Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Underground Pipe Design
Загружено:
jobees7850Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Underground Pipe Design
Загружено:
jobees7850Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
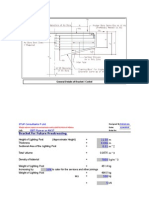
UNCASED DESIGN - Highway Crossing Pipeline (Ref : API RP 1102 - Steel Pipeline Crossing Railroads and Highways) Step
- a - Intial Design Information Pipe and Operational Characterists : Outside Dia Operating pressure Steel Grade Specified Min yield Strength Design factor Longitudinal joint factor Installation Tempreture Max. or Min. operating Temp. Temp. derating factor Wall Thickness Installation & site Characterists : Depth Bored Dia. Soil type Modulus of soil reaction Resilient Modulus Unit Weight Type of longitudinal weld Design wheel load - Signle Axle Design wheel load - tandem Axle Pavement Type Other pipe steel properties : Young's modulus Poisson's ratio Coefficient of thermal expansion Step - b - Check Allowable Barlow Stress Equation 8b with : p D tw F E T SMYS SHi (Barlow) 300 24 0.375 0.72 1 0 52000 FxExSMYS psig in in Shi (Barlow)= pxD/(2tw) For Natural Gas: FxExTxSMYS = For liquid & other products: FxExSMYS = 9600 psi Es vs at 30000 0.3 6.50E-06 ksi per deg F H Bd E' Er uw Ps Pt 3.28 28 Loose Sand 0.5 10 120 ERW 12 10 Flexible ft in ksi ksi lb/ft3 kips kips D p SMYS F E T1 T2 T tw 24 300 X52 52000 0.72 1 N/A N/A N/A 0.375 inch psig psi
in
0 37440 psi
psi
<
OK
Step - c - Circumferential Stress Due to Earth Load c.1 Figure 3 with : tw / D E' 0.0156 0.5 ksi KHe 3250
c.2 Figure 4 with :
H / Bd Soil Type
1.4057143 Loose Sand
Be
0.4
c.3 Figure 5 with : c.4 Equation 1 with :
Bd / D D uw
1.167 24 in 120 lb/ft3 0.0694444 lb/in3
Ee
1.08
SHe = Khe x Be x Ee x uw x D 2340 psi
Step - d - Impact Factor, Fi, and and Applied Design Surface Pressure, w d.1 Figure 7 for highway with : d.2 Applied Design Surface Pressure, w Section 4.7.2.2.1 : H 3.28 Fi 1.5
Flexible
Pt w
12 kips 83.3 psi
Step - e - Cyclic Stresses, DSHh & DSLh e.1 Cyclic circumferential stress DSHh e.1.1 Figure 14 with :
tw / D Er D H
0.015625 10 ksi 24 in 3.28 ft
KHh
13
e.1.2 Figure 15 with :
GHh
1.15
e.1.3 Table 2 with : Flexible Pavement Tandem Axles e.1.4 Equation 5 with :
H D
3.28 ft 24 in
R L DSHh = KHh x GHh x R x L x Fi x w 1868.0025 psi
1 1
e.2 Cyclic Longitudinal stress DSLh e.2.1 Figure 16 with :
tw / D Er D H
0.015625 10 ksi 24 in 3.28 ft
KLh
10
e.2.2 Figure 17 with :
GLh
e.2.3 Table 2 with : Flexible Pavement Tandem Axles e.2.4 Equation 6 with :
H D
3.28 ft 24 in
R L DSLh = KLh x GLh x R x L x Fi x w 1249.5 psi
1 1
Step - f - Cercumferential Stress Due to Internal Pressurization, Shi Equation 7 with : p D tw 300 psi 24 in 0.375 in SHi = p x (D-tw) / (2 x tw) 9450.000 psi
Step - g - Principal Stresses S1 , S2 , S3 Es at T1 T2 vs 30000 6.50E-06 0 0 0.3
g.1 Equation 9 with :
SHe DSHh SHi DSLh SHe SHi p S1 S2 S3 S1 - S2 S2 - S3 S3 - S1 F SMYS Seff
2340 psi 1868.0025 psi 9450.000 psi 1249.5 psi 2340 psi 9450.000 psi 300 psi 13658.003 4786.500 -300 8871.503 5086.500 -13958.003 psi psi psi psi psi psi
S1 = SHe + DSHh + Shi 13658.003 psi S2 = DSLh - Es x at (T2-T1) + vs (SHe + SHi) 4786.500 psi S3 = -300 psi
g.2 Equation 10 with :
g.3 Equation 11 with : g.4 Effictive Stress, Seff Equation 12 with :
Seff = Sqrt [1/2{(S1-S2)2 + (S2-S3)2 + (S3-S1)2}] 12235.233 psi
