K= abc 4R
(Heron' s formula; already known to Archimedes)
K = rs K = ra (s - a ) & cyclically K = r ra rb rc
GG27-15
D many pretty formulas are easy consequences of the above area formulas eg A B C sin sin 2 2 2 A B C cos cos 2 2 2
r = 4 R sin
s = 4 R cos
r = s tan
A B C tan tan 2 2 2 & cyclicly
tan
r r A = = a 2 s-a s
abc = 4 Rrs
GG27-16
some trig eqns that are true for all angles A, B, C such that their sum is a straight angle: A + B + C = 180 o = p r ; hence these formulas hold for the angles A, B, C of any triangle
GG27-17
sin A + sin B + sin C = 4 cos
A B C cos cos 2 2 2 A B C sin sin 2 2 2
cos A + cos B + cos C = 1 + 4 sin
sin 2 A + sin 2 B + sin 2C = 4 sin A sin B sin C cos 2 A + cos 2 B + cos 2C + 4 cos A cos B cos C + 1 = 0 B sin 4 A + sin 4 B + sin 4C + 4 sin 2 A sin 2B sin 2C = 0 cos 4 A + cos 4 B + cos 4C + 1 = 4 cos 2 A cos 2 B cos 2C
GG27-18
tan A + tan B + tan C = tan A tan B tan C cot A cot B + cot B cot C + cot C cot A = 1 (cot A + cot B + cot C)2 = cot 2 A + cot 2 B + cot 2 C + 2 cot A B C A B C + cot + cot = cot cot cot 2 2 2 2 2 2 A B B C C A = 1 tan + tan tan + tan tan 2 2 2 2 2 2
tan
2 tan A + tan B + tan C = tan 2 A + tan 2 B + tan 2 C + 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
GG27-19
sin 2 A + sin 2 B + sin 2 C = 2 + 2 cos A cos B cos C sin 2 A + sin 2 B - sin 2 C = 2 sin A sin B cos C sin 2 A - sin 2 B + sin 2 C = 2 sin A cos B sin C - sin 2 A + sin 2 B + sin 2 C = 2 cos A sin B sin C
cos 2 A + cos 2 B + cos 2 C = 1 - 2 cos A cos B cos C cos 2 A + cos 2 B - cos 2 C = 1 - 2 sin A sin B cos C cos 2 A - cos 2 B + cos 2 C = 1 - 2 sin A cos B sin C - cos 2 A + cos 2 B + cos 2 C = 1 - 2 cos A sin B sin C
GG27-20
Metatheorem. the formula F ( A, B, C ) is valid p p the formula F A - p, B + , C + is valid 2 2 & cyclicly the formula F ( - A, p - B, p - C ) is valid & cyclicly the formula F ( p - 2 A, p - 2 B, p - 2 C ) is valid the formula F (3 A, 3 B - p, 3 C - p ) is valid & cyclicly p A p B p C the formula F - , - , - is valid 2 2 2 2 2 2 etc
GG27-21
T. if A, B, C are the angles of a triangle then sin 4 A + sin 4 B + sin 4C = 0 ABC rt D
GG27-22
D bioline
Archimedes of Syracuse ca 287-212 BCE Greek mathematician, physicist, inventor; considered to be one of the three greatest mathematicians of all time, the other two being Newton and Gauss
D bioline
Heron of Alexandria fl 62 CE Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer
D bioline
Karl Brandon Mollweide 1774-1825 German mathematician, astronomer, cartographer
GG27-23
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Differential and Integral Calculus - N PiskunovДокумент896 страницDifferential and Integral Calculus - N Piskunovmenkalinan83% (6)
- Fibonacci Sequence in The Phi SpiralДокумент1 страницаFibonacci Sequence in The Phi Spiraldjbroussard100% (3)
- 1-3 Transforming Linear FunctionsДокумент25 страниц1-3 Transforming Linear Functionsbatoul dakroubОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Finite Element MethodДокумент24 страницыFinite Element Methodshivam choudhary0% (1)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- 0563 Bgcse MathematicsДокумент33 страницы0563 Bgcse MathematicsKennedy Absalom ModiseОценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- 11.1 AnswersДокумент13 страниц11.1 AnswersDiksha PatelОценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Kevin Dennis and Steven Schlicker - Sierpinski N-GonsДокумент7 страницKevin Dennis and Steven Schlicker - Sierpinski N-GonsIrokkОценок пока нет
- A4 LinearEquations BP 9 22 14Документ5 страницA4 LinearEquations BP 9 22 14Rey Xander Capio100% (1)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Algebra 2 Vertex Form Practice PDFДокумент4 страницыAlgebra 2 Vertex Form Practice PDFErica MaeОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- 12 Maths CBSE Exam Papers 2015 Chennai Set 1 AnswerДокумент16 страниц12 Maths CBSE Exam Papers 2015 Chennai Set 1 AnswerGeeteshGuptaОценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Laplace Table PDFДокумент2 страницыLaplace Table PDFMuhammad ZОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Properties of EqualityДокумент3 страницыProperties of EqualityElvie Abulencia-Bagsic50% (2)
- History of MathematicsДокумент3 страницыHistory of MathematicsMelОценок пока нет
- Polynomials Chap 2Документ4 страницыPolynomials Chap 2jeetОценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Be A K3 Surface Defined As A Smooth Complete Intersection With EquationsДокумент20 страницBe A K3 Surface Defined As A Smooth Complete Intersection With EquationsnicoОценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- AP Calculus AB - Connections Among The Graphs of F, F', and F'' If The Answer To A Question Cannot Be Determined From The Graph Provided, Write "CBD" at Means To JustifyДокумент2 страницыAP Calculus AB - Connections Among The Graphs of F, F', and F'' If The Answer To A Question Cannot Be Determined From The Graph Provided, Write "CBD" at Means To JustifyRita LimОценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Arzelà-Ascoli Theorem: I (A, B) MДокумент8 страницArzelà-Ascoli Theorem: I (A, B) MKauê SenaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Numpy Arrays: Gert-Ludwig IngoldДокумент56 страницIntroduction To Numpy Arrays: Gert-Ludwig IngoldMusa MohammadОценок пока нет
- Activity (DifferentialCalculus)Документ9 страницActivity (DifferentialCalculus)John Aries Almelor SarzaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Inverse Problems - Guillaume Bal PDFДокумент205 страницIntroduction To Inverse Problems - Guillaume Bal PDFMarcoags26Оценок пока нет
- Mathematical Language & SymbolsДокумент18 страницMathematical Language & SymbolsClaire Angelie RuayaОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- HigherAlgebra 10000931Документ696 страницHigherAlgebra 10000931jurebieОценок пока нет
- Solutions 2 - 640Документ4 страницыSolutions 2 - 640Calixto RhenalsОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Grade VI - 3Документ30 страницMathematics Grade VI - 3Cortez del AiramОценок пока нет
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- New DLP Math q1 Week 7Документ4 страницыNew DLP Math q1 Week 7Celina Katherine Talampas MarquezОценок пока нет
- H2 X RДокумент38 страницH2 X RRuben Ainsten GaussОценок пока нет
- 6.1 - Numbers and OperationsДокумент3 страницы6.1 - Numbers and Operationsguanajuato_christopherОценок пока нет
- Jackson 5 15 Homework SolutionДокумент5 страницJackson 5 15 Homework SolutionAdéliaОценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (120)
- Maths Today 3 RedДокумент413 страницMaths Today 3 RedSinclair LungaОценок пока нет
- Cade MY: Vineet Loomba UnacademyДокумент2 страницыCade MY: Vineet Loomba Unacademyanita rani paloОценок пока нет