Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Guía de Estudios, Prepa Abierta, Parte 4
Загружено:
Visual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Guía de Estudios, Prepa Abierta, Parte 4
Загружено:
Visual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
SUPER ULTRA MEGA GUA DE ESTUDIOS PARA ACREDITAR LA MATERIA DE: INGLES 2
(PARTE 4)
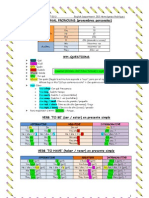
P.302 TEMA: PREGUNTAR EN QUE O EN QUIEN SE COMPLETA LA ACCIN. O sea, preguntar quin es el objeto directo (o el objeto indirecto) Palabras clave: WHAT TO/FOR WHOM. En espaol, ya sabemos cmo preguntar por el objeto directo y objeto indirecto, por ejemplo: Los nios buscaron conchas en la playa. Rodolfo toc el violn para su abuelita. Qu buscaban los nios en la playa? Conchas Para quin toc el violn Rodolfo? Para su abuelita. Este es un ejemplo de Objeto directo. Es un ejemplo de Objeto indirecto.
Ahora vamos a ver un ejemplo con what y un ejemplo con whom en ingls. LO QUE CUENTA EN ESTE TEMA ES LA PREGUNTA eh?? TIEMPO PASADO: What did his secretary translate for him? To whom did Whom did she she teach the teach the symbols? symbols to?
The secretary translated a letter to the Boss Rodriguez. The teacher taught the symbols to the students.
Receta WHAT: 1.-What. 2.-Did. 3.-Sujeto 4.-Verbo en presente simple. 5.-Objeto directo u Objeto indirect. Receta WHOM: 1.-To /For 2.-Whom 3.-Did 4.-Sujeto 5.-Verbo (en presente simple) 6.-Objeto directo o indirecto
She translated a letter for him. She taught the symbols to the students. She taught the symbols the students.
Explicacin: En este tipo de preguntas, utilizamos slo dos Question Words las cuales son what y whom para preguntar Qu? Y A quin? O Para quin? Por ejemplo en las oraciones de arriba Qu tradujo la secretaria para l? O A quien ense ella los smbolos? Recordemos que DID indica que la oracin est en tiempo pasado y si la pregunta lo contiene ya no es necesario que el verbo est en pasado. Si te puedes dar cuenta, las preguntas con What no requieren que pongas antes un to o un for mientras que las preguntas con Who si lo necesitan, pues son las que nos dan el significado de a y para Hay dos formas de hacer este tipo de preguntas, una colocando el to o el for al principio de la oracin y o otra colocndolos al final de la oracin observa los ejemplos! (cuadro amarillo) OJO: En las respuestas a preguntas donde to est al final se puede omitir el to observa la respuesta del cuadro amarillo, esta corresponde a la pregunta del cuadro amarillo y no tiene la palabra to. OJO2: Observa que las respuestas ya no tienen DID por lo que el verbo SI tiene que estar en pasado.
TIEMPO PRESENTE PROGRESIVO. The cashier is cashing the check for the boy. Mary and Jhon are collecting clothes for the poor For whom is he cashing the check? For whom are they collecting clothes? Whom is cashing the check for? Whom are they collecting clothes for? He is cashing the check for the boy. They are collecting clothes for the poor. He is cashing the check the boy They are collecting clothes the poor.
Receta: 1.-What 2.-Verbo to-be 3.-Sujeto 4.-Verbo con ing. 5.-Objeto directo u Objeto indirecto
Receta: 1.-To/for 2.-Whom 3.-Verbo to-be 4.-Sujeto 5.-Verbo con ing. 6.-Objeto directo u Objeto indirect
Explicacin: Continuamos usando to y for para las preguntas con WHOM Sin embargo este es presente progresivo y usamos verbos con terminacin ing para poder preguntar Para quin estn ellos recolectando ropa? Hay dos formas de hacer este tipo de preguntas, una colocando el to o el for al principio de la oracin y o otra colocndolos al final de la oracin Observa los ejemplos! OJO: En las respuestas a preguntas donde to est al final se puede omitir el to observa la respuesta del cuadro amarillo, esta corresponde a la pregunta del cuadro amarillo y no tiene la palabra to.
FUTURO. She will buy a tablet for her daughter. We Will eat apple salad in Christmas. Receta: Receta: 1.-What 1.-To / For 2.-Will 2.Whom 3.-Sujeto. 3.-Will 4.-Verbo en 4.-Sujeto. presente 5.-Verbo en simple. presente 5.-Objeto simple. directo u objeto 6.-Objeto indirecto. directo u objeto indirecto. For whom Will she buy a tablet? Whom Will she buy a tablet for? She will buy a tablet for her. She will buy a tablet her.
