Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
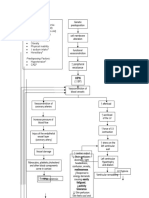
Concept Map Diagnosis and Interventions
Загружено:
menickel3Исходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Concept Map Diagnosis and Interventions
Загружено:
menickel3Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Problem #1: risk for decreased Cardiac Output related to altered electrical conduction as evidenced by HR of 190 General Goal:
Outcome: Patient maintains adequate Cardiac Output related during shift Nursing Intervention: Response to Intervention: Rationales: 1. Provide calm and quiet environment. 1. Calm environment was provided 1. Reduces stimulation and 2. Demonstrate and encourage use of during shift. release of stress-related stress management behaviors such as 2. Stress management behaviors such catecholamines, which can cause relaxation techniques; guided imagery; as relaxation techniques; guided or aggravate dysrhythmias and and slow, deep breathing. imagery; and slow, deep breathing vasoconstriction, increasing 3. Auscultate heart sounds, noting rate, was not done during shift. myocardial workload. rhythm, presence of 3 Auscultation of heart sounds were 2. Reduces stimulation and extra heartbeats, and dropped beats during shift with no extra heartbeats, release of stress-related 4. Monitor vital signs. Assess and dropped beats noticed. catecholamines, which can cause adequacy of cardiac output and 4. .Vital signs were monitored or aggravate dysrhythmias and tissue perfusion, noting significant throughout shift vasoconstriction, increasing variations in BP, pulse myocardial workload. rate equality, respirations, changes in 3. Specific dysrhythmias are more skin color and temperature, clearly detected audibly than by level of consciousness and sensorium, palpation. Hearing extra and urine output during episodes of heartbeats or dropped beats helps dysrhythmias. identify dysrhythmias in the unmonitored client. 4. Although not all dysrhythmias are life-threatening, immediate treatment may be required to terminate dysrhythmia in the presence of alterations in cardiac output and tissue perfusion
Problem#2: Risk for falls related impaired physical mobility. General Goal: Patient will not sustain a fall during this shift. Outcome: Nursing Intervention: Response to Interventions: 1. Encourage use of mobility assistive devices when ambulating and 1. Patient did not transfer during transferring. shift. 2. Patient did not display any fall 2.) Monitor BP for signs of risks related to medications. Polypharmacy during shift BP108/67, RR 17, A&O x4 3. Place items used by the patient 3. 3Tray table, call light, phone and within easy reach, such as call light, personal possessions were urinal, water, telephone kept within reach during shift. 4. ) Encourage the patient to wear 4. Patient refused to wear non slip shoes or slippers with nonskid socks socks during shift. when ambulating
Rationales: 1. Improper use and maintenance of mobility aids such as canes, walkers, and wheelchairs increases the person's risk for falls. 2. Drugs that affect blood pressure and level of consciousness are associated with the highest fall risk. 3. Stretching to get items from bedside tables that are out of reach can disrupt the patient's balance and contribute to falls. 4. ) Nonskid footwear provides sure footing for the patient with diminished foot and toe lift when walking
Problem #3: Situational Low Self-Esteem related to hospitalization as evidenced by reports of feelings of helplessness and uselessness General Goal: ): Patient describes successes in current situations Outcome: Nursing Interventions: Response to Interventions: Rationales: 1. Spend time with the patient, set aside sufficient time so that the 1. Patient expressed feelings about 1. The patient needs time to encounter is unhurried. Provide his situation, fears, and anxieties of express concerns. Spending time environment conducive to the the rehabilitation process during with the patient expresses the expression of feelings shift. nurse's interest in and acceptance 2. ) Use active listening and open2. Patient was able to express of the patient's feelings. ended questions himself about how his frustrations 2. These communication 3. Convey a sense of respect for the with his disability and frustration techniques allow the patient to patient's abilities and strengths in with hospital environment during express concerns, fears, and ideas addition to recognizing problems and shift. without interruption concerns. 3. Acknowledged and encouraged the 3. Assistance with problem 4. Encourage patient to make patients ability to perform selfsolving and reality testing is best decisions about care and to perform hygiene and recognized his sense of provided within the context of a their own self-care. frustration during shift. trusting relationship. 4. Patient performed some self-care, 4. Each success will reinforce patient took part in making decisions positive self-esteem about taking meds and what hygiene he wanted.
