Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ana, Patho Uro
Загружено:
Dan Ataniel EnsaladaОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Ana, Patho Uro
Загружено:
Dan Ataniel EnsaladaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
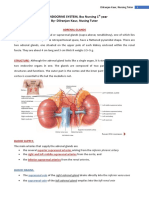
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
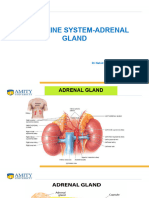
Adrenal Glands Curved over the top of the kidneys, adrenal glands are structurally and functionally two endocrine glands in one. Like the pituitary gland, the adrenals have glandular (cortex) and neural tissue (medulla) parts. The central medulla region is enclosed by the adrenal cortex which contains three separate layers of cells. Hormones of the Adrenal cortex Major groups of steroid hormones such as mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids and sex hormones are produced by the adrenal cortex. These hormones are collectively termed as corticosteroids.
Mineralocorticoids
1. Produced by the outermost layer of the adrenal cortex, the mineralocorticoids, are mainly aldosterone. These hormones play an essential part in regulating the mineral or salt content of the blood particularly the concentrations of sodium and potassium ions. The target organ of the hormone is the kidneys that selectively reabsorbs the minerals or allow them to be flushed out in the body in the form of urine. 2. Increased aldosterone levels in the body would result to rising amounts of reclaimed sodium ions by the kidney tubules and secreting more potassium ions into the urine. When sodium is reabsorbed water follows. Hence, the mineralocorticoids aids in water and electrolyte regulation. 3. Aldosterone is also released when the kidneys produce the enzyme, renin, when blood pressure drops. Production of renin triggers a series of reactions
that form angiotensin II, which is a potent stimulator of aldosterone release. 4. To prevent aldosterone release, atrial natriuretic peptide or ANP is released by the heart. The main goal of releasing ANP is to reduce blood volume and blood pressure.
Glucocorticoids
Glucocorticoids are produced by the middle layer of adrenal cortex which includes contisone and cortisol. The functions of this hormone are: 1. Promotion of normal cell metabolism 2. Helping the body resist long-term stressors, by increasing blood glucose levels. Important information about glucocorticoids: 1. Fats and even proteins are broken down by body cells and converted to glucose when blood levels of glucocorticoids are elevated in the blood. Hence, these hormones are said to be hyperglycemic hormones. 2. Unpleasant effects of inflammation are also controlled by glucocorticoids as they reduce the effects of edema and they reduce the pain by inhibiting some pain-causing molecules called prostaglandins. Thus, because of their anti-inflammatory properties, glucocorticoids are often prescribed as drugs to suppress inflammation for patients with arthritis. 3. Glucocorticoids are released from the adrenal cortex in response to the rising blood levels of ACTH.
Sex Hormones
The adrenal cortex produces the sex hormones regardless of ones gender. Production of sex hormones takes place throughout a persons life but the amount formed is relatively small. It is the innermost layer of the cortex that produces a large amount of androgens, male sex hormones and some estrogen, female sex hormone. Hormones of the Adrenal Medulla Like the knot of nervous tissue where posterior pituitary gland develops, the adrenal medulla has the same development. When this structure is stimulated by the sympathetic nervous system neurons, epinephrine, also called adrenaline, and norepinephrine, otherwise known as noradrenaline, are released into the bloodstream. Collectively, these hormones are called catecholamines.
1. Physical or emotional stress and threat would bring about the fight-or-flight response. The response is necessary to help a person cope up with the stressful situation. One of the organs stimulated in these situations is the adrenal medulla which is responsible for pumping catecholamines or hormones into the bloodstream to enhance and prolong the effects of neurotransmitters of the sympathetic nervous system. 2. Presence of catecholamines has the following effects: increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure and rising blood glucose levels. Also, small passageways of the lungs are dilated with presence of these hormones to cater more oxygen in the blood and a faster circulation to the organs most importantly to the brain, heart and muscles. Increase glucose and oxygen would make the body fit to fight or deal with short-term stressors.
