Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Practice Exam - Solns
Загружено:
bevinjАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Practice Exam - Solns
Загружено:
bevinjАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
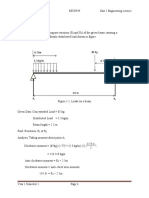
PHYSICS 30 Conservation Laws - Practice Exam
Physics 30
Conservation Laws Practice Exam
SOLUTIONS
Numerical Response
1 2 3 4
9 7 2 3 9 9 3 1 5 2 3 2 2
CCCC CCCC CCC CCCC
CCC CCCC CCC CC
CCCC CCCCCC CCC
CCCC CCCC CCCC CCCC
CCCC CCCC CCC CCCC
CCC CCCC CCCC CCCC
- 1 -
PHYSICS 30 Conservation Laws - Practice Exam
A. MACHINE SCORED
NR. 1 ME
Ti
+ W
F
= ME
Tf
KE
i
+ F d cos = KE
f
850 J + F (0.36 m) cos 180 = 500 J
F = 972 N Answer: 972
1. Since ME
Ti
= 850 J and ME
Tf
= 500 J, the total mechanical energy decreases.
Answer: B
NR. 2 ME
T
= KE + PE
g
= 0.5mv
2
+ mgh
= 0.5 (67 kg) (5 m/s)
2
+ (6.7 kg) (9.81 N/kg) (4.8 m)
= 3.99 10
3
J Answer: 3993
2. If the object loses 2.40 10
3
J of PE
g
, then it gains 2.40 10
3
J of KE.
KE = KE
f
KE
i
KE
f
= KE + KE
i
= KE + 0.5mv
i
2
= +2.40 10
3
J + 0.5 (67 kg) (5 m/s)
2
= 3237.5 J
KE
f
= 0.5 mv
f
2
3237.5 J = 0.5 (67.0 kg) v
f
2
v
f
= 9.83 m/s Answer: D
3. A Physics 30 students lists four characteristics of energetics.
Energy is a scalar, and so direction does not have to be taken into account.
Total energy is conserved throughout most physical situations (if mass remains constant).
Energy can never be negative, and so, calculations are straightforward.
When work is done on an object, the energy of the object always remains constant.
How many of these characteristics are correct?
A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4
NR. 3 E
e
= 0.5 kx
2
2.46 J = 0.5 k (-0.18 m)
2
k = 152 N/m Answer: 152
4. PE
g
(max)
= 0.71 E
e
mgh
max
= 0.71 E
e
(0.37 kg) (9.81 N/kg) h
max
= 0.71 (2.46 J)
h
max
= 0.48 m
= 48 cm Answer: A
- 2 -
PHYSICS 30 Conservation Laws - Practice Exam
5. Weight = mg
300 N = m (9.81 N/kg) m = 30.581 kg
W = E = PE
g
= PE
gf
PE
gi
= mgh
f
- mgh
i
= (30.581 kg) (9.81 N/kg) (1.28 m) - (30.581 kg) (9.81 N/kg) (0.75 m)
= 159 J
P = W / t = 159 J / 0.64 s = 248 W Answer: B
6. The concepts of momentum and inertia are very similar. Which of the following is NOT a
shared characteristic?
A. It is a measure of an objects resistance to changes in velocity.
B. It increases as the mass of the object increases.
C. The value is the same at rest or when the object is moving.
D. The value does not depend on gravitational field strength (i.e. gravity).
7. Impulse = Area
= 0.5 (24 10-2 s) (50 N) + (36 10-2 s) (50 N)
= 24 N s
Impulse = p
f
p
i
p
f
= Impulse + p
i
= 24 kgm/s + 0 = 24 kgm/s Answer: B
8. Ref: East is positive
p
T
= p
T
p
1
+ p
2
= p
1
+ p
2
m
1
v
1
+ m
2
v
2
= m
1
v
1
+ m
2
v
2
(2.0 kg) (5.0 m/s) + (3.0 kg) (-7.0 m/s) = (2.0 kg) (-4.0 m/s) + (3.0 kg) v
v = -1.0 m/s
= 1.0 m/s West Answer: A
9. Ref: Right is positive
p
2
= - p
1
p
2
- p
2
= - (-7000 kgm/s)
(150 kg) v - (150 kg) (82 m/s) = 7000 kgm/s
v = 129 m/s right Answer: C
- 3 -
PHYSICS 30 Conservation Laws - Practice Exam
10. Since p
T
is fully horizontal, it is a simple calculation to find p
T
p
T
= p
T
= m
T
v
= (4.8 kg + 7.2 kg) (9.49 m/s)
= 1.1 102 kgm/s Answer: A
11.
