Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Experiment: 1 To Study Superposition Theorem
Загружено:
hetalsolankiИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Experiment: 1 To Study Superposition Theorem
Загружено:
hetalsolankiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Experiment: 1 To study Superposition Theorem
Experiment: 1
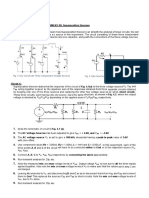
Aim: To study and verify super-position theorem. Apparatus: 1.Analog board of AB83, 2.Connecting Wires, 3.DMM (Digital Multi-meter), 4.Project Board 5.DC power supplies +12V, +5V from external source or ST2612 Analog Lab. Circuit Diagram:
Theorem: The total current in any part of a linear circuit equals the algebraic sum of the currents produced by each source separately. The Superposition Theorem is an important concept in circuit analysis. It allows you to determine a voltage across a component or a branch current by calculating the effect of each source individually, and then algebraically adding each contribution. Superposition may be considered for circuit analysis when
1. There are two or more energy sources. 2. The sources are either voltage or current sources. 3. The circuit is not too complex. Procedure: 1. Connect +12V, +5V DC power supplies at their indicated position from external source or ST2612 Analog Lab. 2. Connect 2mm patch cord between Test Point 1 & 2, 11 & 12, 5 & 6,7 & 8, 4 & 9. 3. Connect an Ammeter between Test Point 3 & 10 to measure current flowing through branch CD in presence of both voltage source. 4. Remove one of the supplies (say +5V) from branch AB by disconnecting patch cords between Test Point 1 & 2 and Connect patch cord between Test point 2 &11. 5. Measure the value of current flowing through branch CD in presence of single voltage source of + 12V. 6. Remove +12V Power supply from branch AB by disconnecting patch cords between Test Point 5 & 6, 8&7 and connect patch cord between Test point 5 & 8. 7. Measure the value of current flowing through branch CD in presence of single Voltage source of + 5V. 8. Compare the amount of current flowing in presence of both of the source with the sum of current flowing in case of individual source. 9. Repeat above procedure for other branches.
Observation Table: For V1=5v and V2=0v (S.C.),
Branch: 1 I1= ______ I1= ______ I1total = ______
Branch: 2 I2= ______ I2= ______ I2total = ______
Branch: 3 I3= ______ I3= ______ I3total = ______
For V1=0v (S.C.) and V2=12v,
Branch: 1 I1= ______ I1= ______ I1total = ______
Branch: 2 I2= ______ I2= ______ I2total = ______
Branch: 3 I3= ______ I3= ______ I3total = ______
For V1=5v and V2=12v,
Branch: 1 I1= ______ I1= ______ I1total = ______
Conclusion:
Branch: 2 I2= ______ I2= ______ I2total = ______
Branch: 3 I3= ______ I3= ______ I3total = ______
Вам также может понравиться
- EE4001 Assigment 2Документ4 страницыEE4001 Assigment 2Octav EnachiОценок пока нет
- Superposition Theorem LabДокумент2 страницыSuperposition Theorem LabOkwal33% (3)
- 203 Lab04 Circuits Sum08 PDFДокумент6 страниц203 Lab04 Circuits Sum08 PDFJun MendozaОценок пока нет
- Bhopal Institute of Technology New Lab ManualДокумент391 страницаBhopal Institute of Technology New Lab ManualDeepak Kumar Rajak100% (1)
