Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Italy Report
Загружено:
vttrlcОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Italy Report
Загружено:
vttrlcАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
STATUS REPORT ON LIGHT WATER REACTOR ACTIVITY IN ITALY
Fosco Bianchi ENEA Report for IAEA -TWG - LWR 15th Meeting (Vienna, 26-28 July 2010) 1. The Italian Electricity Market In 2009, electricity demand decreased by 5.7% on the previous year reaching 320,3 TWh, as consequence of economic crisis. It was covered by domestic generation (86.7%) and by imports (13.3%) from neighbouring countries (France, Switzerland, Austria, Slovenia and Greece). It is worth underlining that this drop was an event unique for its intensity, as a decrease of comparable size happened at the beginning of 50. In regard to the gross electricity production in 2008, the generation by thermal sources decreased of 13,3%, whereas the renewable1 source was up by about 18,8%. In particular the increase was particularly significant for wind (+34,6%; production in 2009 equal to about 6.5 TWh) and photovoltaic generation (+250.6%; 2009 production: 0,68 TWh), whilst geothermal generation had a moderate decrease (3.2%: production in 2009 equal to about 5.3 TWh). The hydro sources rose to 13,2%. Net import/export balance increased by about 12.3% on 2008; in particular the import increased by 8.4%, while the export were down by 37.9% (2.1 TWh against 3.4 TWh in 2008). It is worth underlining that the net import of electricity is mainly of nuclear origin. With regard to the fuels dependency, natural gas source has confirmed its leading role in thermal generation, even if the power generated by natural gas in 2009 decreased to a share of 44,1% of the gross total production. Natural gas and oil consumption for electric power generation decreased in 2009 by 14,9% and 17,8%, respectively compared to 2008. Therefore the diversification of energy sources is a key point for the Italian policy and long-term strategy, of not easy solution owing to constraints deriving from the liberalization of the electric market, the mitigation of the climate change and the nuclear energy acceptability. Table 1 summarizes production data for the period (2002 2009). In 2009 the installed capacity rose by 2.9% (2.8 GW) reaching a value of 101.4 GW, thanks to renewable plants (wind and photovoltaic) got in operation. Industry remains the sector with the greater share on the electricity consumption (43,5%), service industries occupies the second place (31,6%), farming (1,9%) and domestic use (23,0%). In any case service industries had the better performance compared to 2008 (+1,3%), folowed by domestic use (0.8%), instead the consuptions of industry and farming decreased by 13,8% and 0.3%, respectively. 10 region out of 20 were in deficit of production (3 with a deficit greater than 50%).
Wind, photovoltaic and geothermal
2. Meaningful event on nuclear energy source Some meaningful events may be interpreted as a concrete step towards the renaissance of nuclear in Italy: the publication on the Official Gazette n. 195 (August 21, 2008) of the law 6 August 2008, n.133, Urgent provisions for economic development, simplification, competitiveness, the stabilization of public finance and tax equalization, which stated the renaissance of nuclear energy, because it announced for the first time after the 1987 moratorium a new national energy plan with the goal of implementing nuclear power plants in the national territory and promoting also research on Generation IV nuclear systems and nuclear fusion; the promulgation of the Law 23 July 2009, n. 99, Provisions for the development and internationalization of enterprises, and energy, which, among other initiatives, provides the key elements for the nuclear renaissance in Italy. In particular the law introduces the following significant facts: 1. The Government is entitled to establish: a. Legislative procedures for NPPs as well as nuclear fuel fabrication facilities, radioactive wastes and spent fuel storage and disposal facilities siting and licensing; b. Compensatory measures for the involved stakeholders; c. A unified licensing process; d. Decommissioning funding scheme; e. A communication campaign. 2. CIPE (Interministerial Committee for Economic Planning) shall define acceptable plant designs for the new NPPs and the criteria to promote the constitution of consortia; 3. Establishment of a new independent Nuclear Safety Agency; 4. Reorganization new mission of SOGIN; 5. Establishment of the National Agency for New Technologies, Energy and Sustainable Economic Development, which maintain the same acronym of the former ENEA; 6. Promotion of innovation in the nuclear sector. the issuing the law by decree 15 February 2010, n. 31, published in the Official Gazette n 55 of 8 March, 2010, intitled Regulation on siting localization, realization and operation of NPPs for electricity production in the national territory, of nuclear fuel fabrication facilities, of spent fuel storage and radioactive wastes disposal facilities, as well as compensatory measures for the involved stakeholders and communication campaign, in accordance with Art. 25 of the law 23 July 2009, n. 99, which establishes: 1. A new licensing process for NPPs, which implies a single license, combining the current parallel licensing processes and encompassing also the EIA (Environmental Impact Assessment); 2. Qualification of nuclear operators in the various nuclear fields: 3. Decommissioning funds have to be accumulated on the basis of an initial, periodic and final assessment of the actual decommissioning costs that will be defined by SOGIN and approved by the Energy Authority; 4. Substantial economic incentives are indicated in the areas where new NPPs will be installed for persons, industries and institutions; 5. The process to identify a site for the national radioactive waste repository to host existing and future radioactive wastes; it will provide a disposal site for LILW and an interim storage facility for HLW and spent fuel: 6. On the same site a Technology Park will be built, including a Center for Studies and Tests;