g.5 Check allowable effective Stress Equation 13 with :
0.72 52000 psi 12235.233 psi Seff
F x SMYS =
37440 psi
F x SMYS
>
OK
Step - h - Check Fatigue h.1 Girth welds Table 3 Equation 17 with : DSLh for X52 steel SFG SFG x F
F DSLh
0.72 1249.5 psi SFG x F
12000 psi 8640 psi
<
OK
h.2 Longitudinal welds Table 3 Equation 17 with : DSHh
F DSHh
0.72 1868.0025 psi SFL x F
for X52 steel SFL SFL x F
21000 psi (ERW) 15120 psi
<
OK
Вам также может понравиться
- Crossing Calculation API RP1102 (TEMPLATE)Документ1 страницаCrossing Calculation API RP1102 (TEMPLATE)bebas_amarah100% (5)
- Crossing Calculation API RP1102 (TEMPLATE)Документ1 страницаCrossing Calculation API RP1102 (TEMPLATE)Hendra Yudistira100% (1)
- Buried Pipe Analysis Based On ALAДокумент6 страницBuried Pipe Analysis Based On ALADonald.KОценок пока нет
- API RP 1102 SpreadsheetДокумент5 страницAPI RP 1102 Spreadsheetdrramsay100% (4)
- Pipeline Highway Crossing Design SpreadsheetДокумент11 страницPipeline Highway Crossing Design SpreadsheetBeljun FloresОценок пока нет
- HDD Installation CalculationsДокумент4 страницыHDD Installation Calculationslive4sankar100% (1)
- HDD Design Calculation for Sonamura GGS Pipeline ProjectДокумент22 страницыHDD Design Calculation for Sonamura GGS Pipeline ProjectPer Bagus HandokoОценок пока нет
- Underground Pipe Stress Check CalculationsДокумент6 страницUnderground Pipe Stress Check Calculationsani_datОценок пока нет
- Laying 30Документ13 страницLaying 30Ashok SwamiОценок пока нет
- Buried Pipe Design for Deep Rock Petroleum TerminalДокумент12 страницBuried Pipe Design for Deep Rock Petroleum TerminalMichael J. BaneОценок пока нет
- Eng Pipe DesignДокумент12 страницEng Pipe DesignEsapermana Riyan100% (1)
- Calculation Hdpe 24 InchДокумент5 страницCalculation Hdpe 24 InchBachtiar Ramadhan100% (1)
- Buried PipeДокумент11 страницBuried PipePrashant Agrawal100% (4)
- HDD DesignДокумент7 страницHDD Designanon_824061466Оценок пока нет
- HDD Design Calculaton of Pond & Temple Area Crossing at CH.0+882 KM For 12'' PDFДокумент5 страницHDD Design Calculaton of Pond & Temple Area Crossing at CH.0+882 KM For 12'' PDFdeepak kumarОценок пока нет
- API RP 1102 - Highways AnalysisДокумент62 страницыAPI RP 1102 - Highways Analysispeloto100% (1)
- HDD Calc As Per PRCДокумент8 страницHDD Calc As Per PRClive4sankar100% (1)
- Structural AnalysisДокумент12 страницStructural Analysisabhishek5810Оценок пока нет
- HDD CalculationДокумент5 страницHDD Calculationiwan100% (1)
- HDD Design and MethodologyДокумент14 страницHDD Design and MethodologyVipin Gupta100% (4)
- Flowline Road Crossing CalculationДокумент7 страницFlowline Road Crossing CalculationZeeshan Ahuja100% (2)
- Pipeline Buoyancy AnalysisДокумент12 страницPipeline Buoyancy AnalysisbonnicoОценок пока нет
- Design Radius of Curvature - Horizontal Directional DrillingДокумент6 страницDesign Radius of Curvature - Horizontal Directional DrillingBenaknaik S GajannavarОценок пока нет
- Solid Wall HDPE Pipe: NRCS NEH 636 Chap. 52 Buried Pipeline Design CalculationsДокумент13 страницSolid Wall HDPE Pipe: NRCS NEH 636 Chap. 52 Buried Pipeline Design CalculationsBalaji HariОценок пока нет
- Thrust Block CalculationДокумент12 страницThrust Block CalculationMegatech Engineering Consultants100% (1)
- Pipe Lowering CalculationДокумент8 страницPipe Lowering CalculationMochamad Safarudin50% (4)
