Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Enplate Ni 434 E
Загружено:
Magda FaragИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Enplate Ni 434 E
Загружено:
Magda FaragАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
ENPLATE Ni 434 E
High speed, stable, ammonia free electroless nickel process
INTRODUCTION ENPLATE Ni 434E is a high speed, extremely bright electroless nickel process with a moderate phosphorus content, designed for optimum bath performance. This process offers excellent high temperature stability. The ENPLATE Ni 434E process chemically deposits a uniform nickel-phosphorus alloy on a wide variety of substrates. The process contains no ammonia. The ENPLATE Ni 434E is supplied as three separate liquid concentrates. ENPLATE Ni 434E A and ENPLATE Ni 434E B are used for bath make-up and ENPLATE Ni 434E A and ENPLATE Ni 434E C are used for replenishment. ENPLATE Ni 434 E meets MIL-C-26074E, AMS 2404 and AMS 2405 specifications. Features of the ENPLATE Ni 434E process * * * * * Excellent stability/extended bath life Fast plating rate Effective bath performance at low surface area to volume ratio Superior brightness Ease in waste treatment of spent plating bath (ammonia free)
Issued Spsds
: 13 Sep 2001 : 07 Dec 1999
ENPLATE Ni 434E Technical data sheet Page 2 of 10
ENPLATE NI 434E PHYSICAL PROPERTIES Typical result Phosphorus Content, wt% Melting Point (eutectic) C Coefficient of Thermal Expansion. m /m/C Thermal Conductivity, cal/cm/sec/C Electrical Resistivity microhm-cm Magnetic Properties Hardness Vickers HV 100 100g load, 75 m deposit, steel As plated Heat treated @ 1 hr 400C Wear Properties Taber Abraser Wear test Taber Wear Index Wt. loss mg/1000 cycles As plated Heat treated @ 1hr. 400C Corrosion Related Properties Salt spray test* (ASTM B117) 35C 5% NaCl, 25m deposit, hours to first corrosion spot 2024 Aluminium 1010 carbon Steel Nitric Acid Test Conc. nitric acid 42 Be 30 sec room temp 25 m steel Hydrochloric Acid Test 50% HC1, 3 min, room temp 25m steel * 5.0 to 8.5 880 to 960 13 to 15 0.0105 to 0.0135 50 to 100 Slightly Magnetic
500 to 680 760 to 870
15 to 18 4 to 8
100 100 Fail **
Pass**
**
ASTM test is performed on a flat panel. More complex or rough parts may show initial spotting in fewer hours. ASTM B117 salt spray is primarily a porosity test and only effective as a screening tool to show the difference afforded by alternative processes. It is not, however, a quantitative corrosion test. Fail is indicated by any significant discoloration of the deposit.
EQUIPMENT Anodically protected stainless steel tanks are recommended. Polypropylene or polypropylene-lined tanks can also be used. Steam teflon super coils, or type 316 stainless steel electric immersion heaters may be used. Note: Electric heaters must be properly earthed (earth leakage) and equipped with over-temperature hazard protected, also low liquid level shut-off devices are recommended. In-tank filtration is recommended. Clean, low-pressure air agitation through bottom-mounted stainless steel, CPVC or polypropylene pipes is highly recommended. Clean air, free of oil and dirt is required; shop air should not be used.