7. The licensing processes for the repository and for the Technology Park for temporary storage of spent nuclear fuel and high level radioactive wastes, and for disposal of intermediate and low level radioactive wastes, as well as relevant scientific research and technological development; 8. Public participation and information with regard to radioactive waste and spent fuel management policies is also mandated by the law. the publication on the Official Gazette n.156 on July7, 2010 of the legislative decree n., April 27, 2010 Approval of the statute for Nuclear Safety Agency, which is the only national authority for safety, security, safeguards and radioprotection.
In addition the Government is committed to issue a nuclear strategy document that will include criteria for site selection in terms of population and socio-economic parameters, earthquake intensity and hydrology among others. Utilities will then be able to present plans for development within these suitable areas. It is anticipated that the Government position will be considering 2 technologies as compatible with its plans that envisage 8 nuclear units; in particular it is conceivable that both EPR and AP1000 could be acceptable in the Government strategy. Important bilateral agreements were signed by the Government with France, Japan, USA and Russia, which have been the background for several bilateral agreements at industrial and R&D levels. Ansaldo, ENEL, SOGIN, ENEA and CIRTEN (a university consortium) had signed agreements with corresponding French organizations. Meanwhile the industry is preparing for the new nuclear season. The engineering and manufacturing industries are checking their full compliance with the qualification rules for nuclear supplies. It is the Government goal that the vast majority of new NPPs supplies should be provided in Italy. On the utility side ENEL has signed a strong cooperation strategic plan with EdF and it is committed to build EPR units. A second utility, and maybe a users/investors consortium may be created and it is possible that it will choose a different technology.
3 Activities on LWRs and HWRs The Italian commitment in nuclear fission field has been maintained by ENEA, universities, research companies, industries (ANSALDO Nucleare, Mangiarotti Nuclear, etc.), ERSE, SOGIN and ENEL. It has dealt with the development of nuclear technology, advanced nuclear reactor systems, waste management, fuel cycles, participation in international and European programmes, as well as construction, refurbishment and operation of nuclear power plants abroad, and decommissioning activities. 3.1 ENEAs activities Art. 37 of the above-mentioned law 99/2009 has established that the new ENEA (the former National Agency for New Technologies, Energy and the Environment) becomes the Italian National Agency for New Technologies, Energy and Sustainable Economic Development. In this context, ENEAs main activities are research, innovation technology and advanced services in the energy field - especially nuclear energy - and sustainable economic development . ENEA's definition and organizational process will be finalized by an ad-hoc Law by Decree of Ministry of Economic Development. The ENEA R&D activities on nuclear fission are mainly set in the frame of European and International projects as well as of a three-year R&D national programme based on strategic funding devoted to the National Electric System R&D and focused on the participation to 4
international initiatives like INTD (International Near Term Deployment) and Generation IV nuclear systems. Other important topics that the new ENEA intends to pursue and to reinforce, concern the scientific and technical support to the Nuclear Safety Agency and some scientific key issues related to waste management and the advanced nuclear fuel cycles, scenario studies and, last but not least, Education & Training and communication in the nuclear field. The national programme is being managed through a specific agreement between Ministry of Economic Development (MED) and ENEA, with the joint involvement of CIRTEN (Italian Universities Consortium for Research in Nuclear Technologies), and SIET (an ENEA subsidiary small and medium sized enterprise). The programme is yearly funded at the level of about 6 million Euro and involve about 200 persons. It has been organized into six main domains: Studies on nuclear energy at large, scenario studies, nuclear fuel cycle and proliferation, advising to the concerned National Authorities / Ministries; INTD Reactors, especially concentrated on the International Reactor Innovative and Secure (IRIS), which is an innovative PWR with a modular and integral primary system configuration that satisfies four key requirements: enhanced safety, improved economics, proliferation resistance and waste minimization; Generation IV Systems: Lead-cooled Fast Reactor (LFR), Sodium Fast Reactor (SFR) and Very High Temperature Reactor (VHTR); Scientific support for the activities aimed at location, choice, designing and building of the nuclear waste national repository; Support to the Nuclear Safety Agency for licensing of GENIII reactors in Italy; Education and Communication. The competences and capabilities being developed through the MED-ENEA agreement also represent the essential