Problem #4: Anxiety related to Health care environment General Goal: Patient uses effective coping mechanisms Outcome: Nursing Interventions: 1. Acknowledge awareness of the patient's anxiety 2. Reassure the patient that he is safe. Stay with the patient if this appears necessary. 3. Maintain a calm manner while interacting with the patient 4. Use simple language and brief statements when instructing the patient about self-care measures or about diagnostic and surgical procedures Response to Interventions: 1. Verbalized and acknowledged patients anxiety about pain and over stimulation of hospital environment. 2. Reassured patient whileinteracting with patient during shift. 3. Used calm soft tone when communicating with patient during shift 4. Used simple non jargon age appropriate language when communicating with patient during shift Rationales: Response to Intervention: 1. Because a cause for anxiety cannot always be identified, the patient may feel as though the feelings being experienced are counterfeit. Acknowledgment of the patient's feelings validates the feelings and communicates acceptance of those feelings. 2. The presence of a trusted person may help the person feel less threatened. Anxiety may escalate to a panic level if the patient feels threatened and unable to control environmental stimuli. 3. The health care provider can transmit his or her own anxiety to the hypersensitive patient. The patient's feeling of stability increases in a calm and nonthreatening atmosphere. 4. ) When experiencing moderate
to severe anxiety, patients may be unable to comprehend anything more than simple, clear, and brief instructions
Вам также может понравиться
- C 13Документ11 страницC 13Jo100% (1)
- 106 Prefi Critical Care Nclex ReviewДокумент10 страниц106 Prefi Critical Care Nclex ReviewraigeneОценок пока нет
- Vital Sign Na (1) by ZWBДокумент52 страницыVital Sign Na (1) by ZWBAshraf Ali100% (1)
- InsulinsДокумент1 страницаInsulinsReymart Waitforit DulayОценок пока нет
- Gestational DiabetesДокумент51 страницаGestational Diabeteskhadzx100% (2)
- Intermediate Math For Nurses NAME - WorkbookДокумент7 страницIntermediate Math For Nurses NAME - WorkbookRaniela MaeОценок пока нет
- Diabetes Management ATIДокумент15 страницDiabetes Management ATIJessica ChirinoОценок пока нет
- Pharm ReviewДокумент5 страницPharm ReviewChelsea ChanceОценок пока нет
- Percentage BMI calculator helps determine patient weight statusДокумент36 страницPercentage BMI calculator helps determine patient weight statuskasonde.musonda8Оценок пока нет
- Vital Signs: Aurora Roslin Samosa, Man RNДокумент57 страницVital Signs: Aurora Roslin Samosa, Man RNAlexander DontonОценок пока нет
- Grading edema levels and vital signs chartДокумент3 страницыGrading edema levels and vital signs chartKristina EitelОценок пока нет
- Nursing 212 Final Exam Review - Fall 2017Документ12 страницNursing 212 Final Exam Review - Fall 2017Marc LaBarbera100% (1)
- Insulin Secretion and FunctionДокумент8 страницInsulin Secretion and FunctionWendy EscalanteОценок пока нет
- ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE: System DisorderДокумент1 страницаACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE: System DisorderDeo FactuarОценок пока нет
- (Osborn) Chapter 47: Osborn, Et Al., Test Item File For Medical-Surgical Nursing: Preparation For PracticeДокумент19 страниц(Osborn) Chapter 47: Osborn, Et Al., Test Item File For Medical-Surgical Nursing: Preparation For PracticeKittiesОценок пока нет
- ABC Dictionary of Urinary SystemДокумент26 страницABC Dictionary of Urinary Systemaby_romero9750% (2)
