Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
As Answers Camb 2003 June A Level Paper 1 2 9702-1-2
Загружено:
jmok92Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
As Answers Camb 2003 June A Level Paper 1 2 9702-1-2
Загружено:
jmok92Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Prepared by Leong Yee Pak A-level Physics May/June 2003 Paper 1 (9702/01) 1. B mass 2. B Use the formula, W = F.
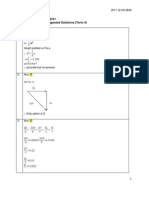
s . Also F = ma. Unit for force = kg ms-2. Hence unit for work = kg ms-2. m = kg m2 s-2 3. B 60o 10N 60o 10N 4. A 5. C Absolute uncertainty = 60o
3 x 327.66 = 9.82 = 10 ms-1 (1 s.f.) 100
6. B 7. C Horizontal component: motion with constant velocity, u cos Vertical component: motion with constant acceleration, uy = u sin , a = - g. Use v = u + at, v = u sin - gt 8. C Displacement = area under the graph. When v increases at a constant rate, grapah of displacement with time is a parabola. When v is constant, graph of displacement with time is a straight line with positive gradient. When v decreases at a constant rate, graph of displacement with time is a inverse parabola. 9. D The shaded areas under the graph represent the distances travelled. 10. D Use F = ma to find acceleration. F = (3m + m) a. a = F / 4m. Now consider only block Y: Use F = ma. Force on Y by X = (3m) x (F / 4m) = 3F / 4 11. B Friction is horizontal forwards. Normal reaction is vertically upwards. Combine the 2 forces by vector addition. 12. A Collision is inelastic. But total momentum is still conversed. 2 x 8 + 4 x 2 = (2 + 4) v 13. D Resultant force = 20 + 20 = 40 N. Resultant torque = 30 x (2r) 14. B (10000 9000) N 15. A 16. C 17. C 18. D Kinetic energy is converted into work done against the braking force. mv2 = F. s First case: m x 102 = F x 10 .(1) Second case: m x 302 = F x s2 . (2) Equation (2) divided by equation (1): s2 / 10 = 900 / 100. s2 = 90 m. 19. B 20. A For the same level of liquid, pressure in the straw = pressure outside. 0.9 p0 + hg = p0. hg = 0.1p0 21. B 22. D For each spring, when tension is extension = 3x. 23. B 24. D 25. C Speed of all e.m. waves = c.
1 W, extension = x. When the tension = W, 3
Use v = f. c = f. .(1) For frequency = Equation (2) divided by equation (1): 2 = 2.
f f , c= 2. ..(2) 2 2 N 1 = Hz t 10 x10 3
26. B Time for 1 complete oscillation = 4 x 2.5 ms = 10 x 10-3 s. f =
27. C The light emitted by each lamp has its phase changing randomly and rapidly. 28. C Use d sin = m. (1.00 x 10-6) sin 35o = 1 x . = 5.74 x 10-7 m 29. B Energy W = QV 30. C Mean current I =
100 + 20 = 60 mA. Use Q = It = (60 x 10-3) x 8.0 = 480 x 10-3 C 2
31. A 32. B Terminal p.d. across the cell = 7.5 V. Hence p.d. across the 15 resistor = 7.5 V. Apply Ohms law to the 15 resistor: 7.5 = I x 15. I = 0.50 A 33. B Resultant resistance in series = 16 k. Two equal resistance in parallel = 16 / 2 = 8.0 k 34. B Use potential divider formula: ratio of V = ratio of R. When Resistance of PQ = 0 ,
V 0 V 50 = . V = 0 V. When resistance of PQ = 50 k. = . V = 7.5 V 9.0 60 9.0 60
35. C Electric field is uniform. 36. D For uniform electric field, use E =
V 700 . E= = 1.4 x 105 Vm-1. Electric filed d 5 x10 3
is from high potential Q to low potential P. 37. B Electric field is out from positive charge, and in into a negative charge. 38. C Number of protons are the same = 6. Hence number of electrons are the same = 6. Number of neutron = nucleon number proton number. Hence, the number of neutrons are different. 39. B 40. D proton = up + up + down. Charge of proton =
2 2 1 e + e + (- e) = e 3 3 3