What Will we eat in Christmas?
We will eat apple salad in Christmas
Explicacin: Continuamos usando to y for para las preguntas con WHOM Sin embargo en tiempo futuro utilizamos el auxiliar WILL seguido del sujeto (nombre o pronombre) y el verbo en presente simple para preguntar cosas como Para quin comprar ella una tablet? Hay dos formas de hacer este tipo de preguntas, una colocando el to o el for al principio de la oracin y o otra colocndolos al final de la oracin observa los ejemplos!
Actividad sugerida Puedes entender el significado de todos los ejemplos? Ejercicios pgina 306-307
P. 309 EXPRESAR EL TIEMPO Y LUGAR DE REALIZACIN DE UN ACTO. Este tema es muy fcil, nos ayuda a sealar la hora y el lugar en que se lleva a cabo un evento, por ejemplo, la fiesta es a las 12:00 pm en el saln infantil o Nosotros llegamos a la iglesia a las 9:00 a.m. Vamos a ver un ejemplo en ingls:
We arrived at the church at the 9:00 Receta: 1.-Sujeto (Nombre o pronombre) 2.-Verbo en el tiempo en el que se necesite y con los auxiliares que necesite. 3.-preposiciones de lugar (in, on, at, behind etc.) 4.-Complemento del lugar. 5.-Complemento de tiempo.
Nosotros llegamos a la iglesia a las 9:00 am. Explicacin, esta oracin est en tiempo pasado, por eso el verbo arrive (arrived) tiene terminacin ED, La palabra at me sirve para indicar la hora y decir a las
PASADO They danced in the at the night club from 11 to 1 last Ellos bailaron en el club nocturno desde las 11 a la 1 night la noche pasada. Observa: el verbo en esta oracin est en tiempo pasado (terminacin ED) PRESENTE. The ghost appears in the tower at the 12:00 a.m. El fantasma aparece en la torre a las 12:00 a.m. Observa: el verbo apear est en tiempo presente y se le aada una S al final, ya que en oraciones con los pronombres He, She & It, al verbo en presente simple se le aade una letra S lo recuerdas? FUTURO: We will arrive to the ship in the afternoon Nosotros llegaremos al barco en la tarde. En este caso, el auxiliar Will va despus del pronombre, seguido del verbo en presente simple.
ESTAS ORACIONES TAMBIN TIENEN SU FORMA NEGATIVA.
PRESENTE Martha and Pedro dont go to the school, today, they go to de forest. Receta: 1.-Sujeto (nombre o pronombre) 2.-Dont o Doesnt 3.-Verbo en presente simple 5.-Complementos de tiempo y lugar Martha y Pedro no van hoy a la escuela, ellos van al bosque. Recuerdas el uso de do y does? Sus versiones negativas son dont y doesnt recuerdas cual se usa en cada pronombre?
PASADO The doctor didnt arrive to the hospital Receta: 1.-Sujeto (nombre o pronombre) 2.-Didnt 3.-Verbo en presente simple 5.-Complementos de tiempo y lugar El doctor no lleg al hospital Explicacin: Didnt es la forma negativa de Did (do en pasado) y se puede usar con todos los pronombres, al tenerlo en una oracin ya no es necesario escribir el verbo en pasado.
FUTURO. We wont arrive in Madrid by nine. Receta: 1.-Sujeto (nombre o pronombre) 2.-Wont 3.-Verbo en presente simple 5.-Complementos de tiempo y lugar Nosotros no podremos llegar a Madrid a las nueve. Wont es la forma negativa de Will, ambas formas se pueden usar con todos los pronombres, al estar junto a un verbo en presente simple lo convierten a futuro.
Observa y trata de comprender estos ejemplos:
puedes escribir una traduccin aproximada?
