Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
RPT MT Y4
Загружено:
Noraini MohamadОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
RPT MT Y4
Загружено:
Noraini MohamadАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
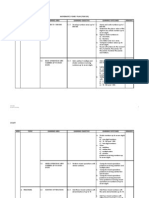
YEARLY LESSON PLAN
Mathematic Primary 4
TOPIC 1: WHOLE NUMBER Learning Area 1: NUMBERS TO 100 000
Week
Learning Objectives 1.1 Develop number sense involving numbers of up to 100 000.
Learning Outcomes 1) Name and write numbers up to 100 000. Determine the place value of the digits in any whole number up to 100 000. Compare value of numbers to 100 000. Round off numbers to the nearest tens, hundreds and thousands.
1 1 1 1
Learning Area 2: ADDITION WITH THE HIGHEST TOTAL OF 100 000
1 1 1 1 2 Multiply any two numbers with the highest product of 100 000. 2.1 Add numbers to the total of 100 000 3.1 Subtract numbers from a number less than 100 000. 1) Add any two to four numbers to 100 000. Solve addition problems. 1) Subtract one or two numbers from a bigger number less than 100 000. Solve subtraction problems. 1) Multiply three-digit numbers with o 100, o 2 two-digit numbers. Multiply four-digit numbers with o one-digit numbers, o o 2 2 10, two-digit numbers.
Learning Area 3: SUBTRACTION WITHIN THE RANGE OF 100000
Learning Area 4: MULTIPLICATION WITH THE HIGHEST PRODUCT OF 100 000
Multiply two-digit numbers with 1 000. Solve multiplication problems.
Learning Area 5: DIVISION WITH THE HIGHEST DIVIDEND OF 100 000
3 Divide a number less than 100 000 by a two-digit numbers. 1) Divide four-digit numbers by o one-digit numbers, o o 3 10, 100 and 1 000, two-digit numbers.
Divide five-digit numbers by o one-digit numbers, o o 10, 100 and 1000, two-digit numbers.
Solve division problems.
CHINESE NEW YEAR LEAVES
Learning Area 6: MIXED OPERATIONS
4 Perform mixed operation involving addition and subtraction. 1) Perform mixed operations involving addition and subtraction with numbers less than o 100, o o 4 1 000, 10 000.
Solve mixed operation problems.
TOPIC 2: FRACTIONS Learning Area 1: PROPER FRACTIONS
Week
4 5
Learning Objectives Name and write proper fractions with denominators up to 10.
Learning Outcomes 1) Name and write proper fractions with denominators up to 10. Compare the value of two proper fractions with o the same denominators, o the numerator of 1 and different denominators up to 10.
Learning Area 2: EQUIVALENT FRACTIONS
5 Express equivalent fractions for proper fractions. 1) Express and write equivalent fractions for proper fractions. Express equivalent fractions to its simplest form.
5 6 Add two proper fractions with denominators up to 10.
Learning Area 3: ADDITION OF FRACTIONS
1) Add two proper fractions with the same denominator up to 10 to its simplest form o with 1 as the numerator for both fractions, o 6 with different numerators. Add two proper fractions with different denominators up to 10 to its simplest form o with 1 as the numerator for both fractions, o 6 7 Subtract proper fractions with denominators up to 10. with different numerators. Solve problems involving addition of proper fractions.
Learning Area 4: SUBTRACTION OF FRACTIONS
1) Subtract two proper fractions with the same denominator up to 10 to its simplest form o with 1 as the numerator for both fractions, o 7 with different numerators. Subtract two proper fractions with different denominators up to 10 to its simplest form o with 1 as the numerator for both fractions, o 7 with different numerators. Solve problems involving subtraction of proper fractions.
TOPIC 3:DECIMALS Learning Area 1: DECIMAL NUMBERS
8 Understand decimal numbers, 1) Name and write decimals with o one decimal place, o 8 two decimal places. Recognise the place value of
o o o 8
tenths, hundredths, tenths and hundredths.
Convert fraction to decimals of o tenths, o o hundredths, tenths and hundredths,
and vice versa
Learning Area 2: ADDITION OF DECIMAL NUMBERS
Week
Learning Objectives Add decimals up to two decimal places.
