Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Seminar Topics
Загружено:
Pragati ChimangalaАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Seminar Topics
Загружено:
Pragati ChimangalaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Basic 3D interaction techniques in Augmented Reality
Ariyana, Y.; Wuryandari, A.I. System Engineering and Technology (ICSET), 2012 International Conference on Topic(s): Communication, Networking & Broadcasting ;Components, Circuits, Devices & Systems ; Computing & Processing (Hardware/Software) ; Power, Energy, & Industry Applications ; Robotics & Control Systems ; Signal Processing & Analysis Digital Object Identifier: 10.1109/ICSEngT.2012.6339281 Publication Year: 2012 , Page(s): 1 - 6 IEEE CONFERENCE PUBLICATIONS | Quick Abstract | PDF (725 KB)
Information technology currently supports the development of human interaction with virtual environment, this development will continue in developing in the form of Human Computer Interaction (HCI). In this study, how the environment 3D virtual computer should be able to recognize human hand as part as virtual object, so it can interact with virtual environment. HCI is a study in which the relationship between humans and computing technology and how computers are designed for easy to use by human, more practical and more intuitive. HCI emphasizes how human interaction with computer technology. This research is using use 3D transformation to digital objects used in computer graphics, transformation of the basis for the movement of digital objects in interaction technique in virtual environment to interact between human hand and virtual object. Tracker is needed in virtual interaction by using Augmented Reality (AR), the problem that arise in AR is how to read marker, so it can display a virtual object that has been computed before, basically is how to read the geometry model of human hand, then the result from the processing of the human hand model geometry is used as a marker, so it can interact with a virtual environment on AR as one of the HCI model implementation. This process is intended for the movement of human hands that have been read as a virtual object can communicate virtually using image processing.
Hand gesture recognition based on shape parameters
Panwar, M. Computing, Communication and Applications (ICCCA), 2012 International Conference on Topic(s): Communication, Networking & Broadcasting ;Components, Circuits, Devices & Systems ; Computing & Processing (Hardware/Software) ; Signal Processing & Analysis Digital Object Identifier: 10.1109/ICCCA.2012.6179213 Publication Year: 2012 , Page(s): 1 - 6 IEEE CONFERENCE PUBLICATIONS | Quick Abstract | PDF (332 KB)
Pattern recognition and Gesture recognition are the growing fields of research. Being a significant part in non verbal communication hand gestures are playing vital role in our daily life. Hand Gesture recognition system provides us an innovative, natural, user friendly way of interaction with the computer which is more familiar to the human beings. GestureRecognition has a wide area of application including human machine interaction, sign language, immersive game technology etc. By keeping in mind the similarities of human hand shape with four fingers and one thumb, this paper aims to present a real time system for hand gesture recognition on the basis of detection of some meaningful shape based features like orientation, centre of mass (centroid), status of fingers, thumb in terms of raised or folded fingers of hand and their respective location in image. The approach introduced in this paper is totally depending on the shape parameters of the handgesture. It does not consider any other mean of hand gesturerecognition like skin color, texture because these image based features are extremely variant to different light conditions and other influences. To implement this approach we have utilized a simple web cam which is working on 20 fps with 7 mega pixel intensity. On having the input sequence of images through web cam it uses some pre-processing steps for removal of background noise and employs K-means clustering for segmenting the hand object
from rest of the background, so that only segmented significant cluster or hand object is to be processed in order to calculate shape based features. This simple shape based approach to hand gesture recognition can identify around 45 different gestures on the bases of 5 bit binary string resulted as the output of this algorithm. This proposed implemented algorithm has been tested over 450 images and it gives approximate recognition rate of 94%.