Mass 1: RCS angle = 331 (-29) 29
y
1
= (76.8 kgm/s) sin 331
= -37.23 kgm/s y
1
p
1
= 76.8 kgm/s
29
y
T
= y
T
y
1
+ y
2
= 0
y
2
= 37.23 kgm/s
y
2
p
2
= 59.76 kgm/s
sin = opp / hyp
sin = 37.23 / 59.76
= 39 Answer: B
NR. 4 ME
Ti
= KE
1
+ KE
2
+ 0.5m
1
v
1
2
+ 0.5m
2
v
2
2
= 0.5 (4.8 kg) (16 m/s)
2
+ 0.5 (7.2 kg) (8.2 m/s)
2
= 862.4 J
ME
Tf
= KE
f
= 0.5 m
T
v
f
2
= 0.5 (12.0 kg) (9.49 m/s)
2
= 540.36 J
ME
lost
= ME
Ti
- ME
Tf
= -322 J
= -3.2 10
2
J Answer: 322
- 4 -
PHYSICS 30 Conservation Laws - Practice Exam
B. WRITTEN RESPONSE
WR #1.
Speed on impact (Ref h = Top of air mattress)
ME
Ti
+ W = ME
Tf
PE
gi
+ W = KE
f
mgh
i
+ W = 0.5mv
f
2
(82 kg) (9.81 N/kg) (17 m) - 4000 J = 0.5 (82 kg) v
f
2
v
f
= 15.4 m/s
Impulse on Person (Ref: Down is positive)
Impulse = m v = m (v
f
v
i
)
= (82.0 kg) (0 - 15.4 m/s)
= -1.26 10
3
N s
= 1.26 10
3
N s upwards
Why the air mattress reduces injuries
Based on F
net
= m v / t,
F
net
has an inverse relationship with time (assuming m v or impulse is constant)
The air bag increases the time for the momentum to decrease to zero.
Increasing the time will decrease the F
net
acting on the stunt person.
This reduces injuries.
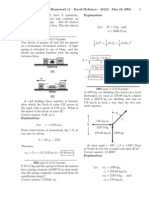
WR #2.
Before explosion:
p
T
= 0 So, x
T
= 0; y
T
= 0
After explosion:
p
1
= 1911 kgm/s p
2
= 1320 kgm/s p
3
= 25 v
x
1
= 1911 kgm/s x
2
= 0 x
3
?
y
1
= 0 y
2
= -1320 kgm/s y
3
?
x
T
= x
T
y
T
= y
T
0 = 1911 + 0 = x
3
0 = 0 + (-1320 kgm/s) + y
3
x
3
= -1911 kgm/s y
3
= 1320 kgm/s
So,
(p
3
)
2
= (1911)
2
+ (1320)
2
p
3
= 2323 kgm/s p
3
= 25v
v
3
= 92.9 m/s 1320 kgm/s
tan = 1320 / 1911
= 34.6 N of W 1911 kgm/s
- 5 -
Вам также может понравиться
- 2011 H2 Chemistry Paper 3 Suggested SolutionsДокумент7 страниц2011 H2 Chemistry Paper 3 Suggested SolutionsLee Jun Hui0% (1)
- 6WG1 TQA Workshop Manual N2223 Ex PDFДокумент3 страницы6WG1 TQA Workshop Manual N2223 Ex PDFmasakp75% (8)
- Physics Unit 3 AssignmentДокумент19 страницPhysics Unit 3 AssignmentJade50% (2)
- Chapter 18 PDFДокумент91 страницаChapter 18 PDF이희인Оценок пока нет
- Physics 303K Test 3 SolutionsДокумент11 страницPhysics 303K Test 3 SolutionsbrunosipodОценок пока нет
- Print EEДокумент14 страницPrint EEMarie Joy EngayОценок пока нет
- Answer Key (Test-6) PhysicsДокумент20 страницAnswer Key (Test-6) Physicssyuvarajno.1Оценок пока нет
- Zeroth Law and Introductory ConceptsДокумент13 страницZeroth Law and Introductory ConceptsMohd Danial Muhd AliОценок пока нет
- Answer Key To Test Prep Physics CHP 9-13Документ6 страницAnswer Key To Test Prep Physics CHP 9-13linlinyc686450% (2)
- Answer PHYSIC STPM Trial Sem 1 2013Документ6 страницAnswer PHYSIC STPM Trial Sem 1 2013Zuraini ArshadОценок пока нет
- 10 Work, Energy and PowerДокумент13 страниц10 Work, Energy and PowerKenzyОценок пока нет
- 103 Phys Ch7 Part2Документ12 страниц103 Phys Ch7 Part2Dennis KimОценок пока нет
- Examples - PhysicsДокумент8 страницExamples - Physicslaila1001Оценок пока нет
- Work Ower EnergyДокумент31 страницаWork Ower EnergyOmprakash Dhaka100% (2)
- Unit 67 2Документ10 страницUnit 67 2Rob SinathОценок пока нет
- Lecture 22Документ62 страницыLecture 22adilafzalkhan4264Оценок пока нет
- PHY Exam 1Документ8 страницPHY Exam 1Samantha GornickОценок пока нет
- Jee Main 2017 Question Paper Solutions Physics 2nd AprilДокумент22 страницыJee Main 2017 Question Paper Solutions Physics 2nd AprilAmit SharmaОценок пока нет
- The Period of A Mass On A SpringДокумент16 страницThe Period of A Mass On A SpringPatrick SibandaОценок пока нет