A-level Physics May/June 2003 Paper 2 9702/02) 1. kg m3 Frequency of count rate or activity or decay constant NC-1 or Vm-1 or kg m s-2 C-1 Momentum or impulse 2.(a) (i) Displacement = Distance from a fixed point in a specified direction. (ii) Car returns to the starting position. Displacement from starting point is zero. (b) (i) 1. v2 = u2 +2as. 282 = 0 + 2 x a x 450. a = 0.87 ms-2. 2. v = u + at. 28 = 0 + 0.87 t. t = 32.2 s. 3. Ek = mv2 = x 800 x 282 = 3.14 x 105 J 4. EP = mgh = 800 x 9.81 x 450 sin 5.0o = 3.07 x 105 J (ii) power = energy / time = (3.14 + 3.07) x 105 / 32.2 = (6.21 x 105) / 32.2 = 1.93 x 104 W (if use power, P = F.v with F = mg sin , wrong answer) (iii) some work also done against friction forces within the internal parts of the engine or work is done against the air resistance. 3.(a) (i) ductile, since there is a large plastic deformation. (ii) 1. L shown at end of the straight line 2. reciprocal / inverse of gradient of straight line region.
(b) (i) 1. circumference = 3 cm, or arc = r Extension = (6.5 /360) x 3 = 0.17 cm 2. strain = extension / length = 0.17 / 250 = 6.8 x 10-4 (ii) stress = force / area = (6.0 x 9.81) / (7.9 x 10-7) = 7.44 x 107 Pa (iii) Young modulus = stress / strain = (7.44 x 107) / (6.8 x 10-4) = 1.2 x 1011 Pa (iv) remove extra load and see if pointer returns to original position or wire returns to original length. 4. (a) 1. Both waves are transverse / longitudinal / same type, 2. Both waves meet at a point, 3. both waves are unpolarised or both polarised in the same direction (b) (i) 1. Give any value between 0.3 mm and 2 mm 2. = ax / D (ii) 1. x = D / a. As D is doubled, x is doubled. Separation increased 2 times, fringes are less bright 2. x = D / a . As increases 1.5 times, x is increased 1.5 times. Separation increased 1.5 times. Fringes are less bright, since the energy is distributed over a wider area, and hence the intensity is less. 3. separation unchanged, fringes are brighter. 5. (a) (i) resistance = V / I = 6.0 / (40 x 10-3) = 150 (ii) At 8.0 V, resistance = 8.0 / (50 x 10-3) = 160 . Change in resistance = 10 (b) (i) When the lamp is supplied with a normal operating p.d. of 6.0 V, from the graph, I = 40 mA. Current in both the resistor and the lamp = 40 mA. Potential difference across the resistor, VR = IR = (40 x 10-3) x 200 = 8.0 V. Since Ohms law is obeyed, the graph is a straight line passing through the origin and it also passes through the point I = 40 mA, V = 8.0 V (ii) E.m.f. = total p.d. across all the resistances = 8.0 + 6.0 = 14.0 V 6. (a) (i) curve is not smooth, there is fluctuations. (ii) curve is the same shape, and the half-life is the same,. Both are not affected by temperature. (b) (i) number of neutrons = 220 86 = 134 220 216 4 (ii) 86 Rn 84 Po + 2 He
Вам также может понравиться
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsОт EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsОценок пока нет
- JC2 (05/06) Physics Common Test 2006 Suggested Answers: Paper 1Документ13 страницJC2 (05/06) Physics Common Test 2006 Suggested Answers: Paper 1wangks1980Оценок пока нет
- VCE Physics Solutions 2017 Sample PaperДокумент6 страницVCE Physics Solutions 2017 Sample PaperLeo JaszОценок пока нет
- PHYSICSДокумент5 страницPHYSICSDaniel GtsadkanОценок пока нет
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2От EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- WBJEE 2014 Physics Question Paper With SolutionsДокумент14 страницWBJEE 2014 Physics Question Paper With SolutionsLokesh KumarОценок пока нет
- H2 Physic 2009 A Level SolutionsДокумент28 страницH2 Physic 2009 A Level Solutionsonnoez0% (2)
- Jee Main 2019 Question Paper Physics January 11 Shift 1Документ20 страницJee Main 2019 Question Paper Physics January 11 Shift 1Surjeet KumarОценок пока нет
- Solution Manual Linear Circuits Analysis - 2e, DecarloДокумент945 страницSolution Manual Linear Circuits Analysis - 2e, DecarloJorge Silva Velez75% (4)
- 2014 A-Level H2 Phy (9646) SolnДокумент19 страниц2014 A-Level H2 Phy (9646) SolnBryan TangОценок пока нет