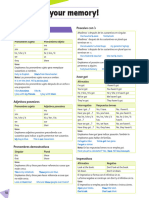
I usually listen to the radio at home in evening The dog stood by the baby all afternoon. He stayed in Canada for six months in 1973 I spoke English to the teacher in class yesterday OJO: Pon atencin al tiempo en que estn los verbos y si no entiendes una palabra, bscala en google traductor o en un diccionario ingls-espaol. P. 331 ESTE ES UN TEMA DE REPASO. PREPOSICIONES DE LUGAR. NOS SIRVEN PARA SEALAR UN LUGAR. IN Sirve para sealar la ubicacin en un lugar geogrfico (pas, ciudad, estado) Sirve para sealar la ubicacin en una CALLE, AVENIDA, DOMICILIO. Seala la ubicacin de un lugar determinado como park store bus station church bank etc. Significa a lo largo de un lugar o cerca de un lugar. En cuestin de preposiciones de lugar, se utiliza para sealar al lugar al que se va. Por ejemplo, El est zarpando para Europa Esta noche salgo para Toluca Tambin se usa para nombrar una cantidad de espacio que se ha recorrido (kilmetros, millas, metros, etc.) -She lives in Mxico. -Karina lives in Tokyo -She meet him in Sonora. -She lives on Amado Nervo street. -Tania buys a new pair of shoes on Guerrero Avenue. -Im at the Mall, where are you? -Luis and Frida are at the Mall buying shoes.
ON
AT
BY
FOR
-He is walking by the park -The river stones are by the rodad. -Theres a tree by the window. He is sailing for Europe (sailing =navegando)
FOR
-I walked for two kilometers. -Every man has to run for a mile. -Alicia Felt for two meters.
FROM-TO
Sirve para sealar cuando se va De un lugar a otro, por ejemplo De la sartn al fuego o De pars a Roma
-Bobby dragged the chair from the corner to de closet, he left marks on the rug. -
P. 315 IN, ON & AT COMO PREPOSICIONES DE TIEMPO. IN Se usa para situarnos en un tiempo: en un suceso, siglo, estacin del ao, mes, maana, tarde o noche. ON Se usa para: das de la semana, una fecha precisa, y en oraciones donde aparece la palabra day AT Se usa para sealar un momento preciso del da como: amanecer, crepsculo, puesta de sol, noche y en una hora especfica. FROM- Se usan para indicar el TO inicio de una accin y su & trmino. Por ejemplo FROM- De la guerra a a la paz UNTIL De la tarde a la noche Ejemplo de suceso: Ejemplo de siglo: Ejemplo d estacin Ejemplo de mes. Transcurso del da. Ejemplo de da de la semana: Fecha precisa: Donde aparece la palabra day Momento preciso del da: Hellen arrived in christmas. Hellen arrived in the XVII century. Hellen arrived in the winter. Hellen arrived in January. Hellen arrived in the morning Hellen arrived on Saturday Hellen arrived on Saturday 15th Hellen arrived on a cold day Hellen arrived at the dawn (amanecer) Hellen arrived at night (noche) Hellen arrived at twilight (crepsculo) Hellen arrived at the sunset (puesta de sol) Hellen arrived at the 6:15 p.m. My moon cooks the new year diner from the 3:00 pm, to the 10:00 pm. You were bothering me from morning to night. He Works to the morning until the night. Francisco drunk to the 7:00 pm, until the 3:00 am. Hellen cries to the night until the dawn. -I worked in the garden for two hours. -I saw tv for twenty minutes. -You were disturbing me for five hours! -Ill finish my book by nine (recuerda que el apostrofe y la doble ele son la contraccin de Will) -You have to sleep by the 5:00 a.m. -The cake has to be ready by the three oclock.
Hora especfica: Ejemplos:
FOR
Cantidad de tiempo que dura una actividad. Sirve para indicar el lmite de tiempo que tenemos para realizar una actividad. Por ejemplo El pastel debe estar listo para las 3:00 o Debes entregar tu examen para las 12 en punto
Ejemplos:
BY
Ejemplos:
ACTIVIDAD SUGERIDA. Puedes comprender las oraciones de ejemplo en este tema y el anterior. Resuelve los ejercicios de las pginas 318 y 319.
P.320 DESCRIBIR EL MODO EN QUE SE EFECTUA UNA ACCIN.