ENPLATE Ni 434E Technical data sheet Page 3 of 10
Exhaust ventilation is recommended to remove solution mist which is caused by agitation or gassing of the solution and which may contain nickel salts. The bath should be kept covered when it contains no work and is at or near operating temperature. FILTRATION Continuous filtration is recommended. To ensure smooth deposits continuous filtration through 5 micron filtration medium is required, (preferably gravity feed bag-type units). A minimum of 6 to 10 solution turnovers per hour is recommended for proper filtration. If continuous filtration is not feasible, the solution must be cooled at the end of the working period, then batch filtered through a 3 micron filtration medium before beginning the next days work. With or without continuous filtration, the tank and filtration equipment will require periodic leaching with 30% nitric acid followed by water rinse and a final deionised or distilled water rinse (with a small amount of potassium carbonate added). AGITATION Horizontal work rod agitation and/or air agitation using a low pressure blower are recommended. Agitation during heating avoids localised overheating which can result in bath plateout. CONTROL As with all electroless nickel solutions, successful plating requires maintaining proper solution control; temperature, pH agitation, filtration and chemistry. The use of automatic controllers/dosing units is strongly recommended. A complete information package on equipment for electroless nickel plating is available on request. Included is information on electroless nickel plating tanks, EN series electroless nickel controllers and ion exchange systems for the removal of nickel from electroless nickel rinses. SOLUTION PREPARATION ENPLATE Ni 434E is supplied as three separate liquid concentrates. ENPLATE Ni 434E A is used for makeup and replenishment, ENPLATE Ni 434E B is used only for make-up, and ENPLATE NI 434E C are used only for replenishment. COMPONENT PROPERTIES ENPLATE Ni 434E A Specific gravity Colour SOLUTION MAKE UP Make up additions ml per litre ENPLATE Ni 434E A ENPLATE Ni 434E B ENPLATE Ni 434E C Deionised or distilled water 60 150 790 1.27 Green ENPLATE Ni 434E B 1.19 Colourless ENPLATE Ni 434E C 1.29 Colourless
ENPLATE Ni 434E Technical data sheet Page 4 of 10
To make up the required amount of operating solution, proceed as follows: 1. 2. 3. 4. Rinse tank thoroughly with deionised or distilled water. Partially fill tank with deionised or distilled water. Add the required amount of ENPLATE Ni 434E A and ENPLATE Ni 434E B, with air or mechanical agitation and fill to working volume with deionised or distilled water. Heat solution to 82 to 91C. Check solution pH. Adjust if necessary with dilute (~50%) potassium carbonate, or (~10%) sulphuric acid.
OPERATING CONDITIONS Solution parameters Temperature C pH Bath loading dm2/l Nickel concentration g/l * Up to 5.2 for aluminium alloys. PERFORMANCE Typical results Plating rate, m/h 88C Solution life, turnovers* Steel Aluminium * ** 17 to 20** microns/hour 8 7 to 8 Typical range 82 to 91 4.7 to 5.2* 0.25 to 2.45 5.2 to 6.0 Optimum value 88 4.9 to 5.2* 1.23 5.8
Turnover occurs when the original concentration of 5.8 g/l nickel metal has been replenished. Increasing the pH as the bath ages, i.e. Beginning at pH 4.7 gradually increasing to pH 5.2, will help to maintain the plating rate.
TEMPERATURE Faster plating rates are obtained at higher temperatures. Low temperatures should be used to retard pitting when heavy deposits are desired. Do not maintain the bath at operating temperature if work is not being processed. This will cause breakdown of the reducer and stabiliser components. Heating the bath above 91C is not recommended. pH pH may be adjusted upward by additions of dilute (~50%) calcined potassium carbonate solution. A high purity, 47% by weight, calcined potassium carbonate solution is available. Sulphuric acid, 10% by volume, may be used to lower pH. Make all additions slowly with constant stirring. When using potassium carbonate for pH adjustment, be especially careful to make additions slowly with stirring to prevent eruption of the bath due to carbon dioxide liberation. pH measurements should be made only after good agitation (and consistent bath temperature) to assure equilibrium concentration of the bath. Narrow range pH papers are recommended when measuring the pH at the tank side. Electrometric pH meters are recommended for accurate measurement of pH. In this case, the buffer and solution temperature must be equal before testing. Because potassium carbonate is used for pH adjustment, a white crystalline precipitate (potassium sulphate) can occur in the electroless nickel bath after approximately 7 to 8 metal turnovers. This is especially true during cooling of an electroless nickel solution and is indicative of an aged bath.
ENPLATE Ni 434E Technical data sheet Page 5 of 10
Note: This precipitate is not a problem and a simple decanting procedure of the precipitate should be performed (together with filtration). If ammonia is not a problem in the effluent, ammonia solution may be used for pH adjustment in place of potassium carbonate if desired. The solution life will be extended (up to 10 metal turnovers) if ammonia is used and the precipitation of potassium sulphate will be prevented. RECOMMENDED PLATING PROCEDURES The quality of the finished product is generally dependent upon the original condition of the workpiece, pretreatment, and the condition and control of the plating solution. Generally, those involved in finishing operations have very little control over the condition of the workpiece as received. Therefore, proper pretreatment, and solution control are essential to minimse rejects and maximise production. CLEANING A water-break and scale-free surface is required for proper adhesion. Routine analysis of cleaners and descalers (acid salts) can minimise rejects. CLEANING SEQUENCE FOR STEEL Time (minutes) 1. 2. 3. ENBOND 808 Hot alkali soal cleaner COLD WATER RINSE (CWR) ENDOX 114 Room temperature electrolytic Periodic reverse cleaner (ending with an anodic cycle) CWR ACTANE 82 Acid dip CWR ENDOX 114 (as step 3 CWR HOT WATER RINSE (HWR) (if necessary, for pre-heating large items) ELECTROLESS NICKEL PLATE 5.0 1.0 2.0
4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
1.0 0.5 to 1.0 1.0 2.0 1.0
ENPLATE Ni 434E Technical data sheet Page 6 of 10
CLEANING SEQUENCE FOR COPPER ALLOYS Time (minutes) 1. ENBOND 160 or ENBOND Z 72 Soak clean COLD WATER (CWR) EBOND 160 Cathodic cleaner ENPLATE AD 485 Mild etch CWR SULPHURIC ACID DIP (10% by volume) CWR ELECTROLESS NICKEL PLATE Promote deposition by cathodic pulse 5.0
2. 3. or 4. 5. 6. 7.
