Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
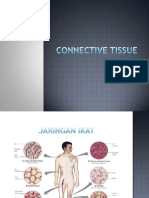
List Down The Types of Connective Tissues and Their Functions
Загружено:
Zahir Jayvee Gayak IIИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
List Down The Types of Connective Tissues and Their Functions
Загружено:
Zahir Jayvee Gayak IIАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1. List down the types of connective tissues and their functions.
The major types of connective tissue are: Loose connective tissue is a mass of widely scattered cells whose matrix is a loose weave of fibers. Many of the fibers are strong protein fibers called collagen. Loose connective tissue is found beneath the skin and between organs. It is a binding and packing material whose main purpose is to provide support to hold other tissues and organs in place. Adipose tissue consists of adipose cells in loose connective tissue. Each adipose cell stores a large droplet of fat that swells when fat is stored and shrinks when fat is used to provide energy. Adipose tissue pads and insulates the animal body. Blood is a loose connective tissue whose matrix is a liquid called plasma. Blood consists of red blood cells, erythrocytes, white blood cells, leukocytes, and thrombocytes or platelets, which are pieces of bone marrow cell. Plasma also contains water, salts, sugars, lipids, and amino acids. Blood is approximately 55 percent plasma and 45 percent formed elements. Blood transports substances from one part of the body to another and plays an important role in the immune system of the animal. Collagen (from the Greek kolla, meaning "glue," and genos, meaning "descent") is a dense connective tissue, also known as fibrous connective tissue. It has a matrix of densely packed collagen fibers. There are two types of collagen: regular and irregular. The collagen fibers of regular dense connective tissue are lined up in parallel. Tendons, which bind muscle to bone, and ligaments, which join bones together, are examples of dense regularconnective tissue. The strong covering of various organs, such as kidneys and muscle, is dense irregular connective tissue. Cartilage (from the Latin cartilago, meaning "gristle") is a connective tissue with an abundant number of collagen fibers in a rubbery matrix. It is both strong and flexible. Cartilage provides support and cushioning. It is found between the discs of the vertebrae in the spine, surrounding the ends of joints such as knees, and in the nose and ears. Bone is a rigid connective tissue that has a matrix of collagen fibers embedded in calcium salts. It is the hardest tissue in the body, although it is not brittle. Most of the skeletal system is comprised of bone, which provides support for muscle attachment and protects the internal organs.
http://www.answers.com/topic/what-are-the-major-types-of-connective-tissue-and-theirfunction#ixzz2DLirFygR
2. What are the components of connective tissue? Describe each component.
1. Cells - All cell types associated with connective tissues may be seen in areolar. a. Fibroblasts - are the most numerous cells in areolar. The cells are large, flat and branching or spindle-shaped. The nucleus is oval and pale in stained smears. The cytoplasm is highly basophilic in young cells indicating increased protein synthesis. In older cells protein synthesis is reduced. Fibroblasts tend to be fixed except during regeneration. Then the cells exhibit slow, gliding movements. b. Macrophages - are most abundant in richly vascular areas. The cells are irregular with short blunt processes. Active or "angry" macrophage show numerous pseudopodia. The nucleus is ovoid and usually indented. The cytoplasm is dark staining with many vacuoles. c. Adipocytes or fat cells can be found scattered throughout areolar tissue. When they make up the major component of a region it is called adipose tissue. Each cell is enmeshed in a "basket" of reticular fibers. d. Mast cells - are found throughout connective tissues but are concentrated near blood vessels. They are easily recognized by their numerous cytoplasmic granules. These granules stain with basic dyes and PAS (periodic acid - Schiff reagent. The granules contain heparin and histamine primarily. e. Leukocytes - There are three types of leukocytes commonly found in areolar C.T.: i. Lymphocytes - are small wbcs about 7um with a large spherical nucleus. Their cytoplasm is basophilic. They can be found in abundance within the mucous membranes of the respiratory and digestive systems. They make up the bulk of the lymphoid nodules in the lamina propria of these tracts. ii. Eosinophiles - are granulocytic wbcs. The nucleus is bilobed. The cytoplasm contains orange acidophilic granules. Eosinophiles are especially abundant in the lamina propria of the digestive and respiratory tracts. They are associated with tissues which play a major role in allergic reactions. iii. Plasma cells - are oblong cells whose nucleus is at one end. The nucleus shows a spoke-like pattern of chromatin. Extensive ER indicates a great deal of protein synthesis. iv. Melanocytes - can be found in areolar tissue although their function is not well understood there. Generally, they are responsible for the manufacture of melanin. 2. Fibers - all fiber types are represented: f. a. Collagenous are the most abundant. b. Elastic fibers are not as common. c. Reticular fibers are generally found where areolar borders on other tissues, especially near basement membranes.