Parte uno: Para describir el MODO en que alguien hace algo, recuerda por fas que debemos usar el adjetivo calificativo junto con la slaba ly. Qu es un adjetivo calificativo? Son palabras que describen personas, lugares, situaciones, INCLUSO FORMAS DE HACER LAS COSAS. Por ejemplo en espaol: rpidamente, calmadamente, cmodamente, felizmente. En ingls, hay muchos adjetivos (investiga algunos) por ejemplo, fast, calm, comfortable, and happy (son los mismos de arriba) pero recuerda que para darles la terminacin mente hay que agregar la slaba ly al final de cada palabra as: quickly, calmly, comfortably, and happily. Veamos un ejemplo en espaol: Ellos examinaron los documentos cuidadosamente ayer en el museo. Observemos el mismo ejemplo en ingls: They examined the documents carefully at the museum yesterday. Repito, los adjetivos son palabras que usamos para DESCRIBIR, personas, lugares, situaciones y formas de hacer las cosas. Veamos ms ejemplos! She used to sit comfortably in front of the fireplace on winter Confortablemente nights He waited for her at the corner patiently yesterday Pacientemente I walked Happily whit Pat in the park yesterday afternoon. Felizmente You drive quickly to take his daughter to the doctor. Rapidamente Paganini played the violin really sadly. Tristemente The rockstar screams so highly. Fuertemente o elevadamente. Your grandfather drive so calmly. calmadamente OJO: el adjetivo calificativo va despus del verbo. *so es una palabra que ponemos antes del adjetivo para indicar exageracin, por ejemplo so calmly = muy calmadamente Comprendes de los ejemplos anteriores? Parte dos. OTRA FORMA DE DESCRIBIR UNA ACCION, A PARTE DE DESCRIBIR EL MODO EN QUE SE REALIZAN ES EL MEDIO POR EL QUE SE REALIZAN, PARA ESO UTILIZAMOS LA PREPOSICIN BY By se usa para describir el medio por el cual se realizan las acciones, por ejemplo Ellos viajarn a Europa por avin o Estoy hablando por telfono, Ellos me pagan por hora. Veamos un ejemplo en ingls: They pay me by hour.
La preposicin by la escribimos antes del medio por el que se esta realizando la accin, veamos ms ejemplos, puedes entender las siguientes oraciones? Are they going to go downtown by car? He arrived by bus. I talked to him by telephone She hurt him by laugh Downtown (centro de la ciudad) realmente necesitas ayuda con esta oracin? Yo creo que no :D Him: significa l, en la modalidad de objeto directo. Laugh (risa)
Parte tres. TAMBIEN SE PUEDE UTILIZAR LA PREPOSICIN IN PARA DESCRIBIR EL MODO EN QUE SE REALIZA UNA ACCIN. Por ejemplo, en espaol decimos: debes ir a la fiesta en vestido de noche debes hablar en voz baja Compra las chamarras en primavera Los aguacates estn en temporada Veamos algunos ejemplos en ingls: He was dressed in rags. She spoke in a loud voice. You must go to the party in night dress. Buy the jackets in spring. The avocados are in season. Parte cuatro. P. 323. TAMBIEN SE PUEDE LAS EXPRECIONES WHITH & WITHOUT PARA DESCRIBIR EL MODO EN QUE SE REALIZA UNA ACCIN. WITH= CON WITHOUT= SIN. La palabra with, significa con (para acompaarla con complementos circunstanciales de instrumento o compaa), por ejemplo lo mat con un cuchillo fue al cine con sus tos La palabra without significa Sin sirve para expresar la falta o carencia de algo, por ejemplo: ella vivi sin amor o no salgas sin suter Veamos unos ejemplos en ingls. Mary is with Jacinto in this picture. I want my coffee with sugar. He kill her with a knife He is riding bicycle without using his hands. Dont go out without a sweater I want my cofee without sugar. Picture =fotografa. My=posesivo de I sugar=azcar. Kill= matar. l est montando en bicicleta sin usar sus manos. Go out=salir sweater en ingles, suter en espaol Rags=harapos. Dress= vestir. Speak= hablar, spoke= hablo, loud= fuerte
Season=temporada. Avocados=aguacates.
P.325 DESCRIBIR LAS CIRCUNSTANCIAS BAJO LAS CUALES OCURRE UNA ACCIN. FOR Se usa para Ejemplos: -These flowers are for the indicar el center table. destino o la -This lock is for special razn de algo. protection. Se usa para Ejemplos: The house is made of logs. indicar (hablando de material base) pertenencia o correspondencia I painted the door of my room. (de que esta (hablando de pertenencia) hecho o a donde pertenece) Seala asunto, Ejemplos: He is talking about sports. materia o tema. (indicar de que estamos The teacher is resolving doubts hablando) about the to-be verb.
OF
Lock=cerradura. Made=hecho Logs=troncos. Painted: pasado de paint. O sea, pint. Door: puerta. About lo podemos traducir como sobre, l est hablando de deportes Doubts=dudas.
ABOUT
ACTIVIDAD SUGERIDA, PAGINAS 326 A 328 DEL LIBRO DE INGLS DOS, PREPARATORIA ABIERTA.
CONTINA EN LA SIGUIENTE PGINA PARA EL LTIMO TEMA.
OJO, EL QUE SEA UN TEMA EXTRA NO QUIERE DECIR QUE NO VA A VENIR EN EL EXAMEN, ES MUY POSIBLE, SIRVE PARA QUE PODAMOS ENTENDER ALGUNAS PREGUNTAS.
