Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Siemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 16
Загружено:
mydearteacherИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Siemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 16
Загружено:
mydearteacherАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
2 Power Transmission and Distribution Solutions
2.1 Overview of Technologies and Services
Feeding the power generated at different locations over long distances into power systems often calls for extraordinary power transmission and distribution solutions. Despite the challenges it poses, however, interconnecting of different regions, countries or even continents remains a viable option for providing these areas with economical access to power (g. 2.1-1). As a solution provider with extensive experience in every aspect of power transmission and distribution, Siemens has already implemented a large number of projects linking power systems or connecting decentralized generating units to the grid. In each case, conditions were unique. And because Siemens strives to provide its customers with the most cost-efcient results, the implemented solutions using different technologies were also unique. Smart grids will help achieve a sustainable development. It is worthwhile mentioning that the smart grid vision is in the same way applicable to the system developments in other regions of the world. Smart grids will help achieve a sustainable development. An increasingly liberalized market will encourage trading opportunities to be identied and developed. Smart grids are a necessary response to the environmental, social and political demands placed on energy supply.
2.1.2 AC/DC Transmission and Distribution
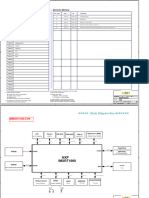
HVDC, FACTS and SIPLINK Todays power transmission systems have the task of transmitting power from point A to point B reliably, safely and efciently. It is also necessary to transmit power in a manner that is not harmful to the environment. Siemens offers comprehensive solutions, technical expertise and worldwide experience to help customers meet these challenges. For each application and technical transmission stage, Siemens offers optimized solutions with SIPLINK (Siemens Multifunctional Power Link), HVDC transmission or FACTS for the most efcient use of AC power systems and lines. Typical applications for FACTS include fast voltage control, increased transmission capacity over long lines, power ow control in meshed systems, and power oscillation damping. With FACTS, more power can be transmitted within the power system. When technical or economical feasibility of conventional threephase technology reaches its limit, HVDC will be the solution (g. 2.1-2). Its main application areas are economical transmission of bulk power over long distances and interconnection of asynchronous power grids. Siemenss latest innovation in highvoltage direct current technology is HVDC PLUS. The advantages of the new system, which employs voltage-sourced converters, include a compact layout of the converter stations and advanced control features such as independent active and reactive power control, and black start capability. For medium-voltage DC transmission, Siemens offers the SIPLINK system. Depending on the application and the conguration of the existing system, SIPLINK will reduce investment, system and lifecycle costs. The system controls the active power and optimizes voltage stability by providing reactive power (section 2.3).
2.1.1 Solutions for Smart and Super Grids with HVDC and FACTS
The power grid of the future must be secure, cost-effective and environmentally compatible. The combination of these three tasks can be tackled with the help of ideas, intelligent solutions as well as advanced technologies. Innovative solutions with HVDC (High-Voltage Direct Current Transmission) and FACTS (Flexible AC Transmission Systems) have the potential to cope with the new challenges. By means of power electronics, they provide features which are necessary to avoid technical problems in the power systems, they increase the transmission capacity and system stability very efciently and help to prevent cascading disturbances. The vision and enhancement strategy for the future electricity networks are, for example, depicted in the program for Smart Grids, which was developed within the European Technology Platform. Features of a future smart grid such as this can be outlined as follows: Flexible: fullling operator needs whilst responding to the changes and challenges ahead Accessible: granting connection access to all network users, particularly for RES and high-efciency local generation with zero or low carbon emissions Reliable: assuring and improving security and quality of supply Economic: providing best value through innovation, efcient energy management and level playing eld competition and regulation