1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.5 to 1.0 1.0
CLEANING AND PREPARATION SEQUENCE FOR ALUMINIUM Time (minutes) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. ENBOND NS-35 COLD WATER RINSE (CWR) ACTANE 70/NITRIC/SULPHURIC ACID SOLUTION Smut remover CWR ALUMON EN Zincate process CWR 50% NITRIC ACID STRIP CWR ACTANE 70 CWR ALUMON EN (can be a repeat of step 5) CWR ENPLATE AL 100 ELECTROLESS NICKEL STRIKE BATH (Optional - particularly useful for castings) CWR ELECTROLESS NICKEL PLATE 5.0 1.0 0.5 to 1.0 1.0 1.0 to 2.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.25 1.0 0.3 to 0.5 1.0
14. 15.
1.0
The delay between cleaning and plating should be the minimum possible. PLATING After proper preparation, parts to be electroless nickel plated are simply immersed in the ENPLATE Ni 434E operating solution for the required time to obtain the desired thickness. REPLENISHMENT Replenishment (see table over) is based on percent nickel activity of the solution. Analysis is required to determine the proper amount of replenishment chemicals. The ENPLATE Ni 434E process is maintained by additions of ENPLATE Ni 434E A and ENPLATE Ni 434E C at a 1:1 ratio. The amount of replenishment chemicals required Can be determined by a simple nickel titration. * For optimum results the nickel concentration should not be allowed to fall below 5.3 g/l.
ENPLATE Ni 434E Technical data sheet Page 7 of 10
The maximum recommended additions (at any one time) should not exceed 10 percent of the original metal content of the operating solution. If additions greater than 10 percent are required, they should be accomplished incrementally between workloads. All replenishment additions should be made with agitation.
ENPLATE NI 434 E REPLENISHMENT SCHEDULE Additions ml/l Ni 434E A Ni 434E C 1.5 3.0 4.5 6.0 7.5 9.0 10.5 12.0 13.5 15.0 16.5 18.0 1.5 3.0 4.5 6.0 7.5 9.0 10.5 12.0 13.5 15.0 16.5 18.0 Remarks Ni concentration g/l % activity 5.8 5.6 5.5 5.3 5.2 5.1 4.9 4.7 4.6 4.5 4.4 4.2 4.1 100 97.5 95.0 92.5 90.0 87.5 85.0 82.5 80.0 77.5 75.0 72.5 70.0
ml EDTA ** titrated 8.5 8.3 8.1 7.9 7.7 7.5 7.2 7.0 6.9 6.7 6.4 6.2 6.0 * **
Replenishment additions should never exceed 10% of the original make-up. When a 5 ml sample is titrated with a 0.0575M EDTA solution.
ANALYTICAL CONTROL Control of the ENPLATE Ni 434E bath is based on the rapid and accurate analysis for nickel metal content as follows: ANALYSIS FOR NICKEL METAL Apparatus needed 5 ml pipette 50 ml burette with 0.1 ml graduations 250 ml erlenmeyer flask Reagents needed 0.0575M EDTA solution: Dissolve 21.4 grams of EDTA - Na2 (disodium ethylene diamine-tetra-acetate) and 6.0 grams of AR grade sodium hydroxide in deionised or distilled water. Allow to cool and dilute to exactly 1 litre with deionised or distilled water using a volumetric flask. Murexide Indicator: Mix 0.2 gram of Murexide (acid ammonium purpurate) with 100 grams of sodium chloride. Grind together with a mortar and pestle. AR grade ammonium hydroxide.
ENPLATE Ni 434E Technical data sheet Page 8 of 10
PROCEDURES 1. 2. With a safety pipette, transfer a 5 ml sample of the bath into the 250 ml Erlenmeyer flask. Add approximately 50 ml deionised or distilled water, 10 ml AR grade ammonium hydroxide, and a "pinch" of murexide indicator. Only sufficient murexide indicator should be added to develop a pale straw colour; too much indicator obscures the end point. Titrate with the EDTA solution to a blue-purple end point.