3. Ground Substance - is characterized as an amorphous jelly thought to occur in sheet-like lamellae.
Вам также может понравиться
- Connective TissuesДокумент11 страницConnective TissuesCamille Ann Faigao FamisanОценок пока нет
- Structure and Functions of the Body: A Hand-Book of Anatomy and Physiology for Nurses and Others Desiring a Practical KnowledgeОт EverandStructure and Functions of the Body: A Hand-Book of Anatomy and Physiology for Nurses and Others Desiring a Practical KnowledgeОценок пока нет
- Connective Tissue - LabДокумент53 страницыConnective Tissue - LabArnold ArzobalОценок пока нет
- Connective TissueДокумент4 страницыConnective TissueLANGWAEMILLОценок пока нет
- Wenmarie D. Co BSMT 3A, Histology: MatrixДокумент5 страницWenmarie D. Co BSMT 3A, Histology: MatrixSayonara WatashinoaiОценок пока нет
- Human Body Tissues Power PointДокумент60 страницHuman Body Tissues Power PointMaxwell C Jay KafwaniОценок пока нет
- Connective Tissue Functions and Components ExplainedДокумент56 страницConnective Tissue Functions and Components ExplainedLAVKESH KUMARОценок пока нет
- Human Body OrganizationДокумент6 страницHuman Body OrganizationWolverineInZenОценок пока нет
- Connective Tisssue (General)Документ29 страницConnective Tisssue (General)James ChabuОценок пока нет
- Connective Tissues Presented By: D F Wangila ConnectiveДокумент27 страницConnective Tissues Presented By: D F Wangila ConnectiveGeorge MunyendoОценок пока нет
- Connectivetissue 3Документ26 страницConnectivetissue 3Tauqeer AhmedОценок пока нет
- Electron Microscopic Cell StructureДокумент26 страницElectron Microscopic Cell StructureMaria ArshadОценок пока нет
- Veta 65. Module 3Документ24 страницыVeta 65. Module 3Melon MelonОценок пока нет
- Plant and Animal Organ Systems FunctionsДокумент18 страницPlant and Animal Organ Systems FunctionsHannah CastroОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - 2013 Animal TissuesДокумент8 страницChapter 1 - 2013 Animal TissuesSiti Juwairiah ZainurinОценок пока нет
- Epithelial Lab ReportДокумент5 страницEpithelial Lab ReportMadiОценок пока нет
- The Connective Tissue: Functions, Structures and ClassificationsДокумент5 страницThe Connective Tissue: Functions, Structures and ClassificationsPia AbilaОценок пока нет
- Act05 Animal Histology and Organology DiscussionДокумент9 страницAct05 Animal Histology and Organology DiscussionPaula Nicole AlanoОценок пока нет
- CH 6 Tissues Animal TissuesДокумент11 страницCH 6 Tissues Animal TissuesRishabh SinghОценок пока нет
- 1.2. Support and Movement SystemsДокумент16 страниц1.2. Support and Movement SystemssamiktshyagiriОценок пока нет
- Histology of Connective TissueДокумент41 страницаHistology of Connective TissueIbe ClementОценок пока нет
- Add InfoДокумент5 страницAdd InfoWestminster AbbeyОценок пока нет
- Types of Tissues and Their FunctionsДокумент39 страницTypes of Tissues and Their FunctionsSnehasish DebnathОценок пока нет
- Histoooooo!!! 345Документ5 страницHistoooooo!!! 345OtencianoОценок пока нет
- Structural Organization in AnimalsДокумент7 страницStructural Organization in AnimalsVedant BondeОценок пока нет
- Module 1-A5-Discussion On Body TissuesДокумент6 страницModule 1-A5-Discussion On Body TissuesWilliam DC RiveraОценок пока нет
- Staining of Connective TissueДокумент3 страницыStaining of Connective TissueJey TeeОценок пока нет
- 11 Biology Notes Ch07 Structural Organisation in AnimalsДокумент6 страниц11 Biology Notes Ch07 Structural Organisation in AnimalsSham PhadtareОценок пока нет
- Study of Animal Tissues: An Overview of Epithelial, Connective, Muscular and Nervous TissuesДокумент60 страницStudy of Animal Tissues: An Overview of Epithelial, Connective, Muscular and Nervous TissuesEntirety 4uОценок пока нет
- Animal Tissue: Chapter - 10 Std. XIДокумент110 страницAnimal Tissue: Chapter - 10 Std. XIYash Soneji100% (2)
- Connective TissueДокумент6 страницConnective Tissueanishpantha530Оценок пока нет
- Tissues (Notes)Документ11 страницTissues (Notes)Rezeil CaОценок пока нет
- The Fascinating World of TissuesДокумент68 страницThe Fascinating World of TissuesO.r. Cadz100% (1)
- Lesson 1 Plant and Animal Tissue Presentation1Документ60 страницLesson 1 Plant and Animal Tissue Presentation1abdullahfahdelm.adiongОценок пока нет
- Histology by Andrea Di Flavio: 55 - Fibers of Connective TissueДокумент13 страницHistology by Andrea Di Flavio: 55 - Fibers of Connective Tissuesebastiano_zapp4929Оценок пока нет