TEMA EXTRA: COMO PREGUNTAR: CUANDO? DONDE? QUE TAN LEJOS? POR CUANTO TIEMPO? COMO? PRENGUNTA SE DICE LA RECETA ES. CUANDO? WHEN? 1.-WHEN. 2.-SUJETO. 3.-VERBO. 4.-COMPLEMENTOS. SE CONTESTA CON IN, ON & AT. EJEMPLOS. WHEN SHE DIED? In 1834 WHEN SHE ARRIVES? On Sunday. WHEN SHE GOES HOME? At the 3:00 p.m. WHERE SHE LIVES? In China. WHERE IS THE BOOK? The book is on the table. -WHERE ARE YOU? Im at the Church. -HOW DID YOU WALK? I walked for two kilometers. -HOW FAR ARE THE TOWERS? They are to five miles -HOW FAR IS THE MOON? The moon is to 384.400 kilometers to the earth -HOW LONG YOU WORKED IN BIMBO? For six years. -HOW LONG YOU WAITED IN THE PARK? For fifteen minutes. -HOW LONG LUIS WAS IN EUROPE? From January to August. -HOW SHE SPEAKS? She speaks loudly. -HOW RENATA AND JULIO RUN? They run quickly.
DONDE?
WHERE
1.-WHERE. 2.-SUJETO. 3.-VERBO. 4.-COMPLEMENTOS.
IN,ON & AT.
QUE TAL LEJOS?
HOW FAR?
1.-HOW FAR. 2.-VERBO TO BE (AM, IS, ARE) 3.-LUGAR BUSCADO.
FOR & TO
POR CUANTO TIEMPO?
HOW LONG?
1.-HOW LONG. 2.-SUJETO 3-VERBO EN PASADO. 4.-COMPLEMENTOS.
FOR & FROM TO.
COMO?
HOW?
1.-HOW. 2.-SUJETO. 3.-VERBO EN PRESENTE SIMPLE.
CON UN ADJETIVO Y LAS SLABAS LY
POR QU MEDIO?
HOW?
1.-HOW. 2.-SUJETO. 3.-VERBO EN EL TIEMPO DESEADO. 4.-COMPLEMENTO.
CON BY EN ESTE CASO BY SIGNIFCA POR
-HOW SHE ARRIVED TO OAXACA? By bus. -HOW THE SPANISH ARRIVE TO AMERICA IN 1492? -By ship.
FIN.
Вам также может понравиться
- Curso de Inglés. Learning With the Best: Vocabulary and Easy PronunciationОт EverandCurso de Inglés. Learning With the Best: Vocabulary and Easy PronunciationРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- Preposiciones in On atДокумент4 страницыPreposiciones in On atMichel CavazosОценок пока нет
- Tema 2 - Las Categorías GramaticalesДокумент15 страницTema 2 - Las Categorías GramaticalesnavirheОценок пока нет
- Coreano IntermedioДокумент16 страницCoreano IntermedioJhannder Aponte67% (9)
- Tipos de Preguntas en InglésДокумент6 страницTipos de Preguntas en InglésEstefanía SolisОценок пока нет
- English Grammar For 3º, 4º ESOДокумент17 страницEnglish Grammar For 3º, 4º ESOCancerbero Cancerbe100% (13)
- Tiempos VerbalesДокумент16 страницTiempos VerbalesJessie GomezОценок пока нет
- Oraciones Sin SujetoДокумент4 страницыOraciones Sin SujetoKenneth Tate0% (1)
- Curso de Om Personal EnglishДокумент29 страницCurso de Om Personal EnglishJesus Ruiz de CastillaОценок пока нет
- Ejercicios EXANI II - 7Документ23 страницыEjercicios EXANI II - 7Mtb TlaltenangoОценок пока нет
- ERA Vs FUE WorksheetДокумент12 страницERA Vs FUE WorksheetCesium LanthanumОценок пока нет
- Lista-De-Abreviaturas Analisis Morfologico y Sintactico PDFДокумент1 страницаLista-De-Abreviaturas Analisis Morfologico y Sintactico PDFLir GinosОценок пока нет
- Guia Unidad 3, InglesДокумент35 страницGuia Unidad 3, InglesSandino LealОценок пока нет
- Sufijos y PrefijosДокумент6 страницSufijos y PrefijosRasenshurikenxОценок пока нет
- Verbo To BeДокумент10 страницVerbo To Bethiago graciaОценок пока нет
- Ingles para PrincipiantesДокумент17 страницIngles para PrincipiantesLuis AntonioОценок пока нет
- El Pequeño Libro de Los Verb Patterns ImprimirДокумент35 страницEl Pequeño Libro de Los Verb Patterns ImprimirYordy Jesus Calixto HernandezОценок пока нет
- Resumen Taller de Redacción IIДокумент39 страницResumen Taller de Redacción IIbzomsabiОценок пока нет
- 2do Año - 2da Clase - 1er Lapso InglesДокумент6 страниц2do Año - 2da Clase - 1er Lapso InglesLesly MayorcaОценок пока нет
- 2020 GUÍA EXPLICATIVA 2, DESEMPEÑO 38 GRADO 7° Periodo 4 2Документ5 страниц2020 GUÍA EXPLICATIVA 2, DESEMPEÑO 38 GRADO 7° Periodo 4 2Santiago GarzónОценок пока нет
