Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Cytarabine
Загружено:
BigBoostingАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Cytarabine
Загружено:
BigBoostingАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
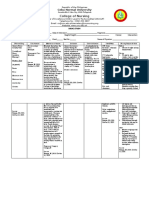
DRUG STUDY AND INFORMATION FORM Generic Name: Cytarabine (Cytosine Arabinoside; Ara-C) Trade Name: Cytosar-U, Tarabine
PFS Drug Class: Pyrimidine Analogs (Cytidine Analog) Structure/Chemistry: Analog of 2-deoxycytidine
Pharmacodynamics
Mechanism of Action: Ara-C contains a 2-hydroxyl that is trans to the 3-hydroxyl of the sugar. The 2-hydroxyl hinders rotation of the base around the nucleoside bond and interferes with base pairing. Ara-C is enters cells through a nucleoside transporter (hENT1, highly expressed in patients with AML and MLL) and then is converted to its active form (5monophosphate ribonucleotide [Ara-CMP]) by deoxycytidine kinase (exhibits polymorphic expression among patients)
Pharmacologic Effects: Ara-C is a potent inhibitor of DNA polymerase, both in DNA synthesis and repair, and blocks the further elongation of the nascent DNA molecule. Checkpoint kinases attempt to repair the offending nucleotide; if unable, DNA strand breaks occur, and apoptosis ensues. The drug must continually inhibit DNA synthesis for a duration of one cell cycle (24 hours) to expose most tumor cells during the S phase of the cycle. Optimal interval for IV bolus doses is between 8 and 12 hours.
Drug Resistance or Tolerance: Primary mechanism of resistance due to loss of activating enzyme deoxycytidine kinase. Enzymatic degradation by cytidine deaminase (Ara-CAra-U) has low activity in AML cells; also by dCMP deaminase (Ara-CMPAra-UMP).
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption: Poor oral bioavailability; must be given IV either rapidly every 12 hours or continuously every 5-7 days. Children tolerate higher doses better than adults. Distribution:
Elimination: t1/2 of 10 mins in plasma.
Metabolism: Most of the drug is rapidly deaminated to Ara-U
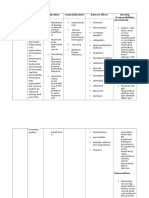
Adverse Side Effects/Toxicity: Myelosuppression (leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia), GI disturbances, stomatitis, conjunctivitis, reversible hepatic enzyme elevations, noncardiogenic pulmonary edema, and dermatitis. Following high doses, an onset of dyspnea, fever, and pulmonary infiltrates may prove fatal. Cerebellar and cerebral toxicity may follow intrathecal administration Drug Interactions:
Therapeutic uses: The most important antimetabolite used to treat AML (acute myelogenous leukemia). Also can treat ALL (acute lymphoblastic leukemia), CML (chronic myelogenous leukemia), acute promyelocytic leukemia, and high-grade lymphomas
Miscellaneous: Either intrathecal administration of cytarabine every four hours for treatment of meningeal or lymphomatous leukemia in the CSF or give depot liposomal formulation (Depocyt) which provides sustained release into the CSF
Вам также может понравиться
- CyclophosphamideДокумент2 страницыCyclophosphamideBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Colestipol Hydrochloride Nursing ConsiderationsДокумент3 страницыColestipol Hydrochloride Nursing ConsiderationsAbby AngОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan for Hypertension ManagementДокумент5 страницNursing Care Plan for Hypertension Managementbhavana100% (1)
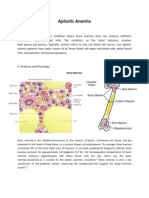
- Aplastic AnemiaДокумент5 страницAplastic AnemiaVenice Marie GargantaОценок пока нет
- CEPHALOSPORINSДокумент18 страницCEPHALOSPORINSVikas SharmaОценок пока нет
- Pradaxa Patient Teaching for Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke RiskДокумент2 страницыPradaxa Patient Teaching for Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke RiskBenОценок пока нет
- Lasilactone PI 201801Документ9 страницLasilactone PI 201801Shivam GuptaОценок пока нет
- KaliumДокумент2 страницыKaliumJustine Kaye Iballa HarligaОценок пока нет
- DrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Документ2 страницыDrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Coleen Mae CamaristaОценок пока нет
- Azathioprine Drug StudyДокумент1 страницаAzathioprine Drug StudyAlexa Lexington Rae Zagado100% (1)