scientific and technical background to support the new nuclear energy government policy, in view of the planned Nuclear Power Plants realizations in Italy at the horizon of 2020. The national programme is also intended to be synergic and coherent with the Generation IV International Forum (GIF) initiative, as well as with a number of projects of the Euratom Framework Programmes in the field of innovative systems and advanced fuel cycles, which ENEA is significantly contributing to. As far as the design certification of the IRIS reactor, ENEA activities are mainly focused on an appropriate integral testing programme to be performed in the SPES-3 facility to be built at the SIET laboratories in Piacenza. Once erected, the facility will simulate IRIS at full height, full pressure and temperature and with volumes and power scaled by factors of 1:100 and 1:150, respectively. The activity is being carried out in the frame of a collaboration with the Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) of US-DOE (United States Department of Energy). Other activities in support to IRIS design concern the plant seismic isolation system, the shielding analyses and the development of key components like the Steam Generator and the Emergency Heat Removal System. In view of the possible ENEA role of Technical Safety Organization in support to the national Nuclear Safety Agency other activities are focused on studies on nuclear safety concerning accident analysis, accident management, severe accidents, reliability and risk analysis, performed within programmes launched by IAEA, NEA-OECD and EU FP, such as the European Severe Accident Research Network of Excellence (SARNET) and ASAMPSA2 (Advanced Safety Assessment Methodologies: Level 2 PSA). Finally, ENEA is member of the European Sustainable Nuclear Energy Technology Platform (SNETP) and of the European Sustainable Nuclear Industrial Initiative (ESNII). In particular, ENEA has significantly contributed to the two fundamental reports of SNETP, namely the Vision 5
Report and the Strategic Research Agenda that address the key issues of fission technologies, as acknowledged in the so-called European Strategic Energy Technology Plan (SET-Plan). ENEA is also participating to the other two most important international initiatives on sustainable nuclear fission, i.e. the Global Nuclear Energy Partnership (GNEP) launched by the US Administration and the International Project on Innovative Nuclear Reactors and Fuel Cycles" (INPRO) under the auspices of the IAEA. 3.2 University activities Besides doing their institutional task in the field of education on nuclear engineering, the universities are participating in both the design of nuclear plants (IRIS and ATUCHA) and researches in specific topics. The main activities in support to the IRIS design are performed by CIRTEN and concern the development of key components (Steam Generator, Emergency Heat Removal System, instrumentation for two-phase flow measurement and reactor vessel downcomer and bottom) by means of experimental campaign, besides seismic analyses of containment and auxiliry building and fragility analysis of equipment components to be considered as a step of seismic PSA. University of Pisa is engaged on the safety analysis of the ATUCHA II PHWR plant and the editing of the Chapter 15 of the Safety Analysis Report, validation of codes against operational transients in Darlington reactor (Canada), seminar and training on scaling, uncertainty and 3-D coupled code calculations in nuclear technology, experimental and analytical analyses on condensation with noncondensable gases in the frame of SARNET project, heat exchange and stability analysis in heated channels for Water reactors at pressure higher than critical (SCWR)2 and partecipation in the IAEA CRP on SCRW design. POLIMI has performed an application of the Emergency Plan Zone (EPZ) methodology to NPPs of Generation II and III in function of plant safety level. University of Rome La Sapienza has carried out neutronic analysis of a SMR core with the purpose of eliminating the chemical c control and reaching high burn-up. 3.3 Industrial and research company activities The company activities on nuclear fission fields have been mainly carried out by Ansaldo Nucleare (ANN), Societ Italiana Esperienze Termoidrauliche (SIET), Mangiarotti Nuclear and ERSE. ANSALDO Nucleare activities The main activities have concerned: Service on Cernavoda Unit 1& 2 (Romania); IRIS plant: design of steam generators; AP 1000: Ansaldo has been involved and is still cooperating with Westinghouse in the following areas: lay-out engineering, piping analysis, structural analysis, PRHR systems, primary containment, equipment access and air-locks and in joint venture with Mangiarotti Nuclear it is responsible of the supply of the containment and PRHR systems and of the technological transfer on different themes: manufacturing, construction, containment and vessel design; Plant Life Extension study for Embalse (Argentina): verification that class-3 SDG (Stand-byDiesel Generators) manoeuvring sequence performances match with original design
A cooperation agreement is presently active with Tsinghua University in Beijing (China). The cooperation for the years (20062009) is financed by the Italian Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MAE) and the Government of Popular Republic of China. In the agreement it is foreseen that Tsinghua University will provide experimental data to be analysed by the University of Pisa with computational tools. Furthermore an inter-University agreement has been recently signed for the years 2007 and 2008 with the Shanghai Jiao Tong University also relating to matters relevant to the design of SCWRs.