- Texto de Ingles Primera ParteДокумент14 страницTexto de Ingles Primera Parteanahi alfaroОценок пока нет
- Reglas en InglesДокумент44 страницыReglas en InglessupervisorareaampmОценок пока нет
- Tiempos Verbales - GUIA NUEVAДокумент12 страницTiempos Verbales - GUIA NUEVAAdrianna LaffontОценок пока нет
- 9B How To Eat OutДокумент10 страниц9B How To Eat OutGuadalupe George PolvoОценок пока нет
- Pasados en InglesДокумент20 страницPasados en Inglesyovana ulloaОценок пока нет
- Apuntes Del Curso de InglésДокумент9 страницApuntes Del Curso de InglésYeremi Brayan Noa UscaОценок пока нет
- Aprendé A Utilizar Las Preposiciones en InglésДокумент8 страницAprendé A Utilizar Las Preposiciones en InglésHeiner MontalvoОценок пока нет
- Curso de Ingles - GramaticaДокумент20 страницCurso de Ingles - GramaticaCristian Lizarazo ZabalaОценок пока нет
- Qué Es La Diferencia Entre To Y For en InglésДокумент25 страницQué Es La Diferencia Entre To Y For en InglésEduardo RacuaОценок пока нет
- Sujeto ResumenДокумент2 страницыSujeto ResumenpalomaОценок пока нет
- Excel Resumen InteresanteДокумент14 страницExcel Resumen InteresanteGrover Marcelo Mendoza CastroОценок пока нет
- 3° Abcd. Ingles. Jesus AponteДокумент9 страниц3° Abcd. Ingles. Jesus AponteemmaОценок пока нет
- Ingles para PrincipiantesДокумент16 страницIngles para PrincipiantesLuis AntonioОценок пока нет
- Ingles 3 Unidad 1Документ22 страницыIngles 3 Unidad 1emg23Оценок пока нет
- Verbos Auxiliares en InglesДокумент6 страницVerbos Auxiliares en InglesMelany Belen LenisОценок пока нет
- Verbo AuxiliarДокумент7 страницVerbo AuxiliarIris AlvaradoОценок пока нет
- Pedagogical Material 2nd Year Ingles Eleazar Garcia 1Документ8 страницPedagogical Material 2nd Year Ingles Eleazar Garcia 1yessica geraldoОценок пока нет
- English Ii Guide 11-12Документ13 страницEnglish Ii Guide 11-12Laura RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Presente Perfecto Simple y ContinuoДокумент5 страницPresente Perfecto Simple y ContinuoAna Giráldez RodríguezОценок пока нет
- 1 Ingles BasicoДокумент64 страницы1 Ingles BasicoDocumentos26Оценок пока нет
- Uso Del ItДокумент8 страницUso Del Itkasuma satoОценок пока нет
- Modulo de InglesДокумент11 страницModulo de InglesLuiis Mejiia100% (2)
- Contenido de Ingles Por Tema y Fecha RecomendadaДокумент25 страницContenido de Ingles Por Tema y Fecha RecomendadaKaren EqzОценок пока нет
- Linguistic AДокумент8 страницLinguistic AJorgeRodriguezОценок пока нет
- La Voz PasivaДокумент49 страницLa Voz PasivaGisel Glamoour VenegasОценок пока нет
- TRABAJO II DE INGLES Microsoft WordДокумент12 страницTRABAJO II DE INGLES Microsoft WordCAROLINA CADENASОценок пока нет
- Presente Simple Explicacion GramaticalДокумент10 страницPresente Simple Explicacion GramaticalKarla Tatiana TorresОценок пока нет
- Anthology 3 English IДокумент23 страницыAnthology 3 English IAlonso Cabrera MartínezОценок пока нет
- GUÍA APZJE 9 Ingles Junio 2020Документ8 страницGUÍA APZJE 9 Ingles Junio 2020Arlington FabregaОценок пока нет
- Uso de Las Preposiciones en InglésДокумент23 страницыUso de Las Preposiciones en InglésGiorgia MartinezОценок пока нет
- Monografia de Ingles FinalДокумент11 страницMonografia de Ingles FinalEdinson SNОценок пока нет
- TopicДокумент4 страницыTopicEdmundo LopezОценок пока нет
- Guia 03 Decimo 11 Abril2021Документ4 страницыGuia 03 Decimo 11 Abril2021juansarmientoОценок пока нет
- Relative Clauses Complex SentencesДокумент3 страницыRelative Clauses Complex SentencesMarina AubreyОценок пока нет
- Guías de Inglés Periodo 3 2021Документ11 страницGuías de Inglés Periodo 3 2021Carolina Montagu AriasОценок пока нет