- Case Presentation Hypokalemic ManДокумент61 страницаCase Presentation Hypokalemic ManHussain AzharОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент5 страницDrug Studyjanelle123 toribioОценок пока нет
- Vincristine (OncovinДокумент4 страницыVincristine (Oncovin9959101161Оценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыDrug StudyKwin SaludaresОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Urinary Tract ObstructionДокумент50 страницPathophysiology of Urinary Tract ObstructionPryo UtamaОценок пока нет
- FluconazoleДокумент3 страницыFluconazoleMary Kate ClarosОценок пока нет
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)Документ23 страницыGastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)Alexis TrinidadОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент5 страницDrug StudyMadsОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Portal HYPERTENSION PDFДокумент11 страницPathophysiology of Portal HYPERTENSION PDFCamilo VidalОценок пока нет
- Medical Ward Drug StudyДокумент9 страницMedical Ward Drug StudygorgeazОценок пока нет
- Nursing Responsibilities for Salbutamol and PrednisoneДокумент7 страницNursing Responsibilities for Salbutamol and PrednisoneAlvin LimОценок пока нет
- Primaxin (Imipenem - Cilistatin)Документ2 страницыPrimaxin (Imipenem - Cilistatin)EОценок пока нет
- Aspirin Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыAspirin Drug StudyIRISH CACAYANОценок пока нет
- Drug Study FinalДокумент5 страницDrug Study FinalJackie Ann Marie DapatОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент13 страницDrug Studyapi-3757116100% (4)
- Mupirocin Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыMupirocin Drug StudymichelleОценок пока нет
- HaemaccelinfДокумент9 страницHaemaccelinfSisca YulistianaОценок пока нет
- Complete Albendazole Information From DrugsДокумент4 страницыComplete Albendazole Information From DrugselephantynoseОценок пока нет
- EstradiolДокумент1 страницаEstradiol3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.Оценок пока нет
- (Product Name) MR Tablet 30mg (Product Name) MR Tablet 60mgДокумент10 страниц(Product Name) MR Tablet 30mg (Product Name) MR Tablet 60mggmsanto7Оценок пока нет
- AlgesiaДокумент1 страницаAlgesiaSaf DicamОценок пока нет
- Generic Classification Dosage Mechanism of Action Indications Adverse ReactionДокумент1 страницаGeneric Classification Dosage Mechanism of Action Indications Adverse ReactionKamille Anne Valdez DavidОценок пока нет
- Ketesse Pain Reliever GuideДокумент8 страницKetesse Pain Reliever GuideDhurai OnelyОценок пока нет
- CefuroximeДокумент11 страницCefuroximeAlmira Ballesteros CestonaОценок пока нет
- Pneumonia Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыPneumonia Drug Studyatienza02Оценок пока нет
- Drug Study (MS)Документ9 страницDrug Study (MS)Kristine GallardoОценок пока нет
- P 398Документ1 страницаP 398Arup Ratan PaulОценок пока нет
- Salazar DsДокумент4 страницыSalazar DsDjayОценок пока нет
- COLCHICINE pptx1800128929Документ15 страницCOLCHICINE pptx1800128929April Mergelle LapuzОценок пока нет
- Sal But AmolДокумент2 страницыSal But AmolCalimlim KimОценок пока нет
- DRUG-STUDY - BALLON, Karlo CДокумент6 страницDRUG-STUDY - BALLON, Karlo CMelinda Cariño BallonОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент14 страницDrug StudyNikki RodrigoОценок пока нет
- Pioglitazone (Actos, Lilly) : May Be Confused With Actidose, ActonelДокумент3 страницыPioglitazone (Actos, Lilly) : May Be Confused With Actidose, Actonelshidyakg100% (1)
- Klindamycin antibiotic guideДокумент2 страницыKlindamycin antibiotic guidechristineleesОценок пока нет
- Medical Management For PneumoniaДокумент2 страницыMedical Management For PneumoniaSue Elaine100% (1)
- DRUG StudyДокумент6 страницDRUG StudyJheryck SabadaoОценок пока нет
- Mesna: Mesna, Sold Under The BrandДокумент17 страницMesna: Mesna, Sold Under The BrandAndry HamdaniОценок пока нет
- CiprofloxacinДокумент2 страницыCiprofloxacinx483xDОценок пока нет
- Drug Study on CelecoxibДокумент11 страницDrug Study on CelecoxibPrincess Brigitte R. PATE�AОценок пока нет
- Brand Name: Ambrolex Generic Name: Ambroxol HCL Indication: Acute andДокумент2 страницыBrand Name: Ambrolex Generic Name: Ambroxol HCL Indication: Acute andianecunar100% (1)