- Cell Biology Review: Blood Smear and Connective TissueДокумент15 страницCell Biology Review: Blood Smear and Connective TissueGabriel ParasОценок пока нет
- ER transports materials throughout the cellДокумент3 страницыER transports materials throughout the cellKeneth Parohinog ABM 1Оценок пока нет
- Animal TissueДокумент14 страницAnimal TissueSagar GavasОценок пока нет
- M 1 PPT-PDF XI Bio CH 7 Structural Organisation in AnimalsДокумент39 страницM 1 PPT-PDF XI Bio CH 7 Structural Organisation in Animalsamarendrar87Оценок пока нет
- Connective TissueДокумент57 страницConnective TissueSunil DhatwaliaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in AnimalsДокумент25 страницChapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animalsamit lakraОценок пока нет
- Body TissuesДокумент10 страницBody TissuesNaanmatha PuspanathanОценок пока нет
- Tissue Anatomy and Physiology: The Four Main Tissue TypesДокумент35 страницTissue Anatomy and Physiology: The Four Main Tissue Typessnp88100% (1)
- Cellular Histology GuideДокумент27 страницCellular Histology GuideJonaya AmpasoОценок пока нет
- Hist 311 CM1 Cu3 Connective TissueДокумент13 страницHist 311 CM1 Cu3 Connective Tissuets5266498Оценок пока нет
- Year 10 Edexcel IGCSE Human Biology Cells Unit 1 NotesДокумент49 страницYear 10 Edexcel IGCSE Human Biology Cells Unit 1 NotesZoonieFR0% (1)
- Cells & Tissues (LS1151 & SM0030) Notes On Histology LecturesДокумент7 страницCells & Tissues (LS1151 & SM0030) Notes On Histology LecturesArezo TanhaОценок пока нет
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsДокумент23 страницыStructural Organisation in AnimalsMothi KarunaОценок пока нет
- NCERT Chapter 6: Tissues (Plant Tissue and Animal Tissue)Документ4 страницыNCERT Chapter 6: Tissues (Plant Tissue and Animal Tissue)Chetan Gautam100% (1)
- TissuesДокумент74 страницыTissuesMonica Sree100% (1)
- CTДокумент84 страницыCTNigusu SolomonОценок пока нет
- L6.1-Connective Tissues-Dr.Ghazal,3rd March 2024 ok_11a16c7a783a8a64fee12418d69adb29Документ32 страницыL6.1-Connective Tissues-Dr.Ghazal,3rd March 2024 ok_11a16c7a783a8a64fee12418d69adb29LT DRAGONXОценок пока нет
- CellДокумент8 страницCellvjaОценок пока нет
- Cell SpecializationadpataionДокумент67 страницCell SpecializationadpataionMarc AnthonyОценок пока нет
- LAS 2 The Cell TypesДокумент11 страницLAS 2 The Cell TypesJeremie CataggatanОценок пока нет
- ANIMAL CELL PARTS AND FUNCTIONSДокумент5 страницANIMAL CELL PARTS AND FUNCTIONSNan Fen Jin Sabolarce100% (1)
- Chapter Review TissueДокумент4 страницыChapter Review TissueGeorge IvyОценок пока нет
- Textus ConnectivusДокумент43 страницыTextus ConnectivusShafiraОценок пока нет
- Zoology Notes: 007 Chapter 4Документ4 страницыZoology Notes: 007 Chapter 4humanupgradeОценок пока нет
- Muscle and Nerve: Unique To Animals Conduct Electricity (Controlled Fashion) Allow For MovementДокумент12 страницMuscle and Nerve: Unique To Animals Conduct Electricity (Controlled Fashion) Allow For MovementZahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- Stoker C23Документ15 страницStoker C23Zahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- Intrams 2013 Schedule of Games OutdoorДокумент4 страницыIntrams 2013 Schedule of Games OutdoorZahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- ProblemДокумент3 страницыProblemZahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- Review Ch04asfsafasДокумент5 страницReview Ch04asfsafasZahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- Outdoor Games Revised 1Документ3 страницыOutdoor Games Revised 1Zahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- Fasciolopsis BuskiДокумент2 страницыFasciolopsis BuskiZahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- CardioДокумент3 страницыCardioZahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- Brief History of Cyanmethemoglobin Method for Hemoglobin DeterminationДокумент5 страницBrief History of Cyanmethemoglobin Method for Hemoglobin DeterminationZahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- Outdoor Games Revised 1Документ3 страницыOutdoor Games Revised 1Zahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- ToxoplasmosisДокумент1 страницаToxoplasmosisZahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- Outdoor Games (Boys) : For More Questions, Please Contact Penny