- SAC 4 - Folio of Electronics Practical ActivitiesДокумент13 страницSAC 4 - Folio of Electronics Practical ActivitiesphongchaychuaОценок пока нет
- 01 ET09 TOC New2Документ3 страницы01 ET09 TOC New2samactrang_uaОценок пока нет
- Circuit Lab ManualДокумент3 страницыCircuit Lab ManualFrankwangczОценок пока нет
- Islamic University of Technology (Iut) : Course: Experiment No Name of The ExperimentДокумент2 страницыIslamic University of Technology (Iut) : Course: Experiment No Name of The ExperimentshiamОценок пока нет
- Experiment in Basics of Electronic TechnologyДокумент13 страницExperiment in Basics of Electronic TechnologyMehedi HasanОценок пока нет
- BEE Lab ReportДокумент7 страницBEE Lab ReportOliu Hasnat RafiОценок пока нет
- Applied Physics LabДокумент59 страницApplied Physics LabEngr Waqas MalikОценок пока нет
- DC Exp 5 Student ManualДокумент5 страницDC Exp 5 Student ManualMuhammad ZayedОценок пока нет
- EEE Network LabДокумент14 страницEEE Network LabPradeep SinglaОценок пока нет
- DC Exp 6 Student ManualДокумент6 страницDC Exp 6 Student ManualAsifur R. HimelОценок пока нет
- Lab 08 - Superposition TheoremДокумент3 страницыLab 08 - Superposition TheoremAamir KhanОценок пока нет
- Laboratory ManualДокумент23 страницыLaboratory ManualAnmol AhsaasОценок пока нет
- Lab ReportДокумент7 страницLab ReportCattosphereОценок пока нет
- NRI Discovery LabДокумент19 страницNRI Discovery Labden headОценок пока нет
- Superposition Theorem States ThatДокумент7 страницSuperposition Theorem States ThatHaj AliОценок пока нет
- Monsoon 2021: EXPERIMENT-05: Superposition TheoremДокумент2 страницыMonsoon 2021: EXPERIMENT-05: Superposition TheoremAnsh SagrohaОценок пока нет
- Circuits Lab Exp 5 ReportДокумент17 страницCircuits Lab Exp 5 Reportਰਣਜੀਤ ਢਿੱਲੋਂОценок пока нет
- Experiment No. 06 B: Title: DC-Power Supply: Block Diagram, Operation and Working AimДокумент14 страницExperiment No. 06 B: Title: DC-Power Supply: Block Diagram, Operation and Working AimStar LordОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Work 3Документ5 страницLaboratory Work 3Makhmud AssentayОценок пока нет
- ECA 1 Lab ManualДокумент92 страницыECA 1 Lab ManualMuhammad EjazОценок пока нет
- ETE 1112 - Basic Electrical Engineering Lab ManualДокумент27 страницETE 1112 - Basic Electrical Engineering Lab ManualSabuj Ahmed100% (1)
- Ee602 Circuit AnalysisДокумент55 страницEe602 Circuit AnalysisArryshah DahmiaОценок пока нет
- EE2155 Electrical Circuits Lab Manual PDFДокумент38 страницEE2155 Electrical Circuits Lab Manual PDFSymmer CulОценок пока нет
- Mam SaimaДокумент8 страницMam SaimaFaheemОценок пока нет
- 2a. Superposition TheoremДокумент4 страницы2a. Superposition Theoremabhioptimus00Оценок пока нет
- 1 2 3 A Sim ElectricalcircuitsДокумент9 страниц1 2 3 A Sim Electricalcircuitsapi-256421289Оценок пока нет
- Linear Circult Analysis Lab-Manual - 16jun 2016 PDFДокумент71 страницаLinear Circult Analysis Lab-Manual - 16jun 2016 PDFHaris -Оценок пока нет
- Mechatronics Lab 1Документ5 страницMechatronics Lab 1daisyhendersonОценок пока нет
- Deccan College of Engineering & Technology: Power Electronics Laboratory ManualДокумент73 страницыDeccan College of Engineering & Technology: Power Electronics Laboratory ManualharshОценок пока нет
- Lab2 For EE 100AДокумент14 страницLab2 For EE 100AJohn evergreen0% (1)