- 5 Formas Diferentes de Hablar Del Futuro en Inglés, ORACIONES INTERROGATIVAS, AFIRMATIVAS Y NEGATIVASДокумент4 страницы5 Formas Diferentes de Hablar Del Futuro en Inglés, ORACIONES INTERROGATIVAS, AFIRMATIVAS Y NEGATIVASRoman Jose Torres HernandezОценок пока нет
- Guia # 1 de Ingles Sexto CamiДокумент20 страницGuia # 1 de Ingles Sexto CamiCamila GarcíaОценок пока нет
- Guía # 1 Inglés 9° 2021Документ15 страницGuía # 1 Inglés 9° 2021Adholf CasthОценок пока нет
- Libro Oficial Diplomado InglesДокумент105 страницLibro Oficial Diplomado InglesMisury FloresОценок пока нет
- Guia Rosetta Stone Level 4Документ8 страницGuia Rosetta Stone Level 4Maria Belen AltamiranoОценок пока нет
- Ingles 1 Actividad 2Документ18 страницIngles 1 Actividad 2yerlin marieffer guerrero jaramilloОценок пока нет
- 4.2 (Num. List) - (Nombre de Alumno) - (Grado y Grupo)Документ9 страниц4.2 (Num. List) - (Nombre de Alumno) - (Grado y Grupo)evolution123456Оценок пока нет
- Documento Sin TítuloДокумент10 страницDocumento Sin TítuloJose Bohorquez DiazОценок пока нет
- MG InglesДокумент9 страницMG InglesMariaОценок пока нет
- Triii (5-8)Документ46 страницTriii (5-8)Visual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecОценок пока нет
- El SustantivoДокумент52 страницыEl SustantivoVisual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecОценок пока нет
- 14 Guia de Estudio Historia Moderna de OccidenteДокумент68 страниц14 Guia de Estudio Historia Moderna de OccidenteAngie BlancarteОценок пока нет
- Triii (5-8)Документ46 страницTriii (5-8)Visual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecОценок пока нет
- 30 Guia de Estudio Ingles IIIДокумент44 страницы30 Guia de Estudio Ingles IIIVisual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecОценок пока нет
- Trii9 12Документ32 страницыTrii9 12Visual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecОценок пока нет
- La Ilustración 3Документ10 страницLa Ilustración 3Visual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecОценок пока нет
- Historia Occidental Preparatoria Abierta Modulo I Hacia 1,700 Con MapasДокумент5 страницHistoria Occidental Preparatoria Abierta Modulo I Hacia 1,700 Con MapasVisual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecОценок пока нет
- Las Colonias de Nueva InglaterraДокумент11 страницLas Colonias de Nueva InglaterraVisual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecОценок пока нет
- La Ilustración 2Документ21 страницаLa Ilustración 2Visual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecОценок пока нет
- NapoleónДокумент16 страницNapoleónVisual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecОценок пока нет
- La IlustraciónДокумент18 страницLa IlustraciónVisual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecОценок пока нет
- La Revolución FrancesaДокумент17 страницLa Revolución FrancesaVisual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecОценок пока нет
- Hechos Sobresalientes deДокумент22 страницыHechos Sobresalientes deVisual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecОценок пока нет
- La Revolución IndustrialДокумент29 страницLa Revolución IndustrialVisual Capivara Abusamadres Lautrec0% (1)
- La Revolución FrancesaДокумент3 страницыLa Revolución FrancesaVisual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecОценок пока нет
- Imprimir CrucigramaДокумент2 страницыImprimir CrucigramaVisual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecОценок пока нет
- Nomina ExcelДокумент6 страницNomina ExcelVisual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecОценок пока нет
- La Independencia de America LátinaДокумент18 страницLa Independencia de America LátinaVisual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecОценок пока нет
- Historia Moderna de Occidente, Módulo I: Hacia 1770Документ25 страницHistoria Moderna de Occidente, Módulo I: Hacia 1770Visual Capivara Abusamadres Lautrec100% (1)