Interference-Avoidance Techniques: Improving Ubiquitous User Experience
Gresset, N.; Halbauer, H.; Koppenborg, J.; Zirwas, W.; Khanfir, H. Vehicular Technology Magazine, IEEE Volume: 7 , Issue: 4 Topic(s): Aerospace ; Computing & Processing (Hardware/Software) ; Signal Processing & Analysis ;Transportation Digital Object Identifier: 10.1109/MVT.2012.2218434 Publication Year: 2012 , Page(s): 37 - 45 IEEE JOURNALS & MAGAZINES | Quick Abstract | PDF (2263 KB)
This article presents interference- avoidance schemes developed in the Advanced Radio Interface Technologies for [Fourth Generation (4G)] Systems (ARTIST4G) Project for three scenarios targeting the deployment of Third-Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), long-term evolution (LTE)-advanced networks, and beyond. In the first scenario, we propose three-dimensional (3-D) beamforming as a flexible technology for taking the best benefit from the internode cooperation, constrained by the core network infrastructure. The second scenario addresses a long-term deployment with nonconstrained internodes cooperation link based on an interference-shaping strategy that allows for exploiting at its maximum the coordinated multipoint concept. Finally, we investigate interference coordination mechanisms for protecting the macro network from a massive deployment of small cells that provides a network capacity increase by high offloading capabilities
Image-Based Remodeling
Colburn, A.; Agarwala, A.; Hertzmann, A.; Curless, B.; Cohen, M.F. Visualization and Computer Graphics, IEEE Transactions on Volume: 19 , Issue: 1 Topic(s): Bioengineering ; Communication, Networking & Broadcasting ; Computing & Processing (Hardware/Software) ;Fields, Waves & Electromagnetics ; Signal Processing & Analysis Digital Object Identifier: 10.1109/TVCG.2012.95 Publication Year: 2013 , Page(s): 56 - 66 IEEE JOURNALS & MAGAZINES Multimedia | Quick Abstract | PDF (1255 KB)
Imagining what a proposed home remodel might look like without actually performing it is challenging. We present an image-based remodeling methodology that allows real-time photorealistic visualization during both the modeling and remodeling process of a home interior. Large-scale edits, like removing a wall or enlarging a window, are performed easily and in real time, with realistic results. Our interface supports the creation of concise, parameterized, and constrained geometry, as well as remodeling directly from within the photographs. Real-time texturing of modified geometry is made possible by precomputing view-dependent textures for all faces that are potentially visible to each original camera viewpoint, blending multiple viewpoints and hole-filling when necessary. The resulting textures are stored and accessed efficiently enabling intuitive real-time realistic visualization, modeling, and editing of the building interior.
Non-rigid surface detection for gestural interaction with applicable surfaces
Ziegler, A.; Belongie, S. Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), 2012 IEEE Workshop on Topic(s): Communication, Networking & Broadcasting ;Components, Circuits, Devices & Systems ; Computing & Processing (Hardware/Software) ; Signal Processing & Analysis Digital Object Identifier: 10.1109/WACV.2012.6163029 Publication Year: 2012 , Page(s): 73 - 80 IEEE CONFERENCE PUBLICATIONS | Quick Abstract | PDF (5960 KB)
In this work we present a novel application of non-rigid surface detection to enable gestural interaction with applicable surfaces. This method can add interactivity to traditionally passive media such as books, newspapers, restaurant menus, or anything else printed on paper. We allow a user to interact with these surfaces in a natural manner and present basic gestures based on pointing and touching. This technique was developed as part of an ongoing effort to create an assisted reading device for the visually impaired. However, it is suited to general applications and can be used as a practical mechanism for interaction with screen-less wearable devices. Our key contributions are a unique application of non-rigid surface detection, a basic gesturing paradigm, and a proof of concept system.
Advanced intersection management for connected vehicles using a multi-agent systems approach
Qiu Jin; Guoyuan Wu; Boriboonsomsin, K.; Barth, M. Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), 2012 IEEE Topic(s): Bioengineering ; Communication, Networking & Broadcasting ; Components, Circuits, Devices & Systems ;Computing & Processing (Hardware/Software) ; General Topics for Engineers (Math, Science & Engineering) ; Power, Energy, & Industry Applications ; Robotics & Control Systems ; Signal Processing & Analysis ; Transportation Digital Object Identifier: 10.1109/IVS.2012.6232287 Publication Year: 2012 , Page(s): 932 - 937 IEEE CONFERENCE PUBLICATIONS | Quick Abstract | PDF (1728 KB)
Transportation is responsible for approximately a third of greenhouse gases (GHG) and a major source of other pollutants including hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and oxides of nitrogen (NOx). Intelligent Transportation System (ITS) technology can be used to lower vehicle emissions and fuel consumption, in addition to reducing traffic congestion, smoothing traffic flow, and improving roadway safety. As wireless communication advances, connected-vehicles-based Advanced Traffic Management Systems (ATMS) have gained significant research interest due to their high potential. In this study, we examine the concept of ATMS for connected vehicles using a multi-agent systems approach, where both vehicle agents and an intersection management agent can take advantage of real-time traffic information exchange. This dynamic strategy allows an intersection management agent to receive state information from vehicle agents, reserve the associated intersection time-space occupancies, and then provide feedback to the vehicles. The vehicle agents then adjust their trajectories to meet their assigned time slot. Based on preliminary simulation experiments, the proposed strategy can significantly reduce fuel consumption and vehicle emissions compared to traditional signal control systems.