Stretch marks Around the waist (trunchal obesity) Back of the head (Buffalo Hump)
Thining of the hair
Thining of the skin
Face (moonfac e)
Vasoconstricti on of blood vessel
Protein wasting
Fat deposition Appetite
enhancement of vasoconstrictive effect of circulatory catecholamine
Sensitivation of A- adrenergic receptors on surface of smooth muscle
Protein catabolism Protein Breakdown
Stimulation of satiety center (hypothalamus)
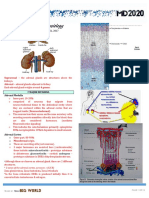
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Defect in gene coding for p53 and p57 Tumor formation arising from adrenal gland affecting both medulla and cortex (ADRENAL ADENOMA)
ADRENAL MEDULLA Formation of Tumor composing of chromffin cells (PHEOCHROMOCYTO MA) Release of catecholamines (norepenephrine and epinephrine) in the blood Release of catecholamines (norepenephrine and epinephrine) in the blood
ADRENAL CORTICAL ADENOMA Stimulation of Melanin synthesis Stimulation of androgen synthesis Virilization Hypersecretion of cortisol
Stimulation of Aldosterone synthesis Hyperaldosteroni sm Hyperaldosteroni sm Na & H20 retention Stimulation of alpha adrenergic receptors High blood pressure
Hyperpigmentati on of skin
Hypercortisoli sm/ CUSHINGS SYNDROME Acne Hirsutis m
Darkened striae
Darkene d skin
Irregular, fluctuating , and small in amount but constant menstruati
Weight gain
Вам также может понравиться
- Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaДокумент28 страницCongenital Adrenal HyperplasiaWindelyn Gamaro0% (1)
- Path o PhysiologyДокумент163 страницыPath o PhysiologyDiorella Marie López González100% (2)
- What Does The Endocrine System Do?Документ10 страницWhat Does The Endocrine System Do?hadiqa azizОценок пока нет
- Bio ReportДокумент4 страницыBio ReportKate MabanagОценок пока нет
- The Endocrine System Study Guide 101 PDFДокумент17 страницThe Endocrine System Study Guide 101 PDFStephanie Kate PelenioОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology of Adrenal GlandДокумент26 страницAnatomy and Physiology of Adrenal GlandYAMINIPRIYANОценок пока нет
- Adrenal Glands: Module 11: Endocrine SystemДокумент9 страницAdrenal Glands: Module 11: Endocrine SystemLANCE GILL Tolentino100% (2)
- Mabes Fluid and ElectrolytesДокумент9 страницMabes Fluid and ElectrolytesMabesОценок пока нет
- Surgical InstrumentsДокумент8 страницSurgical InstrumentsSharmaine Simon91% (11)
- Chapter 18 Endocrine SystemДокумент40 страницChapter 18 Endocrine SystemlolasparkleОценок пока нет
- Chemical Co - OrdinationДокумент21 страницаChemical Co - OrdinationManinder KaurОценок пока нет
- Adrenal GlandsДокумент18 страницAdrenal GlandsNitesh BhuraОценок пока нет
- Clinical Chemistry 3: EndocrinologyДокумент21 страницаClinical Chemistry 3: EndocrinologyRomie Solacito100% (3)
- Chapt10 - PPT Endocrine SystemДокумент57 страницChapt10 - PPT Endocrine SystemBtaman Rock100% (1)
- Seeley's EndocrineДокумент5 страницSeeley's EndocrineEllä PabustanОценок пока нет
- Endocrine System (Lecture)Документ79 страницEndocrine System (Lecture)roselle legsonОценок пока нет
- The Endocrine Glands & Their HormonesДокумент35 страницThe Endocrine Glands & Their HormonesShe JocelynОценок пока нет
- Nursing Research ReviewДокумент13 страницNursing Research Reviewɹǝʍdןnos96% (50)
- I. Gordon'S Typology of 11 Health PatternsДокумент5 страницI. Gordon'S Typology of 11 Health PatternsDan Ataniel EnsaladaОценок пока нет
