Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Nice Guideline On A Eds
Загружено:
Arumi HamasakiОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Nice Guideline On A Eds
Загружено:
Arumi HamasakiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
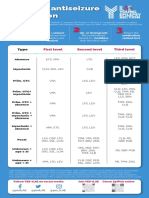
NICE guideline on AEDs
NICE produces guidelines for the treatment and management of health conditions in England and Wales. Its guideline on epilepsy includes recommendations for the drug treatment of different types of seizures.
about NICE NICE is the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. It is an independent organisation working in England and Wales to give guidance to the NHS, healthcare professionals and the community on promoting health and treating and managing health conditions. NICEs clinical guidelines recommend standards for diagnosing, treating and managing specific conditions. Clinical guidelines take into account best practice and evidence-based research to develop the recommendations. The clinical guideline for epilepsy is called The epilepsies: the diagnosis and management of the epilepsies in adults and children in primary and secondary care. Part of this guideline focuses on the recommended anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs) for treating different types of seizures. This factsheet looks at the treatment that NICE recommends for epilepsy. For more detailed information on the guideline for epilepsy visit www.nice.org.uk and search for epilepsy.
29
factsheet
notes The AEDs listed in the tables on the following pages are listed by their generic name (the name of the active ingredient).
The titles of the rows and what they mean
First line treatment this refers to a drug that is tried first and usually used on its own. If more than one AED is listed in this row, only one AED will be chosen and tried on its own. If it does not work, the another may be tried, or a drug from the alternative first line drug list might be used. Alternative first line treatment this is the second round of AEDs that are tried. Like the first line treatment they are usually tried on their own, although sometimes combinations might be used. Adjunctive treatment (or add-on treatment) these are AEDs that might be added to a first line treatment (are used in combination) if a single first line treatment does not control the seizures or is not tolerated (for example, has side effects). Action if adjunctive treatment is not effective or tolerated this is guidance on what to do if adjunctive treatment does not work. In some situations, referral back to a neurologist, or on to specialist neurological services (or tertiary services) might be needed. It may be that the persons diagnosis needs to be looked at, or a more specialist combination of treatment is needed. Cautions this includes situations where extra care is needed when prescribing AEDs. Some AEDs can have specific side effects, or there may be AEDs that make some seizure types worse rather than better.
Call us for a large print version
treatment of focal seizures Treatment of focal seizures in children, young people and adults. First line treatment Alternative first line treatment Cautions Adjunctive treatment (if first line treatment is not effective or tolerated) Action if adjunctive treatment is not effective or tolerated Cautions carbamazepine, lamotrigine levetiracetam, oxcarbazepine, sodium valproate be aware of potential effect of sodium valproate in pregnancy carbamazepine, clobazam, gabapentin, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, oxcarbazepine, sodium valproate, topiramate consider referral to tertiary services (where other AEDs may be tried) be aware of potential effect of sodium valproate in pregnancy
treatment of generalised tonic clonic seizures Treatment of generalised tonic clonic seizures in children, young people and adults. First line treatment Cautions sodium valproate, lamotrigine (if sodium valproate is not suitable) be aware of potential effect of sodium valproate in pregnancy. If the person has myoclonic seizures or may have juvenile myoclonic epilepsy lamotrigine may worsen myoclonic seizures carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine be aware that these drugs may worsen myoclonic or absence seizures clobazam, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, sodium valproate, topiramate be aware of potential effect of sodium valproate in pregnancy. If the person also has absences or myoclonic seizures, or may have juvenile myoclonic epilepsy do not offer carbamazepine, gabapentin, oxcarbazepine, phenytoin, pregabalin, tiagabine or vigabatrin