Вам также может понравиться
- Extra ProblemsДокумент41 страницаExtra ProblemsPragati Chimangala100% (3)
- J) Method Statement For Discharge of Stormwater and Rain WaterДокумент4 страницыJ) Method Statement For Discharge of Stormwater and Rain WaterLee Tin YanОценок пока нет
- FloEFD For Creo InstallДокумент18 страницFloEFD For Creo InstallDarko MarjanovicОценок пока нет
- Manual de Mantenimiento Del Piper PA-24Документ863 страницыManual de Mantenimiento Del Piper PA-24Bruno Starczewski50% (2)
- Emotion and Gesture DetectionДокумент16 страницEmotion and Gesture DetectionIJRASETPublicationsОценок пока нет
- Kinect To ArchitectureДокумент10 страницKinect To ArchitectureEvo MoraesОценок пока нет
- Gesture Controlled Virtual MouseДокумент8 страницGesture Controlled Virtual MouseIJRASETPublicationsОценок пока нет
- A Survey Paper On Controlling Computer UДокумент5 страницA Survey Paper On Controlling Computer UgrushaОценок пока нет
- Journal - A Smart Attendance System Based On Face Recognition Challenges and EffectsДокумент6 страницJournal - A Smart Attendance System Based On Face Recognition Challenges and EffectsAbdulkadir Shehu bariОценок пока нет
- Real Time Finger Tracking and Contour Detection For Gesture Recognition Using OpencvДокумент4 страницыReal Time Finger Tracking and Contour Detection For Gesture Recognition Using OpencvRamírez Breña JosecarlosОценок пока нет
- Deep Learning Based Image Recognition For 5G SmartДокумент19 страницDeep Learning Based Image Recognition For 5G SmartVM SARAVANAОценок пока нет
- Durodoye Et Al.Документ22 страницыDurodoye Et Al.Adeyemo Uthman AdedejiОценок пока нет
- 09 Handout 1Документ3 страницы09 Handout 1Daniela RoldanОценок пока нет
- Iee Paper IotДокумент3 страницыIee Paper Iotpp ccОценок пока нет
- Computers: An Integrated Mobile Augmented Reality Digital Twin Monitoring SystemДокумент20 страницComputers: An Integrated Mobile Augmented Reality Digital Twin Monitoring SystemNorman SuliОценок пока нет
- Controlled Hand Gestures Using Python and OpenCVДокумент7 страницControlled Hand Gestures Using Python and OpenCVIJRASETPublicationsОценок пока нет
- Multi-Access Edge Computing Open Issues ChallengesДокумент13 страницMulti-Access Edge Computing Open Issues ChallengesRamadan GadahОценок пока нет
- Enhanced Technique For Multiple Face Detection Based On LBPH (Local Binary Patterns Histograms) A ReviewДокумент6 страницEnhanced Technique For Multiple Face Detection Based On LBPH (Local Binary Patterns Histograms) A ReviewIJRASETPublicationsОценок пока нет
- Air Mouse Journal 4Документ6 страницAir Mouse Journal 4Sowmiya SowmiОценок пока нет
- ITC571 - Emerging Technologies and Innovation - Assessment Item 5Документ12 страницITC571 - Emerging Technologies and Innovation - Assessment Item 5stella angelinОценок пока нет
- Ijecet: International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering & Technology (Ijecet)Документ7 страницIjecet: International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering & Technology (Ijecet)IAEME PublicationОценок пока нет
- A Review On Hand Gesture RecognitionДокумент7 страницA Review On Hand Gesture RecognitionIJRASETPublicationsОценок пока нет
- Thesis Rajarshi Sanyal PDFДокумент150 страницThesis Rajarshi Sanyal PDFJuan LimachiОценок пока нет
- Optimized Hand Gesture Based Home Automation For FeeblesДокумент11 страницOptimized Hand Gesture Based Home Automation For FeeblesIJRASETPublicationsОценок пока нет
- Long distance face recognition enhances IoT servicesДокумент14 страницLong distance face recognition enhances IoT servicesEASACOLLEGEОценок пока нет