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityДокумент3 страницыCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityShiva TorinsОценок пока нет
- NURSING CARE PLAN ASSESSMENT FOR CONFUSED PATIENT ON HEMODIALYSISДокумент3 страницыNURSING CARE PLAN ASSESSMENT FOR CONFUSED PATIENT ON HEMODIALYSISgagandipkS100% (1)
- NCP DM and HCVDДокумент3 страницыNCP DM and HCVDMAYBELINE OBAOB100% (1)
- Filgrastim Boosts Neutrophil Recovery After ChemotherapyДокумент3 страницыFilgrastim Boosts Neutrophil Recovery After ChemotherapyKyla Barrera TabungarОценок пока нет
- AspirinДокумент1 страницаAspirinAmanda CoadОценок пока нет
- UROKINASE (Kinlytic)Документ4 страницыUROKINASE (Kinlytic)Mikaela Gabrielle GeraliОценок пока нет
- Anxiety R:T Death ThreatДокумент8 страницAnxiety R:T Death ThreatAlfredo BaulaОценок пока нет
- Impaired Tissue Perfusion Related To The Weakening / Decreased Blood Flow To The Area of Gangrene Due To Obstruction of Blood VesselsДокумент3 страницыImpaired Tissue Perfusion Related To The Weakening / Decreased Blood Flow To The Area of Gangrene Due To Obstruction of Blood VesselsKat AlaОценок пока нет
- IBSДокумент1 страницаIBSIris MambuayОценок пока нет
- Community Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandCommunity Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- Obgyn Abbreviations For RotationДокумент2 страницыObgyn Abbreviations For RotationBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- The Mental Status ExaminationДокумент16 страницThe Mental Status Examinationeloisa.abcedeОценок пока нет
- GI High YieldДокумент1 страницаGI High YieldBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Neurologic Presentations of HIV/AIDSДокумент23 страницыNeurologic Presentations of HIV/AIDSBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- NervesДокумент139 страницNervesBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- The Mirror Neuron System: Luigi Cattaneo, MD Giacomo Rizzolatti, MDДокумент4 страницыThe Mirror Neuron System: Luigi Cattaneo, MD Giacomo Rizzolatti, MDBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Guideline Watch: Practice Guideline For The Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder, 2Nd EditionДокумент9 страницGuideline Watch: Practice Guideline For The Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder, 2Nd EditionBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- GI NotesДокумент19 страницGI NotesBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Lectura 1 PDFДокумент73 страницыLectura 1 PDFgroudon_18Оценок пока нет
- Psychosomatic MedicineДокумент14 страницPsychosomatic MedicineGiuseppe RutiglianiОценок пока нет
- Bone Cancer Chart 2012Документ8 страницBone Cancer Chart 2012BigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Cross Sections of Upper LimbДокумент12 страницCross Sections of Upper LimbBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Guideline Watch: Practice Guideline For The Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder, 2Nd EditionДокумент9 страницGuideline Watch: Practice Guideline For The Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder, 2Nd EditionBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Triangles of The Neck Vertebral ArteryДокумент6 страницTriangles of The Neck Vertebral ArteryBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Psychiatric Genetics: Progress Amid Controversy: Margit Burmeister, Melvin G. Mcinnis and Sebastian ZöllnerДокумент14 страницPsychiatric Genetics: Progress Amid Controversy: Margit Burmeister, Melvin G. Mcinnis and Sebastian ZöllnerBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Muscles NervesДокумент3 страницыMuscles NervesBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Neoplasias TableДокумент3 страницыNeoplasias TableBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Blue Boxes For MusculoskeletalДокумент16 страницBlue Boxes For MusculoskeletalBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Neuro Phase Notes MS-1Документ43 страницыNeuro Phase Notes MS-1BigBoostingОценок пока нет
