Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ch17 Dynamics
Загружено:
Aaron WoodИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Ch17 Dynamics
Загружено:
Aaron WoodАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
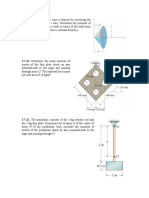
17.1-3 Moment of inertia Planar kinematics Equations of motion 17-25.
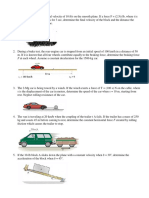
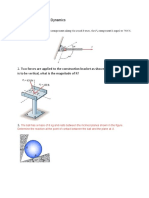
The 4-Mg uniform canister contains nuclear waste material encased in concrete. If the mass of the spreader beam BD is 50 kg, determine the largest vertical acceleration a of the system so that each of the links AB and CD are not subjected to a force greater than 30 kN and links EF and GH are not subjected to a force greater than 34 kN.
17-30. The lift truck has a mass of 70 kg and mass center at G. Determine the largest upward acceleration of the 120-kg spool so that no reaction on the wheels exceeds 600 N.
17-45. The handcart has a mass of 200 kg and center of mass at G. Determine the largest magnitude of force P that can be applied to the handle so that the wheels at A or B continue to maintain contact with the ground. Neglect the mass of the wheels.
17-53. The 50-kg uniform crate rests on the platform for which the coefficient of static friction is JLs = 0.5. If at the instant = 30 the supporting links have an angular velocity w = 1 rad/s and angular acceleration a = 0.5 rad/s^2, determine the frictional force on the crate.
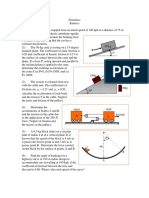
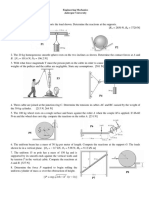
17.4 fixed axis 17-62. The pendulum consists of a 30-lb sphere and a l0-lb slender rod. Compute the reaction at the pin 0 just after the cord AB is cut.
17-70. The 1 00-lb uniform rod is at rest in a vertical position when the cord attached to it at B is subjected to a force of P = 50 lb. Determine the rod's initial angular acceleration and the magnitude of the reactive force that pin A exerts on the rod. Neglect the size of the smooth peg at C.
17-81. The disk has a mass of 20 kg and is originally spinning at the end of the strut with an angular velocity of w = 60 rad/s. If it is then placed against the wall, where the coefficient of kinetic friction is k = 0.3, determine the time required for the motion to stop. What is the force in strut BC during this time?
17.5 general plane motion 17-94. The uniform 50-lb board is suspended from cords at C and D. If these cords are subjected to constant forces of 30 lb and 45 lb, respectively, determine the initial acceleration of the board's center and the board's angular acceleration. Assume the board is a thin plate. Neglect the mass of the pulleys at E and F.
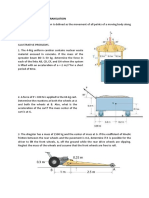
-17-101. The lawn roller has a mass of 80 kg and a radius of gyration kG = 0.175 m. If it is pushed forward with a force of 200 N when the handle is at 45, determine its angular acceleration. The coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the ground and the roller are s = 0.12 and k = 0.1, respectively.
17-105. The spool has a mass of 100 kg and a radius of gyration kG = 0.3 m. If the coefficients of static and kinetic friction at A are s = 0.2 and k = 0.15, respectively, determine the angular acceleration of the spool if P = 600 N.
17-123. The SOO-kg concrete culvert has a mean radius of 0.5 m. If the truck has an acceleration of 3 m/s2, determine the culvert's angular acceleration. Assume that the culvert does not slip on the truck bed, and neglect its thickness.