Gayak (09339460922)Документ1 страницаOutdoor Games (Boys) : For More Questions, Please Contact Penny Gayak (09339460922)Zahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- Emotional Behavior of Adults Could Be Triggered in The WombДокумент2 страницыEmotional Behavior of Adults Could Be Triggered in The WombZahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- A Caesarean SectionДокумент5 страницA Caesarean SectionZahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- Table and Interpretsafsafation RevisedДокумент6 страницTable and Interpretsafsafation RevisedZahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- Aa RRL ResearchsafsafsafsafДокумент16 страницAa RRL ResearchsafsafsafsafZahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- Table and Interpretsafsafation RevisedДокумент6 страницTable and Interpretsafsafation RevisedZahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- Pipette Slides-RLD4Документ44 страницыPipette Slides-RLD4thasrioОценок пока нет
- Table Cat2fsafasfДокумент2 страницыTable Cat2fsafasfZahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- Research (Hypothesis and CF)Документ1 страницаResearch (Hypothesis and CF)Zahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- Eating DisorderДокумент3 страницыEating DisorderZahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- Feel Pain and Let GoДокумент2 страницыFeel Pain and Let GoZahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- AidsДокумент4 страницыAidsZahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- Clean and Green1Документ4 страницыClean and Green1Zahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- AidsДокумент4 страницыAidsZahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- Spiritual NursingДокумент13 страницSpiritual NursingZahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- Organ TransplantДокумент2 страницыOrgan TransplantAlexa A. AldayОценок пока нет
- Anaphylactic ReactionДокумент9 страницAnaphylactic ReactionZahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- Professional Growth of Nursing Students Through Extracurricular ActivitiesДокумент1 страницаProfessional Growth of Nursing Students Through Extracurricular ActivitiesZahir Jayvee Gayak IIОценок пока нет
- Calculator For SW Density Changes - Effect of List On Ships DraftДокумент3 страницыCalculator For SW Density Changes - Effect of List On Ships DraftHein Thurein KyawОценок пока нет
- Din en 1320-1996Документ18 страницDin en 1320-1996edcam13Оценок пока нет
- How To Use Dr. Foster's Essentials: Essential Oils and BlendsДокумент5 страницHow To Use Dr. Foster's Essentials: Essential Oils and BlendsemanvitoriaОценок пока нет
- Homework Helpers - Chemistry PDFДокумент311 страницHomework Helpers - Chemistry PDFTamby100% (1)
- Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate: Riefing - Nfrared BsorptionДокумент4 страницыTenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate: Riefing - Nfrared BsorptionMostofa RubalОценок пока нет
- Proteccion Contra Sobretensiones PDFДокумент84 страницыProteccion Contra Sobretensiones PDFgilbertomjcОценок пока нет
- Grade 9 Unit 1 - Part 1: Square RootsДокумент20 страницGrade 9 Unit 1 - Part 1: Square RootsWilson ZhangОценок пока нет
- HTTP Verbs GET POST PUT PATCH DELETE (39Документ12 страницHTTP Verbs GET POST PUT PATCH DELETE (39Jefferson EducacionОценок пока нет
- FLIGHT CONTROLS: TROUBLESHOOTING AND COMPONENTSДокумент3 страницыFLIGHT CONTROLS: TROUBLESHOOTING AND COMPONENTSBernardino Ferreira JúniorОценок пока нет
- Filtros MaquinasДокумент34 страницыFiltros MaquinasAndres AlfonzoОценок пока нет
- Real Possibility of Future ConditionДокумент3 страницыReal Possibility of Future ConditionHusОценок пока нет
- Exercise Questions (Materials) .: BFT 112 Introduction To EngineeringДокумент1 страницаExercise Questions (Materials) .: BFT 112 Introduction To EngineeringSK DarsyanaaОценок пока нет
- Chinkon Kishin - Origens Shintoístas Do Okiyome e Do Espiritismo Na MahikariДокумент2 страницыChinkon Kishin - Origens Shintoístas Do Okiyome e Do Espiritismo Na MahikariGauthier Alex Freitas de Abreu0% (1)
- Marketing Strategy of Air-Conditioning Companies: Project SynopsisДокумент13 страницMarketing Strategy of Air-Conditioning Companies: Project SynopsisSrikanta ChoudhuryОценок пока нет
- General Science EnvironmentДокумент28 страницGeneral Science EnvironmentHamza MujahidОценок пока нет