- API RP 1102 SpreadsheetДокумент6 страницAPI RP 1102 Spreadsheetm_michael_cОценок пока нет
- Virtual Anchor Length - KBRДокумент22 страницыVirtual Anchor Length - KBRSammar Adhikari100% (2)
- Wall Thickness Calculation ASME B31!8!2007Документ1 страницаWall Thickness Calculation ASME B31!8!2007shafeeqm3086Оценок пока нет
- HDD Crossing Calculation 2Документ26 страницHDD Crossing Calculation 2Denstar Ricardo Silalahi93% (29)
- Perhitungan Kekuatan PipelineДокумент9 страницPerhitungan Kekuatan PipelineRAHMAN HakimОценок пока нет
- 24in Pipeline Buoyancy CalculationДокумент1 страница24in Pipeline Buoyancy CalculationAdaghara67% (3)
- Jasa Engineering untuk Kajian Teknis Perubahan Metode CrossingДокумент3 страницыJasa Engineering untuk Kajian Teknis Perubahan Metode Crossingdenstar silalahi0% (1)
- API RP 1102 SpreadsheetДокумент5 страницAPI RP 1102 SpreadsheetBehroozОценок пока нет
- Anchor Block Design (Typical) AB-1Документ9 страницAnchor Block Design (Typical) AB-1Madhu KurmiОценок пока нет
- HORIZONTAL DIRECTIONAL DRILLING CALCULATIONДокумент4 страницыHORIZONTAL DIRECTIONAL DRILLING CALCULATIONbulituk100% (1)
- My CalculationsДокумент39 страницMy CalculationsWaqas Khan ChannarОценок пока нет
- Buried Pipe Design FinalДокумент10 страницBuried Pipe Design FinalDipesh100% (1)
- Upheaval Buckling PipelineДокумент11 страницUpheaval Buckling PipelineRYZKI EFENDI SIMANULANGОценок пока нет
- Upheavel Buckling CalculationДокумент8 страницUpheavel Buckling Calculationsaravanakkumar boominahtanОценок пока нет
- Buried Pipe DesignДокумент18 страницBuried Pipe DesignSrutha KeerthiОценок пока нет
- CW Pipe Thickness Calculation - 80% Vacuum - With RCCДокумент39 страницCW Pipe Thickness Calculation - 80% Vacuum - With RCCAshitava Sen0% (1)
- HDPE Pipe Calculation MethodsДокумент7 страницHDPE Pipe Calculation Methodssabahiraq100% (2)
- PIPELINE WALL THICKNESS CALCULATIONSДокумент24 страницыPIPELINE WALL THICKNESS CALCULATIONSMohsin RazaОценок пока нет
- Thrust Block 1Документ1 страницаThrust Block 1Jen EmeraldОценок пока нет
- Wall Thickness Calculation Verification under StressДокумент1 страницаWall Thickness Calculation Verification under StresshhgjdfОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Loads on Buried Pipe Track CrossingДокумент6 страницAnalysis of Loads on Buried Pipe Track CrossingDivesh rahul50% (2)
- Tender227 VOL II PDFДокумент945 страницTender227 VOL II PDFrasnowmah2012Оценок пока нет
- Wheel Load AnalysisДокумент8 страницWheel Load Analysistsoheil100% (2)
- Mathcad - Case-4 (22 OD) HYDДокумент4 страницыMathcad - Case-4 (22 OD) HYDAdvisОценок пока нет
- Mathcad - Case-1 (40 Od) InstallДокумент4 страницыMathcad - Case-1 (40 Od) InstallAdvisОценок пока нет
- Wellbore Hydraulics, Pressure Drop CalculationsДокумент85 страницWellbore Hydraulics, Pressure Drop CalculationsDan Morrell100% (1)
- D TD G BHP P G D P: Ko o F D Gas Ko SurДокумент5 страницD TD G BHP P G D P: Ko o F D Gas Ko SurlikpataОценок пока нет
- Skirt Support TrialДокумент11 страницSkirt Support TrialAbhishek Nag0% (1)
- E4.5 Flange Cover CalcДокумент10 страницE4.5 Flange Cover CalcTanCM100% (1)
- Drilling HydraulicДокумент52 страницыDrilling HydraulicHeris Sitompul100% (1)
- Pveng: Pressure Vessel Engineering LTDДокумент11 страницPveng: Pressure Vessel Engineering LTDSivateja NallamothuОценок пока нет