- I. Gordon'S Typology of 11 Health PatternsДокумент5 страницI. Gordon'S Typology of 11 Health PatternsDan Ataniel EnsaladaОценок пока нет
- HTMA Mineral RatiosДокумент3 страницыHTMA Mineral RatiosluckydexxxОценок пока нет
- Summary Table Endocrine Review - OneДокумент5 страницSummary Table Endocrine Review - OneIndigoSilverОценок пока нет
- The Endocrine SystemДокумент13 страницThe Endocrine SystemThenmozhi SivajiОценок пока нет
- Lecture 15 - Adrenal Gland BNS KUMДокумент17 страницLecture 15 - Adrenal Gland BNS KUMabdulsaboor30Оценок пока нет
- Endo 3 Notes PDFДокумент9 страницEndo 3 Notes PDFDilОценок пока нет
- Endocrine System: Pituitary Gland and HypothalamusДокумент9 страницEndocrine System: Pituitary Gland and HypothalamusRohan Sahu0% (1)
- AdrenalДокумент5 страницAdrenalJC MolОценок пока нет
- The Endocrine System:: Chemical Signals in AnimalsДокумент13 страницThe Endocrine System:: Chemical Signals in AnimalsbobОценок пока нет
- UNIT 6 (Endocrine System)Документ7 страницUNIT 6 (Endocrine System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloОценок пока нет
- Adrenal GlandДокумент16 страницAdrenal GlandTanya SinghОценок пока нет
- Endokrin 1Документ34 страницыEndokrin 1dianpn27Оценок пока нет
- What Is A Hormone?: HormonesДокумент89 страницWhat Is A Hormone?: HormonesMarkus van der WesthuizenОценок пока нет
- Adrenal GlandДокумент3 страницыAdrenal GlandRene Anne Darcera-TanОценок пока нет
- Adrenal Gland Grp5Документ17 страницAdrenal Gland Grp5Kathrine GoОценок пока нет
- Endocrine SystemДокумент4 страницыEndocrine SystemMarmie Babaran GallibuОценок пока нет
- The Adrenal Glands Are Located Above Each KidneyДокумент2 страницыThe Adrenal Glands Are Located Above Each KidneySam BernsteinОценок пока нет
- Module 9 The Endocrine SystemДокумент15 страницModule 9 The Endocrine SystemMisha WilliamsОценок пока нет
- Adrenal MedullaДокумент3 страницыAdrenal Medullaelvie21Оценок пока нет
- HormonesДокумент124 страницыHormonesMr T KillworthОценок пока нет
- 4 Endocrine 3Документ23 страницы4 Endocrine 3ShenОценок пока нет
- L14Документ2 страницыL14MilenaОценок пока нет
- 3010 Adrenal and Parathyroid HormonesДокумент21 страница3010 Adrenal and Parathyroid HormonesDenesha KaurОценок пока нет
- Hormones: Hormonal Control Nervous ControlДокумент5 страницHormones: Hormonal Control Nervous Controlvaibhav trivediОценок пока нет
- The Endocrine System NotesДокумент6 страницThe Endocrine System NotesRohit AnthuliaОценок пока нет
- Hormones BSN-1-mergedДокумент24 страницыHormones BSN-1-mergedzahraОценок пока нет
- Endocrine System and Excretion WordДокумент10 страницEndocrine System and Excretion WordJoachim “Jayrz” MwambireОценок пока нет
- Adrenal HormonesДокумент2 страницыAdrenal HormonesEli JanОценок пока нет
- Insufisiensi Adrenal (Dr. Makbul)Документ52 страницыInsufisiensi Adrenal (Dr. Makbul)Rahmat AzimiОценок пока нет
- Endocrine System-Adrenal GlandДокумент18 страницEndocrine System-Adrenal GlandAkshat RastogiОценок пока нет
- Presented BY Prof. (Zoology) The Women University Multan: Dr. Nahid KaurarДокумент34 страницыPresented BY Prof. (Zoology) The Women University Multan: Dr. Nahid KaurarSohaib NasirОценок пока нет
- AP100 Final Exam Study GuideДокумент27 страницAP100 Final Exam Study Guidebhilligoss35100% (1)
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationДокумент9 страницChemical Coordination and IntegrationAjay JamwalОценок пока нет