16
Siemens Energy Sector Power Engineering Guide Edition 7.0
Вам также может понравиться
- Peg 70 Kap 02Документ50 страницPeg 70 Kap 02megamaster2010Оценок пока нет
- Power Transmission and DistributionДокумент50 страницPower Transmission and DistributionGhayath OmerОценок пока нет
- 04 Power TransmissionДокумент64 страницы04 Power TransmissionRafael FurquimОценок пока нет
- PEG - 70 - KAP - 01 Smart Grids and The New Age of EnergyДокумент0 страницPEG - 70 - KAP - 01 Smart Grids and The New Age of Energywilliamb285Оценок пока нет
- Smart and Bulk Power TransmissionДокумент24 страницыSmart and Bulk Power TransmissionTaner YenerОценок пока нет
- Power Transmission and Distribution SolutionsДокумент50 страницPower Transmission and Distribution SolutionsudayakumartОценок пока нет
- Smart Grids and The New Age of Energy - EEPДокумент11 страницSmart Grids and The New Age of Energy - EEPvetsasОценок пока нет
- Transitioning To Smart MV/LV Substations As The Cornerstone of Your Smart GridДокумент18 страницTransitioning To Smart MV/LV Substations As The Cornerstone of Your Smart GridGerard MarracheОценок пока нет
- AREVA Smart Grid Solution - V4Документ43 страницыAREVA Smart Grid Solution - V4Puthanveedu Rajan SantoshОценок пока нет
- Siemens Energy Sector Edition 7.1: 16 Power Engineering GuideДокумент64 страницыSiemens Energy Sector Edition 7.1: 16 Power Engineering GuideCristian TeranОценок пока нет
- Power Engineering Guide Edition 7 1Документ542 страницыPower Engineering Guide Edition 7 1Abhishek Kumar100% (1)
- 16.prospects ofVoltage-Sourced Converters (VSC) Applications in DCTransmission SystemsДокумент5 страниц16.prospects ofVoltage-Sourced Converters (VSC) Applications in DCTransmission SystemsWahyu HarianjaОценок пока нет
- Smart Grids: For A Brighter FutureДокумент6 страницSmart Grids: For A Brighter FutureHemanth SairamОценок пока нет
- Gomis-Bellmunt Et Al. - 2020 - Flexible Converters For Meshed HVDC Grids From Flexible AC Transmission Systems (FACTS) To Flexible DC Gr-AnnotatedДокумент14 страницGomis-Bellmunt Et Al. - 2020 - Flexible Converters For Meshed HVDC Grids From Flexible AC Transmission Systems (FACTS) To Flexible DC Gr-AnnotatedSanzad LumenОценок пока нет
- HVDC Plus The Smart WayДокумент10 страницHVDC Plus The Smart WayOana IanoleОценок пока нет
- Prospects of Voltage-Sourced Converters VSC ApplicДокумент6 страницProspects of Voltage-Sourced Converters VSC ApplicMuhammad Aulia RachmanОценок пока нет
- Smart Grid in TransmissionДокумент46 страницSmart Grid in TransmissionAnil PalamwarОценок пока нет
- 1.1 What Are The Issues With Existing Grid?Документ35 страниц1.1 What Are The Issues With Existing Grid?Vijay RajuОценок пока нет
- An Advanced Protection Scheme For Enabling An LVDC Last Mile Distribution NetworkДокумент8 страницAn Advanced Protection Scheme For Enabling An LVDC Last Mile Distribution Networkmusharraf saeedОценок пока нет
- From Smart Grid To Super Grid Solutions WithДокумент6 страницFrom Smart Grid To Super Grid Solutions WithMohit Kumar ChowdaryОценок пока нет
- HVDC Plus Basic and PrincipalsДокумент24 страницыHVDC Plus Basic and Principalstkdrt2166Оценок пока нет
- Datatransmissionthroughpowerline 150307034245 Conversion Gate01 PDFДокумент10 страницDatatransmissionthroughpowerline 150307034245 Conversion Gate01 PDFSanthosh V RaajendiranОценок пока нет
- 11 Power System Analysis and PlanningДокумент14 страниц11 Power System Analysis and PlanningRafael FurquimОценок пока нет
- Siemens Power Engineering Guide Transmission DistributionДокумент332 страницыSiemens Power Engineering Guide Transmission DistributionSuresh K Krishnasamy100% (1)
- Siemens - Power Engineering Guide - Transmission & DistributionДокумент332 страницыSiemens - Power Engineering Guide - Transmission & DistributionAhmed Gaafer100% (10)
- Aricent Electrical Utility WhitepaperДокумент9 страницAricent Electrical Utility Whitepaperap_venezuelaОценок пока нет
- Siemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 48Документ1 страницаSiemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 48mydearteacherОценок пока нет
- More Flexibility For The Manufacturing Industry: LI, LD and BD2 Busbar Trunking SystemsДокумент8 страницMore Flexibility For The Manufacturing Industry: LI, LD and BD2 Busbar Trunking Systemscc_bauОценок пока нет
- Hybrid Power Considerations For Today's Telecommunications: A White Paper byДокумент5 страницHybrid Power Considerations For Today's Telecommunications: A White Paper byDennis Ugochukwu OkwuonuОценок пока нет
- Siemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 23Документ1 страницаSiemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 23mydearteacherОценок пока нет
- 9 1526549792 - 17-05-2018 PDFДокумент6 страниц9 1526549792 - 17-05-2018 PDFAnonymous lPvvgiQjRОценок пока нет
- MVDC - The New Technology For Distribution NetworksДокумент5 страницMVDC - The New Technology For Distribution Networksahmedallehyani5aОценок пока нет
- SVC PLUS The Efficient WayДокумент8 страницSVC PLUS The Efficient WayPushkarEEОценок пока нет
- MVDC - The New Technology For Distribution NetworksДокумент5 страницMVDC - The New Technology For Distribution NetworksClaudio Antonio Paredes CarrascoОценок пока нет
- Lecture Notes Unit 2 Smart Grid1Документ25 страницLecture Notes Unit 2 Smart Grid1Saurabh BhardwajОценок пока нет
- FACTS - Flexible Alternating Current Transmission System For Cost Effective and Reliable Transmission of Electrical EnergyДокумент11 страницFACTS - Flexible Alternating Current Transmission System For Cost Effective and Reliable Transmission of Electrical EnergyYellaji AllipilliОценок пока нет
- ARTECHE CS Drivers Considerations Future Trends ENДокумент6 страницARTECHE CS Drivers Considerations Future Trends ENLuis GonzalezОценок пока нет
- Shaping The Future of Global Energy DeliveryДокумент5 страницShaping The Future of Global Energy DeliverypavantomarОценок пока нет
- 2022 Ams CSD Research Needs FinalДокумент8 страниц2022 Ams CSD Research Needs FinalSirish OrugantiОценок пока нет
- Multilevel LVDC Distribution System With Voltage Unbalancing and Disturbance Rejection Control TopologyДокумент15 страницMultilevel LVDC Distribution System With Voltage Unbalancing and Disturbance Rejection Control TopologyNexgen TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Facts and HVDC Light For Power System Interconnections Rolf Grünbaum, Bruno Halvarsson, Aleksander Wilk-Wilczynski ABB Power Systems AB, SwedenДокумент18 страницFacts and HVDC Light For Power System Interconnections Rolf Grünbaum, Bruno Halvarsson, Aleksander Wilk-Wilczynski ABB Power Systems AB, SwedenShipra DewanganОценок пока нет
- Eltek Flat Pack 2Документ44 страницыEltek Flat Pack 2Vinícius Dias Giribola100% (2)
- of The Day! - : Guide To Harmonics With AC DrivesДокумент6 страницof The Day! - : Guide To Harmonics With AC DrivesSugeng SumarnoОценок пока нет
- ECv3i1 Energy Transformation TechnologiesДокумент4 страницыECv3i1 Energy Transformation TechnologiesSreenu ThejaОценок пока нет
- Future LV Distribution Network Design PDFДокумент6 страницFuture LV Distribution Network Design PDFAlwin Anno SastraОценок пока нет
- Methods for Increasing the Quality and Reliability of Power System Using FACTS DevicesОт EverandMethods for Increasing the Quality and Reliability of Power System Using FACTS DevicesОценок пока нет
- Joint RES and Distribution Network Expansion Planning Under a Demand Response FrameworkОт EverandJoint RES and Distribution Network Expansion Planning Under a Demand Response FrameworkОценок пока нет
- PowerFactory Applications for Power System AnalysisОт EverandPowerFactory Applications for Power System AnalysisFrancisco M. Gonzalez-LongattОценок пока нет
- Power Digitization Unveiled: Navigating the Digital Frontier of EnergyОт EverandPower Digitization Unveiled: Navigating the Digital Frontier of EnergyОценок пока нет
- Recent Advances in Electrical Engineering: Applications OrientedОт EverandRecent Advances in Electrical Engineering: Applications OrientedОценок пока нет
- Tips For Daylighting 2013Документ137 страницTips For Daylighting 2013mydearteacherОценок пока нет
- Sustentabilidade Materiais Construcao 69Документ1 страницаSustentabilidade Materiais Construcao 69mydearteacherОценок пока нет
- Sustentabilidade Materiais Construcao 41Документ1 страницаSustentabilidade Materiais Construcao 41mydearteacherОценок пока нет
- Philips Lighting Manual 5ft Ed R1Документ111 страницPhilips Lighting Manual 5ft Ed R1mydearteacherОценок пока нет