Вам также может понравиться
- Steel Design 2 3Документ21 страницаSteel Design 2 3Gracielle NebresОценок пока нет
- 70-Triumph T120 Repair-Manual-63-70 PDFДокумент236 страниц70-Triumph T120 Repair-Manual-63-70 PDFSimon TudorОценок пока нет
- Isuzu Engine Cooling SystemДокумент21 страницаIsuzu Engine Cooling SystemToan100% (1)
- Welding Procedure Specification (WPS) : (Applicable Code/Standard: ISO 15614-2 Edition 2005)Документ2 страницыWelding Procedure Specification (WPS) : (Applicable Code/Standard: ISO 15614-2 Edition 2005)saioman100% (7)
- Mil STD 278FДокумент128 страницMil STD 278Fexwhiskeyhouse100% (1)
- Design and Evaluation of Inflatable Wings For UavsДокумент290 страницDesign and Evaluation of Inflatable Wings For UavsmegustalazorraОценок пока нет
- Question Bank Engg. MechanicsДокумент18 страницQuestion Bank Engg. MechanicsSakendra Kumar0% (2)
- Tutorial 2-Equilibrium 1Документ2 страницыTutorial 2-Equilibrium 1Sai KrishnaОценок пока нет
- Statics of Rigid BodiesДокумент12 страницStatics of Rigid BodiesJoanne-chan Mingi100% (1)
- Final Ps - Static.01 EquliДокумент4 страницыFinal Ps - Static.01 EquliashisОценок пока нет
- RTP PipeДокумент15 страницRTP PipeHellClown1982Оценок пока нет
- Bedford Statics Practice ProblemsДокумент6 страницBedford Statics Practice Problemsstats12Оценок пока нет
- Motor EnclosuresДокумент20 страницMotor EnclosuresCristele Mae Garcia100% (1)
- TB021 Grease SamplingДокумент7 страницTB021 Grease SamplingИгорь100% (1)
- Instruction Manual CMO 24-26-28/TCMO 28 MK 2: Reciprocating CompressorДокумент185 страницInstruction Manual CMO 24-26-28/TCMO 28 MK 2: Reciprocating CompressorGiovanni Colonna67% (3)
- CH 17Документ7 страницCH 17Amer JumahОценок пока нет
- Trabajo Energia en Una Partícula EjerciciosДокумент7 страницTrabajo Energia en Una Partícula EjerciciosFabricio Espinoza GamarraОценок пока нет
- CH 19Документ4 страницыCH 19Amer JumahОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 7 8Документ3 страницыTutorial 7 8Zahida ParnisОценок пока нет
- F at Each Wheel. Assume A Constant Deceleration For The 1500-kg CarДокумент12 страницF at Each Wheel. Assume A Constant Deceleration For The 1500-kg CarAndre BocoОценок пока нет
- Homework Chap 3Документ12 страницHomework Chap 3Aeon ReignОценок пока нет
- Sheet 7 - Work and Energy-10807Документ9 страницSheet 7 - Work and Energy-10807Bahaa RaghebОценок пока нет
- Final 08 Engg SolДокумент6 страницFinal 08 Engg SolyanelaОценок пока нет
- Constant Speed of 6 Ft/s. Determine How Fast The Boat Approaches The Pier at The Instant The Rope Length AB Is 50 FTДокумент6 страницConstant Speed of 6 Ft/s. Determine How Fast The Boat Approaches The Pier at The Instant The Rope Length AB Is 50 FTAndrea 75Оценок пока нет
- Opción Múltiple: Ecuación de Movimiento Fuerza y AceleraciónДокумент11 страницOpción Múltiple: Ecuación de Movimiento Fuerza y AceleraciónDiego Naspud UrgilesОценок пока нет
- Assignment-3 - Engg Mech PDFДокумент6 страницAssignment-3 - Engg Mech PDFNiteshОценок пока нет
- EngmechДокумент1 страницаEngmechJuan De la CruzОценок пока нет
- Engineering Mechanics (ME 105) Tutorial Sheet-4Документ4 страницыEngineering Mechanics (ME 105) Tutorial Sheet-4nsbaruaoleОценок пока нет
- Work Sheet G9 Unit 3&4Документ2 страницыWork Sheet G9 Unit 3&4Amarch BahiluОценок пока нет
- Engineering Mechanics (ME 105) Tutorial Sheet-4Документ3 страницыEngineering Mechanics (ME 105) Tutorial Sheet-4baruaoleОценок пока нет