requirements (2008-2009); BOP service within the outage 2010 oriented to carry out the intervention planned to get the required life extension; Mochovce 3 & 4: ENEL engineering service: home design activity, technical assistance for the following areas: QA, planning, process machinery, circuit lay-out, I&C, erection, QA survewillance and commissioning; Decommissioning activities for Italian plants: Trino, Caorso, Latina, CISAM reactor (secondary cooling system).
MANGIAROTTI Nuclear activities Besides the activities in China for the construction of AP 1000 NPPs, Mangiarotti has been awarded contracts: in 2008 for design and fabrication of the stainless steel pressure vessels and tanks for Flamanville-3 EPR plant; in 2009 to fabricate Low and Intermediate Level Waste canisters for the Decommissioning activity to be performed by Sogin: in 2009 a contract for the realization of casks by AREVA-TM SIET activities SIET has ben involved in the detailled design of the experimental facility SPES-3 simulating IRIS plant, realization of a facility for testing heater rods simulating the IRIS core, studies in support to the development of two flow instrumentation, besides study for refurbishement of all facilities (IETI, SPES, etc.) to be used for the qualification of components and systems of GEN III NPPs to be erected in Italy. ERSE activities ERSE has organized its nuclear researches in the view of possible new installations in the Italian electricity system. Efforts have been dedicated to the assessment of reactor physics models in order to develop a fastrunning methodology for reproducing the core behavior in support to LEGO-PST, a proprietary tool for real-time simulation of the whole plant. In the field of safety, studies have been focused to revise the methodology for the core degradation analysis, risk of fuel recriticality, corium coolability and evolution of containment atmosphere following a severe accident (in connection with the EU project ASAMPSA2). A validation campaign on aerosol transport models for the evaluation of source term has been carried out in support to the development of the proprietory code ECART, paying particular attention to the resuspension phenomenon and to the retention of radioactive particulate within containment concrete cracks (in connection with the EU project SARNET, and in cooperation with the Finnish VTT and the French CEA). Further activities have been managed to evaluate the requirements of the Italian electric grid, as well as the qualification of electric components, in the light of future connections of large nuclear power plants like EPR and AP1000. 4. SOGIN activities SOGIN SpA (Nuclear Installation Management Company) has been created in 1999 in the framework of the National electric system reform and its main mission has been the decommissioning of the Italian nuclear installations, both the NPPs definitely stopped as a consequence of a Government decision subsequent to a Post-Chernobyl referendum in 1987 and the ENEA nuclear research installations. The Decree by Law 15 February 2010, n. 31 has expanded its mandate, as indicated below:
All radioactive wastes generated during future plant operation will be transferred to SOGIN for disposal SOGIN has the responsibility of identifying a site, design, build and operate a large Technology Park, that will be a boost for R&D as well as industrial applications in the area of decommissioning and waste management as well as in other adjacent areas On the same site a national repository for low and intermediate level wastes as well as an interim storage for high level wastes will be designed, built and operated by SOGIN. The Technology Park will also be a centre for education and training of the new resources interested to work in the nuclear field The Technology Park constitutes a key element not only for the acceptance of the integrated waste storage facilities by the population, but also for the development of the nuclear energy in Italy: the R&D activities will included decommissioning, waste management and radioprotection researches, but also advanced activities such as partitioning, transmutation and studies for an ADS reactor with the objective of waste burning. The Park will be also be a an education and training pole where Italian and international researchers, universities and industrial realities will come together in order to create opportunities and spin-off companies, with the ultimate goal of becoming an excellence centre for Italy and both collaborate and rival with its European counterparts. Without doubt the most important new element outlined by the recently re-introduced Italian nuclear option is the mandate given to SOGIN to developed the Technology Park (PTN) which, as outlined earlier, will be at the same time a R&D centre, a training and human resources development structure, the site for the national repository and the place for the centralized interim storage facility for the Italian high level waste. In parallel with the research activities and in order to draw from the experience of the researches and highly specialized personnel that will be present at the site, a national training centre will be established with the aim to become an element of excellence for radioprotection and nuclear safety. It will become a reference centre