Learning Outcomes 1) Add any two to four decimals of one decimal place involving o decimals only, o o whole numbers and decimals, mixed decimals.
Add any two to four decimals of two decimal places involving o decimals only, o o whole numbers and decimals, mixed decimals.
Solve problems involving addition of decimal numbers.
Learning Area 3: SUBTRACTION OF DECIMAL NUMBERS WEEK 10: SCHOOL EXAMS
9 Subtract decimals up to two decimal places. 1) Subtract one to two decimals from a decimal of one decimal place involving o decimals only, o mixed decimals, o whole numbers and decimals (mixed decimals). Subtract one to two decimals of one or two decimal places. Solve problems involving subtraction of decimals.
9 9
Learning Area 4: MULTIPLICAITION OF DECIMAL NUMBERS
10 Multiply decimals up to two decimal places with a whole number. 1) Multiply any decimal of one decimal place with o one-digit number, o 10, 100 and 1000. Multiply any decimals of two decimal places with o one-digit number, o 10 10, 100 and 1000. Solve problems involving multiplication of decimals.
10
WEEK 11: SCHOOL HOLIDAYS Learning Area 5: DIVISION OF DECIMAL NUMBERS
12 Divide decimals up to two decimal places by a whole number. 1) Divide decimals of one decimal place by o one-digit number, o 12 12 10. Divide decimals of two decimal places by one-digit number. Divide decimals by a whole number with the dividend value of 3
12
up to two decimal places. Solve problems involving division of decimals.
WEEK 13: SCHOOL EXAMS & REVISION TOPIC 4: MONEY Learning Area 1: MONEY UP TO RM10 000
Week
14 14 14 15 15 15 16 16
Learning Objectives 1. Understand and use the vocabulary related to money. 2. Use and apply knowledge of money in real life.
Learning Outcomes 1) Read and write the value of money up to RM10 000. 1) Add money up to RM10 000. Subtract money from up to RM10 000. Multiply money to the highest product of RM10 000. Divide money with dividend not more than RM10 000. Perform mixed operation involving addition and subtraction involving money up to RM10 000. Round off money to the nearest ringgit. 2) Solve problems involving money of up to RM10 000
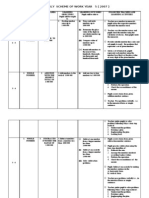
TOPIC 5: TIME Learning Area 1: READING AND WRITING TIME
Week
16
Learning Objectives Understand, read and write time in hours and minutes.
Learning Outcomes 1) Read time in hours and minutes according to the 12hours system. Write time in hours and minutes according to the 12-hours system.
16
Learning Area 2: TIME SCHEDULE
17 17 17 1, Construct a simple schedule. 2. Read a calendar. 1) Construct, read and extract information from a simple schedule. 1) Extract information from a calendar. Solve simple real life problems involving reading the calendar.
WEEK 17: SCHOOL EXAMS & REVISION Learning Area 3: RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN UNITS OF TIME
18 Understand the relationship between units of time. 1) State the relationship between units of time:o 1 day = 24 hours, o o 18 Convert o o o o 18 years to days, and vice versa, decades to years, and vice versa, years to months, and vice versa, hours to days, and vice versa. 1 year = 365 / 366 days, 1 decade =10 years.
Convert time from o hours to minutes, and vice versa, o versa, o versa, hours and minutes to minutes, and vice minutes to hours and minutes, and vice
Learning Area 4: BASIC OPERATION INVOLVING TIME
Week
19
Learning Objectives Add, subtract, multiply and divide units of time.
Learning Outcomes 1) Add time involving conversion of units with answers in compound units of : o hours and minutes, o o years and months, decades and years.
19
Subtract time involving conversion of units with answers in compound units of : o hours and minutes, o o years and months, decades and years.
19
Multiply time involving conversion of units with answers in compound units of : o hours and minutes, o o years and months, decades and years.
WEEK 20: REVISION OF TEST PAPERS WEEK 21: MID TERM EXAMINATIONS WEEK 22&23: SCHOOL HOLIDAYS
24 Divide time involving conversion of units with answers in compound units for time duration of : o hours and minutes, o o 25 years and months, decades and years.