- H2 Physic 2010 A Level SolutionsДокумент32 страницыH2 Physic 2010 A Level Solutionsonnoez50% (4)
- Ship Magnetism and the Magnetic Compass: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Navigation and Nautical CoursesОт EverandShip Magnetism and the Magnetic Compass: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Navigation and Nautical CoursesРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- Em Waves JeeДокумент14 страницEm Waves JeeTobiramaОценок пока нет
- Final ExamA1-2019-1Документ4 страницыFinal ExamA1-2019-1trinh.lenukieuОценок пока нет
- 2010 H2 Physics Paper 9646/03 suggested solutionsДокумент8 страниц2010 H2 Physics Paper 9646/03 suggested solutionslaslover100% (1)
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesОт EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesОценок пока нет
- 07 08 I FinalДокумент9 страниц07 08 I FinalMahmoud FariedОценок пока нет
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresОт EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- R A DeCarlo and P Lin Linear Circuit Analysis SДокумент945 страницR A DeCarlo and P Lin Linear Circuit Analysis STommyc102477% (13)
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyОт EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyОценок пока нет
- Question Bank For High School Science/Physics/DPMT2005: QuestionsДокумент4 страницыQuestion Bank For High School Science/Physics/DPMT2005: QuestionsDhika PutraОценок пока нет
- Electricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsОт EverandElectricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- H2 Physic 2008 A Level SolutionsДокумент21 страницаH2 Physic 2008 A Level Solutionsonnoez40% (5)
- FAP0025 Tutorial Solutions PDFДокумент25 страницFAP0025 Tutorial Solutions PDFRuben BenjaniОценок пока нет
- H2 Physic 2007 A Level SolutionsДокумент19 страницH2 Physic 2007 A Level SolutionsonnoezОценок пока нет
- Rec3 SolutionsДокумент6 страницRec3 SolutionsOscar Martinez0% (1)
- MS - Phy - PB-2 - Set (A) - Sis - 2023-24-1Документ13 страницMS - Phy - PB-2 - Set (A) - Sis - 2023-24-1tanmay.sachdeva123Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ10 страницChapter 1cse.220840131017Оценок пока нет
- Lecture 22Документ62 страницыLecture 22adilafzalkhan4264Оценок пока нет
- 64-141 W01 B. Atkinson (Final)Документ15 страниц64-141 W01 B. Atkinson (Final)Anonymous nWZpzni3Оценок пока нет
- H2 Physics J2 CT1 2013 Paper 2 SolutionsДокумент10 страницH2 Physics J2 CT1 2013 Paper 2 SolutionsMichael LeungОценок пока нет
- Solucionario Capitulo 19 Física Serway and FaughnДокумент14 страницSolucionario Capitulo 19 Física Serway and FaughnRafael ColindresОценок пока нет
- Sakshi: AIEEE - 2003Документ39 страницSakshi: AIEEE - 2003Praveen Kumarpillai100% (1)
- Power System ProblemДокумент10 страницPower System ProblemDanylle Lajera DiazОценок пока нет
- Hayt Cap 8 SolutionДокумент26 страницHayt Cap 8 SolutionVitor Campos100% (4)
- ch32 PDFДокумент14 страницch32 PDFRodrigo S QuirinoОценок пока нет
- ESAS Physics QuestionsДокумент22 страницыESAS Physics QuestionsErika Mae OrlinaОценок пока нет
- PHY101 Mega File MidtermДокумент63 страницыPHY101 Mega File MidtermHumaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 09Документ16 страницChapter 09서승찬88% (8)
- ECE QuestionsДокумент12 страницECE QuestionsSimran SiОценок пока нет
- Examples - PhysicsДокумент8 страницExamples - Physicslaila1001Оценок пока нет
- DR - Hannan Saadeh Solved Problems PDFДокумент50 страницDR - Hannan Saadeh Solved Problems PDFAbdОценок пока нет
- =F sinθ : R= F F R= F F R= FДокумент46 страниц=F sinθ : R= F F R= F F R= FYhelly27Оценок пока нет
- 2013 CBSE XIIScience 4 1 SET1 SectioncДокумент9 страниц2013 CBSE XIIScience 4 1 SET1 SectioncShashank ShekharОценок пока нет
- Compile BLM Ada Punya Anggi Nina Rana DiviДокумент10 страницCompile BLM Ada Punya Anggi Nina Rana DiviSelma Regita MahardiniОценок пока нет