Alternative first line treatment Cautions Adjunctive treatment (if first line treatment is not effective or tolerated) Cautions
treatment of absence seizures Treatment of absence seizures in children, young people and adults. First line treatment Cautions Alternative first line treatment Adjunctive treatment (if first line treatment is not effective or tolerated) Action if adjunctive treatment is not effective or tolerated Cautions ethosuximide, sodium valproate (offer first if additional tonic clonic seizures are likely) be aware of potential effect of sodium valproate in pregnancy lamotrigine try a combination of ethosuximide, lamotrigine or sodium valproate. consider referral to tertiary services (where other AEDs may be tried) do not offer carbamazepine, gabapentin, oxcarbazepine, phenytoin, pregabalin, tiagabine or vigabatrin
Call us for a large print version
treatment of myoclonic seizures Treatment of myoclonic seizures in children, young people and adults. First line treatment Cautions Alternative first line treatment Cautions Adjunctive treatment (if first line treatment is not effective or tolerated) Action if adjunctive treatment is not effective or tolerated Cautions sodium valproate be aware of potential effect of sodium valproate in pregnancy levetiracetam, topiramate be aware that topiramate has poorer side effects than sodium valproate or levetiracetam levetiracetam, sodium valproate, topiramate consider referral to tertiary services (where other AEDs may be tried) be aware of potential effect of sodium valproate in pregnancy. Do not offer carbamazepine, gabapentin, oxcarbazepine, phenytoin, pregabalin, tiagabine or vigabatrin
treatment of tonic and atonic seizures Treatment of tonic and atonic seizures in children, young people and adults. First line treatment Cautions Adjunctive treatment (if first line treatment is not effective or tolerated) Action if adjunctive treatment is not effective or tolerated Cautions sodium valproate be aware of potential effect of sodium valproate in pregnancy lamotrigine consider referral to tertiary services (where other AEDs may be tried) do not offer carbamazepine, gabapentin, oxcarbazepine, pregabalin, tiagabine or vigabatrin
All information in the tables on this factsheet is taken from The epilepsies: the diagnosis and management of the epilepsies in adults and children in primary and secondary care, NICE clinical guideline 137, NICE, 2012. For more information visit www.nice.org.uk
Epilepsy Society April 2012 Epilepsy Society, Chesham Lane Chalfont St Peter, Bucks SL9 0RJ
Epilepsy Society is the working name for The National Society for Epilepsy, registered charity number 206186
www.epilepsysociety.org.uk
Every effort is made to ensure that all information is correct. Please note that information may change after printing. This information is not a substitute for advice from your own doctors. Epilepsy Society is not responsible for any actions taken as a result of using this information.
Monday to Friday 10am to 4pm Confidential (national call rate)
01494 601 400
helpline
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Simpo 5 - Nonsurgical Approach of Abdominal Pain - DR Putut SPPDДокумент34 страницыSimpo 5 - Nonsurgical Approach of Abdominal Pain - DR Putut SPPDArumi HamasakiОценок пока нет
- Activity Number Title Objective Timing: Table 3 - 1. Summary of Recommended ActivitiesДокумент1 страницаActivity Number Title Objective Timing: Table 3 - 1. Summary of Recommended ActivitiesArumi HamasakiОценок пока нет
- Activity Number Title Objective Timing: Recommended Activities For Topic 1 - Outbreak InvestigationДокумент1 страницаActivity Number Title Objective Timing: Recommended Activities For Topic 1 - Outbreak InvestigationArumi HamasakiОценок пока нет
- Lyrics When U'r GoneДокумент6 страницLyrics When U'r GoneArumi HamasakiОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Respiratory SystemДокумент9 страницPathophysiology of Respiratory SystemArumi HamasakiОценок пока нет