Solve problems involving basic operations of time: o hours and minutes, o o years and months, decades and years.
Learning Area 5: TIME DURATION
Week
26 26
Learning Objectives Use and apply knowledge of time to find the duration.
Learning Outcomes 1) Read and state the start and end of an event from a schedule. Calculate the duration of an event from a schedule in o minutes, o hours, o hours and minutes within a day and two consecutive live days. Calculate the start or the end of an event from a given duration of time and read the start or end of an event.
26
TOPIC 6: LENGTH
5
Learning Area 1: MEASURING LENGTH
27 27 Measure lengths using standard units. 1) Read measurement of length using units of milimetre. Write measurement of length to the nearest scales of tenth division for: o centimetre, o 27 metre. Measure and record lengths of objects using units of o millimetre, o o 27 centimetre and milimetre, metre and centimetre.
Estimate the lengths of objects in o millimetre, o o metre and millimetre, centimetre and millimetre.
27
Understand the relationship between units of length. Learning Objectives
1) State the relationship between centimetre and milimetre.
Learning Area 2: RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN UNITS OF LENGTH
Week
28
Learning Outcomes Convert units of length from: o milimetres to centimetres and vice versa, o compound units to a single unit.
Learning Area 3: BASIC OPERATIONS INVOLVING LENGTH
Week
28
Learning Objectives 1. Add and subtract length.
Learning Outcomes 1) Add units of length, involving conversion of units in; o millimetre, o o metre and centimetre, centimetre and millimetre.
Subtract units of length, involving conversion of units in; o millimetre, o o 29 2. Multiply and divide length. metre and centimetre centimetre and millimetre
1) Multiply units of length, involving conversion of units, by; o a one-digit number, o 10, 100, 1000.
WEEK 30: MONTHLY EXAMINATION
31 Divide units of length, involving conversion of units, by; o a one-digit number; 10, 100, 1000. Solve problems involving basic operations on length.
31
TOPIC 7: MASS Learning Area 1: MEASURING MASS
Week
32 32
Learning Objectives Measure mass using standard units.
Learning Outcomes 1) Measure of masses using in units of kilogram and gram. Read measurement of masses to the nearest scales division of kilograms and grams. 6
32
Estimate the masses of objects using kilograms and grams.
Learning Area 2: RELATONSHIP BETWEEN UNITS OF MASS
Week
33
Learning Objectives Understand the relationship between units of mass.
Learning Outcomes 1) Convert units of mass from o kilograms to grams, o o o kilograms and grams to grams, kilograms and grams to kilograms.
Learning Area 3: BASIC OPERATIONS INVOLVING MASS
33 1. Add and subtract involving units of mass. 1) Add mass involving units of mass in; o kilograms, o o 33 grams, kilograms and grams.
Subtract mass involving units of mass in; o kilograms, o o grams, kilograms and grams.
33
2. Multiply and divide units of mass.
Multiply mass involving conversion of units, with o a one-digit number, o 10, 100, 1000.
33
Divide mass involving conversion of units : o one-digit number, o 10, 100, 1000. Solve problems involving basic operations with mass.
33
WEEK 34: HARI RAYA LEAVES & MID TERM HOLIDAYS
TOPIC 8: VOLUME OF LIQUID Learning Area 1: MEASURING VOLUME OF LIQUID
Week
35 35
Learning Objectives Measure and compare volume of liquid using standard units.
Learning Outcomes 1) Read measurement of volume of liquid in litres and mililitres. Write measurement of volume of liquid to the nearest scales of tenth division for o litre, o mililitre.
35 35 35 Understand the relationship between units of volume of liquid.
Measure and record the volume of liquid in litres and mililitres. Estimate the volume of liquid in litres and mililitres.
Learning Area 2: RELATONSHIP BETWEEN UNITS OF VOLUME OF LIQUID
1) Convert units of volume, from o litres to mililitres, o o o 36 1. Add and subtract units of volume. mililitres to litres, litres and mililitres to litres, litres and mililitres to milillitres.