- VincristineДокумент2 страницыVincristineBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- TretinoinДокумент2 страницыTretinoinBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Cranial Nerve TractsДокумент2 страницыCranial Nerve TractsBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- ThalidomideДокумент2 страницыThalidomideBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- CNS PharmДокумент16 страницCNS PharmBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- OfatumumabДокумент2 страницыOfatumumabBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- S Mechanism of Action: Inhibits Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) Which Leads To The AccumulationДокумент2 страницыS Mechanism of Action: Inhibits Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) Which Leads To The AccumulationBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- RituximabДокумент2 страницыRituximabBigBoosting100% (2)
- ProcarbazineДокумент2 страницыProcarbazineBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- MercaptopurineДокумент2 страницыMercaptopurineBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- NilotinibДокумент2 страницыNilotinibBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Genetics of Corn LabДокумент25 страницGenetics of Corn LabScience House100% (2)
- Primary Vs Secondary Sexual CharacteristicsДокумент3 страницыPrimary Vs Secondary Sexual CharacteristicsThennarasu RamachandranОценок пока нет
- Barrett Hoekstra 2011 - Molecular SpandrelsДокумент14 страницBarrett Hoekstra 2011 - Molecular SpandrelsMilenaОценок пока нет
- Cell Division GizmoДокумент5 страницCell Division GizmoMeg //Оценок пока нет
- DNA Ekstrakromosomal, Sifat, Dan Kegunaannya: Soraya RahmanisaДокумент33 страницыDNA Ekstrakromosomal, Sifat, Dan Kegunaannya: Soraya RahmanisaRiska PriyaniОценок пока нет
- CB6 Photosynthesis FactorsДокумент2 страницыCB6 Photosynthesis FactorsSiaОценок пока нет
- Art and DesignДокумент3 страницыArt and DesignGabriela SaОценок пока нет
- DNA & Forensic ScienceДокумент5 страницDNA & Forensic Sciencecarygrant_2003Оценок пока нет
- Chromocult Coliform PDFДокумент4 страницыChromocult Coliform PDFAndres GalárragaОценок пока нет
- Spot 4 Class XiДокумент3 страницыSpot 4 Class XiJeevan RaajОценок пока нет
- Biomolecules ChartДокумент2 страницыBiomolecules ChartKelvin Patrick EnriquezОценок пока нет
- Cell Biology (Publication Analysis 1996-2007)Документ3 страницыCell Biology (Publication Analysis 1996-2007)Ilma MardiahОценок пока нет
- Allysa Marie Silbol Beed I1Документ3 страницыAllysa Marie Silbol Beed I1Allysa Marie SilbolОценок пока нет
- Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) : Wesam Mohammed EmharibДокумент8 страницMajor Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) : Wesam Mohammed Emharibنسيم حامدОценок пока нет
- Ch15L2 - The Digestive System Short VersionДокумент17 страницCh15L2 - The Digestive System Short VersionWalayat KhanОценок пока нет
- BYJUS Study - Plan - 03 - Class - 11 - PCMBДокумент20 страницBYJUS Study - Plan - 03 - Class - 11 - PCMBCSE 44 Prajwal BhajeОценок пока нет
- 02 Flow of Energy in Ecosystems Text-MergedДокумент14 страниц02 Flow of Energy in Ecosystems Text-Mergedsurya narayanaОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry of MuscleДокумент68 страницBiochemistry of MuscleWisnu KuncoroОценок пока нет
- What Is SociobiologyДокумент5 страницWhat Is Sociobiology何 彥儒Оценок пока нет
- Anemia of Chronic Disease PDFДокумент14 страницAnemia of Chronic Disease PDFSuci PurnamaОценок пока нет
- KanaДокумент401 страницаKanaAnonymous eFIUdYVWWu100% (2)
- Topic 5 - Induced Pluripotent Stem CellsДокумент28 страницTopic 5 - Induced Pluripotent Stem CellsMorapeli Real MJОценок пока нет
- Medical DictionaryДокумент2 страницыMedical DictionaryMeghanaОценок пока нет
- UNIT 5 Livings BeingsДокумент8 страницUNIT 5 Livings BeingsAlba etceteraОценок пока нет
- Es UbdДокумент4 страницыEs Ubdapi-275510930Оценок пока нет
- Staphylococcus Aurew: Specific Solute Effects With Special Reference ToДокумент11 страницStaphylococcus Aurew: Specific Solute Effects With Special Reference ToWassini BensОценок пока нет
- BIOTECHNOLOGYДокумент16 страницBIOTECHNOLOGYKriyaОценок пока нет
- Airborne Microbes of Medical and Agricultural Importance MCB 403Документ5 страницAirborne Microbes of Medical and Agricultural Importance MCB 403abu firdawsОценок пока нет
- 3 2+chromosomesДокумент1 страница3 2+chromosomesCryzZОценок пока нет
- Experiment No. 6 Power of Enzyme!Документ4 страницыExperiment No. 6 Power of Enzyme!Denisse Angelie CastroОценок пока нет