Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
P2 Forces and Terminal Velocity Intermediate
Загружено:
downendscienceИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
P2 Forces and Terminal Velocity Intermediate
Загружено:
downendscienceАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
P2 Forces and Terminal Velocity
Intermediate
75 minutes
75 marks
Page 1 of 16
Q1.
A mans car will not start, so two friends help him by pushing it.
By pushing as hard as they can for 12 seconds they make the car reach a speed of
3 metres per second.
(a)
Calculate the acceleration they give to the car.
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................. Answer ................ m/s2
(2)
(b)
Whilst pushing the car the two friends together do a total of 2400 joules of work.
Calculate their total power.
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................ Answer ................ watts
(2)
(c)
Another motorist has the same problem. The two friends push his car along the same
stretch of road with the same force as before.
It takes them 18 seconds to get the second car up to a speed of 3 metres per second.
What does this tell you about the mass of the second car?
(You can ignore forces of friction.)
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
(2)
Page 2 of 16
(d)
On a flat stretch of a motorway a lorry driver changes into top gear. He then makes the
lorry go as fast as he can.
The graph shows what happens to the speed of the lorry.
Explain why the speed of the lorry increases at first but then levels out.
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
(3)
(Total 9 marks)
Q2.
A sky-diver steps out of an aeroplane.
After 10 seconds she is falling at a steady speed of 50m/s.
She then opens her parachute.
After another 5 seconds she is once again falling at a steady speed.
This speed is now only 10m/s.
(a)
Calculate the sky-divers average acceleration during the time from when she opens her
parachute until she reaches her slower steady speed. (Show your working.)
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(3)
Page 3 of 16
(b)
Explain, as fully as you can:
(i)
why the sky-diver eventually reaches a steady speed (with or without her parachute).
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(3)
(ii)
why the sky-divers steady speed is lower when her parachute is open.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(c)
The sky-diver and her equipment have a total mass of 75kg. Calculate the gravitational
force acting on this mass. (Show your working.)
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
Answer ........................................ N
(1)
(Total 8 marks)
Q3.
A book weighs 6 newtons.
A librarian picks up the book from one shelf and puts it on a shelf 2 metres higher.
Page 4 of 16
(a)
Calculate the work done on the book. [Show your working].
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(3)
(b)
The next person to take the book from the shelf accidentally drops it.
The book accelerates at 9.8m/s.
Use this information to calculate the mass of the book. [Show your working].
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
Answer ................................. kg.
(3)
(c)
If the book was dropped from an aeroplane high in the sky, it would accelerate to
begin with. Eventually it would fall at a steady speed.
Explain, in as much detail as you can, why this happens.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(3)
(Total 9 marks)
Page 5 of 16
Q4.
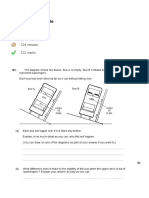
When a bungee-jump is made the jumper steps off a high platform. An elastic cord from the
platform is tied to the jumper.
The diagram below shows different stages in a bungee-jump.
Forces A, B and C are forces acting on the jumper at each stage.
(a)
Name force A.
....................................................................................................................................
(1)
(b)
The motion of the jumper is shown in the diagrams.
By comparing forces A, B and C, state how the motion is caused in:
(i)
diagram X;
............................................................................................................................
(ii)
diagram Y;
............................................................................................................................
(iii)
diagram Z.
............................................................................................................................
(3)
Page 6 of 16
(c)
The table gives results for a bungee cord when it is being stretched.
STRETCHING FORCE (N)
100
200
400
600
800
LENGTH OF CORD (m)
20
24
32
40
48
(i)
Plot a graph of these results on the graph paper.
(3)
(ii)
Use the graph to find the length of the cord before it was stretched.
Length .................... m
(1)
(Total 8 marks)
Page 7 of 16
Q5.
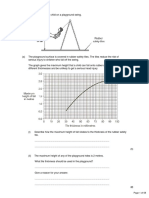
A hot air balloon called Global Challenger was used to try to break the record for travelling
round the world.