Learning Area 3: BASIC OPERATIONS INVOLVING V0LUME OF LIQUID
1) Add volume of liquid involving conversion of units in; o litre, o o 36 mililitre, litre and mililitre.
Subtract volume of liquid involving conversion of units in : o litre, o o mililitre, litre and mililitre.
36
2. Multiply and divide units of volume.
1) Multiply volume of liquid involving conversion of units by : o a one-digit number, o 10, 100, 1000. Divide volume of liquid involving conversion of units by: o a one-digit number, o 10, 100, 1000. Solve problems involving volume of liquids.
36
36
WEEK 37: UPSR TOPIC 9: SHAPE AND SPACE Learning Area 1: TWO-DIMENSIONAL SHAPES
Week
38
Learning Objectives 1. Understand the perimeter of a two-dimensional shape.
Learning Outcomes 1) Identify the sides of a: o square, o o rectangle, triangle.
38
Measure and record the perimeter of a: o square, o rectangle, 8
o 38 2. Understand the area of a twodimensional shape.
triangle.
1) Identify the dimensions of a: o square, o rectangle. Compare with unit squares the size of a: o rectangle, o square. Measure and record the dimensions of squares and rectangles. 1) Calculate the area of squares and rectangles. Solve problems involving perimeter and area of twodimensional shapes.
38
38 39 39 3. Find the area and perimeter two-dimensional shapes.
Learning Area 2: THREE-DIMENSIONAL SHAPES
39 39 1. Understand the volume for cubes and cuboids. 1) Identify the dimensions of cubes and cuboids. Compare with a unit cube: o cuboid o 39 39 39 2. Find the volume for cubes and cuboids. cube Measure and record the dimensions of cubes and cuboids. 1) Calculate the volume of cubes and cuboids. Solve problems involving volume of cubes and cuboids.
TOPIC 10: DATA HANDLING Learning Area 1: PICTOGRAPH
Week
40
Learning Objectives Use a pictograph to read and display data.
Learning Outcomes 1) Describe a pictograph featuring o the picture used to represent data, o o o the title of the graph, what the axes represent, What one unit of picture represent.
40 40 40
2) Extract and interpret information from pictographs. Construct pictographs to illustrate given information. Solve a given problem by organising and interpreting numerical data in pictographs.
Learning Area 2: BAR GRAPH
40 Use bar graphs to read and display data. 1) Describe a bar graph featuring o the title of the graph, o 40 40 40 what the axes represent, 2) Extract and interpret information from bar graphs. Construct bar graphs to illustrate given information. Solve a given problem by organising and interpreting numerical data in bar graphs. WEEK 40&41: REVSISION WEEKS WEEK 42: FINAL YEAR EXAM WEEK 43: REVISON OF TEST PAPER 9
WEEK 44 45 : OVERVIEW OF NEXT YEAR SYLLABUS
10
Вам также может понравиться
- Math Fluency Activities for K–2 Teachers: Fun Classroom Games That Teach Basic Math Facts, Promote Number Sense, and Create Engaging and Meaningful PracticeОт EverandMath Fluency Activities for K–2 Teachers: Fun Classroom Games That Teach Basic Math Facts, Promote Number Sense, and Create Engaging and Meaningful PracticeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- IMDSI22Документ82 страницыIMDSI22Dang JinlongОценок пока нет
- LLM Letter Short LogoДокумент1 страницаLLM Letter Short LogoKidMonkey2299Оценок пока нет
- A Teachers' Journey: Phenomenological Study On The Puritive Behavioral Standards of Students With Broken FamilyДокумент11 страницA Teachers' Journey: Phenomenological Study On The Puritive Behavioral Standards of Students With Broken FamilyNova Ariston100% (2)