- WBJEE 2010 Question Paper With SolutionДокумент50 страницWBJEE 2010 Question Paper With SolutionLokesh Kumar67% (3)
- Chapter 05Документ12 страницChapter 05Sanjoy JenaОценок пока нет
- JEE Main Exam 2022 Session 2 - 27 Jul Shift 1Документ25 страницJEE Main Exam 2022 Session 2 - 27 Jul Shift 1Jeshu SinghОценок пока нет
- Nsep Solution 2012Документ14 страницNsep Solution 2012Yatish GoyalОценок пока нет
- Chapter 10Документ17 страницChapter 10blooms93Оценок пока нет
- As Answers Camb 2007 May Paper 2Документ3 страницыAs Answers Camb 2007 May Paper 2jmok92Оценок пока нет
- As Answers Camb 2005 June Paper 2Документ2 страницыAs Answers Camb 2005 June Paper 2jmok92Оценок пока нет
- As Answers Camb 2004 June Paper 2Документ2 страницыAs Answers Camb 2004 June Paper 2jmok92Оценок пока нет
- As Answers Camb 2003 Oct Nov Paper 2 9702 02Документ2 страницыAs Answers Camb 2003 Oct Nov Paper 2 9702 02jmok92Оценок пока нет
- As Answers Camb 2004 Nov Paper 2Документ2 страницыAs Answers Camb 2004 Nov Paper 2jmok92Оценок пока нет
- As Answers Camb 2002 June Paper 2Документ1 страницаAs Answers Camb 2002 June Paper 2jmok92Оценок пока нет
- As Answers Camb 2002 Specimen Paper 1 and 2Документ2 страницыAs Answers Camb 2002 Specimen Paper 1 and 2jmok92Оценок пока нет
- As Answers Camb 2002 Nov Paper 2Документ1 страницаAs Answers Camb 2002 Nov Paper 2jmok92Оценок пока нет
- 1 The Classroom Learning AcademyДокумент6 страниц1 The Classroom Learning AcademyJR3A Grace Low Shing WeiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5Документ14 страницChapter 5Angelo ColendresОценок пока нет
- Modbus Mapping - Apex 100Документ24 страницыModbus Mapping - Apex 100AnandSreeОценок пока нет
- Plan For Today: Dry Friction Belt FrictionДокумент17 страницPlan For Today: Dry Friction Belt FrictionMr. JoestarОценок пока нет
- GIS Overview PresentationДокумент30 страницGIS Overview PresentationHaripriya PalemОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 - TheveninДокумент9 страницChapter 5 - TheveninLin ChongОценок пока нет
- A Ishiki Physics ProjectДокумент3 страницыA Ishiki Physics ProjectD. N. BainОценок пока нет
- Surface and Volume Charge Densities WorksheetДокумент2 страницыSurface and Volume Charge Densities WorksheetAyurvaidyaОценок пока нет
- IS:11592Документ64 страницыIS:11592Santanu KararОценок пока нет
- 15 - Piezo Pyro & FerroelectricityДокумент23 страницы15 - Piezo Pyro & FerroelectricityMd. Rafiqul Islam50% (2)
- Reactive Power Management Solutions GuideДокумент72 страницыReactive Power Management Solutions GuideSatyendra Kumar100% (2)
- R. A. C. Slater Auth. Engineering Plasticity Theory and Application To MetalДокумент432 страницыR. A. C. Slater Auth. Engineering Plasticity Theory and Application To MetalPrakash M AngadiОценок пока нет
- Report On State of The Art of Test Methods Seventh Framework Programme Theme 7 TransportДокумент53 страницыReport On State of The Art of Test Methods Seventh Framework Programme Theme 7 TransportJose LizarragaОценок пока нет
- Experiment 4 Conclusion Physics LabДокумент2 страницыExperiment 4 Conclusion Physics LabYna Lafuente100% (1)
- House WiringДокумент9 страницHouse WiringhassjayawardanaОценок пока нет
- Simplified Design of Building Frames Using First Order AnalysysДокумент20 страницSimplified Design of Building Frames Using First Order AnalysysfdejbrizuelaОценок пока нет
- Int. J. Multiphase Flow Vol. 12, No. 5, Pp. 745-758, 1986Документ14 страницInt. J. Multiphase Flow Vol. 12, No. 5, Pp. 745-758, 1986rockyОценок пока нет
- Réle Temporizador - 3RP1574-1NP30Документ7 страницRéle Temporizador - 3RP1574-1NP30jorge garciaОценок пока нет