- American International University-Bangladesh: Department of Electrical and Electronic EngineeringДокумент4 страницыAmerican International University-Bangladesh: Department of Electrical and Electronic EngineeringRuham RofiqueОценок пока нет
- BASICEEL Expt8 Lab Report JvbautistaДокумент12 страницBASICEEL Expt8 Lab Report JvbautistaJelyn BenjaminОценок пока нет
- Elvis II y MultisimДокумент17 страницElvis II y MultisimHermes PolancoОценок пока нет
- Objectives: I. DC Circuit BasicsДокумент10 страницObjectives: I. DC Circuit BasicsNabeeL 6669Оценок пока нет
- Chapter One1Документ29 страницChapter One1مسلم محمودОценок пока нет
- Lab 6Документ5 страницLab 6Stephen BridgesОценок пока нет
- DC Lab - Exp - 3 - Student - Manual (Spring 22-23)Документ3 страницыDC Lab - Exp - 3 - Student - Manual (Spring 22-23)Bahesty Monfared AkashОценок пока нет
- Mini Project: The Construction of 9 - 12 Volt DC Power Supply 1.0 ObjectivesДокумент8 страницMini Project: The Construction of 9 - 12 Volt DC Power Supply 1.0 ObjectivesChyNaluri89Оценок пока нет
- EEE 202 Lab Experiment SheetДокумент3 страницыEEE 202 Lab Experiment SheetAlamgir Kabir ShuvoОценок пока нет
- EE42 100 Cch-Lecure11 071713-CleanДокумент31 страницаEE42 100 Cch-Lecure11 071713-CleanozanistzОценок пока нет
- Circuit LabДокумент7 страницCircuit LabBiftu ShibbireОценок пока нет
- Basic DC Circuits ExperimentДокумент2 страницыBasic DC Circuits ExperimentTez HarrietОценок пока нет
- CKT LabManual 21-22Документ11 страницCKT LabManual 21-22Anirban MandalОценок пока нет
- Locktronics FEEДокумент70 страницLocktronics FEEDavid LaurenceОценок пока нет
- LAB # 02 To Determine Unknown Loop Currnts in An Ac/Dc Circuits ObjectiveДокумент6 страницLAB # 02 To Determine Unknown Loop Currnts in An Ac/Dc Circuits ObjectiveImaad KhanОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Manual BTY309 Biomedical Circuits and Networks LaboratoryДокумент45 страницLaboratory Manual BTY309 Biomedical Circuits and Networks LaboratoryRiya KumariОценок пока нет
- Electric Circuits: Lab Manual Experiment No 6Документ5 страницElectric Circuits: Lab Manual Experiment No 6HM FaisalОценок пока нет
- EE 287 Circuit Theory: Presented By: Dr. Philip Yaw OkyereДокумент30 страницEE 287 Circuit Theory: Presented By: Dr. Philip Yaw Okyeresamuel fiifi yeboahОценок пока нет
- Lab 03 Dependent SourceДокумент6 страницLab 03 Dependent SourcefarhanОценок пока нет
- Voltage Drop Test 122718Документ3 страницыVoltage Drop Test 122718Abdul JabbarОценок пока нет
- Bee Lab ManualДокумент40 страницBee Lab ManualDk gamingОценок пока нет
- BEE Lab ExpДокумент17 страницBEE Lab ExpShahid AdnanОценок пока нет
- Work TheoremsДокумент45 страницWork TheoremsSaikat LayekОценок пока нет
- Thevenin'Stheorems: S. No. Name of The Component Specifications Range QuantityДокумент3 страницыThevenin'Stheorems: S. No. Name of The Component Specifications Range QuantitysunilkumareceОценок пока нет
- UG Course Structur FinalДокумент79 страницUG Course Structur FinalGargi PatnaikОценок пока нет
- Internal Question Paper CKT THEORYДокумент2 страницыInternal Question Paper CKT THEORYGargi RoyОценок пока нет
- Method of Moments and Circuit Network Theory in Antenna AnalysisДокумент3 страницыMethod of Moments and Circuit Network Theory in Antenna AnalysisEditor IJRITCC100% (1)