- UAV Design TrainingДокумент17 страницUAV Design TrainingPritam AshutoshОценок пока нет
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 5От EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 5Оценок пока нет
- Primary School ‘KS1 (Key Stage 1) – Maths - Publications Guide – Ages 5-7’ eBookОт EverandPrimary School ‘KS1 (Key Stage 1) – Maths - Publications Guide – Ages 5-7’ eBookОценок пока нет
- EP001 LifeCoachSchoolTranscriptДокумент13 страницEP001 LifeCoachSchoolTranscriptVan GuedesОценок пока нет
- Positive Psychology in The WorkplaceДокумент12 страницPositive Psychology in The Workplacemlenita264Оценок пока нет
- Project Chalk CorrectionДокумент85 страницProject Chalk CorrectionEmeka Nicholas Ibekwe100% (6)
- Daily Lesson Log Quarter 1 Week 1Документ5 страницDaily Lesson Log Quarter 1 Week 1John Patrick Famadulan100% (1)
- Yearly Plan Year 3Документ8 страницYearly Plan Year 3Shima OmarОценок пока нет
- Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematic YEAR 5Документ17 страницYearly Lesson Plan Mathematic YEAR 5SanjukuttyОценок пока нет
- Test Table of Specification Primary School Mathematics: TotalДокумент2 страницыTest Table of Specification Primary School Mathematics: TotalSriraj DurailimgamОценок пока нет
- MT Akhir THN 4 K1 & K2Документ3 страницыMT Akhir THN 4 K1 & K2Dollar GОценок пока нет
- Jsu PKBS 1 Yr 4Документ3 страницыJsu PKBS 1 Yr 4kupcai_powerОценок пока нет
- RPT MT THN4Документ14 страницRPT MT THN4Sk Saujana Impian DuaОценок пока нет
- RPT MT THN4Документ17 страницRPT MT THN4Yakin DayyanОценок пока нет
- RPT MT THN4Документ14 страницRPT MT THN4startecerОценок пока нет
- MT Akhir THN 4 K1 & K2Документ3 страницыMT Akhir THN 4 K1 & K2Zulkiflee HaronОценок пока нет
- RPT Matematik Tahun 4Документ11 страницRPT Matematik Tahun 4mees-samaОценок пока нет
- Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Year 4 (Semester One)Документ2 страницыYearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Year 4 (Semester One)Sharifah Sazarah Wan AhmadОценок пока нет
- Yearly Scheme of Work Year 4 2013Документ15 страницYearly Scheme of Work Year 4 2013muhdmudzakkirОценок пока нет
- Test Table of Specification Primary School Mathematics: TotalДокумент2 страницыTest Table of Specification Primary School Mathematics: TotalMohd HaizalОценок пока нет
- RPT: Mathematics Year 5Документ20 страницRPT: Mathematics Year 5man_zero1984Оценок пока нет
- RPT & Plan-J Math Year 5 2012Документ26 страницRPT & Plan-J Math Year 5 2012sapuanazianОценок пока нет
- RPT & Plan-J Math Year 4Документ27 страницRPT & Plan-J Math Year 4Syafiah EppieОценок пока нет
- RPT Mathematics Year 4Документ9 страницRPT Mathematics Year 4YoNz AliaTiОценок пока нет
- MT Yearly Plan Year 1 6Документ6 страницMT Yearly Plan Year 1 6abusufian80Оценок пока нет
- Yearly Plan MathsДокумент8 страницYearly Plan MathsTasaratha Rajan AnamalaiОценок пока нет
- Test Table of SpecificationДокумент2 страницыTest Table of SpecificationNorzawiah SuhaimiОценок пока нет
- Topic Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes: Yearly Plan Mathematics Year 5Документ19 страницTopic Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes: Yearly Plan Mathematics Year 5ranj19869Оценок пока нет
- RPT MT THN4Документ14 страницRPT MT THN4hafidie83Оценок пока нет
- Year 6: Topic 1: Whole NumbersДокумент29 страницYear 6: Topic 1: Whole NumbersMuhammad Azrieen SamsudinОценок пока нет
- RPT & Plan-J Math Year 5 2010Документ20 страницRPT & Plan-J Math Year 5 2010Zoe KooОценок пока нет
