Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
B. Equivalent Axial (N) and Lateral (Q) Loads: SD SD
Загружено:
Rahul MalaniОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
B. Equivalent Axial (N) and Lateral (Q) Loads: SD SD
Загружено:
Rahul MalaniАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
b.
Equivalent axial (NSd) and lateral (qSd) loads
The equivalent axial force should be taken as:
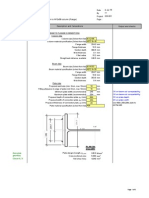
Stiffener cross section:
Flange width 180mm, t=20mm
Web height: 400mm Thickness: 10mm
Known values from previous page 4000 mm plate length or stiffener length l 1000 mm plate width, stiffener spacing. s 20 mm plate thickness t Young modulus of elasticity E 200.00 Gpa x,Sd 180.00 MPa axial stress in plate and stiffener with compressive stresses as positive Since kl >= s, then kl= LG, then kg 5.59 [], where kl is buckling factor for plate between stiffeners. 13.49 [], where kG is buckling factor for plate with the stiffeners removed. Since Sd <= then: = 0.00 MPa
Known values: LG 3000 mm wfl 180 mm tfl 20 mm hw 400 mm tw 10 mm Sd 0.00 MPa M 1.15 []
girder length flange width flange thickness
web height web thickness design shear stress resulting material factor
Since kg > Thus: crl 404.27 MPa crg 60.99 MPa
The cross sectional area of stiffener is As and the full plate cross section area s.t = Therefore, the equivalent axial force, NSd
7600 mm^2; 20000 mm^2 4.968 MN
Note: Known values from previous page Known values Calculated values Final results
Hint: See Section 7.2 DNV-RP-C201
The equivalent lateral line load should be taken as: Wes and Is are determined by cross section analysis
Cross Section Analysis
Flange width 180mm, t=20mm
Web height: 400mm Thickness: 10mm
Known values from previous page 20 mm plate thickness t 1000 mm plate width, stiffener spacing. s Se 756.41 mm the effective plate width
pSd fy
0.1508 MPa 300.00 MPa
Section properties: Afl 3600 Aw 4000 Ap 20000 Apes 15128 zfl 430 zw 220 zp 10 95.22 COG dfl-es 316.52 dw-es 106.52 dpes -103.48 ces 344.78
mm^2 mm^2 mm^2 mm^2 mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm
Where: flange cross section area web cross section area plate cross section area, use s. plate cross section area, use Se. flange COG, counted from base web COG, counted from base plate COG, counted from base COG of stiffener + plate, use s. distance of zfl and COGes distance of dw and COGes distance of dp and COGpes distance from COGes to the outer fiber
Section properties: Ifl 120000 Iw 53333333 Ip 666667 Ipes 504271 dfl 334.78 dw 124.78 dp -85.22 Is 665128696 zpes 10 COGes 113.48 Ies 622003068 Wes 1804044
mm^4 mm^4 mm^4 mm^4 mm mm mm mm^4 mm mm mm^4 mm^3 Note:
Where: flange cross section moment of inertia web cross section moment of inertia plate cross section moment of inertia, use s. plate cross section moment of inertia, use Se. distance of zfl and COG distance of dw and COG distance of dp and COG moment of inertia of stiffener with full plate width effective plate COG, counted from base COG of stiffener + plate, use Se. moment of inertia of stiffener with effective plate width section modulus for stiffener with effective plate at flange tip
Then, the factor kc an C0 is determined as follows: kc 62.24 [] C0 0.001446 [] 1.00 [] p0 0.0723 MPa Finally, the equivalent lateral line load, qSd qsd 223.11 N/mm
Known values: mc 13.3 [] y1,Sd 50.00 MPa y2,Sd 50.00 MPa
mc =13.3 for continuous stiffeners or, = 8.9 for simple supported stiffeners (sniped stiffeners)
Where: y1,Sd larger design stress in the transverse direction, with tensile stresses taken as negative y2,Sd smaller design stress in the transverse direction, with tensile stresses taken as negative
Вам также может понравиться
- Offshore Mechanics: Structural and Fluid Dynamics for Recent ApplicationsОт EverandOffshore Mechanics: Structural and Fluid Dynamics for Recent ApplicationsОценок пока нет