- 2021 P1 Worked Solutions: EtontuitioncentreДокумент7 страниц2021 P1 Worked Solutions: EtontuitioncentrealacerrrrОценок пока нет
- Brilliant'S Full Syllabus Test 4: For Our Students Towards Joint Entrance Examination, 2013Документ21 страницаBrilliant'S Full Syllabus Test 4: For Our Students Towards Joint Entrance Examination, 2013cshubham23Оценок пока нет
- Suggested Solution To 2010 Jc2 Physics Prelims H2 P1: Section A (MCQS) Ans: BДокумент17 страницSuggested Solution To 2010 Jc2 Physics Prelims H2 P1: Section A (MCQS) Ans: BDavid ArdiansyahОценок пока нет
- q1 A Block of Mass M 500 KG Is Released Form Rest FromДокумент2 страницыq1 A Block of Mass M 500 KG Is Released Form Rest Frommon chériОценок пока нет
- Physics Cumulative Test # 1 - SolutionДокумент6 страницPhysics Cumulative Test # 1 - SolutionTalha Syed NaqviОценок пока нет
- Lectu 14Документ4 страницыLectu 14YeviraArinDiyanaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 25 Solutions: V - 14.0 V and Q - N W Q, So W Q (V) ( - 9.63Документ28 страницChapter 25 Solutions: V - 14.0 V and Q - N W Q, So W Q (V) ( - 9.63Alender Jesus Vargas TovarОценок пока нет
- 01-11-Physics IДокумент270 страниц01-11-Physics Ikalley minogОценок пока нет
- Physics 111 Homework Solution #5Документ20 страницPhysics 111 Homework Solution #5jhunОценок пока нет
- CBSE Sample Paper For Class 11 Physics Mock Paper 1 With SolutionsДокумент26 страницCBSE Sample Paper For Class 11 Physics Mock Paper 1 With SolutionsAyushi ShahОценок пока нет
- Sample Paper-02 Physics (Theory) Class - Xi Answers: Weight Alpg LPG A A L M GДокумент9 страницSample Paper-02 Physics (Theory) Class - Xi Answers: Weight Alpg LPG A A L M GKabir BiswalОценок пока нет
- L 8 Dec 2003 SolutionДокумент45 страницL 8 Dec 2003 SolutionAnonymous 83o62cОценок пока нет
- =F sinθ : R= F F R= F F R= FДокумент46 страниц=F sinθ : R= F F R= F F R= FYhelly27Оценок пока нет
- Exam Possible Questions: Velocity at HДокумент31 страницаExam Possible Questions: Velocity at HJake FryОценок пока нет
- R A DeCarlo and P Lin Linear Circuit Analysis SДокумент945 страницR A DeCarlo and P Lin Linear Circuit Analysis STommyc102477% (13)
- Exercise Chapter 1 and 2 Kelompok 9Документ5 страницExercise Chapter 1 and 2 Kelompok 9Puskesmas BatusepuluhОценок пока нет
- HW 06 SolnДокумент19 страницHW 06 SolnKristin Dikiciyan100% (1)
- Solution To 2010 VJC Prelim H2 P1Документ9 страницSolution To 2010 VJC Prelim H2 P1cjcsucksОценок пока нет
- Resistive Forces SolutionsДокумент4 страницыResistive Forces SolutionsdicksquadОценок пока нет
- Energy Problems 1Документ22 страницыEnergy Problems 1Cassidy GonzalezОценок пока нет
- Chap6 PhysicsДокумент23 страницыChap6 PhysicsMadhavi SivanОценок пока нет
- 7 Introduction To MechanicsДокумент9 страниц7 Introduction To MechanicsmvhokoОценок пока нет
- Dyn AssignmentДокумент8 страницDyn AssignmentTekle AschuОценок пока нет
- Example: Given: A 0.5 KG Ball of Negligible SizeДокумент9 страницExample: Given: A 0.5 KG Ball of Negligible SizegОценок пока нет
- CH19Документ79 страницCH19Diego Orlando Garzón VОценок пока нет
- Examples of ProbsДокумент8 страницExamples of ProbsSantosh G PattanadОценок пока нет
- SM 14Документ78 страницSM 14zahidahОценок пока нет
- 2022 JPJC Prelim H2 Physics P1 SolnДокумент8 страниц2022 JPJC Prelim H2 Physics P1 Solnlarrystan139Оценок пока нет
- Y1S1 Roll.3 MG Kyaw Zaw Naing, Engineering ScienceДокумент14 страницY1S1 Roll.3 MG Kyaw Zaw Naing, Engineering ScienceKyaw Zaw NaingОценок пока нет