The graph shows how the height_ of the balloon changed during the flight.
The balloon took off from Marrakesh one hour after the burners were lit and climbed rapidly.
(a)
Use the graph to find:
(i)
the maximum height_ reached.
Maximum height_ .............................. metres.
(ii)
the total time of the flight.
Total time ........................................... hours.
(2)
(b)
Several important moments during the flight are labelled on the graph with the letters A, B,
C, D, E and F.
At which of these moments did the following happen?
(i)
The balloon began a slow controlled descent to 2500 metres. ........................
(ii)
The crew threw out all the cargo on board in order to stop
a very rapid descent.
.......................
(iii)
The balloon started to descend from 9000 metres.
.......................
(3)
(Total 5 marks)
Page 8 of 16
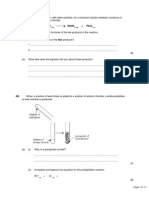
Q6.
A sky-diver jumps from a plane.
The sky-diver is shown in the diagram below.
(a)
Arrows X and Y show two forces acting on the sky-diver as he falls.
(i)
Name the forces X and Y.
X ..........................................................
Y ..........................................................
(2)
(ii)
Explain why force X acts in an upward direction.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(iii)
At first forces X and Y are unbalanced.
Which of the forces will be bigger? .......................................
(1)
(iv)
How does this unbalanced force affect the sky-diver?
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
Page 9 of 16
(b)
After some time the sky-diver pulls the rip cord and the parachute opens.
The sky-diver and parachute are shown in the diagram below.
After a while forces X and Y are balanced.
Underline the correct answer in each line below.
Force X has
increased / stayed the same / decreased.
Force Y has
increased / stayed the same / decreased.
The speed of the sky-diver will
increase / stay the same / decrease.
(3)
Page 10 of 16
(c)
The graph below shows how the height_ of the sky-diver changes with time.
(i)
Which part of the graph, AB, BC or CD shows the sky-diver falling at a
constant speed?
................................................
(1)
(ii)
What distance does the sky-diver fall at a constant speed?
Distance .............................. m
(1)
(iii)
How long does he fall at this speed?
Time .................................... s
(1)
Page 11 of 16
(iv)
Calculate this speed.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
Speed .............................. m/s
(2)
(Total 14 marks)
Q7.
(a) When a car is driven efficiently the engine gives a constant forward pull on the car as
the car accelerates to its maximum speed. During this time frictional forces and air
resistance oppose the forward motion of the car. The sketch graphs below show how the
cars speed increases when only the driver is in the car, and when the driver has a
passenger in the car.
(i)
How does the acceleration of the car change with time?
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii)
What conclusion can be made about the resultant (net) forward force on the car as
its speed increases?
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
Page 12 of 16
(ii)
On the graph, draw a line to show how you would expect the cars speed to vary if it
carried three passengers.
(1)
(b)
The manufacturer of a family car gave the following information.
Mass of car 950g
The car will accelerate from 0 to 33 m/s in 11 seconds.
(i)
Calculate the acceleration of the car during the 11 seconds.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
Answer .....................................................
(2)
(ii)
Calculate the force needed to produce this acceleration.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
Answer .................................. N
(2)
(iii)
The manufacturer of the car claims a top speed of 110 miles per hour. Explain why
there must be a top speed for any car.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 9 marks)
Q8.
(a)
The diagram shows the horizontal forces that act on a moving motorbike.
Page 13 of 16
(i)
Describe the movement of the motorbike when force A equals force B.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(ii)
What happens to the speed of the motorbike if force B becomes smaller
than force A?
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(b)
The graph shows how the velocity of a motorbike changes when it is travelling along a
straight road.
(i)
What was the change in velocity of the motorbike in the first 5 seconds?
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii)
Write down the equation which links acceleration, change in velocity and time taken.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(iii)
Calculate the acceleration of the motorbike during the first 5 seconds.
Show clearly how you work out your answer and give the unit.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
Acceleration = .............................................
(3)
Page 14 of 16
(c)
A car is travelling on an icy road.