- Trunnion load calcsДокумент4 страницыTrunnion load calcsChirag Shah50% (2)
- Reinforced Concrete Stair Design CalculationsДокумент3 страницыReinforced Concrete Stair Design Calculationsmdelacua2Оценок пока нет
- Corbel RainaДокумент13 страницCorbel RainaMadhurimaMitra100% (1)
- Ad Dmis Ssion ns2 2020 0-21 Han Ndbo Ook: Bach Helor of Des Sign (B B.Des.)Документ25 страницAd Dmis Ssion ns2 2020 0-21 Han Ndbo Ook: Bach Helor of Des Sign (B B.Des.)jobees7850Оценок пока нет
- Viteee 2020Документ24 страницыViteee 2020UtkarshОценок пока нет
- Size Your AC - Calculate Air Conditioner SizeДокумент3 страницыSize Your AC - Calculate Air Conditioner Sizejobees7850Оценок пока нет
- Mto SlipwayДокумент2 страницыMto Slipwayjobees7850Оценок пока нет
- NДокумент1 страницаNjobees7850Оценок пока нет
- Calculation of CG X : Raft FoundationДокумент4 страницыCalculation of CG X : Raft Foundationjobees7850Оценок пока нет
- Class10 Maths NotesДокумент28 страницClass10 Maths Notesjobees7850Оценок пока нет
- 8m Octagonal Pole Technical SubmittalДокумент34 страницы8m Octagonal Pole Technical Submittaljobees7850Оценок пока нет
- Hap Calculations - Etr-1Документ10 страницHap Calculations - Etr-1jobees7850Оценок пока нет
- Delhi Private School Preboard Science ExamДокумент34 страницыDelhi Private School Preboard Science Examjobees78500% (1)
- Design Calculations Tower Crane Foundation - Rev-CДокумент13 страницDesign Calculations Tower Crane Foundation - Rev-Cjobees785075% (8)
- Rebellion in The Forest History Final CompiledДокумент13 страницRebellion in The Forest History Final Compiledjobees7850Оценок пока нет
- Storm Water Runoff Package Spreadsheet - U.S. UnitsДокумент11 страницStorm Water Runoff Package Spreadsheet - U.S. Unitsjobees7850Оценок пока нет
- FoundationДокумент17 страницFoundationjobees7850Оценок пока нет
- IITK-GSDMA Wind Codes DocumentДокумент105 страницIITK-GSDMA Wind Codes DocumentMadusha Galappaththi100% (2)
- Lokfix PDFДокумент4 страницыLokfix PDFnafis2uОценок пока нет
- Porta Davit 500 Product BrochureДокумент4 страницыPorta Davit 500 Product Brochurejobees7850Оценок пока нет
- CP 620 - 1Документ2 страницыCP 620 - 1jobees7850Оценок пока нет
- EarthquakeДокумент37 страницEarthquakeJinoop PvОценок пока нет
- IITK-GSDMA Wind Codes Project ReportДокумент106 страницIITK-GSDMA Wind Codes Project ReportFung MakОценок пока нет
- Base Plate1Документ6 страницBase Plate1jobees7850Оценок пока нет
- Navy Blast Resistant StructuresДокумент358 страницNavy Blast Resistant StructuresjakejohnsОценок пока нет
- Barred T - Aramco StandardДокумент1 страницаBarred T - Aramco Standardjobees7850Оценок пока нет
- Design Calculations For Light MastДокумент23 страницыDesign Calculations For Light Mastjobees7850Оценок пока нет
- Combined Footing - Type2Документ60 страницCombined Footing - Type2jobees7850Оценок пока нет
- ASTM A36 vs BS 10025 S275 JR Steel ComparisonДокумент1 страницаASTM A36 vs BS 10025 S275 JR Steel Comparisonjobees7850100% (1)
- Design Calculations For Light MastДокумент24 страницыDesign Calculations For Light Mastjobees7850100% (17)
- Flex Spiral Wound GasketsДокумент49 страницFlex Spiral Wound GasketsJomer J Simpson100% (1)
- Barred T - Dep StandardДокумент1 страницаBarred T - Dep StandardJobi GeorgeОценок пока нет
- Builders Foundation HandbookДокумент124 страницыBuilders Foundation Handbookvelarajan100% (11)