- Ageing and Life Extension of Offshore Structures: The Challenge of Managing Structural IntegrityОт EverandAgeing and Life Extension of Offshore Structures: The Challenge of Managing Structural IntegrityОценок пока нет
- Jacket Launching AnalysisДокумент7 страницJacket Launching Analysisiw2fualОценок пока нет
- Ballasting Calculation For The Transportation of PLEMsДокумент17 страницBallasting Calculation For The Transportation of PLEMsBolarinwa100% (1)
- Seafastening Holding Down BracketДокумент1 страницаSeafastening Holding Down BracketRohan Karande50% (2)
- Miscellaneous Calculations: 1 Sea Transport Forces On CargoДокумент4 страницыMiscellaneous Calculations: 1 Sea Transport Forces On CargoAgarry EmmanuelОценок пока нет
- Mathcad - Dog Plate CalculationДокумент4 страницыMathcad - Dog Plate CalculationAkhmad Syahroni100% (1)
- Grillage&Seafastening DesignExampleДокумент66 страницGrillage&Seafastening DesignExamplefelipecmello100% (1)
- Grillage Seafastening DesignExampleДокумент66 страницGrillage Seafastening DesignExampleeОценок пока нет
- 8E.3 - Barge - Deflection - Sea - TransДокумент11 страниц8E.3 - Barge - Deflection - Sea - TransSiva ShankarОценок пока нет
- Cargo Acceleration Forces WWW - Thenavalarch.com V2.0 SIДокумент12 страницCargo Acceleration Forces WWW - Thenavalarch.com V2.0 SIPaulo Bruno100% (2)
- Wind Area and Forces For Beam Wind: Item Description CH Cs Projected Area (SQ.M) Pressure (N/SQ.M)Документ10 страницWind Area and Forces For Beam Wind: Item Description CH Cs Projected Area (SQ.M) Pressure (N/SQ.M)Amit KumarОценок пока нет
- Seafastening ExcelДокумент13 страницSeafastening ExcelRiyan EsapermanaОценок пока нет
- MOORING CALCULATIONS (S)Документ6 страницMOORING CALCULATIONS (S)halimОценок пока нет
- PDFДокумент5 страницPDFSameera JayaratneОценок пока нет
- Seafastening DesignДокумент14 страницSeafastening DesigntristanxpОценок пока нет
- Quayside Mooring Analysis - Floatel Triumph at Kemaman (P30049-MA-REV 0) (2095)Документ35 страницQuayside Mooring Analysis - Floatel Triumph at Kemaman (P30049-MA-REV 0) (2095)cliff1234Оценок пока нет
- Mooring Hands CalcsДокумент8 страницMooring Hands CalcsLyudmyla Bobina100% (1)
- Transportation Analysis Dynamic Forces Calculation: + Roll Heave (Load Case 101)Документ2 страницыTransportation Analysis Dynamic Forces Calculation: + Roll Heave (Load Case 101)Booraj DuraisamyОценок пока нет
- Sacs-Basics PDFДокумент113 страницSacs-Basics PDFanilОценок пока нет
- Seafastening Design CheckДокумент3 страницыSeafastening Design CheckBolarinwa100% (2)
- 23 Mooring Analysis During ShorepullДокумент53 страницы23 Mooring Analysis During ShorepullNoverdo Saputra100% (1)
- Barge Stability GuidelinesДокумент10 страницBarge Stability Guidelinesnautilus73100% (2)
- LGS Seafastening Design - Revision 3Документ2 страницыLGS Seafastening Design - Revision 3ksangeeth2000Оценок пока нет
- Seafastening Design Calculation - Transportation LoadsДокумент1 страницаSeafastening Design Calculation - Transportation LoadsBolarinwa100% (5)
- 8E.2 - Evaluation - Barge - MotionДокумент7 страниц8E.2 - Evaluation - Barge - MotionSiva ShankarОценок пока нет
- OCIMF Environment Forces Calculator On VLCCДокумент9 страницOCIMF Environment Forces Calculator On VLCCshahjada100% (1)
- Sea FasteningДокумент2 страницыSea FasteningOlanrewaju Tope100% (1)
- Sea Fastening PDFДокумент57 страницSea Fastening PDFsantosh bharathyОценок пока нет
- Catenary Mooring Line Shape Tool (Version 1)Документ1 страницаCatenary Mooring Line Shape Tool (Version 1)SaidОценок пока нет
- CEN TOOL - Standard Padeyes - V4-Rollup Padeye SheaveДокумент5 страницCEN TOOL - Standard Padeyes - V4-Rollup Padeye SheaveLaurentiu TeacaОценок пока нет
