Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Pathophysiology of CHF
Загружено:
Imae Mayo60%(5)60% нашли этот документ полезным (5 голосов)
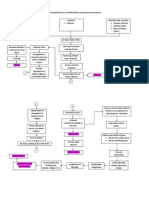
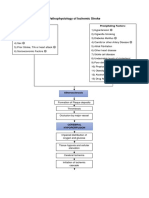
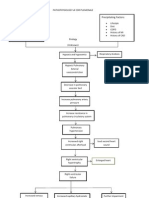
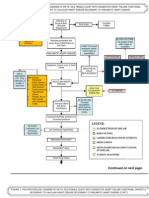
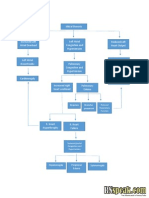
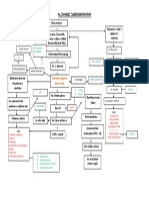
5K просмотров1 страницаHeart failure occurs due to non-modifiable risk factors like age, gender, and valvular disease as well as modifiable lifestyle factors such as smoking, alcohol, obesity, and hypertension. This leads to increased left atrial pressure and blood backing up into the lungs, reducing stroke volume and tissue perfusion while increasing pulmonary capillary pressure and fluid buildup in the lungs causing pulmonary edema, hypoxia, and activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system to increase blood volume and pressure. Signs include dyspnea, cough, fatigue, and reduced kidney function.
Исходное описание:
Pathophysiology of CHF
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документHeart failure occurs due to non-modifiable risk factors like age, gender, and valvular disease as well as modifiable lifestyle factors such as smoking, alcohol, obesity, and hypertension. This leads to increased left atrial pressure and blood backing up into the lungs, reducing stroke volume and tissue perfusion while increasing pulmonary capillary pressure and fluid buildup in the lungs causing pulmonary edema, hypoxia, and activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system to increase blood volume and pressure. Signs include dyspnea, cough, fatigue, and reduced kidney function.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
60%(5)60% нашли этот документ полезным (5 голосов)
5K просмотров1 страницаPathophysiology of CHF
Загружено:
Imae MayoHeart failure occurs due to non-modifiable risk factors like age, gender, and valvular disease as well as modifiable lifestyle factors such as smoking, alcohol, obesity, and hypertension. This leads to increased left atrial pressure and blood backing up into the lungs, reducing stroke volume and tissue perfusion while increasing pulmonary capillary pressure and fluid buildup in the lungs causing pulmonary edema, hypoxia, and activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system to increase blood volume and pressure. Signs include dyspnea, cough, fatigue, and reduced kidney function.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
Pathophysiology
Non-modifiable risk factors: - Age - Gender - Valvular heart disease Reduced myocardial contractility Increased cardiac workload Decreased diastolic filling Obstruction of left atrial emptying Modifiable risk factors: - Lifestyle - Smoking - Excessive alcohol consumption - Obesity - hypertension
Increased left atrial pressure
Blood dams back into the pulmonary capillary bed
Decreased stroke volume
Decreased tissue perfusion Pressure of blood into the pulmonary capillary bed increases
Fluid shift into the intraalveolar space and interalveolar space
Increased cellular hypoxia
Decreased blood flow to the kidney
Pulmonary edema
RAAS stimulation
Signs and symptoms: Dyspnea Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea Orthopnea Rales/crackles Moist cough Blood tinged frothy sputum Dizziness Fatigue Weakness
Vasoconstriction and reabsorption of sodium and water
Increased blood volume Increased systemic BP
Вам также может понравиться
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failuretinayko100% (1)
- Stroke PathophysiologyДокумент3 страницыStroke PathophysiologyMaureen EricaОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Predisposing Factors Precipitating/Aggravating FactorsДокумент1 страницаPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Predisposing Factors Precipitating/Aggravating Factorsguillermojerry100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Hypertensive Cardiovascular DiseaseДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology of Hypertensive Cardiovascular Diseasekhrizaleeh100% (10)
- Pathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke FinalДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke FinalAcohCChao75% (4)
- Pathophysiology HypertensionДокумент1 страницаPathophysiology HypertensionAlinor Abubacar100% (3)
- Congestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramДокумент3 страницыCongestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramJacinthaVanathayahОценок пока нет
- Angina Pectoris PathophysiologyДокумент2 страницыAngina Pectoris Pathophysiologydana88% (8)
- Pathophysiology of Myocardial Infarction (STEMI)Документ2 страницыPathophysiology of Myocardial Infarction (STEMI)michaela100% (3)
- Pathophysiology CHFДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology CHFPerry Oliver AlvarezОценок пока нет
- Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramДокумент3 страницыMyocardial Infarction Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramAbi Habiling100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureTrixia Almendral100% (2)
- The Pathology of Congestive Heart FailureДокумент4 страницыThe Pathology of Congestive Heart FailureMar Ble50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Heart FailureДокумент4 страницыPathophysiology of Heart FailureTiger Knee100% (2)
- (Cor Pulmonale) PATHOPHYSIOLOGYДокумент2 страницы(Cor Pulmonale) PATHOPHYSIOLOGYmilayango67% (3)