- M3 Yearly Plan Year 6 (2014)Документ8 страницM3 Yearly Plan Year 6 (2014)Anonymous wgrNJjAОценок пока нет
- Rancangan Tahunan Matematik Tahun 5 - 2012Документ8 страницRancangan Tahunan Matematik Tahun 5 - 2012mrdan100% (1)
- JSU Matematik Tahun 5 KSSRДокумент2 страницыJSU Matematik Tahun 5 KSSRSNMRОценок пока нет
- Rancangan Tahunan MatematikДокумент19 страницRancangan Tahunan MatematikHailmi OthmanОценок пока нет
- Math Y6 Yearly PlanДокумент7 страницMath Y6 Yearly PlanAnna NintehОценок пока нет
- RPT MT THN4Документ14 страницRPT MT THN4Malcom X MalcomОценок пока нет
- Year 5 MathДокумент46 страницYear 5 MathRashidah MatОценок пока нет
- Rancangan Tahunan Matematik Tahun 6 - 2012Документ6 страницRancangan Tahunan Matematik Tahun 6 - 2012mrdanОценок пока нет
- Whole NumbersДокумент4 страницыWhole Numbersmr.itfreakОценок пока нет
- Maths Year 6 Yearly PlanДокумент6 страницMaths Year 6 Yearly PlanMohd RedzuanОценок пока нет
- Rpt&Plan-j Math Year 4Документ27 страницRpt&Plan-j Math Year 4Kee SekKhaiОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year 5) : Week Topic / Learning Areas Learning Objectives / Learning Outcome RemarksДокумент8 страницMathematics Yearly Plan (Year 5) : Week Topic / Learning Areas Learning Objectives / Learning Outcome RemarksMhreal PetronasОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year 6) Sk. Kem Terendak 1 Encik Ramli Bin BabaДокумент4 страницыMathematics Yearly Plan (Year 6) Sk. Kem Terendak 1 Encik Ramli Bin BabaFaridah Binti KamaludinОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year Six) : 1. Whole NumbersДокумент3 страницыMathematics Yearly Plan (Year Six) : 1. Whole NumbersAdemizan AhadОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year Six) : 1. Whole NumbersДокумент3 страницыMathematics Yearly Plan (Year Six) : 1. Whole NumbersRamziah BongsuОценок пока нет
- NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNДокумент6 страницNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNor AishahОценок пока нет
- Previous Present: K O S M K P M Y E A RДокумент16 страницPrevious Present: K O S M K P M Y E A RSdr SafrulОценок пока нет
- Rancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 5 2012 MS Excell Shared by AzyДокумент13 страницRancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 5 2012 MS Excell Shared by AzyTravis MonroeОценок пока нет
- Rancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 6 2013 BiДокумент10 страницRancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 6 2013 Binaim8889Оценок пока нет
- Year 5:: NUMBERS TO 1 000 000Документ47 страницYear 5:: NUMBERS TO 1 000 000Rusehaiza Bin Md DarusОценок пока нет
- Yearly Plan Mathematic Year 6Документ8 страницYearly Plan Mathematic Year 6Rosni OthmanОценок пока нет
- Rancangan Tahunan Matematik Tahun 5 2013Документ8 страницRancangan Tahunan Matematik Tahun 5 2013Nurulnaim OmarОценок пока нет
- Yearly Scheme of Work Year 4: Norahazleenda Hairuman SK Trolak SelatanДокумент16 страницYearly Scheme of Work Year 4: Norahazleenda Hairuman SK Trolak SelatanSalwa HanimОценок пока нет
- 1 Weekly Test: Mathematic YEAR 6Документ9 страниц1 Weekly Test: Mathematic YEAR 6Yatt KrafОценок пока нет
- Test Table of Specification Primary School Mathematics: Easy Moderate ComplexДокумент3 страницыTest Table of Specification Primary School Mathematics: Easy Moderate ComplexSiti Noorfatimah IbrahimОценок пока нет
- Yearly Plan Math Year 5 2013Документ11 страницYearly Plan Math Year 5 2013rdmasrinОценок пока нет