3.
Calculation ml EDTA x 0.675 = g/l of nickel metal Replenishment Nickel metal content should be maintained at an average range of 5.3 - 6.3 g/l. For each 1 g/l of nickel metal to be replenished, add 10 ml/l of ENPLATE Ni 434E A and 10 ml of ENPLATE Ni 434E C. Check the pH of the solution and adjust, if necessary. ANALYSIS FOR HYPOPHOSPHITE Normally, replenishment additions of ENPLATE Ni 434E based on the analysis for nickel metal will keep the concentration of reducer at its proper level. However, the consumption of reducer may not always be at the same rate; therefore, it is advisable to run occasional analyses to ensure that it is in the recommended range (26.5 to 29 g/l). If it is not within the recommended range, replenish using ENPLATE Ni 434E C as outlined below. Apparatus needed 250 ml glass stoppered iodine flask 2 ml pipette 50 ml pipette 5 ml dropping pipette 25 ml graduate 50 ml burette Reagents needed 0.10N Iodine solution 50% v/v Hydrochloric Acid 0.10N sodium thiosulphate (Na2S2O3)* * These are available as ready-to-use solutions or as measured concentrates your local laboratory chemical supply house. in ampoules from
PROCEDURE 1. 2. 3. 4. With a safety pipette, transfer a 2 ml sample of the solution into a stoppered iodine flask. Add 25 ml of 50% v/v hydrochloric acid. With a safety pipette, transfer 50 ml of the 0.10N standard iodine solution into the flask. Stopper the flask and set in the dark for exactly 30 minutes. Solution temperature should be 20 2C. Titrate with 0.10N sodium thiosulphate until the solution is faintly yellow-brown. Add a few millilitres of Starch solution and continue titration to the disappearance of the blue-mauve coloration.
Calculation (50 ....ml Thiosulphate) x 2.65 = g/l hypophosphite
ENPLATE Ni 434E Technical data sheet Page 9 of 10
REPLENISHMENT Reducer should be maintained at 26.5 to 29 g/l. For every 1 g/l low add 2 ml/l of ENPLATE Ni 434E C. STRIPPING ENSTRIP EN 79 and ENSTRIP EN 86 are non-cyanide, alkaline strippers utilising advanced technology. They dissolve electroless nickel deposits up to 125 m thick from steel by immersion. These products are particularly effective in removing high phosphorus deposits that could be difficult to remove with other strippers. The expected stripping rate will range from 10 to 15 m/h. Solution life will vary depending upon method and condition of operation, but should hold nickel metal at the level of 15 to 30 g/l of ENSTRIP EN 79 or ENSTRIP EN 86. ENSTRIP EN 79 and ENSTRIP EN 86 are also effective in stripping electroless nickel deposits from copper, and copper alloys, stainless steel, kovar, and some nickel based alloys. Proper cleaning of the part is required before stripping. Soak cleaning followed by reactivation of the deposit surface with 50% hcl is recommended for parts that are carbonised and oxidised due to storage or extended service. Cathodic activation in ACTANE 82 using carbon anodes is recommended for aged or heavily oxidised deposits. SOLDERABILITY Soldering to ENPLATE Ni 434E can be effectively accomplished with a fully active flux. Direct soldering to electroless nickel is difficult, particularly as the deposit ages and forms oxides on the surface. If direct soldering is desired, this should be done as soon as possible after plating. WASTE TREATMENT Operating solutions of ENPLATE Ni 434E contain nickel and are very slightly acidic. Before disposing of the spent solution, the nickel should be removed and the pH adjusted to the regulated limits. A customer bulletin is available detailing nickel removal. Be sure to consult local agencies with regard to regulations concerning pH limits and nickel bearing sludge disposal. PRECAUTIONARY INFORMATION CAUTION ENPLATE Ni 434E A, Ni 434E B, Ni 434E C and ENPLATE Ni 434E operating solution may cause irritation. HAZARD ENPLATE Ni 434E A, contains nickel sulphate, sensitivity to nickel may cause skin irritation. ENPLATE Ni 434E B, and ENPLATE Ni 434E C contain hypophosphite and may cause irritation. Heating dried salts to temperatures over 245C may produce toxic and flammable phosphine gas. HANDLING INFORMATION Always wear chemical safety goggles, rubber gloves, and protective clothing when handling ENPLATE Ni 434E A, B and C and the ENPLATE Ni 434E operating solutions. Exhaust ventilation is recommended to remove mist or vapours that may be generated during make up and operation. Wash thoroughly after handling.