for all organizations that are active in the nuclear field, including institutions, industry, operators and universities as well both in Italy. Relationship with similar centres in other countries will place this centre in an international networking which is essential for the development of nuclear energy. The transportation of Caorso NPPs spent fuel to AREVAs facilities continued and it is planned to be concluded by early summer 2010. The transfer of Caorsos fuel will mark the removal from the national territory of all spent fuel with the exception of 64 elements of Uranium/Thorium (originally irradiated in the US Elk River power reactor), which is currently stored in the ITREC plant pool. For these elements, several options are being considered, included repatriation to the USA and dry storage on site, while the national interim storage site for HLW will be established. The decision to build a national repository for radioactive waste has provided some planning and strategic elements that were not available before. However, a number of urgent issues have to be solved before the availability of the repository in order to allow for the continuation of the decommissioning activities. At the end of 2009 a contract, conditional on the full approval by all national authorities involved, has been signed with Energy Solutions for the transfer and subsequent disposal of 1.600 t of low activity radioactive waste to USA. The decision has been reached on the basis of a detailed costbenefit analysis. In order to address the issue of organic wastes, SOGIN started the design and implementation of a Wet Oxidation Process at the Trino site in cooperation with Ansaldo Nucleare and Granit 8
Technologies, a Swiss independent company. In particular, Sogin will develop the system to extract the resins from their current containers and the post-treatment system for process residues. It will also handle approval procedures and ensure that the materials resulting from treatment comply with requirements for its disposal. Design and construction of two cementation facilities for the high level liquid wastes existing on the Saluggia and Trisaia sites is still ongoing, while a review and improvement of the Overall Decommissioning Plans of the ENEA research sites has been started with the important support of the extensive experience and considerable capabilities of UKAEA. Last year has been particularly important for SOGIN both for the satisfactory progress of the decommissioning activities in all the 8 managed sites. The most significant in terms of complexity, technological challenges and innovation are the following: Trino NPP: while the entire decommissioning program has been accelerated and its conclusion has been moved backward from 2018 to 2013, the decommissioning license is still pending; however, a number of activities proceeded on the basis of specific special authorizations. Caorso NPP: in addition to the removal of the spent fuel as detailed earlier, major asbestos removal works have been carried out over the whole plant, but in particular from the off-gas system, whose active charcoal has been removed and whose stack has been dismantled. Moreover, the dismantlement of the turbine building thermal cycle piping and equipment started, while Sogin presented the license application for the Phadec chemical decontamination system. Latina NPP has mainly seen the continuation of works started in 2008 and in particular the characterization of the lower ducts of the primary circulation system, the dismantling of the upper ducts, the construction of the interim storage building and of a building dedicated to treatment and conditioning of operational radioactive sludges, the sludge extraction system, a cementation facility and finally a storage building of the cemented wastes. One of the major problems still under investigation with the cooperation of other operators in France, Spain and UK is the treatment and disposal of the irradiated graphite of the reactor core. This remains one of the outstanding issue for the completion of a decommissioning plan of a gas-graphite reactor. Garigliano NPP: asbestos removal continued on the primary system inside the primary containment. Upgrading of auxiliary systems in the containment is continuing. Also field preparation for the construction of the new waste interim storage building has been completed. Operational waste trench remediation is continuing. Major activities carried out at the various fuel cycle facilities in 2009 have been: the completion of the mock up trials for the high level liquid waste cementation plant and the award of the contract for the construction of the plant in Trisaia. In addition the design for the removal of the underground cemented block of operational wastes. the upgrade of the fire-extinguishing system (estimated to be completed in mid 2010) of the plutonium facility in Casaccia and the tests for the dismantlement of plutonium glove boxes. the procedures of characterization, treatment and decontamination of the pool leak collection gap and the new water supplying system were completed at the EUREX site in Saluggia. the dismantling of the production line at Bosco Marengo facility has been completed, leaving only the ventilation system to be removed to complete the site decommissioning.