- Sea Math Skills ChecklistДокумент8 страницSea Math Skills Checklistvillo1973Оценок пока нет
- Year 3: Topic: Numbers Learning Area: Numbers T0 10 000Документ63 страницыYear 3: Topic: Numbers Learning Area: Numbers T0 10 000Mieza MiОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year 4)Документ9 страницMathematics Yearly Plan (Year 4)Mhreal PetronasОценок пока нет
- Rancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 6 2013 BiДокумент10 страницRancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 6 2013 BiNajwa NurОценок пока нет
- Sukatan Pelajaran Matematik KBSRДокумент13 страницSukatan Pelajaran Matematik KBSRAhimin KerisimОценок пока нет
- GCSE Mathematics Numerical Crosswords Higher Tier Written for the GCSE 9-1 CourseОт EverandGCSE Mathematics Numerical Crosswords Higher Tier Written for the GCSE 9-1 CourseОценок пока нет
- Possessive Determiners: A. 1. A) B) C) 2. A) B) C) 3. A) B) C) 4. A) B) C) 5. A) B) C) 6. A) B) C) 7. A) B) C)Документ1 страницаPossessive Determiners: A. 1. A) B) C) 2. A) B) C) 3. A) B) C) 4. A) B) C) 5. A) B) C) 6. A) B) C) 7. A) B) C)Manuela Marques100% (1)
- Ismb ItpДокумент3 страницыIsmb ItpKumar AbhishekОценок пока нет
- MS Lync - Exchange - IntegrationДокумент29 страницMS Lync - Exchange - IntegrationCristhian HaroОценок пока нет
- Unbound DNS Server Tutorial at CalomelДокумент25 страницUnbound DNS Server Tutorial at CalomelPradyumna Singh RathoreОценок пока нет
- ACCA F2 2012 NotesДокумент18 страницACCA F2 2012 NotesThe ExP GroupОценок пока нет
- Galman V PamaranДокумент7 страницGalman V PamaranChow Momville EstimoОценок пока нет
- Muscles of The Dog 2: 2012 Martin Cake, Murdoch UniversityДокумент11 страницMuscles of The Dog 2: 2012 Martin Cake, Murdoch UniversityPiereОценок пока нет
- Masoneilan - 78 Series Air Filter Regulators IOMДокумент8 страницMasoneilan - 78 Series Air Filter Regulators IOMNithyAОценок пока нет
- IOT Architecture IIДокумент29 страницIOT Architecture IIfaisul faryОценок пока нет
- S Setting Value, C Check Value) OT Outside Tolerance (X Is Set)Документ1 страницаS Setting Value, C Check Value) OT Outside Tolerance (X Is Set)BaytolgaОценок пока нет
- Caradol sc48 08Документ2 страницыCaradol sc48 08GİZEM DEMİRОценок пока нет
- Extract The .Msi FilesДокумент2 страницыExtract The .Msi FilesvladimirОценок пока нет
- Table of Specification 1st QДокумент5 страницTable of Specification 1st QVIRGILIO JR FABIОценок пока нет
- ST3 ManualДокумент48 страницST3 ManualRon FosterОценок пока нет
- Nescom Test For AM (Electrical) ImpДокумент5 страницNescom Test For AM (Electrical) Impشاہد یونسОценок пока нет
- Benjamin Franklin - The Indian Treaties (1938)Документ450 страницBenjamin Franklin - The Indian Treaties (1938)Spiritu SanctoОценок пока нет
- DCN Dte-Dce and ModemsДокумент5 страницDCN Dte-Dce and ModemsSathish BabuОценок пока нет
- Verniers Micrometers and Measurement Uncertainty and Digital2Документ30 страницVerniers Micrometers and Measurement Uncertainty and Digital2Raymond ScottОценок пока нет
- Introducing The Thinkcentre M70A. A Desktop You DefineДокумент3 страницыIntroducing The Thinkcentre M70A. A Desktop You DefineSiti RohayatiОценок пока нет
- Bgrim 1q2022Документ56 страницBgrim 1q2022Dianne SabadoОценок пока нет
- Directorate of Technical Education, Admission Committee For Professional Courses (ACPC), GujaratДокумент2 страницыDirectorate of Technical Education, Admission Committee For Professional Courses (ACPC), GujaratgamailkabaaaapОценок пока нет
- Homeopatija I KancerДокумент1 страницаHomeopatija I KancermafkoОценок пока нет