- Momentum Review QuestionsДокумент5 страницMomentum Review Questionssomeguy01123Оценок пока нет
- PhysДокумент7 страницPhysCristine Gen HernandezОценок пока нет
- Center of MassДокумент5 страницCenter of MassMahesh VashisthОценок пока нет
- Bugtong, Trixie Jael P.Документ10 страницBugtong, Trixie Jael P.yeng botzОценок пока нет
- Practice Midterm 02Документ8 страницPractice Midterm 02Ha ViОценок пока нет
- Ch1 HW3 SolutionsДокумент7 страницCh1 HW3 SolutionsCharles YamashiroОценок пока нет
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsОт EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsОценок пока нет
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresОт EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Financial Accounting Notes 3Документ45 страницFinancial Accounting Notes 3bevinjОценок пока нет
- Financial Accounting Notes 2bДокумент49 страницFinancial Accounting Notes 2bbevinjОценок пока нет
- The Theory of Trade and InvestmentДокумент24 страницыThe Theory of Trade and InvestmentbevinjОценок пока нет
- Financial Accounting Notes 1&2Документ62 страницыFinancial Accounting Notes 1&2bevinjОценок пока нет
- Essential Concepts: Lesson 2Документ34 страницыEssential Concepts: Lesson 2bevinjОценок пока нет
- Work With Families Family and Child Welfare: Step Six of The Decision TreeДокумент72 страницыWork With Families Family and Child Welfare: Step Six of The Decision TreebevinjОценок пока нет
- Computer Software: Application Software Systems Software Operating SystemsДокумент38 страницComputer Software: Application Software Systems Software Operating SystemsbevinjОценок пока нет
- ElasticityДокумент71 страницаElasticitybevinjОценок пока нет
- NetworkingДокумент20 страницNetworkingbevinjОценок пока нет
- Theoretical Foundations: Prices, Markets, and Management: Institute of Modern Sciences & Arts (IMSA)Документ43 страницыTheoretical Foundations: Prices, Markets, and Management: Institute of Modern Sciences & Arts (IMSA)bevinjОценок пока нет
- StorageДокумент7 страницStoragebevinjОценок пока нет
- Basic Computer OperationДокумент19 страницBasic Computer OperationbevinjОценок пока нет
- GenerationsДокумент31 страницаGenerationsbevinjОценок пока нет
- File Systems and Databases: Database Systems: Design, Implementation, and Management, Fifth Edition, Rob and CoronalДокумент36 страницFile Systems and Databases: Database Systems: Design, Implementation, and Management, Fifth Edition, Rob and CoronalbevinjОценок пока нет
- Unit 8 Project and Programme Management - P2M For Enterprise Innovation StructureДокумент12 страницUnit 8 Project and Programme Management - P2M For Enterprise Innovation StructurebevinjОценок пока нет
- Unit 14 Project Management Plan and Global Delivery Model: StructureДокумент15 страницUnit 14 Project Management Plan and Global Delivery Model: StructurebevinjОценок пока нет
- Unit 10 Project Management Process: StructureДокумент19 страницUnit 10 Project Management Process: StructurebevinjОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 Basics of Project Management: StructureДокумент20 страницUnit 1 Basics of Project Management: StructurebevinjОценок пока нет
- Unit 4 Concepts of Managing Conflict, Quality and IS: StructureДокумент17 страницUnit 4 Concepts of Managing Conflict, Quality and IS: StructurebevinjОценок пока нет
- Unit 9 Guide To Systematic Scientific Project Management: StructureДокумент12 страницUnit 9 Guide To Systematic Scientific Project Management: StructurebevinjОценок пока нет