Describe and explain what might happen to the car when the brakes are applied.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(d)
Name three factors, other than weather conditions, which would increase the overall
stopping distance of a vehicle.
1 ..................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
2 ..................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
3 ..................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(3)
(Total 13 marks)
Page 15 of 16
Page 16 of 16
Вам также может понравиться
- Csec Physics 2010-18 p2 (Solutions)Документ105 страницCsec Physics 2010-18 p2 (Solutions)mariella85% (20)
- Powerboat Handling Illustrated: How to Make Your Boat Do Exactly What You Want It to DoОт EverandPowerboat Handling Illustrated: How to Make Your Boat Do Exactly What You Want It to DoРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (6)
- O Level Physics Formula SheetДокумент2 страницыO Level Physics Formula SheetJereme Cheong93% (56)
- Speed Distance TimeДокумент9 страницSpeed Distance Timebipin jain67% (3)
- Motion and Vectors ExamДокумент9 страницMotion and Vectors ExamClaudia PinnaОценок пока нет
- Incompressible Flow Turbomachines: Design, Selection, Applications, and TheoryОт EverandIncompressible Flow Turbomachines: Design, Selection, Applications, and TheoryОценок пока нет
- Mechanics Exam Questions AS: Minutes MarksДокумент75 страницMechanics Exam Questions AS: Minutes MarksSheikh SamirОценок пока нет
- Circular MotionДокумент6 страницCircular MotionCaesha ColemanОценок пока нет
- Class-X Physics Home Work-1B (Theory) : Chapter: Physical Quantity, Kinematics, DynamicsДокумент18 страницClass-X Physics Home Work-1B (Theory) : Chapter: Physical Quantity, Kinematics, DynamicsNuha TasniahОценок пока нет
- Physics Qs and MsДокумент33 страницыPhysics Qs and MsFatma OsmanОценок пока нет
- Leo 1 10Документ233 страницыLeo 1 10David Urie100% (1)
- Physics principles and motion graph analysisДокумент6 страницPhysics principles and motion graph analysisRadia Khandaker ProvaОценок пока нет
- DCS A-10c Flight Manual enДокумент673 страницыDCS A-10c Flight Manual enRussОценок пока нет
- P2 Forces and Motion QuestionsДокумент61 страницаP2 Forces and Motion Questionsaby25118850% (2)
- A-level Physics exam questionsДокумент86 страницA-level Physics exam questionsMoses Junior100% (1)
- Platform Interference in Wireless Systems: Models, Measurement, and MitigationОт EverandPlatform Interference in Wireless Systems: Models, Measurement, and MitigationРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- ES 12 Lecture 1 Rectilinear and Curvilinear MotionДокумент51 страницаES 12 Lecture 1 Rectilinear and Curvilinear MotionMarian Galvez-Luis100% (1)
- Physics Mechanics) QuestionsДокумент40 страницPhysics Mechanics) QuestionsN4y33mОценок пока нет
- Tutorial Shallow Water FoamДокумент26 страницTutorial Shallow Water FoamdeechibaОценок пока нет
- Practice Test - Forces and Motion - Triple Science Year 10Документ9 страницPractice Test - Forces and Motion - Triple Science Year 10Gd Acceler8Оценок пока нет
- P2 Forces and Motion QuestionsДокумент72 страницыP2 Forces and Motion QuestionsSharuvindan NairОценок пока нет
- Kinematics (Revision)Документ3 страницыKinematics (Revision)Usman AmeenОценок пока нет
- P2 Forces and Motion IntermediateДокумент16 страницP2 Forces and Motion IntermediatedownendscienceОценок пока нет
- End of Term RevisionДокумент127 страницEnd of Term RevisionEsa FarhanОценок пока нет
- Aircraft Flight Mechanics: Andrew BensonДокумент50 страницAircraft Flight Mechanics: Andrew BensonAndrew BensonОценок пока нет
- As Physics Unit 1 Strctured QuestionsДокумент14 страницAs Physics Unit 1 Strctured QuestionsZeenia IfОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент19 страницUntitledBobby AzadОценок пока нет
- Changes in Energy 1 QPДокумент6 страницChanges in Energy 1 QPMiniОценок пока нет