- IVY TECH NURSING LAB INFORMATIONДокумент7 страницIVY TECH NURSING LAB INFORMATIONSethОценок пока нет
- Med Admin Practice QuestionsДокумент5 страницMed Admin Practice QuestionsArmelle DelvaОценок пока нет
- Fluids and Electrolytes ConceptДокумент31 страницаFluids and Electrolytes ConceptDarwin AndalОценок пока нет
- Life and DeathДокумент23 страницыLife and DeathJea Joel MendozaОценок пока нет
- Nursing Process Overview: Health Assessment NotesДокумент40 страницNursing Process Overview: Health Assessment NotesEliakim III InsongОценок пока нет
- Hytension For 16 Years Men (64 Years Old) Cigarette Smoking (32 Pack Years) Alcoholic Drinker For 32 Years Fond of Eating Fatty Foods Physical Inability Sodium Intake HereditaryДокумент3 страницыHytension For 16 Years Men (64 Years Old) Cigarette Smoking (32 Pack Years) Alcoholic Drinker For 32 Years Fond of Eating Fatty Foods Physical Inability Sodium Intake HereditaryJohn Paulo CatacutanОценок пока нет
- COPD Nursing Care Focuses on Lung Damage ManagementДокумент10 страницCOPD Nursing Care Focuses on Lung Damage ManagementCharisma Pastor100% (1)
- Endocrine SystemДокумент21 страницаEndocrine SystemMark DimarucutОценок пока нет
- The Heart's Chambers and ValvesДокумент29 страницThe Heart's Chambers and ValvesomarОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology CHFДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology CHFKit LaraОценок пока нет
- Adrenal Insufficiency and Addison's DiseaseДокумент8 страницAdrenal Insufficiency and Addison's DiseaseyancefinceОценок пока нет
- HO - Burns Environmental EmergenciesДокумент7 страницHO - Burns Environmental EmergenciesSteven Paul DaclesОценок пока нет
- Medication - ALT-Template - Enoxaparin SodiumДокумент1 страницаMedication - ALT-Template - Enoxaparin SodiumNancyAmissahОценок пока нет
- Wet to Damp DressingsДокумент2 страницыWet to Damp DressingsCarrie TranОценок пока нет
- Condition Drug Class: Cardiovascular MedicationsДокумент5 страницCondition Drug Class: Cardiovascular MedicationsCasey Fioravante100% (1)
- Respiratory meds guide for new nursesДокумент2 страницыRespiratory meds guide for new nursesmlbrown8Оценок пока нет
- Cardiac Meds To MemorizeДокумент4 страницыCardiac Meds To MemorizekellyaeОценок пока нет
- NUR1213L May2013 FinalДокумент23 страницыNUR1213L May2013 FinalOzzy Viadnes MalanaОценок пока нет
- Fundamental's FinalДокумент21 страницаFundamental's FinalShaunn Diesto Caberto100% (1)
- Preparation Worksheets For NUR 345 Heart Failure SimДокумент14 страницPreparation Worksheets For NUR 345 Heart Failure SimclarimerОценок пока нет
- 151 Nursing DocumentationДокумент24 страницы151 Nursing DocumentationNasrullah UllahОценок пока нет
- VSim Pharm (Mary Richards)Документ3 страницыVSim Pharm (Mary Richards)Jay Blastic's arts and FunОценок пока нет
- vSim CLINICAL REPLACEMENT PACKETДокумент14 страницvSim CLINICAL REPLACEMENT PACKETBhargav DaveОценок пока нет
- Newborn Hal ManualДокумент74 страницыNewborn Hal ManualPedz RomanoОценок пока нет
- PEDS Final Questions ATI Questions and AnswersДокумент14 страницPEDS Final Questions ATI Questions and Answersianshirow834Оценок пока нет
- Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceДокумент27 страницFluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceSimmi Sidhu100% (1)
- Myasthenia Gravis: An Autoimmune Neurologic DisorderДокумент16 страницMyasthenia Gravis: An Autoimmune Neurologic DisorderHibba NasserОценок пока нет
- Normal Laboratory Values - Patient Test Reference RangesДокумент10 страницNormal Laboratory Values - Patient Test Reference RangesGita Elisa Berlina GintingОценок пока нет