ENPLATE Ni 434E Technical data sheet Page 10 of 10
CONTAINER INFORMATION Keep containers tightly closed. Store indoors in a cool dry, frost free area away from acids, salts, or oxidisers. Loosen closure cautiously when opening. Do not re-use containers. Wash before disposal. Improper disposal or re-use of containers may be dangerous and illegal. HANDLING AND SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS For detailed information consult the material safety data sheets for this product. Please read material safety data sheets carefully before using this product. DISCLAIMER All recommendations and suggestions in this bulletin concerning the use of our products are based upon tests and data believed to be reliable. Since the actual use by others is beyond our control, no guarantee expressed or implied, is made by Enthone, its subsidiaries of distributors, as to the effects of such use or results to be obtained, nor is any information to be construed as a recommendation to infringe any patent. ADDRESSES
AUSTRIA Enthone-OMI (Austria) GmbH Gromarktstrae 20 1232 Wien, Austria Tel.: 43-161668440 Fax.: 43-16167084 ITALY Enthone-OMI (Italia) S.p.A. Via B. Buozzi, 20 20097 San Donato Milanese MI< Italy Tel.: 39-02518941 Fax: 39-025279890 GREAT BRITAIN Enthone-OMI (UK) Ltd. Forsyth Road, Sheerwater, Woking Surrey GU21 5RZ, England Tel.: 44-1483758400 Fax: 44-1483728837 HUNGARY Enthone-OMI Hungaria KFT Ipari Park 19 2330 Dunaharaszti, Hungary Tel.: 36-24460-566 Fax: 36-24460-577 PORTUGAL Enthone-OMI Portugal Lda. Rua Bouca dos Estilhadouros 271 4445-044 Alfena Portugal Tel.: 351-229686620 Fax: 351-229686623 FRANCE Enthone-OMI (France) S.A. Rue Lon Jouhaux Croissy-Beaubourg 77312 Marne la Valle, France Tel.: 33-160059360/Fax:33-143026784 GERMANY Enthone-OMI (Deutschland) GmbH Elisabeth-Selbert-Strasse 4 40764 Langenfeld, Germany Tel.: 49-21738490-0 Fax: 49-21738490-200 SPAIN Enthone-OMI (Espana) S.A. 118, Carretera Reial 08960 Sant Just Desvern, Barcelona Espana Tel.: 34-934803388/Fax:34-934803389 CZECHIE Enthone-OMI (CZ), S.r.o. Severovychodnl V 146/1541 14100 Praha 4, Sporilov, Czechie Tel.: 420-272770665 Fax: 420-272767842 TURKEY Enthone-OMI (Trkiye) A.S. Ikitelli Organize Sanayi Turgut zal Cd Galvano Teknik Sitesi, A Blok No.33, Ikitelli, Instanbul Turkey Tel.: 90-2126710384/Fax: 90-2126710388 BENELUX Enthone-OMI (Benelux) B.V. Koenendelseweg 29 5222 BG s-Hertogenbosch The Netherlands Tel.: 31-736280111/Fax: 31-736219283 SWITZERLAND ERNE Ag Industriestrasse 24 8108 Dllikon, Zrich, Switzerland Tel.: 41-18441144 Fax: 41-18441145 SWEDEN Enthone-OMI (Sverige) A.B. Sderleden 106 60006 Norrkping, Sweden Tel.: 46-11240600 Fax: 46-11126833 POLAND Enthone-OMI Polska Sp.z.o.o. U1 Obuwnicza 3 26-100 Skarzysko-Kamienna Poland Tel:48-412521523/fax: 48-412521574
Вам также может понравиться
- 704 Na OHEДокумент7 страниц704 Na OHEBoris KundačinaОценок пока нет
- Iz260 PDFДокумент6 страницIz260 PDFKaRenthLuNaОценок пока нет
- Technical Data Sheet: Alzincate enДокумент3 страницыTechnical Data Sheet: Alzincate enLuuThiThuyDuongОценок пока нет
- Technical Data Sheet: Ginplate Ni 425Документ9 страницTechnical Data Sheet: Ginplate Ni 425LuuThiThuyDuongОценок пока нет
- Du-Zinc 019Документ7 страницDu-Zinc 019KaRenthLuNaОценок пока нет
- Nichel Sulphamate BathДокумент5 страницNichel Sulphamate Bathanasrl2006Оценок пока нет
- SurtecДокумент7 страницSurtecbrahymОценок пока нет