- 2 Moments Hydraulics CM Self Study QuestionsДокумент48 страниц2 Moments Hydraulics CM Self Study QuestionsRiyan PurewalОценок пока нет
- Forces and Motion P2 Set-AДокумент21 страницаForces and Motion P2 Set-AAnonymous jwdY0VОценок пока нет
- Work, Energy & PowerДокумент16 страницWork, Energy & PowerSam LankaОценок пока нет
- Work, Energy and PowerДокумент44 страницыWork, Energy and Powercaramelrobin17Оценок пока нет
- MAE 108 Design Experiment: Biplane Wing and Stagger (R.A.F 15)Документ51 страницаMAE 108 Design Experiment: Biplane Wing and Stagger (R.A.F 15)SubhasreeОценок пока нет
- Core Practical 1 QuestionsДокумент3 страницыCore Practical 1 QuestionsDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- Phys p2Документ16 страницPhys p2Kalana GamageОценок пока нет
- Culminating ReportДокумент64 страницыCulminating Reportblackhawk5145Оценок пока нет
- FT 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Dynamics)Документ6 страницFT 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Dynamics)Syed Jawwad JD JamaliОценок пока нет
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationДокумент16 страницUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationHany ElGezawyОценок пока нет
- Forces & Braking 3 QPДокумент15 страницForces & Braking 3 QPdeepheat_008Оценок пока нет
- P3 07 MomentsДокумент76 страницP3 07 MomentsOmar AbdallaОценок пока нет
- P2 1 Higher QuestionsДокумент104 страницыP2 1 Higher QuestionsjesudassajОценок пока нет
- 1st Worksheet Physics Term 4Документ4 страницы1st Worksheet Physics Term 4Keith BryceОценок пока нет
- Institute of Space Technology VC10 Performance ReportДокумент55 страницInstitute of Space Technology VC10 Performance ReportTalha KhalidОценок пока нет
- Mechanics Worksheet 3 G 11 Mar 21Документ6 страницMechanics Worksheet 3 G 11 Mar 21rajvir singhОценок пока нет
- Physics Mock Exam 1: Mrs - Sara Salah +2/01020088624Документ12 страницPhysics Mock Exam 1: Mrs - Sara Salah +2/01020088624Yousef Abdel HamidОценок пока нет
- Year 9 Forces TestДокумент17 страницYear 9 Forces Testaysha kamar halabiОценок пока нет
- Gravity and Motion on the MoonДокумент27 страницGravity and Motion on the MoonMrBastedОценок пока нет
- Wolejsza State PIL 181 2005Документ52 страницыWolejsza State PIL 181 2005JosepОценок пока нет
- P2 2 Standard QuestionsДокумент68 страницP2 2 Standard QuestionsjesudassajОценок пока нет
- How parachutes help spacecraft and shuttles land safelyДокумент2 страницыHow parachutes help spacecraft and shuttles land safelyYu SunОценок пока нет
- Q1. The Diagram Shows A Fork-Lift Truck With A Load of 2.4 Kn. The Clockwise MomentДокумент9 страницQ1. The Diagram Shows A Fork-Lift Truck With A Load of 2.4 Kn. The Clockwise Momentdeepheat_008Оценок пока нет
- Further MechanicsДокумент39 страницFurther MechanicsLio EditzОценок пока нет
- 1 The World's Tallest Building Is The Burj Khalifa in Dubai, UAEДокумент14 страниц1 The World's Tallest Building Is The Burj Khalifa in Dubai, UAEPaing Khant KyawОценок пока нет
- Motion & ProjectilesДокумент17 страницMotion & ProjectilesSanimul KawserОценок пока нет
- Energy, Work & Power Questions: Physics AS (Unit1) Work Sheet-4 TopicДокумент10 страницEnergy, Work & Power Questions: Physics AS (Unit1) Work Sheet-4 Topicmomentum bdОценок пока нет
- 2.1 Motion & ProjectilesДокумент27 страниц2.1 Motion & Projectilesrabin bajagainОценок пока нет
- Physics Unit 1 Questions 1Документ13 страницPhysics Unit 1 Questions 1panda bearОценок пока нет
- Pages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 21-9 - Chapter Kinematic and Vector DiagramДокумент2 страницыPages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 21-9 - Chapter Kinematic and Vector Diagramlelon ongОценок пока нет
- 2 Momentum and Energy Calculations Self Study QuestionsДокумент33 страницы2 Momentum and Energy Calculations Self Study QuestionsNyraStardollОценок пока нет