- Real Time Video Recognition of Signs For Deaf and Dump Using Deep LearningДокумент5 страницReal Time Video Recognition of Signs For Deaf and Dump Using Deep LearningIJRASETPublicationsОценок пока нет
- Microprocessors and Microcontrollers Tech TalkДокумент9 страницMicroprocessors and Microcontrollers Tech TalkMuppalla praveen kumarОценок пока нет
- Air Writing and Recognition SystemДокумент8 страницAir Writing and Recognition SystemIJRASETPublicationsОценок пока нет
- A Comprehensive Review On Edge ComputingДокумент17 страницA Comprehensive Review On Edge ComputingIJRASETPublicationsОценок пока нет
- 2024 02 23 581779v1 FullДокумент59 страниц2024 02 23 581779v1 FulldfggvgdfОценок пока нет
- I Fog SimДокумент22 страницыI Fog Simibrahim1Оценок пока нет
- Feature Based Head Pose Estimation for CДокумент12 страницFeature Based Head Pose Estimation for CLucky SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Cataloging of Road Traffic Signs (Building Deep Learning Model and Android Application)Документ15 страницCataloging of Road Traffic Signs (Building Deep Learning Model and Android Application)IJRASETPublicationsОценок пока нет
- Connected Cars ThesisДокумент5 страницConnected Cars Thesisdawnrobertsonarlington100% (2)
- A Collaborative Internet of Things Architecture For Smart Cities and Environmental MonitoringДокумент14 страницA Collaborative Internet of Things Architecture For Smart Cities and Environmental MonitoringKrishna Prasad SatamrajuОценок пока нет
- Survey On Digital Twin Edge Networks DITEN TowardsДокумент22 страницыSurvey On Digital Twin Edge Networks DITEN TowardsMikassa AckrОценок пока нет
- Wireless Mouse Using Tri Axis MEMS Ijariie1386 Volume 1 15 Page 33 40Документ8 страницWireless Mouse Using Tri Axis MEMS Ijariie1386 Volume 1 15 Page 33 40Anup M UpadhyayaОценок пока нет
- 48 A Albert Prasanna Kumar SimulationДокумент6 страниц48 A Albert Prasanna Kumar SimulationchfakhtОценок пока нет
- Future Computing With Iot and Cloud Computing: D. S. ParkДокумент7 страницFuture Computing With Iot and Cloud Computing: D. S. ParkAravind PadmanabhanОценок пока нет
- Special Issue On "Optics For AI and AI For Optics"Документ3 страницыSpecial Issue On "Optics For AI and AI For Optics"Saqib KamalОценок пока нет
- Computer Communications: Mingliang Hou, Mengyuan Wang, Wenhong Zhao, Qichao Ni, Zhen Cai, Xiangjie KongДокумент9 страницComputer Communications: Mingliang Hou, Mengyuan Wang, Wenhong Zhao, Qichao Ni, Zhen Cai, Xiangjie Konguttam sinhОценок пока нет
- A Multi-Model Edge Computing Offloading Framework For Deep Learning Application Based On Bayesian OptimizationДокумент13 страницA Multi-Model Edge Computing Offloading Framework For Deep Learning Application Based On Bayesian OptimizationAbdullah Mansour AlgashwiОценок пока нет
- Seminar (IS-526) : Edge Intelligence: The Con Uence of Edge Computing and ArtificialДокумент20 страницSeminar (IS-526) : Edge Intelligence: The Con Uence of Edge Computing and ArtificialYoginderSinghОценок пока нет
- Fog Computing A PrimerДокумент3 страницыFog Computing A PrimerPalanikumarОценок пока нет
- Edge Computing: Seminar OnДокумент12 страницEdge Computing: Seminar OnJangle Sagar0% (1)
- Sensors: Analysis of Machine Learning Algorithms For Anomaly Detection On Edge DevicesДокумент22 страницыSensors: Analysis of Machine Learning Algorithms For Anomaly Detection On Edge Devicestuantele81Оценок пока нет
- Vision Based Hand Gesture RecognitionДокумент6 страницVision Based Hand Gesture RecognitionAnjar TriyokoОценок пока нет
- Leveraging Mobile Net and Yolo Algorithm for Enhanced Perception in Autonomous DrivingДокумент5 страницLeveraging Mobile Net and Yolo Algorithm for Enhanced Perception in Autonomous DrivingInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Algorithm Hand TrackingДокумент29 страницAlgorithm Hand TrackingvinhphxrОценок пока нет