Вам также может понравиться
- Rosk Slope StabilityДокумент2 страницыRosk Slope StabilityvttrlcОценок пока нет
- RR207Документ48 страницRR207vttrlcОценок пока нет
- Ground Vibrations Associated With Installing EnlarДокумент8 страницGround Vibrations Associated With Installing EnlarvttrlcОценок пока нет
- Svinkin 2006Документ15 страницSvinkin 2006vttrlcОценок пока нет
- Angular Distortion Structures Pointv Linear GuideДокумент13 страницAngular Distortion Structures Pointv Linear GuideFrancisco Ordoñez MuñozОценок пока нет
- The PAntheon in RomeДокумент14 страницThe PAntheon in Romevttrlc100% (1)
- Impacts From Three-Dimensional Effect On The Wall Deflection Induced by A Deep Excavation in Kaohsiung, TaiwanДокумент6 страницImpacts From Three-Dimensional Effect On The Wall Deflection Induced by A Deep Excavation in Kaohsiung, TaiwanvttrlcОценок пока нет
- Dynamic Increase Factors For ConcreteДокумент18 страницDynamic Increase Factors For ConcreteSindy Puello LópezОценок пока нет
- Excavation Induced Building Response by Laminate Beam MethodДокумент6 страницExcavation Induced Building Response by Laminate Beam MethodvttrlcОценок пока нет
- MULTIPLE ROOTS REVERSE CUTHILL-McKEE MET PDFДокумент10 страницMULTIPLE ROOTS REVERSE CUTHILL-McKEE MET PDFvttrlcОценок пока нет
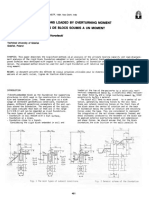
- Design of The Foundations Loaded by Overturning Moment Stabilite Des Fondations de Blocs Soumis A Un MomentДокумент4 страницыDesign of The Foundations Loaded by Overturning Moment Stabilite Des Fondations de Blocs Soumis A Un MomentvttrlcОценок пока нет
- Remap:: A Computer Code That TransfersДокумент26 страницRemap:: A Computer Code That TransfersvttrlcОценок пока нет
- Profile Front MinimizationДокумент12 страницProfile Front MinimizationvttrlcОценок пока нет
- Dynamic Increase Factors For ConcreteДокумент18 страницDynamic Increase Factors For ConcreteSindy Puello LópezОценок пока нет
- A146814 PDFДокумент82 страницыA146814 PDFvttrlcОценок пока нет
- b001855 PDFДокумент148 страницb001855 PDFvttrlcОценок пока нет
- Dynamic Increase Factors For ConcreteДокумент18 страницDynamic Increase Factors For ConcreteSindy Puello LópezОценок пока нет
- Dtic Ada114540 PDFДокумент151 страницаDtic Ada114540 PDFvttrlcОценок пока нет
- MP Avt 265 06 PDFДокумент18 страницMP Avt 265 06 PDFvttrlcОценок пока нет
- Explosion Damage Assessment - and Structural Inte'Lpity EvaluationДокумент46 страницExplosion Damage Assessment - and Structural Inte'Lpity EvaluationvttrlcОценок пока нет
- Explosion Damage Assessment - and Structural Inte'Lpity EvaluationДокумент46 страницExplosion Damage Assessment - and Structural Inte'Lpity EvaluationvttrlcОценок пока нет
- MP Avt 265 06 PDFДокумент18 страницMP Avt 265 06 PDFvttrlcОценок пока нет
- Dtic Ada066998Документ274 страницыDtic Ada066998vttrlcОценок пока нет
- Egu2016 11390Документ1 страницаEgu2016 11390vttrlcОценок пока нет
- DemДокумент1 страницаDemvttrlcОценок пока нет
- STR95029FU2Документ7 страницSTR95029FU2vttrlcОценок пока нет
- Plastic-Damage Macro-Model For Non-Linear Masonry Structures Subjected To Cyclic or Dynamic LoadsДокумент8 страницPlastic-Damage Macro-Model For Non-Linear Masonry Structures Subjected To Cyclic or Dynamic LoadsvttrlcОценок пока нет
- Fahrman BP D 2016Документ206 страницFahrman BP D 2016vttrlcОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Case AnswersДокумент1 страницаCase Answersearth2558Оценок пока нет