- Project Management Table of Contents PMДокумент5 страницProject Management Table of Contents PMbevinjОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 2 Air-Standard CyclesДокумент3 страницыTutorial 2 Air-Standard CyclesPhineas sehoanaОценок пока нет
- NPHO Syllabus LatestДокумент3 страницыNPHO Syllabus LatestSanvir RulezzОценок пока нет
- Project Project Project Project 4 4 4 4Документ5 страницProject Project Project Project 4 4 4 4anthony_vidalОценок пока нет
- Electrochromic Nio Thin Films Prepared by Spin Coating: F. Özütok S. Demiri E. ÖzbekДокумент5 страницElectrochromic Nio Thin Films Prepared by Spin Coating: F. Özütok S. Demiri E. ÖzbekSoufianeBenhamidaОценок пока нет
- Wind PumpДокумент6 страницWind PumpCarlos Castillo PalmaОценок пока нет
- Aeroacoustics of Savonius WTДокумент10 страницAeroacoustics of Savonius WTBattle SagaОценок пока нет
- Model 5 Operating and Maintenance ManualДокумент98 страницModel 5 Operating and Maintenance ManualgfollertОценок пока нет
- Electrical Machines Lab ManualДокумент68 страницElectrical Machines Lab Manualgopi_90550% (2)
- PHD Thesis Energy StorageДокумент4 страницыPHD Thesis Energy Storagelodyicxff100% (2)
- WORKING DOC EV Extrication UPDATED 140822Документ29 страницWORKING DOC EV Extrication UPDATED 140822Syahrir ShahОценок пока нет
- 2 GettingStartedWithOpenFOAM PDFДокумент22 страницы2 GettingStartedWithOpenFOAM PDFIjaz FazilОценок пока нет
- Biomass Student HandbookДокумент21 страницаBiomass Student HandbookPillai AkhilОценок пока нет
- Schrdter 2008Документ46 страницSchrdter 2008hidayat231984Оценок пока нет
- Air Compressor LubricantsДокумент1 страницаAir Compressor LubricantsRifki AndriyanОценок пока нет
- 4878 PaperДокумент13 страниц4878 PaperLawrence Lim Ah KowОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1 DR Shery PDFДокумент21 страницаLecture 1 DR Shery PDFhskakОценок пока нет
- Dvigatel Cummins Nta855 g4Документ2 страницыDvigatel Cummins Nta855 g4HanОценок пока нет
- Miller-Dimension 562 Spec-Sheet 2014Документ1 страницаMiller-Dimension 562 Spec-Sheet 2014LodyОценок пока нет
- Gain Energy Insight and Control With PowerlogicДокумент8 страницGain Energy Insight and Control With PowerlogiccesОценок пока нет
- Catalogo de Equipo de Aire AcondicionadoДокумент886 страницCatalogo de Equipo de Aire AcondicionadoGabo RocketPower MorenoОценок пока нет
- EMI Reduction and PCB Layout TechniquesДокумент3 страницыEMI Reduction and PCB Layout Techniquesfelixrajesh0% (1)
- Me 200 Exam 1 SolutionДокумент8 страницMe 200 Exam 1 Solutionqasim zaheerОценок пока нет
- Diagram A ElectricoДокумент16 страницDiagram A Electricojulio cesarОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Electrical Circuits: Polytechnic University of The Philippines - Binan CampusДокумент106 страницFundamentals of Electrical Circuits: Polytechnic University of The Philippines - Binan CampusEsmeralda Joyce RaymundoОценок пока нет
- Occupational Safety HealthДокумент729 страницOccupational Safety HealthSarah AqirahОценок пока нет
- A Conduit Bending Guide On How To Bend An OffsetДокумент16 страницA Conduit Bending Guide On How To Bend An OffsetmarkОценок пока нет
- Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic InductionДокумент10 страницFaraday's Law of Electromagnetic InductionMylz MendozaОценок пока нет
- Plumbing Interview Questions by Prosen SirДокумент10 страницPlumbing Interview Questions by Prosen SirBlue Eye'sОценок пока нет