- Technical Service Data Sheet: Cupratech Ac 382Документ5 страницTechnical Service Data Sheet: Cupratech Ac 382Jitendra Kumar SinghОценок пока нет
- Ginplate Electroless Nickel 422: Technical Data SheetДокумент5 страницGinplate Electroless Nickel 422: Technical Data SheetLuuThiThuyDuongОценок пока нет
- Bright Nickel ProcessДокумент10 страницBright Nickel Processshanmukha MechanicalОценок пока нет
- Ginplate Ni - 426: Technical Data SheetДокумент7 страницGinplate Ni - 426: Technical Data SheetLuuThiThuyDuongОценок пока нет
- Tds Colsid ApdДокумент6 страницTds Colsid ApdMario PerezОценок пока нет
- Cobre CianuradoДокумент3 страницыCobre CianuradohumbertotorresrОценок пока нет
- Bright Chrome HR 75Документ12 страницBright Chrome HR 75Ringga sonifaОценок пока нет
- Surtec 680: Protection UpgradedДокумент7 страницSurtec 680: Protection Upgradedyudhien4443Оценок пока нет
- CN1056907A - A Kind of Process For Brightly Plating of Zinc For Metal Wire - Google PatentsДокумент6 страницCN1056907A - A Kind of Process For Brightly Plating of Zinc For Metal Wire - Google PatentsMuhammad SaqibОценок пока нет
- Argalux 64 Ds v11Документ23 страницыArgalux 64 Ds v11Tran Manh Vu100% (1)
- Do's & Don'ts For Impurities in Nickel Plating SolutionsДокумент2 страницыDo's & Don'ts For Impurities in Nickel Plating SolutionsHiden HidenОценок пока нет
- Semilux 100 Ds v05Документ28 страницSemilux 100 Ds v05Tran Manh VuОценок пока нет
- Bright Acid Copper For Wire and Grounding Rods: E-Brite 202GДокумент6 страницBright Acid Copper For Wire and Grounding Rods: E-Brite 202GUsman ali Cheema100% (1)
- Hard Chrome 105 Plating ProcesДокумент3 страницыHard Chrome 105 Plating ProcesKishora BhatОценок пока нет
- Manual 8XX Titrando ENДокумент38 страницManual 8XX Titrando ENLê Duy ThăngОценок пока нет
- Spectra 977 Process: Technical Data SheetДокумент2 страницыSpectra 977 Process: Technical Data SheetLuuThiThuyDuongОценок пока нет
- 65 Surtec 821Документ6 страниц65 Surtec 821vgciasen100% (2)
- TecTalis 1200Документ6 страницTecTalis 1200Julio OlveraОценок пока нет
- Silverlume PLUS Ds v09Документ26 страницSilverlume PLUS Ds v09Tran Manh VuОценок пока нет
- Bright Zinc PlatingДокумент3 страницыBright Zinc PlatingHacı OsmanОценок пока нет
- Technical Data Sheet: Performa 560Документ10 страницTechnical Data Sheet: Performa 560Diego NavaОценок пока нет
- Tripass ELV 2000Документ7 страницTripass ELV 2000thanh duc LeОценок пока нет
- 1.2 Chrome Solution Analysis ProceduresДокумент5 страниц1.2 Chrome Solution Analysis ProceduresRodolfo PerezОценок пока нет
- E-Brite B-150: Brass Plating ProcessДокумент7 страницE-Brite B-150: Brass Plating Processm daneshpourОценок пока нет
- NiSO4 MSDSДокумент7 страницNiSO4 MSDSCoralie ShrosbreeОценок пока нет
- NCZ PDFДокумент19 страницNCZ PDFnirai101259Оценок пока нет
- ZINCROLYTE Ni V - MEIS - 174581 040719Документ15 страницZINCROLYTE Ni V - MEIS - 174581 040719Diego NavaОценок пока нет
- New Concepts Non Cyanide Alkaline ZincДокумент35 страницNew Concepts Non Cyanide Alkaline ZincJOSE ANGEL CARRASCO100% (1)
- Tds Iza-2500 (Revision V) 170411Документ20 страницTds Iza-2500 (Revision V) 170411Stephany RojasОценок пока нет
- Met-Kleen 140 (7.8.13)Документ1 страницаMet-Kleen 140 (7.8.13)tribolasОценок пока нет
- Stannolume Bright Acid Tin: Technical Data SheetДокумент7 страницStannolume Bright Acid Tin: Technical Data SheetLuuThiThuyDuong100% (2)