- Fluid Balance in Clinical PracticeДокумент8 страницFluid Balance in Clinical Practicefernando_vaz2010100% (1)
- Anti Neoplastic and Immunosupressant DrugsДокумент29 страницAnti Neoplastic and Immunosupressant DrugsAshraf Moby100% (1)
- Summary of Normal Laboratory ValuesДокумент7 страницSummary of Normal Laboratory ValuesIvan Matthew SuperioОценок пока нет
- Diabetes Study GuideДокумент4 страницыDiabetes Study GuideNicole Brassington0% (1)
- Pharmacology BДокумент3 страницыPharmacology BJoey Park0% (1)
- The Dangers of SmokingДокумент2 страницыThe Dangers of SmokingEvi Febri RahmawatiОценок пока нет
- Fluid and Electrolyte Final OutputДокумент19 страницFluid and Electrolyte Final OutputNatasha Alaine E. CayabyabОценок пока нет
- HTNДокумент15 страницHTNNatukunda DianahОценок пока нет
- ABG Reference GuideДокумент1 страницаABG Reference GuideUnclePorkchopОценок пока нет
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideОт EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideОценок пока нет
- Hyper-coagulation, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandHyper-coagulation, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- Vascular Responses to PathogensОт EverandVascular Responses to PathogensFelicity N.E. GavinsОценок пока нет
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS I: Passbooks Study GuideОт EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS I: Passbooks Study GuideОценок пока нет
- VARKДокумент6 страницVARKmenickel3Оценок пока нет
- Heath Promotion EssayДокумент8 страницHeath Promotion Essaymenickel3Оценок пока нет
- Alterations of Pulmonary Function OutlineДокумент13 страницAlterations of Pulmonary Function Outlinemenickel3Оценок пока нет
- Nursing Delivery SystemsДокумент9 страницNursing Delivery Systemsmenickel3Оценок пока нет
- Ticket in Skills Lab Week 3Документ11 страницTicket in Skills Lab Week 3menickel3Оценок пока нет
- Ticket in DemerolДокумент13 страницTicket in Demerolmenickel3Оценок пока нет
- I. The Background StuffДокумент6 страницI. The Background StuffNick OrtizОценок пока нет
- Normal Adult Lab Values Blood GasesДокумент1 страницаNormal Adult Lab Values Blood Gasesmenickel3Оценок пока нет
- A&P Final 2011Документ22 страницыA&P Final 2011menickel3Оценок пока нет
- Pharm Final 1011Документ79 страницPharm Final 1011menickel3Оценок пока нет
- Concept MapДокумент6 страницConcept Mapmenickel3100% (1)
- Exam 3 pathophysiology Cancer growth types and characteristicsДокумент7 страницExam 3 pathophysiology Cancer growth types and characteristicsmenickel3Оценок пока нет
- A Method of Functional Behavioral Assessment Is Called Th1Документ15 страницA Method of Functional Behavioral Assessment Is Called Th1menickel3Оценок пока нет
- Nursing Study Guide Page 2Документ7 страницNursing Study Guide Page 2menickel3Оценок пока нет
- Nursing Exam 2Документ13 страницNursing Exam 2menickel3Оценок пока нет
- Critical CareДокумент5 страницCritical CareYousef Khalifa0% (1)
- SIEMENS 05 Application Manual For HospitalsДокумент114 страницSIEMENS 05 Application Manual For HospitalsShailesh ChettyОценок пока нет
- March 2013 Board of Nursing NoticesДокумент528 страницMarch 2013 Board of Nursing NoticesJames LindonОценок пока нет
- Learning Activity No. 6Документ13 страницLearning Activity No. 6Jonah MaasinОценок пока нет
- Covid 19 Open LetterДокумент5 страницCovid 19 Open LetterKOLD News 13Оценок пока нет
- Thesis ShereeДокумент78 страницThesis ShereeSheree Nichole GuillerganОценок пока нет