- 2006205 CC AssignmentДокумент13 страниц2006205 CC Assignmenttanishk ranjanОценок пока нет
- Ijett V14P237 PDFДокумент4 страницыIjett V14P237 PDFRahul RajОценок пока нет
- Hand Gesture Recognition Using OpenCV and PythonДокумент7 страницHand Gesture Recognition Using OpenCV and PythonEditor IJTSRDОценок пока нет
- An Artificial Intelligence Mechanism For The Prediction of Signal Strength in Drones To IoT Devices in Smart CitiesДокумент10 страницAn Artificial Intelligence Mechanism For The Prediction of Signal Strength in Drones To IoT Devices in Smart Citiesmartin muduvaОценок пока нет
- Sensors 21 06023 v3Документ30 страницSensors 21 06023 v3chahde SaraОценок пока нет
- Multitier Fog Computing With Large-Scale Iot Data Analytics For Smart CitiesДокумент10 страницMultitier Fog Computing With Large-Scale Iot Data Analytics For Smart Citiesdan_intel6735Оценок пока нет
- IRJMETSTemplateДокумент4 страницыIRJMETSTemplatekaakhilesh159Оценок пока нет
- IoT Based Low-Cost Robotic Agent Design For Disabled and Covid-19 Virus Affected PeopleДокумент4 страницыIoT Based Low-Cost Robotic Agent Design For Disabled and Covid-19 Virus Affected PeopleLakshmi PriyaОценок пока нет
- R T H G R S D A: EAL IME AND Esture Ecognition Ystem For Ynamic PplicationsДокумент11 страницR T H G R S D A: EAL IME AND Esture Ecognition Ystem For Ynamic PplicationsSabir BhatiОценок пока нет
- Validation of Aeronautical Fuselage Channel Model For Iris Air-Traffic Management Via SatelliteДокумент7 страницValidation of Aeronautical Fuselage Channel Model For Iris Air-Traffic Management Via SatelliteShanmukh GollapudiОценок пока нет
- ACM - CSUR - Fog Computing For Sustainable Smart Cities - A Survey Var 1Документ36 страницACM - CSUR - Fog Computing For Sustainable Smart Cities - A Survey Var 1Pas SatОценок пока нет
- Elbeqqal 2018Документ9 страницElbeqqal 2018Dickson Scott Rosales CanoОценок пока нет
- Edge AI A Survey - 2023 - Internet of Things and Cyber Physical SystemsДокумент22 страницыEdge AI A Survey - 2023 - Internet of Things and Cyber Physical Systemspachar223Оценок пока нет
- Real Time Vision-Based Hand Gesture Recognition For Robotic ApplicationДокумент10 страницReal Time Vision-Based Hand Gesture Recognition For Robotic ApplicationkrishnagdeshpandeОценок пока нет
- Digital Technologies – an Overview of Concepts, Tools and Techniques Associated with itОт EverandDigital Technologies – an Overview of Concepts, Tools and Techniques Associated with itОценок пока нет
- Number Theory Relating To RSAДокумент4 страницыNumber Theory Relating To RSAPragati ChimangalaОценок пока нет
- Code Coverage AnalysisДокумент12 страницCode Coverage AnalysisPragati Chimangala100% (1)
- Steps in ProcessДокумент8 страницSteps in ProcessPragati ChimangalaОценок пока нет
- Greedy Method 16-11-2013Документ72 страницыGreedy Method 16-11-2013Pragati ChimangalaОценок пока нет
- SQMChapter 6 NotesДокумент6 страницSQMChapter 6 NotesPragati ChimangalaОценок пока нет
- SQMChapter 6 NotesДокумент6 страницSQMChapter 6 NotesPragati ChimangalaОценок пока нет
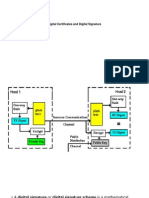
- Digital Certificates and Digital SignatureДокумент5 страницDigital Certificates and Digital SignaturePragati ChimangalaОценок пока нет
- Big oДокумент21 страницаBig oPragati ChimangalaОценок пока нет
- Free Guide Top Ten Secrets of Book Writing Naren SimoneДокумент33 страницыFree Guide Top Ten Secrets of Book Writing Naren SimonePragati ChimangalaОценок пока нет
- Data CubesДокумент8 страницData CubesPragati ChimangalaОценок пока нет
- Marketing Research of Pre-Start-UpДокумент2 страницыMarketing Research of Pre-Start-UpafsalpkgroupОценок пока нет