- A815 PDFДокумент8 страницA815 PDFExport priminoxОценок пока нет
- Diseño Tambor CoqueДокумент0 страницDiseño Tambor CoqueCesar Rodriigzz' BrachoОценок пока нет
- RCC Water Tank Construction TenderДокумент12 страницRCC Water Tank Construction Tendersurya0588Оценок пока нет
- Toshiba 13A26 PDFДокумент39 страницToshiba 13A26 PDFJOMAREYОценок пока нет
- General Issues and The Recommended StandardsДокумент60 страницGeneral Issues and The Recommended StandardsTomislav RogićОценок пока нет
- Lyophilic and Lyophobic SolsДокумент7 страницLyophilic and Lyophobic Solssatvik guptaОценок пока нет
- ACI Building Code Requirements for Thin Shells and Folded PlatesДокумент84 страницыACI Building Code Requirements for Thin Shells and Folded PlateskrishnanunniОценок пока нет
- Almex Light Weight BrochureДокумент16 страницAlmex Light Weight BrochureGijoОценок пока нет
- Textile and Garments InformationДокумент7 страницTextile and Garments InformationMd.Tipu SultanОценок пока нет
- Reaktor (R-01) DesignДокумент5 страницReaktor (R-01) DesignalОценок пока нет
- Manuf Pacop Pink Green Blue RedДокумент46 страницManuf Pacop Pink Green Blue RedShane KimОценок пока нет
- Chapter 12 - P-N JunctionДокумент69 страницChapter 12 - P-N JunctionShelly RismawatiОценок пока нет
- Method Statement FOR SIKATOP SEAL 107Документ4 страницыMethod Statement FOR SIKATOP SEAL 107faizbukhariОценок пока нет
- Reactive Dye PrintingДокумент15 страницReactive Dye Printingsandipsoni221811Оценок пока нет
- Troubleshooting Auto Cutting Atom - Ver1.0Документ15 страницTroubleshooting Auto Cutting Atom - Ver1.0Etsis Sari PujanggiОценок пока нет
- 2 PerformanceofflowingwellsДокумент16 страниц2 PerformanceofflowingwellsnciriОценок пока нет
- Masterpact NW-NTДокумент184 страницыMasterpact NW-NTCarito Ahumada100% (1)
- Utilization of Waste Plastic in Manufacturing of Paver BlocksДокумент4 страницыUtilization of Waste Plastic in Manufacturing of Paver BlocksAragorn RingsОценок пока нет
- SEMIKRON DataSheet SKKE 15 07170871 PDFДокумент4 страницыSEMIKRON DataSheet SKKE 15 07170871 PDFVinicius Veiverberg DillОценок пока нет
- ME2112-Lab Manual-1 (Vs Rev)Документ5 страницME2112-Lab Manual-1 (Vs Rev)ZihОценок пока нет
- Corrosion of Chrome PlatingДокумент37 страницCorrosion of Chrome PlatingdavideОценок пока нет
- Quality Metrics For Aerospace: Tim Robertson PQA Nasa/JplДокумент20 страницQuality Metrics For Aerospace: Tim Robertson PQA Nasa/Jplnikhil jОценок пока нет
- PCL Handbook 2017 Lub1007eДокумент228 страницPCL Handbook 2017 Lub1007eMahmoud MohamedОценок пока нет
- Metiche AnalDesign FRP Poles PDFДокумент26 страницMetiche AnalDesign FRP Poles PDFMojtaba Mohammad PourОценок пока нет
- Aqua Culture Brochure - Fusi TechДокумент2 страницыAqua Culture Brochure - Fusi Techsaradhi sravan kumarОценок пока нет
- Carbide ToolingДокумент90 страницCarbide ToolingHuron Industrial SupplyОценок пока нет
- Palm Oil MSDSДокумент5 страницPalm Oil MSDSCaliche Omn100% (1)
- Painting Specification for Aegean Refinery ProjectДокумент18 страницPainting Specification for Aegean Refinery Projectraluca_19735597Оценок пока нет
- Manufacturer'S Test Certificate: National Builtech Trading and Contracting CoДокумент1 страницаManufacturer'S Test Certificate: National Builtech Trading and Contracting CoNBTC Tubes & PipesОценок пока нет