- Moments Practice Exam Questions: NameДокумент13 страницMoments Practice Exam Questions: NameIreoluwa FodekeОценок пока нет
- Physics/Science: Edexcel GCSEДокумент28 страницPhysics/Science: Edexcel GCSEfractoremОценок пока нет
- Feasibility Study and Future Projections of Suborbital Space Tourism at the Example of Virgin GalacticОт EverandFeasibility Study and Future Projections of Suborbital Space Tourism at the Example of Virgin GalacticОценок пока нет
- Waves 1 HomeworkДокумент6 страницWaves 1 HomeworkdownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Useful Products Marks FoundationДокумент5 страницC2 Useful Products Marks FoundationdownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Useful Products Marks HigherДокумент4 страницыC2 Useful Products Marks HigherdownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Useful Products FoundationДокумент9 страницC2 Useful Products FoundationdownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Useful Products HigherДокумент6 страницC2 Useful Products HigherdownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Useful Products Marks IntermediateДокумент7 страницC2 Useful Products Marks IntermediatedownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Useful Products IntermediateДокумент13 страницC2 Useful Products IntermediatedownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Structures and Bonding Marks HigherДокумент9 страницC2 Structures and Bonding Marks HigherdownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Representing Reactions Marks FoundationДокумент3 страницыC2 Representing Reactions Marks FoundationdownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Structures and Bonding IntermediateДокумент13 страницC2 Structures and Bonding IntermediatedownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Structures and Bonding Marks IntermediateДокумент9 страницC2 Structures and Bonding Marks IntermediatedownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Representing Reactions Marks HigherДокумент8 страницC2 Representing Reactions Marks HigherdownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Structures and Bonding HigherДокумент14 страницC2 Structures and Bonding HigherdownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Structures and Bonding Marks FoundationДокумент8 страницC2 Structures and Bonding Marks FoundationdownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Structures and Bonding FoundationДокумент18 страницC2 Structures and Bonding FoundationdownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Quantitative Chemistry Marks HigherДокумент8 страницC2 Quantitative Chemistry Marks HigherdownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Representing Reactions Marks IntermediateДокумент6 страницC2 Representing Reactions Marks IntermediatedownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Representing Reactions IntermediateДокумент11 страницC2 Representing Reactions IntermediatedownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Patterns of Behaviour Marks IntermediateДокумент6 страницC2 Patterns of Behaviour Marks IntermediatedownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Representing Reactions HigherДокумент11 страницC2 Representing Reactions HigherdownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Representing Reactions FoundationДокумент3 страницыC2 Representing Reactions FoundationdownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Patterns of Behaviour Marks FoundationДокумент9 страницC2 Patterns of Behaviour Marks FoundationdownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Quantitative Chemistry HigherДокумент12 страницC2 Quantitative Chemistry HigherdownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Quantitative Chemistry Marks IntermediateДокумент7 страницC2 Quantitative Chemistry Marks IntermediatedownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Quantitative Chemistry Marks FoundationДокумент3 страницыC2 Quantitative Chemistry Marks FoundationdownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Quantitative Chemistry IntermediateДокумент13 страницC2 Quantitative Chemistry IntermediatedownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Quantitative Chemistry FoundationДокумент4 страницыC2 Quantitative Chemistry FoundationdownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Patterns of Behaviour IntermediateДокумент14 страницC2 Patterns of Behaviour IntermediatedownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Patterns of Behaviour Marks HighДокумент7 страницC2 Patterns of Behaviour Marks HighdownendscienceОценок пока нет
- C2 Patterns of Behaviour HighДокумент12 страницC2 Patterns of Behaviour HighdownendscienceОценок пока нет
- Intergalactic Filaments Spin: Qianli Xia, Mark C. Neyrinck, Yan-Chuan Cai, Miguel A. Arag On-CalvoДокумент21 страницаIntergalactic Filaments Spin: Qianli Xia, Mark C. Neyrinck, Yan-Chuan Cai, Miguel A. Arag On-CalvoMilan StepanovОценок пока нет
- Position Time Graphs-Displacement: K. W. NicholsonДокумент6 страницPosition Time Graphs-Displacement: K. W. NicholsonGabrielitoОценок пока нет
- The Laws and Velocity of Planetary Motion: Section - 10 FДокумент3 страницыThe Laws and Velocity of Planetary Motion: Section - 10 FFiyory TassewОценок пока нет
- Preliminary Mechanics Exam: Classical Mechanics Problems and SolutionsДокумент139 страницPreliminary Mechanics Exam: Classical Mechanics Problems and SolutionsLawrence Lim Ah KowОценок пока нет
- Sir Isaac Newton and His LawsДокумент2 страницыSir Isaac Newton and His Lawserikamurray06Оценок пока нет
- Lab Report LinearMotionДокумент7 страницLab Report LinearMotionAshley StraubОценок пока нет
- Rigid Body Dynamics Theory - EДокумент45 страницRigid Body Dynamics Theory - Ethinkiit100% (3)
- A Beginners Guide To RoboticsДокумент9 страницA Beginners Guide To RoboticsUdit PeAce SangwanОценок пока нет
- Application of DifferentiationДокумент4 страницыApplication of DifferentiationnishagoyalОценок пока нет
- Torque Web QuestДокумент3 страницыTorque Web QuestRex FortezaОценок пока нет
- Physics ReviewerДокумент52 страницыPhysics ReviewerMr. DADAОценок пока нет
- Free Fall and Motion PDFДокумент36 страницFree Fall and Motion PDFMark Francis HernandezОценок пока нет
- Phy FormulaДокумент1 страницаPhy FormulaCarlos Albert MeguizoОценок пока нет
- JR InterДокумент4 страницыJR InterAswani Kumar67% (3)
- Newtons Law of MotionДокумент25 страницNewtons Law of MotionJoca RiveraОценок пока нет
- Engineering Mechanics ForcesДокумент115 страницEngineering Mechanics Forcesxiomi boxОценок пока нет
- PHYFUN1 SyllabusДокумент6 страницPHYFUN1 SyllabusBrian SoanОценок пока нет
- 100 QuestionsДокумент189 страниц100 Questionsasdfsd2345Оценок пока нет
- Vibration Assisted Milling Techniques for Precision ManufacturingДокумент35 страницVibration Assisted Milling Techniques for Precision ManufacturingHimanshu BisariaОценок пока нет
- Shoot For Your Grade Lab Write UpДокумент5 страницShoot For Your Grade Lab Write Upapi-254812059Оценок пока нет
- Radioss Theory Manual: 11.0 Version - Jan 2011 Large Displacement Finite Element AnalysisДокумент19 страницRadioss Theory Manual: 11.0 Version - Jan 2011 Large Displacement Finite Element AnalysispraveenОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Analytical Mechanics: Lagrange's EquationsДокумент39 страницIntroduction To Analytical Mechanics: Lagrange's EquationszihadОценок пока нет
- ALFSJM2018G1WT04 SolutionДокумент4 страницыALFSJM2018G1WT04 SolutionKARNAОценок пока нет
- Equation Sheet: Combined / PhysicsДокумент1 страницаEquation Sheet: Combined / PhysicsKza1Оценок пока нет
- VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS Chapter 16Документ19 страницVECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS Chapter 16Yohanes Elia PОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Motion Part 1Документ20 страницChapter 2 Motion Part 1Mircea PanteaОценок пока нет