- VF1 Technicalspecifications 031997 EN PDFДокумент43 страницыVF1 Technicalspecifications 031997 EN PDFelectricistОценок пока нет
- Design of Miniature Maglev Using Hybrid MagnetsДокумент4 страницыDesign of Miniature Maglev Using Hybrid MagnetsErmin FazlicОценок пока нет
- MDN 1508DSДокумент108 страницMDN 1508DSdocazanОценок пока нет
- Restaurant Pub VIP Lounge Camp Pune SaleДокумент4 страницыRestaurant Pub VIP Lounge Camp Pune SaleChandrashekhar Naikare0% (1)
- Fiedler's Contingency Model of Leadership Effectiveness: Background and Recent DevelopmentsДокумент24 страницыFiedler's Contingency Model of Leadership Effectiveness: Background and Recent DevelopmentsEdielyn Gonzalvo GutierrezОценок пока нет
- Gfps System Specification PVC C Metric en PDFДокумент24 страницыGfps System Specification PVC C Metric en PDFMohammed sabatinОценок пока нет
- Me 2403 Power Plant Engineering - Short Question and AnswersДокумент16 страницMe 2403 Power Plant Engineering - Short Question and AnswersBIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANОценок пока нет
- By Himanshu Panwar Asst. Prof. Civil Engineering Department AkgecДокумент34 страницыBy Himanshu Panwar Asst. Prof. Civil Engineering Department AkgecAlok0% (1)
- Nmo & DmoДокумент29 страницNmo & DmoJessica Julien100% (1)
- Model Manajemen Rantai Pasok Industri Perikanan Tangkap Berkelanjutan Di Propinsi MalukuДокумент12 страницModel Manajemen Rantai Pasok Industri Perikanan Tangkap Berkelanjutan Di Propinsi MalukuEmanuellaОценок пока нет
- Final year project presentationДокумент13 страницFinal year project presentationbadg15594Оценок пока нет
- Jobber JR DetailsДокумент2 страницыJobber JR DetailsUrvish PatelОценок пока нет
- Product Specification: Part Name: OEL Display Module Part ID: UG-2864HSWEG01 Doc No.: SAS1-9046Документ30 страницProduct Specification: Part Name: OEL Display Module Part ID: UG-2864HSWEG01 Doc No.: SAS1-9046mariОценок пока нет
- Occupant Manikin Introduction: 95th Percentile Male Driver ModelДокумент9 страницOccupant Manikin Introduction: 95th Percentile Male Driver ModelarstjunkОценок пока нет
- Mini-Split Service GuideДокумент49 страницMini-Split Service Guideady_gligor7987Оценок пока нет
- Post TensioningДокумент13 страницPost TensioningAbdullah AhamedОценок пока нет
- Dual-Band Band Pass Filters Using Stub-Loaded ResonatorsДокумент3 страницыDual-Band Band Pass Filters Using Stub-Loaded ResonatorsfracosoeОценок пока нет
- FREE UX Books @UXlinksДокумент4 страницыFREE UX Books @UXlinksSyaifudin MashuriОценок пока нет
- Diffusion of InnovationДокумент40 страницDiffusion of Innovationlali62Оценок пока нет
- Dekut Teaching Practice ManualДокумент20 страницDekut Teaching Practice Manualstephen njorogeОценок пока нет
- BS Basics Boundary Scan PDFДокумент2 страницыBS Basics Boundary Scan PDFShankar ArunmozhiОценок пока нет
- Transportation System, Analysis and Modelling (CE-632) : Carried Out by Group-3Документ15 страницTransportation System, Analysis and Modelling (CE-632) : Carried Out by Group-3Naman Kumar100% (2)
- Mario Stifano Graphic Designer CVДокумент1 страницаMario Stifano Graphic Designer CVmariostifanoОценок пока нет
- Lets Play BingoДокумент17 страницLets Play BingoRosana SanchezОценок пока нет
- Meteor Burst Communications. Request For Expertise, Russian Fed, Ukraine, Etc DCSTДокумент3 страницыMeteor Burst Communications. Request For Expertise, Russian Fed, Ukraine, Etc DCSTSkybridge Spectrum FoundationОценок пока нет
- New Components Help Prevent Air Leaks in Improved Fuel Ratio Control Groups (1278)Документ3 страницыNew Components Help Prevent Air Leaks in Improved Fuel Ratio Control Groups (1278)TASHKEELОценок пока нет