- Recent Advances in Pathophysiology and Current Management of ItchДокумент5 страницRecent Advances in Pathophysiology and Current Management of ItchArumi HamasakiОценок пока нет
- Laparoscopic Versus Open Appendectomy: Is There A Difference?Документ2 страницыLaparoscopic Versus Open Appendectomy: Is There A Difference?Arumi HamasakiОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Applying TDM To Anti Epileptic DrugsДокумент42 страницыApplying TDM To Anti Epileptic DrugsMohd Azrie AbdullahОценок пока нет
- Anti-Epileptic DrugsДокумент7 страницAnti-Epileptic DrugsSampada ghodkiОценок пока нет
- Barbitricos RevNeurologa PDFДокумент10 страницBarbitricos RevNeurologa PDFMonserratОценок пока нет
- Table 17-3Документ2 страницыTable 17-3Dragutin PetrićОценок пока нет
- Thyroid Data Pediatric PatientДокумент31 страницаThyroid Data Pediatric Patientبشير حيدرОценок пока нет
- p2018b3 SampleДокумент21 страницаp2018b3 SampleAhmad FahroziОценок пока нет
- Efficacy and Safety of Levetiracetam in Pediatric EpilepsyДокумент4 страницыEfficacy and Safety of Levetiracetam in Pediatric EpilepsyDian ArdiansyahОценок пока нет
- ASM Pharmacology and Clinical Efficacy 2021 PDFДокумент29 страницASM Pharmacology and Clinical Efficacy 2021 PDFIchrak GhachemОценок пока нет
- Lista de Precios 2019: Alvarez Martinez HaydeeДокумент2 страницыLista de Precios 2019: Alvarez Martinez HaydeeedgarОценок пока нет
- Manajemen Akuntasi Farmasi (Daftar Sediaan Obat)Документ3 страницыManajemen Akuntasi Farmasi (Daftar Sediaan Obat)Khoirun nisa100% (1)
- (PORSOLT) Comparative Anticonvulsant Activity of Carbamazepine Lamotrigine and Valproate in The Mouse and in The RatДокумент1 страница(PORSOLT) Comparative Anticonvulsant Activity of Carbamazepine Lamotrigine and Valproate in The Mouse and in The RatBestka ZaushaОценок пока нет
- Medicamentos Essenciais para Jovens MedicosДокумент2 страницыMedicamentos Essenciais para Jovens MedicosVieira MarceloОценок пока нет
- Lamotrigine and Other Antiepileptics On Sleep Architecture - No Effect PDFДокумент5 страницLamotrigine and Other Antiepileptics On Sleep Architecture - No Effect PDFNones NoneachОценок пока нет
- Anticonvulsant Quiz AnswersДокумент26 страницAnticonvulsant Quiz AnswersRammy KhanОценок пока нет
- Review of The Newer Antiepileptic Drugs PDFДокумент28 страницReview of The Newer Antiepileptic Drugs PDFnickyОценок пока нет
- Clinically Significant Pharmacokinetic Drug Interactions With Carbamazepine - SpringerLinkДокумент42 страницыClinically Significant Pharmacokinetic Drug Interactions With Carbamazepine - SpringerLinkDavid HCОценок пока нет
- Benzo Conversion ChartДокумент2 страницыBenzo Conversion ChartAl_CodaОценок пока нет
- Status Epilepticus ManagementДокумент1 страницаStatus Epilepticus ManagementMuhammad Daniala SyuhadaОценок пока нет
- Gabapentin 100Документ2 страницыGabapentin 100ingrid devi carissaОценок пока нет
- R KasusДокумент3 страницыR KasusYanpow Boromania0% (1)
- Ni PT Istri Putri Lantiani PDFДокумент4 страницыNi PT Istri Putri Lantiani PDFputrilantianiОценок пока нет
- Newer Antiepileptic Drugs and Recent Advances in Drug Therapy of EpilepsyДокумент9 страницNewer Antiepileptic Drugs and Recent Advances in Drug Therapy of EpilepsySanjay NavaleОценок пока нет
- Antiepileptic Drugs-Good LectureДокумент55 страницAntiepileptic Drugs-Good LecturealijanmarwatОценок пока нет
- Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 7th Ed. - Acetone PDFДокумент19 страницUllmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 7th Ed. - Acetone PDFCarla100% (2)
- Antiepileptic Drugs 2019 Elearning PDFДокумент39 страницAntiepileptic Drugs 2019 Elearning PDFMalvika BabuОценок пока нет
- Anti Epileptic DrugsДокумент89 страницAnti Epileptic DrugsInderjeet SohalОценок пока нет
- Aed Part 2 PDFДокумент5 страницAed Part 2 PDFVijay SharmaОценок пока нет
- Update On Antiepileptic - Drugs 2019 PDFДокумент29 страницUpdate On Antiepileptic - Drugs 2019 PDFRahul RaiОценок пока нет
- Latihan Analisis Abc No Nama Obat Jumlah Obat Harga Satuan (RP)Документ7 страницLatihan Analisis Abc No Nama Obat Jumlah Obat Harga Satuan (RP)Nur FadliahОценок пока нет
- AntiepilepticiДокумент29 страницAntiepilepticiIskraОценок пока нет