- Plating - Interpharm PDFДокумент4 страницыPlating - Interpharm PDFvasudev_nОценок пока нет
- Laton AtotechДокумент6 страницLaton AtotechKaRenthLuNaОценок пока нет
- Zinc PlatingДокумент4 страницыZinc Platingrohitpatil330% (1)
- Iz250y PDFДокумент10 страницIz250y PDFKaRenthLuNa100% (1)
- Techseal Silver SL GДокумент11 страницTechseal Silver SL GAnh Quang NgoОценок пока нет
- Nickel General Operating InstructionsДокумент14 страницNickel General Operating InstructionsNicole fralixОценок пока нет
- Safecoat Hard AnodizingДокумент47 страницSafecoat Hard AnodizingyahsooyОценок пока нет
- Preparation of Sheet Steel For Porcelain EnamelingДокумент9 страницPreparation of Sheet Steel For Porcelain EnamelingMohammad YoussefiОценок пока нет
- Chromium PlatingДокумент66 страницChromium PlatingManikandan SudharsanОценок пока нет
- Lucite400 Acrylic LQ TDSДокумент6 страницLucite400 Acrylic LQ TDSLjy AlarvaОценок пока нет
- Decorative Chromium PlatingДокумент8 страницDecorative Chromium Platingcauthon82Оценок пока нет
- Determination of Sulfate ConcentrationДокумент3 страницыDetermination of Sulfate Concentrationm daneshpourОценок пока нет
- Test Cells For Plating PDFДокумент7 страницTest Cells For Plating PDFR.SubramanianОценок пока нет
- Argoshine Bright Silver: Salient FeaturesДокумент3 страницыArgoshine Bright Silver: Salient FeaturesJitendra Kumar SinghОценок пока нет
- Bright Acid Tin ProcessДокумент5 страницBright Acid Tin ProcessRC Villeda67% (3)
- Corrosion Inhibitors in Conversion Coatings. IIIДокумент7 страницCorrosion Inhibitors in Conversion Coatings. IIIAnonymous 6tg80e6BqAОценок пока нет
- Acid Zinc 2Документ6 страницAcid Zinc 2Muhammad SaqibОценок пока нет
- Buffoli Booklet - USA PhoscoatingДокумент138 страницBuffoli Booklet - USA PhoscoatingMark GarrettОценок пока нет
- Zonax Brass SaltsДокумент5 страницZonax Brass SaltsDenno WahonoОценок пока нет
- Kemtek Ni - 512: Semi Bright Electroless Nickel ProcessДокумент4 страницыKemtek Ni - 512: Semi Bright Electroless Nickel ProcessAbbas RangoonwalaОценок пока нет
- Enig En300 NickelДокумент6 страницEnig En300 Nickelrotaru_ionОценок пока нет
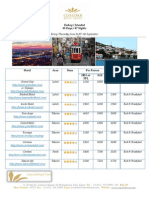
- Meal Plan CHD (05 - 11) Per Person Stars Area Hotel: Turkey / Istanbul 08 Days / 07 NightsДокумент2 страницыMeal Plan CHD (05 - 11) Per Person Stars Area Hotel: Turkey / Istanbul 08 Days / 07 NightsMagda FaragОценок пока нет
- Hardener of The Black Enamel Specs.Документ4 страницыHardener of The Black Enamel Specs.Magda FaragОценок пока нет
- Enplate Ni 434 EДокумент10 страницEnplate Ni 434 EMagda FaragОценок пока нет
- Book Greatest Miracle PDFДокумент653 страницыBook Greatest Miracle PDFasanadoОценок пока нет
- Corrosion Metallurgy Failure AnalysisДокумент2 страницыCorrosion Metallurgy Failure AnalysisMagda FaragОценок пока нет
- Enplate Ni 434 EДокумент10 страницEnplate Ni 434 EMagda FaragОценок пока нет
- Corrosion Metallurgy Failure AnalysisДокумент2 страницыCorrosion Metallurgy Failure AnalysisMagda FaragОценок пока нет
- MetallurgyДокумент8 страницMetallurgyadam1950Оценок пока нет
- Sheet Metal Forming PDFДокумент6 страницSheet Metal Forming PDFMada PerwiraОценок пока нет
- QualityДокумент36 страницQualityShobitha UchilОценок пока нет
- Sheet Metal Forming PDFДокумент6 страницSheet Metal Forming PDFMada PerwiraОценок пока нет
- Pulse Anodizing in An Existing Anodizing LineДокумент4 страницыPulse Anodizing in An Existing Anodizing LineMagda FaragОценок пока нет