- DNV Os C104 2014Документ40 страницDNV Os C104 2014Moe LattОценок пока нет
- SACS Motion StabilityДокумент64 страницыSACS Motion Stabilityramy abazaОценок пока нет
- B616-212.002 PP 3-9 Smit BRKT Strength CalcsДокумент7 страницB616-212.002 PP 3-9 Smit BRKT Strength Calcsnavalzero910100% (1)
- Mooring Forces Port or STBD On Quay WWW - Thenavalarch.com Rev 1Документ10 страницMooring Forces Port or STBD On Quay WWW - Thenavalarch.com Rev 1Mohamed Elfawal100% (1)
- 0013-nd Rev 8.1 28-Jun-16 Guidelines For Load-Outs PDFДокумент38 страниц0013-nd Rev 8.1 28-Jun-16 Guidelines For Load-Outs PDFMark InnesОценок пока нет
- Aj30 Reporttow, SeafasteningДокумент64 страницыAj30 Reporttow, Seafasteningsabah8800100% (7)
- Technical Standards and Commentaries For Port and Harbours Faclilities in JapanДокумент5 страницTechnical Standards and Commentaries For Port and Harbours Faclilities in JapandalifyОценок пока нет
- Ground Bearing Capacity Calculation and Jetty Bearing Capacity Calculation Load Out Topside SvneДокумент6 страницGround Bearing Capacity Calculation and Jetty Bearing Capacity Calculation Load Out Topside SvneTran Van DaiОценок пока нет
- Vessel Motion and Accelerations Noble DentonДокумент1 страницаVessel Motion and Accelerations Noble DentonGanesh100% (1)
- Ballast CalculationДокумент18 страницBallast Calculationsamprof4vw93% (15)
- Sea Fastening Desig MannualДокумент36 страницSea Fastening Desig Mannualjamesmec20013588100% (2)
- Engineering Aspects of Offshore Heavy Heavy-Lift & TransportationДокумент31 страницаEngineering Aspects of Offshore Heavy Heavy-Lift & Transportationmarc121080% (5)
- Longitudinal Strength Analysis of Barge Kreuz 282 During CPP2 JacketДокумент106 страницLongitudinal Strength Analysis of Barge Kreuz 282 During CPP2 JacketSanieBurhan100% (3)
- Calculation For Hull Strength Construction in Offshore Structures PDFДокумент10 страницCalculation For Hull Strength Construction in Offshore Structures PDFcxb07164Оценок пока нет
- H0a C03al A1Документ2 страницыH0a C03al A1iw2fualОценок пока нет
- Stiffened Plate Buckling DNV-RP-C201 Rev02-December-2011Документ9 страницStiffened Plate Buckling DNV-RP-C201 Rev02-December-2011Farid TataОценок пока нет
- Composite Steel GirderДокумент10 страницComposite Steel GirdersorowareОценок пока нет
- Proper Bolt Axial Tightening Force and Proper Tightening TorqueДокумент1 страницаProper Bolt Axial Tightening Force and Proper Tightening Torquecmms88Оценок пока нет
- Proper Bolt Axial Tightening ForceДокумент1 страницаProper Bolt Axial Tightening ForcePrabhu SelvaRajОценок пока нет
- V Psi Am 2Документ8 страницV Psi Am 2kissistvanОценок пока нет
- ComputationДокумент13 страницComputationLester MuscaОценок пока нет
- FootingДокумент84 страницыFootingUma MaheshОценок пока нет
- 321 Chapter 5 Splice DesignДокумент91 страница321 Chapter 5 Splice DesignHemant Ramesh NarkarОценок пока нет
- Lifting LugДокумент8 страницLifting LugAzwan ShahОценок пока нет
- RC Beam Design CCAA - Revised 1.2 JWWДокумент12 страницRC Beam Design CCAA - Revised 1.2 JWWFerdie TolosaОценок пока нет
- Design and Fabrication of Wedge Milling FixtureДокумент28 страницDesign and Fabrication of Wedge Milling FixturedbzdivikОценок пока нет
- Beam-Column Connection To BS5950Документ6 страницBeam-Column Connection To BS5950Mitra RampersadОценок пока нет
- End Plate-Splice ConnectionДокумент76 страницEnd Plate-Splice ConnectionHemant Ramesh Narkar100% (6)
- Retaining Wall With AnchorsДокумент11 страницRetaining Wall With Anchorsmailmaverick8167100% (3)
- Mba 2011 Annamali Part1Документ4 страницыMba 2011 Annamali Part1Reshmi VinuОценок пока нет
- GujvatДокумент137 страницGujvatRahul MalaniОценок пока нет
- Range and EnduranceДокумент10 страницRange and EnduranceSwarna MayuriОценок пока нет