- Design and Implementation of Van de Graaff GeneratorДокумент3 страницыDesign and Implementation of Van de Graaff GeneratorInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Shan Armaine Cabela - Week 1 - Electromagnetism LAS ODL and BDLДокумент3 страницыShan Armaine Cabela - Week 1 - Electromagnetism LAS ODL and BDLShan Armaine CabelaОценок пока нет
- Basic Shaft Alignments System PDFДокумент53 страницыBasic Shaft Alignments System PDFNatarajan RajaОценок пока нет
- HCI634JДокумент8 страницHCI634J3efooОценок пока нет
- Replacement in Anticipation of Failure.Документ11 страницReplacement in Anticipation of Failure.mbapritiОценок пока нет
- ACS758 Datasheet PDFДокумент22 страницыACS758 Datasheet PDFdominhsonОценок пока нет
- OLTC - Circulating CurrentДокумент16 страницOLTC - Circulating CurrentAsif MominОценок пока нет
- Y8 Revision SlidesДокумент49 страницY8 Revision SlidesMariaОценок пока нет
- TIH 025-030 Bearing HeatermanualДокумент106 страницTIH 025-030 Bearing HeatermanualcoupercouperОценок пока нет
- Arithmetic Logic Unit: ObjectiveДокумент4 страницыArithmetic Logic Unit: ObjectiveNour YoussefОценок пока нет
- Abstract of IE RulesДокумент6 страницAbstract of IE RulesNavneet SinghОценок пока нет
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseОт EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (69)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowОт EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (48)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingОт EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessОт EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (6)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismОт EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (500)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceОт EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (23)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidОт EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1395)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayОт EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (125)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesОт EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2193)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishОт EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (18)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsОт EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (94)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterОт EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (409)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeОт EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeОценок пока нет
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)От EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (155)
- In Search of Schrödinger’s Cat: Quantum Physics and RealityОт EverandIn Search of Schrödinger’s Cat: Quantum Physics and RealityРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (380)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldОт EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (8)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceОт EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityОт EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (75)
- The 60 Minute Quantum Physics Book: Science Made Easy For Beginners Without Math And In Plain Simple EnglishОт EverandThe 60 Minute Quantum Physics Book: Science Made Easy For Beginners Without Math And In Plain Simple EnglishРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (4)
- Starry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationОт EverandStarry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (158)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseОт EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (13)
- The Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsОт EverandThe Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)