- Eng 1450Документ4 страницыEng 1450Zeshan MeoОценок пока нет
- 9432Документ18 страниц9432Dan EsentherОценок пока нет
- Methods of Analysis and Selected Topics (DC) : Publishing As Pearson (Imprint) BoylestadДокумент92 страницыMethods of Analysis and Selected Topics (DC) : Publishing As Pearson (Imprint) BoylestadFaisal UddinОценок пока нет
- Application of Fourier SeriesДокумент20 страницApplication of Fourier SeriesFiaz FiazОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Solutions To ExercisesДокумент70 страницChapter 4 Solutions To ExercisesLuis D UrciaОценок пока нет
- CMO 24 s2008 Annex IVB List of LABORATORY Requirements For ECEДокумент31 страницаCMO 24 s2008 Annex IVB List of LABORATORY Requirements For ECEcathyОценок пока нет
- Lab 7 Thevenin, Norton and Maximum Power TransferДокумент12 страницLab 7 Thevenin, Norton and Maximum Power Transferfarisizzwan23Оценок пока нет
- Egr 271 SyllabusДокумент9 страницEgr 271 Syllabusapi-341484216Оценок пока нет
- ESE Syllabus 2013: A. Civil EngineeringДокумент9 страницESE Syllabus 2013: A. Civil EngineeringSumit BalguvharОценок пока нет
- AC Sweep and Signal Analysis: Hspice - Book: Hspice - ch09 1 Thu Jul 23 19:10:43 1998Документ28 страницAC Sweep and Signal Analysis: Hspice - Book: Hspice - ch09 1 Thu Jul 23 19:10:43 1998JatinKumarОценок пока нет
- Electronic Circuit Analysis and Design Second Edition: Donald A. NeamenДокумент8 страницElectronic Circuit Analysis and Design Second Edition: Donald A. NeamenjibonbookОценок пока нет
- EE 103 Lecture4Документ14 страницEE 103 Lecture4Talha MohsinОценок пока нет
- Catalouge Engg2012Документ32 страницыCatalouge Engg2012rbc123Оценок пока нет
- Network Theory Syllabus 2Документ12 страницNetwork Theory Syllabus 2anuОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8 Small Sinal Analysis of FETДокумент46 страницChapter 8 Small Sinal Analysis of FETsakibОценок пока нет
- Jntuk R07 ECE SyllabusДокумент83 страницыJntuk R07 ECE Syllabussravankumar493100% (1)
- Calicut B.Tech Electrical and Electronics SyllabusДокумент150 страницCalicut B.Tech Electrical and Electronics SyllabusJinu Madhavan0% (1)
- MSC (Computational and Integrative Sciences) : M.Sc. ProgrammeДокумент21 страницаMSC (Computational and Integrative Sciences) : M.Sc. ProgrammeDIKCHHA AGRAWALОценок пока нет
- EEE New SyllabusДокумент50 страницEEE New SyllabusShihabuddin Mohammad FaisalОценок пока нет
- Network Theory A RajasekaranДокумент169 страницNetwork Theory A RajasekaranparantnОценок пока нет
- Ece 310Документ10 страницEce 310Arlyn AzzamОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1-Electrical Elements - Series & Parallel Circuits.Документ49 страницLecture 1-Electrical Elements - Series & Parallel Circuits.MAENYA BRUCE OYONDIОценок пока нет
- Circuit Theory: Two-Port CircuitsДокумент21 страницаCircuit Theory: Two-Port CircuitsJhon ValenciaОценок пока нет
- Feedback AmplifiersДокумент43 страницыFeedback AmplifiersMuraliОценок пока нет
- Origins of The Equivalent Circuit Concept: The Voltage-Source EquivalentДокумент10 страницOrigins of The Equivalent Circuit Concept: The Voltage-Source EquivalentSiva GuruОценок пока нет
- Electrical Engee&Comp SciДокумент32 страницыElectrical Engee&Comp SciVishnu Kumar NadarОценок пока нет