- Exercise 13 EditДокумент10 страницExercise 13 EditSamantha De JesusОценок пока нет
- 10SUMMARYENDOCRINESYSTEMДокумент14 страниц10SUMMARYENDOCRINESYSTEMArvenBitasОценок пока нет
- Endocrine SystemДокумент10 страницEndocrine SystemSujatha AluguriОценок пока нет
- Endocrine SystemДокумент27 страницEndocrine SystemJessica CulangoОценок пока нет
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 22 PDFДокумент8 страниц11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 22 PDFSaurav SoniОценок пока нет
- Adrenal Glands WORDДокумент6 страницAdrenal Glands WORDFredie O HadjimudinОценок пока нет
- BioSci LO#2Документ16 страницBioSci LO#2AudzkieОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9 - Endocrine System NotesДокумент9 страницChapter 9 - Endocrine System Notesvictoria skoubourisОценок пока нет
- B.SC - Hons. Biotechnology 4th Sem Dr. Arvind ShuklaДокумент7 страницB.SC - Hons. Biotechnology 4th Sem Dr. Arvind Shuklamain.manishapatelОценок пока нет
- Endocrine SystemДокумент19 страницEndocrine Systemethel roseОценок пока нет
- Sistem Endokrin: Oleh: Dr. Siska Anggreni Lubis, SPKKДокумент25 страницSistem Endokrin: Oleh: Dr. Siska Anggreni Lubis, SPKKRichas Interisti SumatraОценок пока нет
- The Endocrine System: Properties: Mechanisms of Hormone ActionДокумент5 страницThe Endocrine System: Properties: Mechanisms of Hormone ActionaudreyОценок пока нет
- The Endocrine System Overview/ Introduction: Nur112: Anatomy and Physiology ISU Echague - College of NursingДокумент6 страницThe Endocrine System Overview/ Introduction: Nur112: Anatomy and Physiology ISU Echague - College of NursingWai KikiОценок пока нет
- Lecture10 CommunicationIII 1Документ30 страницLecture10 CommunicationIII 1Liana Rose MeregildoОценок пока нет
- Met 8.2Документ22 страницыMet 8.2LT DRAGONXОценок пока нет
- PNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNДокумент4 страницыPNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNaadeshthite476Оценок пока нет
- Adrenal Glands: Subject AboutДокумент17 страницAdrenal Glands: Subject AboutHareth mohammad mahmod NawajaОценок пока нет
- Functional Anatomy of The Adrenal GlandДокумент9 страницFunctional Anatomy of The Adrenal GlandPaula SchaeferОценок пока нет
- Adrenalglandlecture 111115200310 Phpapp01Документ25 страницAdrenalglandlecture 111115200310 Phpapp01varshasharma05Оценок пока нет
- Anatomy of The Endocrine System: Hypothalamus Brain Thalamus Nervous SystemДокумент13 страницAnatomy of The Endocrine System: Hypothalamus Brain Thalamus Nervous SystemUmer Shahzad ANSERОценок пока нет
- Endocrine GlandsДокумент13 страницEndocrine GlandsJoan GalarceОценок пока нет
- Hormonal CoordinationДокумент4 страницыHormonal Coordinationtalithaonkabetse723Оценок пока нет
- Adrenal Fatigue: Understanding the Symptoms: How Malfunctioning Adrenal Glands Negatively Affect the BodyОт EverandAdrenal Fatigue: Understanding the Symptoms: How Malfunctioning Adrenal Glands Negatively Affect the BodyОценок пока нет
- Autism, Deaf, Adhd, Learning DisabilityДокумент3 страницыAutism, Deaf, Adhd, Learning DisabilityDan Ataniel EnsaladaОценок пока нет
- HO 1 Introduction To MNCHN EINC 6may2013Документ5 страницHO 1 Introduction To MNCHN EINC 6may2013Dan Ataniel EnsaladaОценок пока нет
- BreastfeedingДокумент13 страницBreastfeedingDan Ataniel EnsaladaОценок пока нет