- <HTML><HEAD><META HTTP-EQUIV="REFRESH" CONTENT="0;URL="></HEAD><BODY> </BODY></HTML>Документ25 страниц<HTML><HEAD><META HTTP-EQUIV="REFRESH" CONTENT="0;URL="></HEAD><BODY> </BODY></HTML>Rahul MalaniОценок пока нет
- CNC ReportДокумент109 страницCNC ReportRahul MalaniОценок пока нет
- 3 CNC Programming R2Документ51 страница3 CNC Programming R2KANAV BHARDWAJОценок пока нет
- DIVERTER VALVES Gravity Type Diverter Valves MULTIPORT DIVERTER VALVESДокумент1 страницаDIVERTER VALVES Gravity Type Diverter Valves MULTIPORT DIVERTER VALVESLucas Meirelles SiqueiraОценок пока нет
- Chequered-Plate CALCULATIONДокумент19 страницChequered-Plate CALCULATIONRamuAlagappan100% (2)
- 4000 Liter Pharma Sweed Updates AQE9kZWVQLsbjb36Документ1 страница4000 Liter Pharma Sweed Updates AQE9kZWVQLsbjb36belkacem kisriОценок пока нет
- Craftsman Air Compressor ManualДокумент12 страницCraftsman Air Compressor Manualddefig50% (2)
- AMCA 204-05 Balance Quality and Vibration Levels For FansДокумент26 страницAMCA 204-05 Balance Quality and Vibration Levels For FansDjaffar SalahouiОценок пока нет
- Gravimetic FeedersДокумент26 страницGravimetic FeedersLyndsey Cooper100% (1)
- Esareka Penstock E-CatalogДокумент12 страницEsareka Penstock E-CatalogM Alim Ur RahmanОценок пока нет
- Bellow Seal Valves PDFДокумент18 страницBellow Seal Valves PDFAnil S ChaudharyОценок пока нет
- Question: 3. The S-N Curve For An Acetal Polymer Is Shown in Fig. 1. A. SuДокумент4 страницыQuestion: 3. The S-N Curve For An Acetal Polymer Is Shown in Fig. 1. A. SuVanesaaОценок пока нет
- Exxonmobil - Serpentina H2S Management Project: Material Requisition For H2S Absorbent Modular SkidДокумент21 страницаExxonmobil - Serpentina H2S Management Project: Material Requisition For H2S Absorbent Modular SkidPrakash RajОценок пока нет
- Flightlab Ground School 8. Maneuvering Loads, High-G ManeuversДокумент7 страницFlightlab Ground School 8. Maneuvering Loads, High-G ManeuversJose Ariel ChejanovichОценок пока нет
- S110-10, S1110-10 SchematicДокумент1 страницаS110-10, S1110-10 SchematicWattsОценок пока нет
- Checklist For Roof Skin CasingДокумент7 страницChecklist For Roof Skin CasingRamalingam PrabhakaranОценок пока нет
- GDC LAYOUT UpdatedДокумент1 страницаGDC LAYOUT UpdatedPradneshОценок пока нет
- Unmanned Machinery Space OperationДокумент1 страницаUnmanned Machinery Space OperationcaptaincadenaОценок пока нет
- B. Tech. II - Class Time Table - 2023-24 - OddДокумент2 страницыB. Tech. II - Class Time Table - 2023-24 - OddYusuf GoriawalaОценок пока нет
- LMW CNCДокумент5 страницLMW CNClionlionsherОценок пока нет
- Calculation of Heat and Mass BalanceДокумент18 страницCalculation of Heat and Mass BalanceJitendra Bhatia100% (3)
- Me472 Failure Analysis and DesignДокумент2 страницыMe472 Failure Analysis and DesignSreehari SОценок пока нет
- DKK Agustus' 20Документ58 страницDKK Agustus' 20sryОценок пока нет
- Report of Inspection, Testing & Maintenance of Standpipe SystemsДокумент8 страницReport of Inspection, Testing & Maintenance of Standpipe SystemsCubzlookОценок пока нет
- Carding: A Fi RST GlanceДокумент6 страницCarding: A Fi RST GlanceMohamed NaeimОценок пока нет
- Alu Piston PUMPДокумент24 страницыAlu Piston PUMPv8wfm8d8r7Оценок пока нет
- Manual de Partes Zaranda Modelo TSH6203 Terex PDFДокумент44 страницыManual de Partes Zaranda Modelo TSH6203 Terex PDFHenry DiazОценок пока нет
- AP2D Series PumpДокумент12 страницAP2D Series PumpSoeLettОценок пока нет
- Operation Manual - Manual de Operación HC 109Документ39 страницOperation Manual - Manual de Operación HC 109Cesar Gajardo Gonzalez Horacio0% (1)
- MANUAL - PL-400 Anexo 1Документ9 страницMANUAL - PL-400 Anexo 1Josh TОценок пока нет
- Limits, Fits and Tolerances: Prof. S. S. PandeДокумент31 страницаLimits, Fits and Tolerances: Prof. S. S. PandeM PankajОценок пока нет
- Protig III AirДокумент18 страницProtig III AirkiowacОценок пока нет