- Congestive Heart Failure PathophysiologyДокумент16 страницCongestive Heart Failure PathophysiologyDale LaurenteОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (10)
- Congestive Heart FailureДокумент8 страницCongestive Heart Failureiancel_038893% (27)
- Cerebrovascular Accident PathophysiologyДокумент1 страницаCerebrovascular Accident PathophysiologyBerde KangleonОценок пока нет
- Pleural EffusionДокумент1 страницаPleural Effusionarvinian01100% (2)
- Pathophysiology CVAДокумент1 страницаPathophysiology CVANenette Aquino100% (2)
- Coronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyДокумент3 страницыCoronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyElmer Balgos Alinsog50% (4)
- Pathophysiology of HCVDДокумент5 страницPathophysiology of HCVDNicolne Lorraine100% (1)
- C. Pathophysiology (Schematic Diagram) Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsДокумент2 страницыC. Pathophysiology (Schematic Diagram) Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsMarynette MapaОценок пока нет
- Final Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology PDFДокумент3 страницыFinal Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology PDFDave JoshuaОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Heart FailureДокумент1 страницаPathophysiology of Heart FailureabbeeyyОценок пока нет
- Patho of MIДокумент2 страницыPatho of MIInchan Montesines0% (1)
- Pathophysiology of CVAДокумент1 страницаPathophysiology of CVAChristine Joy Ilao PasnoОценок пока нет
- HCVD Cad Cva InfarctionДокумент2 страницыHCVD Cad Cva InfarctionMiguel Carlos Tacderan100% (1)
- Pathophysiology CHFДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology CHFKim Franzel M. Rabe100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure III With Pleural EffusionДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure III With Pleural EffusionKen100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Disease: Predisposing Factors Etiology Precipitating FactorsДокумент4 страницыPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Disease: Predisposing Factors Etiology Precipitating FactorsLilot Antonio Rodriguez Vinarao100% (5)
- Pathophysiology (Chronic Renal Failure)Документ3 страницыPathophysiology (Chronic Renal Failure)marshmalou86% (7)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureMel Izhra N. MargateОценок пока нет
- Stroke PathophysiologyДокумент2 страницыStroke PathophysiologyJaessa Feliciano100% (2)
- Congestive Heart Failure Schematic DiagramДокумент1 страницаCongestive Heart Failure Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis100% (1)
- PathophysiologyДокумент4 страницыPathophysiologyCee SanchezОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Cardiovascular SystemДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Cardiovascular Systembanyenye25Оценок пока нет
- Laennecs Cirrhosis PathophysiologyДокумент2 страницыLaennecs Cirrhosis PathophysiologyTrixie Al Marie100% (3)
- Acute Respiratory Failure Pa Tho PhysiologyДокумент4 страницыAcute Respiratory Failure Pa Tho Physiologyroseanne18100% (4)
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentJohn Michael FernandezОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)Документ1 страницаPathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)rexale ria100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Pulmonary Embolism (Loria.J)Документ2 страницыPathophysiology of Pulmonary Embolism (Loria.J)Justine Mae Loria0% (1)
- Concept MapДокумент4 страницыConcept Mapdejosep_informaticsОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart Failurea_samiane64% (11)
- Myocardial Infarction: Nonmodifiable Factors: Modifiable FactorsДокумент4 страницыMyocardial Infarction: Nonmodifiable Factors: Modifiable FactorsHearty ArriolaОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentByron Paz Te100% (1)
- Pathophysiology - HyperthyroidismДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology - HyperthyroidismCaren Reyes100% (5)
- Pathophysiology of HTN and CHF Leading To Pleural Effusion Causing Cardiac Tamponade Secondary To PericarditisДокумент1 страницаPathophysiology of HTN and CHF Leading To Pleural Effusion Causing Cardiac Tamponade Secondary To Pericarditisjake251996Оценок пока нет
- Fluid and Hemo Dynamic Imbalances W 2Документ49 страницFluid and Hemo Dynamic Imbalances W 2erwilli5Оценок пока нет
- Pulmonary Edema: Prepared By: South West Education CommitteeДокумент65 страницPulmonary Edema: Prepared By: South West Education CommitteedanradulescuОценок пока нет
- Copd Cad Pathophysiology (Revised)Документ3 страницыCopd Cad Pathophysiology (Revised)Israel Soria EsperoОценок пока нет
- Edema Hyperemia CongestionДокумент23 страницыEdema Hyperemia Congestionraanja2Оценок пока нет
- Cardiac ArrhythmiaДокумент3 страницыCardiac Arrhythmiajae_lee_73Оценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Cardiovascular SystemДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Cardiovascular SystemMon GabrielОценок пока нет
- Seminar On Heart Failure: Presented by Neethu.MДокумент59 страницSeminar On Heart Failure: Presented by Neethu.MNeethu JayasankarОценок пока нет
- Types of Shock: Cardiovascular Dysfunction Chapter 48Документ1 страницаTypes of Shock: Cardiovascular Dysfunction Chapter 48meeeenonОценок пока нет
- Alcoholic Cardiomyopathy: Ventricular DilatationДокумент1 страницаAlcoholic Cardiomyopathy: Ventricular DilatationDee SarajanОценок пока нет
- CHFSP 2005Документ36 страницCHFSP 2005Andy F MonroeОценок пока нет
- Clinical Aspect of Heart FailureДокумент67 страницClinical Aspect of Heart FailureAri Bandana TasrifОценок пока нет