- Sopa de Letras Historia NapoleonДокумент1 страницаSopa de Letras Historia NapoleonVisual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecОценок пока нет
- Historia La Independencia de Norteamerica Parte 2Документ22 страницыHistoria La Independencia de Norteamerica Parte 2Visual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecОценок пока нет
- Partic I PioДокумент23 страницыPartic I PioVisual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecОценок пока нет
- Clase de Excel 1Документ10 страницClase de Excel 1Visual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecОценок пока нет
- Nomina ExcelДокумент6 страницNomina ExcelVisual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecОценок пока нет
- Ejersicio 1.Документ2 страницыEjersicio 1.Visual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecОценок пока нет
- Triii (1-4)Документ54 страницыTriii (1-4)api-3701913Оценок пока нет
- HMOLДокумент240 страницHMOLVisual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecОценок пока нет
- Formato CondicionalДокумент6 страницFormato CondicionalVisual Capivara Abusamadres LautrecОценок пока нет
- Morfología Manual PiattiДокумент17 страницMorfología Manual PiattiLore FookesОценок пока нет
- Inglés NovenoДокумент9 страницInglés NovenoLuisa Maria AlarconОценок пока нет
- I Corrección de Errores MorfosintácticosДокумент34 страницыI Corrección de Errores MorfosintácticosFernando García SaezОценок пока нет
- Ortografia de Las Silabas ExplicacionДокумент10 страницOrtografia de Las Silabas ExplicacionPaulaОценок пока нет
- Palabras Compuestas Lenguaje 9°Документ4 страницыPalabras Compuestas Lenguaje 9°tsu tsuОценок пока нет
- Oraciones GramaticalesДокумент3 страницыOraciones GramaticalesAbdel Jafeth100% (1)
- Grados Del AdjetivoДокумент4 страницыGrados Del AdjetivoMaría de la Merced Suárez CálizОценок пока нет
- Grammar and Vocabulary Reference SpanishДокумент41 страницаGrammar and Vocabulary Reference SpanishANEОценок пока нет
- CursoDeQuechua Cap 2Документ16 страницCursoDeQuechua Cap 2Islam IndoamericanoОценок пока нет
- Tema 1Документ16 страницTema 1lolaОценок пока нет
- Definición y Clases de Preposiciones para Cuarto Grado de SecundariaДокумент4 страницыDefinición y Clases de Preposiciones para Cuarto Grado de SecundariaDayana OchoaОценок пока нет
- Creación de Palabras en Inglés y en EspañolДокумент4 страницыCreación de Palabras en Inglés y en EspañolLuciana Diciero0% (1)
- Libro Raz. VerbalДокумент215 страницLibro Raz. VerbalVictor De La Cruz VОценок пока нет
- Análisis Morfológico. 4. 1Документ4 страницыAnálisis Morfológico. 4. 1rodrigo aguilarОценок пока нет
- Segmentación de Las Formas VerbalesДокумент4 страницыSegmentación de Las Formas VerbalesMiguel Calleja de la PuenteОценок пока нет
- Guã A Completa de SintaxisДокумент14 страницGuã A Completa de SintaxisMarta Santos FuentesОценок пока нет
- 31 de Agosto Español 7-3Документ11 страниц31 de Agosto Español 7-3alejandro rojas valenciaОценок пока нет
- Ejercicio de Oración y Frase1Документ5 страницEjercicio de Oración y Frase1Alejandro EspinalОценок пока нет
- Clase Cuarto Semana 14Документ9 страницClase Cuarto Semana 14Marco LópezОценок пока нет
- PronombrecdДокумент2 страницыPronombrecdHernan Cama HuahualuqueОценок пока нет
- Incorrecciones IdiomáticasДокумент19 страницIncorrecciones IdiomáticasBee Joss100% (1)
- Formas Nominales LatínДокумент2 страницыFormas Nominales LatínÁngel Martín100% (1)
- Pretérito Imperfeito Do IndicativoДокумент5 страницPretérito Imperfeito Do IndicativocarolinaraedОценок пока нет
- 1 de SecundariaДокумент3 страницы1 de SecundariaRohner Guevara TorresОценок пока нет