- NLM Subjective Problems-SP-NPJC 1-June 13Документ19 страницNLM Subjective Problems-SP-NPJC 1-June 13Mohit GargОценок пока нет
- Pokhara University Applied Mechanics - I Question PapersДокумент4 страницыPokhara University Applied Mechanics - I Question PapersBuddhisagar BastolaОценок пока нет
- Dynamics (Kinetics)Документ2 страницыDynamics (Kinetics)HeliosОценок пока нет
- PROBLEM - SOLVING - Friction and 2nd Law UstДокумент34 страницыPROBLEM - SOLVING - Friction and 2nd Law UstMarj Ladica MangaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 - Supplementary ProblemsДокумент11 страницChapter 3 - Supplementary Problems김김김치Оценок пока нет
- Stat No. 4 - FrictionДокумент3 страницыStat No. 4 - FrictionRufus TanhuecoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Newton - S Laws of Motion - Problem SetsДокумент5 страницChapter 3 Newton - S Laws of Motion - Problem SetsSimon ManansalaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 To 10Документ22 страницыChapter 3 To 10Angelica Ecal Migriño67% (3)
- Unit V - Unid End Questions - EMДокумент6 страницUnit V - Unid End Questions - EMNaresh JonnaОценок пока нет
- Handout 4Документ1 страницаHandout 4Ann NavarroОценок пока нет
- Friction (MEC 107)Документ2 страницыFriction (MEC 107)Piyush JaiswalОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 - Force and MotionДокумент4 страницыChapter 3 - Force and MotionJerico LlovidoОценок пока нет
- Examples MomentumДокумент9 страницExamples Momentumettypasewang0% (1)
- Plate5 StaticsДокумент4 страницыPlate5 StaticsMark Emman CaseresОценок пока нет
- Pretest in Statics and DynamicsДокумент6 страницPretest in Statics and DynamicsMarifer CavintaОценок пока нет
- HW05 Metu PDFДокумент2 страницыHW05 Metu PDFFatih BodrumОценок пока нет
- Mechanics 5Документ11 страницMechanics 5Rey Kevin OrtuosteОценок пока нет
- CO-4 Assignment QuestionsДокумент7 страницCO-4 Assignment QuestionsrajeswariОценок пока нет
- MAK 217 2. ÖdevДокумент2 страницыMAK 217 2. ÖdevBünyamin TatarОценок пока нет
- Rev2, ENGR 62, StanfordДокумент40 страницRev2, ENGR 62, StanfordsuudsfiinОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 3 WEДокумент5 страницTutorial 3 WE2B Dai Ko DUPLICATEОценок пока нет
- SP015 PSPM 1 2019.2020Документ4 страницыSP015 PSPM 1 2019.2020SUREINTHARAAN A/L NATHAN MoeОценок пока нет
- TD Statics of Particle and Rigid BodyДокумент5 страницTD Statics of Particle and Rigid BodyUng ChannoutdomОценок пока нет
- Determine The Force Developed in Members GB G F of The Bridge Truss State If These Membel-S Are Tension or CompressionДокумент23 страницыDetermine The Force Developed in Members GB G F of The Bridge Truss State If These Membel-S Are Tension or CompressionNarang ViОценок пока нет
- Engineering Mechanics (ME 105) Tutorial Sheet-4Документ3 страницыEngineering Mechanics (ME 105) Tutorial Sheet-4Vikrant SharmaОценок пока нет
- Q1. The Man Pushes On The 30-kg Crate With A Force F. The Force IsДокумент2 страницыQ1. The Man Pushes On The 30-kg Crate With A Force F. The Force IsMertYakarОценок пока нет
- EMech Prob Set II EqulibriumДокумент3 страницыEMech Prob Set II Equlibriumsubhafkt.2005Оценок пока нет
- Work Sheet 3 AДокумент9 страницWork Sheet 3 Adaniel hambissaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Worksheet (F Ma)Документ3 страницыChapter 3 Worksheet (F Ma)Obsinet ObsinetОценок пока нет