- Ghibellines Guelphs: Dante AlighieriДокумент1 страницаGhibellines Guelphs: Dante AlighieriDan Ataniel EnsaladaОценок пока нет
- Organizational StructureДокумент7 страницOrganizational StructureDan Ataniel EnsaladaОценок пока нет
- Gestational Trophoblastic TumorДокумент4 страницыGestational Trophoblastic TumorDan Ataniel EnsaladaОценок пока нет
- ArbovirusДокумент27 страницArbovirusDan Ataniel EnsaladaОценок пока нет
- Gantt Chart, Pert & CPMДокумент6 страницGantt Chart, Pert & CPMFrancois KokОценок пока нет
- Review of Anatomy and Physiology of Blood Vessels and BloodДокумент9 страницReview of Anatomy and Physiology of Blood Vessels and BloodDan Ataniel EnsaladaОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology (FINAL)Документ41 страницаPathophysiology (FINAL)Dan Ataniel EnsaladaОценок пока нет
- Teaching Plan: Significance in Nursing ManagementДокумент6 страницTeaching Plan: Significance in Nursing ManagementDan Ataniel EnsaladaОценок пока нет
- Case Study Uro FinalДокумент44 страницыCase Study Uro FinalDan Ataniel EnsaladaОценок пока нет
- Ana, Patho UroДокумент5 страницAna, Patho UroDan Ataniel EnsaladaОценок пока нет
- Principles of OrganizationДокумент7 страницPrinciples of OrganizationDan Ataniel EnsaladaОценок пока нет
- Need Motivates The Behaviour of A Person.: Human Needs TheoryДокумент8 страницNeed Motivates The Behaviour of A Person.: Human Needs TheoryDan Ataniel EnsaladaОценок пока нет
- A-Level Coordination (Kugonza)Документ41 страницаA-Level Coordination (Kugonza)kasumbaashraf3Оценок пока нет
- Adrenal Cortex HormonesДокумент21 страницаAdrenal Cortex HormonesAaa JjjjОценок пока нет
- Endocrine System: Dr. Dedi Ardinata, M.Kes Physiology Department Medical School of University Sumatera UtaraДокумент94 страницыEndocrine System: Dr. Dedi Ardinata, M.Kes Physiology Department Medical School of University Sumatera UtaraAdryansyah ChaniagoОценок пока нет
- Terpenes and SteroidsДокумент38 страницTerpenes and SteroidsZabrina Tan CuaОценок пока нет
- Adrenal Cortex DR - GomezДокумент13 страницAdrenal Cortex DR - Gomezvicbart11Оценок пока нет
- Kumar2018 ReferenceWorkEntry EndocrineSystem PDFДокумент26 страницKumar2018 ReferenceWorkEntry EndocrineSystem PDFRamchand Bruce PhagooОценок пока нет
- Effect of Adrenocorticoid HyperfunctionДокумент3 страницыEffect of Adrenocorticoid HyperfunctionNurkhairunnisa A. KadirОценок пока нет
- Suprarenal GlandДокумент19 страницSuprarenal GlandKay BristolОценок пока нет
- Battens Disease ReadingДокумент23 страницыBattens Disease Readinghimanshugupta811997Оценок пока нет
- Endocrine PhysiologyДокумент197 страницEndocrine Physiologyrediet shimekachОценок пока нет
- Depart. Farmakologi Dan Terapeutik: Universitas Sumatera Utara-MedanДокумент19 страницDepart. Farmakologi Dan Terapeutik: Universitas Sumatera Utara-MedanMasyithah TetaОценок пока нет
- Adrenal CortexДокумент8 страницAdrenal CortexEdward XiamОценок пока нет
- FS APD Adrenal Insufficiency EN612Документ2 страницыFS APD Adrenal Insufficiency EN612egyseptiansyahОценок пока нет
- 3-Adrenal Glands and Its Hormones-MWДокумент103 страницы3-Adrenal Glands and Its Hormones-MWAbditsion DhiisaniiОценок пока нет
- Goodman Aula 1 e 2Документ17 страницGoodman Aula 1 e 2Danilo TetОценок пока нет
- Chapt 18 WorksheetДокумент15 страницChapt 18 WorksheetSaraОценок пока нет
- Endocrine Answer KeyДокумент10 страницEndocrine Answer KeyJoyce LimОценок пока нет