- 20 Electrostatics-Coulomb's LawДокумент5 страниц20 Electrostatics-Coulomb's Laweltytan50% (2)
- Chap 16 No 1Документ2 страницыChap 16 No 1blackwellbert0% (1)
- EPA 608 Certification Test QuestionsДокумент96 страницEPA 608 Certification Test Questionslanzea91% (65)
- Tegostab B 8466Документ2 страницыTegostab B 8466Boyce ZhangОценок пока нет
- Biomerieux Mini Vidas - User ManualДокумент506 страницBiomerieux Mini Vidas - User ManualValeria GenoveseОценок пока нет
- Nucleating Agents For High-Density Polyethylene-A ReviewДокумент14 страницNucleating Agents For High-Density Polyethylene-A ReviewCao TúОценок пока нет
- Recognizing and Naming Binary Ionic CompoundДокумент30 страницRecognizing and Naming Binary Ionic CompoundNeal RobinОценок пока нет
- Techcross Electro-Cleen Operation - Maintenance - andSafetyManual (OMSM) - Rev. 0.1 - Dated April 21 - 2018Документ250 страницTechcross Electro-Cleen Operation - Maintenance - andSafetyManual (OMSM) - Rev. 0.1 - Dated April 21 - 2018Panda Radu100% (1)
- Kunal JRFДокумент3 страницыKunal JRFAakash KumarОценок пока нет
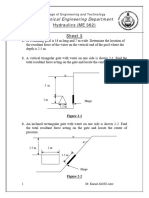
- Sheet 3Документ6 страницSheet 3Keroles SabryОценок пока нет
- P5 Effective StressДокумент28 страницP5 Effective StressMiguel TabaОценок пока нет
- Biology: Osmosis and Diffusion Lab Using Potato Cores Class: 3B Mr. Boyer Name: Simon HanДокумент10 страницBiology: Osmosis and Diffusion Lab Using Potato Cores Class: 3B Mr. Boyer Name: Simon Han서연김Оценок пока нет
- Engineering Mechanics Statics and Dynamics Irving H Shames PDFДокумент2 страницыEngineering Mechanics Statics and Dynamics Irving H Shames PDFNeci CardenoОценок пока нет
- Fencing Drawing-Proposal As On 15.02.2023Документ1 страницаFencing Drawing-Proposal As On 15.02.2023Bittudubey officialОценок пока нет
- Detailed Lesson PlanДокумент5 страницDetailed Lesson PlanGspr BoJoyОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Grade 11Документ198 страницChemistry Grade 11Jan92% (24)
- CruДокумент33 страницыCruRenanОценок пока нет
- CLASS VIII QUESTION BANK - 17 Stars and Solar SystemДокумент7 страницCLASS VIII QUESTION BANK - 17 Stars and Solar SystemSurbhi NayarОценок пока нет
- Perturbation ExamplesДокумент6 страницPerturbation Exampleserad_5Оценок пока нет
- E 698 - 99 - Rty5oc1sruqДокумент10 страницE 698 - 99 - Rty5oc1sruqtam daoОценок пока нет
- PPG - PSX700 (FD)Документ15 страницPPG - PSX700 (FD)scibduser001Оценок пока нет
- Excel Work Book For Heat ExchangersДокумент88 страницExcel Work Book For Heat Exchangerspk dasОценок пока нет
- CATALISEДокумент13 страницCATALISEANTONIO RAUL MANUELОценок пока нет
- The Basic Problems With SolutionsДокумент6 страницThe Basic Problems With SolutionsManvitha ReddyОценок пока нет
- 49 5 02 AOAC Official Method 2001 04 Determination of FumonisinsДокумент3 страницы49 5 02 AOAC Official Method 2001 04 Determination of Fumonisinsbanu güngörОценок пока нет
- Direct Dyes: Submitted To: Dr. Bushra Nasar By: Saba ArshadДокумент11 страницDirect Dyes: Submitted To: Dr. Bushra Nasar By: Saba ArshadQuratul AinОценок пока нет
- Chemical EquilibriumДокумент6 страницChemical EquilibriumBoodhonee AvinashОценок пока нет
- AIPMT 2013 Code W1 Question PaperДокумент43 страницыAIPMT 2013 Code W1 Question PaperNageswarОценок пока нет
- Answer KEY of Nature of Light Online TestДокумент12 страницAnswer KEY of Nature of Light Online TestKhanОценок пока нет
- HMT 2Документ2 страницыHMT 2Arul KumarОценок пока нет