- Sustentabilidade Materiais Construcao 67Документ1 страницаSustentabilidade Materiais Construcao 67mydearteacherОценок пока нет
- Siemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 514Документ1 страницаSiemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 514mydearteacherОценок пока нет
- Siemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 521Документ1 страницаSiemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 521mydearteacherОценок пока нет
- Siemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 495Документ1 страницаSiemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 495mydearteacherОценок пока нет
- Siemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 505Документ1 страницаSiemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 505mydearteacherОценок пока нет
- Siemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 506Документ1 страницаSiemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 506mydearteacherОценок пока нет
- Siemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 490Документ1 страницаSiemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 490mydearteacherОценок пока нет
- Siemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 489Документ1 страницаSiemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 489mydearteacherОценок пока нет
- As 2129-2000 Flanges For Pipes Valves and FittingsДокумент7 страницAs 2129-2000 Flanges For Pipes Valves and FittingsSAI Global - APACОценок пока нет
- Fourth Edition by William StallingsДокумент22 страницыFourth Edition by William Stallingskstu1112Оценок пока нет
- Britain'S First "Super-Car": T TH Hee A AS ST TO ON N M MA AR RT Tiin N V V88Документ4 страницыBritain'S First "Super-Car": T TH Hee A AS ST TO ON N M MA AR RT Tiin N V V88Javier RieraОценок пока нет
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationДокумент6 страницDisclosure To Promote The Right To InformationAyoub BouguernОценок пока нет
- i-MX RT1060 EVK SchematicДокумент17 страницi-MX RT1060 EVK SchematicsyntroniksОценок пока нет
- Ee Taman Juata PermaiДокумент407 страницEe Taman Juata PermaidaninoteОценок пока нет
- Career Objective: 60.20% MarksДокумент2 страницыCareer Objective: 60.20% MarksSumit JangraОценок пока нет
- C Chap08Документ25 страницC Chap08Srinidhi UpadhyaОценок пока нет
- Haad B Hospital Morgue UnitДокумент7 страницHaad B Hospital Morgue UnitIonut SomneaОценок пока нет
- BS en 10021-93 (1999)Документ20 страницBS en 10021-93 (1999)Олег СоловьевОценок пока нет
- Unified Proposal UpdatedДокумент14 страницUnified Proposal UpdatedBhattarai PrashantОценок пока нет
- 2CMC710006K0001 Phase ShifterДокумент2 страницы2CMC710006K0001 Phase ShifterpedroОценок пока нет
- 02 - Halaman JudulДокумент47 страниц02 - Halaman JudulTommy FimiОценок пока нет
- 3 Underlying TechnologiesДокумент49 страниц3 Underlying TechnologiesTutun JuhanaОценок пока нет
- Oracle Enhanced RetroPayДокумент22 страницыOracle Enhanced RetroPayhamdy200150% (2)
- SOP For CAPA Handling ProcedureДокумент17 страницSOP For CAPA Handling Procedurelounes.asma30Оценок пока нет
- Msds Aluminium FoilДокумент7 страницMsds Aluminium FoillatifahОценок пока нет
- THK LM Guide SystemДокумент668 страницTHK LM Guide SystemSzabo CsabaОценок пока нет
- Afl Fsm-60s Splicer Spec SheetДокумент2 страницыAfl Fsm-60s Splicer Spec SheetFiberOpticStockCoОценок пока нет
- Ewo PDFДокумент2 страницыEwo PDFKellyОценок пока нет
- EUWA ES 3.08 Wheel and Rim Markings.Документ4 страницыEUWA ES 3.08 Wheel and Rim Markings.Gopu PushpangadhanОценок пока нет
- Highway SpecificationДокумент85 страницHighway SpecificationAkaninyeneОценок пока нет
- CL AssignmentДокумент64 страницыCL AssignmentJitul RajbongshiОценок пока нет
- UG - CAO.00014 Foreign Part 147 Approvals User Guide For MTOEДокумент70 страницUG - CAO.00014 Foreign Part 147 Approvals User Guide For MTOEDiana DumitracheОценок пока нет
- DBS3900 GSM Technical Description (V100R012 - 06) (PDF) - enДокумент89 страницDBS3900 GSM Technical Description (V100R012 - 06) (PDF) - enadnantk01Оценок пока нет
- 250 K WДокумент17 страниц250 K WTapan KapoorОценок пока нет
- Nginx Modules Reference r3Документ243 страницыNginx Modules Reference r3No NameОценок пока нет
- Fence ProjectДокумент15 страницFence ProjectAhmad Ramin Abasy100% (1)
- 1100 Series PerkinsДокумент2 страницы1100 Series PerkinsGilberto Diaz CastilloОценок пока нет
- Pres 2Документ15 страницPres 2Karim MagdyОценок пока нет