- Final Exam Open Book, Closed Notes, Do Not Write On This Sheet, Show All WorkДокумент5 страницFinal Exam Open Book, Closed Notes, Do Not Write On This Sheet, Show All Workandi suntoroОценок пока нет
- Quiz No. 3Документ2 страницыQuiz No. 3naikin_1031Оценок пока нет
- Assignment2 PDFДокумент3 страницыAssignment2 PDFAloysius LeañoОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 3Документ19 страницTutorial 3Maria CutajarОценок пока нет
- University of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 4 (Chapter 3)Документ5 страницUniversity of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 4 (Chapter 3)Vivin MathewОценок пока нет
- EM Assinment 6Документ5 страницEM Assinment 6Atul GaurОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 8 PDFДокумент16 страницTutorial 8 PDFBharat SaiОценок пока нет
- Og Humwbp 02Документ8 страницOg Humwbp 02Trash PandaОценок пока нет
- Convection Heat TransferДокумент49 страницConvection Heat TransferAli almansouriОценок пока нет
- DT466 Valve AdjustmentДокумент15 страницDT466 Valve Adjustmentחנניה מוסОценок пока нет
- Design and Development of Pneumatic Cotton Picker: Durgesh Gupta, Jayesh Teli, Paras Badhe, Suraj BanhattiДокумент3 страницыDesign and Development of Pneumatic Cotton Picker: Durgesh Gupta, Jayesh Teli, Paras Badhe, Suraj Banhattidurgesh3guptaОценок пока нет
- FXDQ-NBVE Technical Data PDFДокумент13 страницFXDQ-NBVE Technical Data PDFLuis CarlosОценок пока нет
- 52402-BDK-PIP-CS-010 Pipe Wall Thickness Rev 0Документ3 страницы52402-BDK-PIP-CS-010 Pipe Wall Thickness Rev 0sudjonoОценок пока нет
- Application Note .: Measuring Torsional Operational Deflection Shapes of Rotating ShaftsДокумент8 страницApplication Note .: Measuring Torsional Operational Deflection Shapes of Rotating Shaftsjhon vargasОценок пока нет
- Grade 9 - Tle Eim Assessment W1-2Документ6 страницGrade 9 - Tle Eim Assessment W1-2Neeson AlveroОценок пока нет
- Pre Shrunk Machine SopДокумент6 страницPre Shrunk Machine SoplanhotelsОценок пока нет
- Science 10 Motion ReviewДокумент5 страницScience 10 Motion ReviewVishal PonugotiОценок пока нет
- Continuum Mech Problem Set #3Документ1 страницаContinuum Mech Problem Set #3behzadОценок пока нет
- Specification Ranger DX800Документ4 страницыSpecification Ranger DX800Nugraha SandyОценок пока нет
- E 1211 - 97 - RteymtetukveДокумент6 страницE 1211 - 97 - RteymtetukveLENDОценок пока нет
- Test Procedures For The Determination of Desiccant Adsorption CapacityДокумент4 страницыTest Procedures For The Determination of Desiccant Adsorption CapacityAnirudh BaviskarОценок пока нет
- M7R Install InstructionsДокумент8 страницM7R Install InstructionstaylorОценок пока нет
- Flow Control ValvesДокумент7 страницFlow Control ValvesSasko DimitrovОценок пока нет
- 1-s2.0-S1359431121013430-Main (Innovations in Pulsating Heat Pipes From Origins To Future Perspectives)Документ9 страниц1-s2.0-S1359431121013430-Main (Innovations in Pulsating Heat Pipes From Origins To Future Perspectives)noxОценок пока нет
- Ed 9221 - Finite Element Methods in Mechanical DesignДокумент4 страницыEd 9221 - Finite Element Methods in Mechanical DesignRajesh KannanОценок пока нет
- Piston Only PagesДокумент13 страницPiston Only Pagesirwandi trinovОценок пока нет
- 6614 SKF Agri Hub For Tillage DisksДокумент8 страниц6614 SKF Agri Hub For Tillage DisksAlvaro MunozОценок пока нет