- Ego7 Manual enДокумент76 страницEgo7 Manual ensullivanj69Оценок пока нет
- Wire Rope: - Bright - 6 X 19 - Fibre CoreДокумент8 страницWire Rope: - Bright - 6 X 19 - Fibre CoreQuynh NguyenОценок пока нет
- Metaphors As Ammunition The Case of QueeДокумент19 страницMetaphors As Ammunition The Case of QueeMarijana DragašОценок пока нет
- Experimental Design and Optimization MethodsДокумент38 страницExperimental Design and Optimization MethodssudalaiyandiОценок пока нет
- TED BENTON: Is Capitalism Sustainable?Документ2 страницыTED BENTON: Is Capitalism Sustainable?api-25932856Оценок пока нет
- Dr. Ghusoon Mohsin Ali: Al-Mustansiriya University College of Engineering Electrical Engineering DepartmentДокумент89 страницDr. Ghusoon Mohsin Ali: Al-Mustansiriya University College of Engineering Electrical Engineering Departmentهمام الركابي100% (1)
- Pricelist Mobil Area Jabodetabek Semester 2 2022 TerbaruДокумент108 страницPricelist Mobil Area Jabodetabek Semester 2 2022 TerbarutonymuzioОценок пока нет
- Etabloc Technical DataДокумент108 страницEtabloc Technical Dataedward ksbОценок пока нет
- Aminet 110 en PDFДокумент17 страницAminet 110 en PDFWahid AliОценок пока нет
- Water System BOQ 16.12.2023 R0Документ144 страницыWater System BOQ 16.12.2023 R0moinu85Оценок пока нет
- Higher-Order InteractionsДокумент6 страницHigher-Order Interactions山木Оценок пока нет
- Resultados de La Web: GDDS - Traducción Al Español - Ejemplos Inglés - Reverso ..Документ3 страницыResultados de La Web: GDDS - Traducción Al Español - Ejemplos Inglés - Reverso ..Jo PaterninaОценок пока нет
- MR 20 Nissan PDFДокумент1 639 страницMR 20 Nissan PDFFREDYRUFO AZA MORALES83% (6)
- Psychopathology: Dr. Shafqat Huma MBBS, FCPS (Psychiatry) Fellowship in Addiction Psychiatry (USA)Документ48 страницPsychopathology: Dr. Shafqat Huma MBBS, FCPS (Psychiatry) Fellowship in Addiction Psychiatry (USA)sfrtr100% (1)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityОт EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (13)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsОт EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityОт EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsОт EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (3)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionОт EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (402)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeОт EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeОценок пока нет
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedОт EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (78)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementОт EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (40)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsОт EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (169)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossОт EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (4)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesОт EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (34)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessОт EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (327)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsОт EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsОценок пока нет
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingОт EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (4)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeОт EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (253)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingОт EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (41)
- The Stress-Proof Brain: Master Your Emotional Response to Stress Using Mindfulness and NeuroplasticityОт EverandThe Stress-Proof Brain: Master Your Emotional Response to Stress Using Mindfulness and NeuroplasticityРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (109)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingОт EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (33)
- The Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossОт EverandThe Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (4)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaОт EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisОт EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (8)