- Application of Computer Simulation Modeling in The Health Care SectorДокумент21 страницаApplication of Computer Simulation Modeling in The Health Care SectorAlbert CiamОценок пока нет
- Healthcare WorkersДокумент15 страницHealthcare WorkerspharezeОценок пока нет
- List of Current Aeromedical Examiners as of 2010Документ26 страницList of Current Aeromedical Examiners as of 2010naveenbalaОценок пока нет
- 1 The Good DoctorДокумент7 страниц1 The Good DoctorComunicaciones Jehova ReinaОценок пока нет
- Interface Such As A Zoo, Farm or Animal Market.: CarriersДокумент3 страницыInterface Such As A Zoo, Farm or Animal Market.: CarriersGuga MamiseishviliОценок пока нет
- Brief Communication: A Business Model Analysis of Telecardiology ServiceДокумент7 страницBrief Communication: A Business Model Analysis of Telecardiology ServiceZarah Alifani DzulhijjahОценок пока нет
- Nutritional Status-Consolidated-2021-2022Документ1 страницаNutritional Status-Consolidated-2021-2022Laarni Kiamco Ortiz EpanОценок пока нет
- File Thuyết TrìnhДокумент3 страницыFile Thuyết TrìnhBích TuyềnОценок пока нет
- Manual of Travel Medicine & Health, 2nd Ed, 2003Документ641 страницаManual of Travel Medicine & Health, 2nd Ed, 2003Alfan Bayu Firmansyah100% (2)
- Medical Technologist Angelina BalonquitДокумент3 страницыMedical Technologist Angelina BalonquitMae Angeline BalonquitОценок пока нет
- Health Informatics vs. Health Information Management: Him Seminar, April 26, 2019Документ22 страницыHealth Informatics vs. Health Information Management: Him Seminar, April 26, 2019api-382689726Оценок пока нет
- RA No. 2382 (The Medical Act of 1959)Документ6 страницRA No. 2382 (The Medical Act of 1959)Rachel AcalОценок пока нет
- Clinical ExemplarДокумент4 страницыClinical Exemplarapi-272451466Оценок пока нет
- Skrining Tuberkulosis (TB) Paru: Field Epidemiology and Training Program (FETP) Universitas Gadjah MadaДокумент6 страницSkrining Tuberkulosis (TB) Paru: Field Epidemiology and Training Program (FETP) Universitas Gadjah MadaYulia FondaОценок пока нет
- Ethical Dilemmas Concerning The Dental Treatment of Patients With Hearing ImpairmentДокумент13 страницEthical Dilemmas Concerning The Dental Treatment of Patients With Hearing Impairmentl.limОценок пока нет
- HESI Community TopicsДокумент2 страницыHESI Community TopicsBeth AnnОценок пока нет
- Politicians must understand science says researcher Guadalupe SabioДокумент2 страницыPoliticians must understand science says researcher Guadalupe SabioIlaria iudiceОценок пока нет
- South Autralia RMO Application GuideДокумент35 страницSouth Autralia RMO Application GuideSOMANATHAN UMAHSUTHANОценок пока нет
- 2019 01 07 - Enabling Interoperability For Social and Behavioral Determinants of Health DataДокумент69 страниц2019 01 07 - Enabling Interoperability For Social and Behavioral Determinants of Health DataDaniel VreemanОценок пока нет
- Tingkat Kepuasan Konsumen Terhadap Pelayanan Kefarmasian Di Apotek Ganesha Farma Kabupaten LamonganДокумент14 страницTingkat Kepuasan Konsumen Terhadap Pelayanan Kefarmasian Di Apotek Ganesha Farma Kabupaten LamonganRenna FitrianaОценок пока нет
- Clinical Trial Details of Pegylated Interferon Alfa-2b for COVID-19Документ9 страницClinical Trial Details of Pegylated Interferon Alfa-2b for COVID-19chintanОценок пока нет
- Artikel Nyeri IngДокумент7 страницArtikel Nyeri IngPuspita Sari FiazОценок пока нет
- Dead ReckoningДокумент4 страницыDead ReckoningDouglas PageОценок пока нет
- Esarean Ction: Cadalin, Fremelen Rose Cedamon, CarloДокумент18 страницEsarean Ction: Cadalin, Fremelen Rose Cedamon, CarloMonette Abalos MendovaОценок пока нет