- ABAP Hints and Tips - Adding Custom Fields To POs, Outline Agreements, and RFOsДокумент1 страницаABAP Hints and Tips - Adding Custom Fields To POs, Outline Agreements, and RFOsccnicola2Оценок пока нет
- Master of Education USMДокумент2 страницыMaster of Education USMArchana MunusamyОценок пока нет
- Amh Studie MenopauseДокумент1 страницаAmh Studie Menopausevibe1Оценок пока нет
- Johari Window: A MODEL of Self Awareness, Personal Development, Group Development and Understanding RelationshipДокумент17 страницJohari Window: A MODEL of Self Awareness, Personal Development, Group Development and Understanding RelationshipShalvvОценок пока нет
- BCTRDC Strategic PlanДокумент7 страницBCTRDC Strategic PlanbalondojeremyОценок пока нет
- Management AccountingДокумент5 страницManagement AccountingKen LunОценок пока нет
- Simplex Method (Minimization Example) : Object FunctionДокумент6 страницSimplex Method (Minimization Example) : Object FunctionDarya MemonОценок пока нет
- List of Directors of DrdoДокумент6 страницList of Directors of Drdolund0% (1)
- Water Technology Initiative (Wti) : Broad Topics of RelevanceДокумент26 страницWater Technology Initiative (Wti) : Broad Topics of RelevanceKalimuthu PaulpandianОценок пока нет
- S Wave AntennaДокумент102 страницыS Wave AntennaQuan LuongОценок пока нет
- Technology EntrepreneurshipДокумент2 страницыTechnology Entrepreneurshipnur nadia natashaОценок пока нет
- 5 Programme Schedule 30th Oct 2015 FinalДокумент4 страницы5 Programme Schedule 30th Oct 2015 FinalArchana TiwariОценок пока нет
- BRAHMOS History - Monika ChansoriaДокумент5 страницBRAHMOS History - Monika ChansoriaEdson Neves Jr.Оценок пока нет
- University of Sargodha (Main Campus) BS Botany Regular 3rd Merit List 2018-636807805789906224Документ2 страницыUniversity of Sargodha (Main Campus) BS Botany Regular 3rd Merit List 2018-636807805789906224Umer FarooqОценок пока нет
- Projective TechniquesДокумент11 страницProjective TechniquesSwarnim SrivastavaОценок пока нет
- Iterative and Incremental DevelopmentДокумент4 страницыIterative and Incremental DevelopmentheenadttОценок пока нет
- NSTP2Документ4 страницыNSTP2Poy Mariano AdesОценок пока нет
- National Apprenticeship Training Scheme (NATS) Aspirations DetailsДокумент1 страницаNational Apprenticeship Training Scheme (NATS) Aspirations DetailsArjun KrishnaОценок пока нет
- Anderson Manufacturing and Development CoДокумент9 страницAnderson Manufacturing and Development CoShivanjali KambleОценок пока нет
- Global Orphan Drug Pipeline AnalysisДокумент0 страницGlobal Orphan Drug Pipeline AnalysisNeeraj ChawlaОценок пока нет
- Horizon 2020 Project Factory - Smart Manufacturing ProgrammeДокумент2 страницыHorizon 2020 Project Factory - Smart Manufacturing ProgrammeManuelaОценок пока нет
- MBR NetworkДокумент4 страницыMBR NetworkSam YoonОценок пока нет
- 863 Project ChinaДокумент3 страницы863 Project ChinaAvinash KumarОценок пока нет
- Unique Properties of All Stem Cells PDFДокумент1 страницаUnique Properties of All Stem Cells PDFExicanLifeSciencesОценок пока нет
- Advocacy Versus Inquiry in A Group Decision MakingДокумент5 страницAdvocacy Versus Inquiry in A Group Decision MakingLuis NashОценок пока нет
- 브릭스 리딩 150 Bricks Story Reading 150 Level 1Документ69 страниц브릭스 리딩 150 Bricks Story Reading 150 Level 1giayoonnaОценок пока нет
- DRDOДокумент8 страницDRDOPiyush BhattОценок пока нет
- WaKIDS AssessmentДокумент1 страницаWaKIDS Assessmentsunnews820Оценок пока нет