Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
OSI Model Layers: Layer Function Protocols Network Components Application
Загружено:
John SextonОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
OSI Model Layers: Layer Function Protocols Network Components Application
Загружено:
John SextonАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
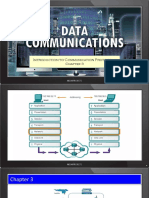
OSI Model Layers
Layer Application
User Interface
Function
used for applications specifically written to run over the network allows access to network services that support applications; directly represents the services that directly support user applications handles network access, flow control and error recovery Example apps are file transfer,e-mail, NetBIOSbased applications Translates from application to network format and vice-versa all different formats from all sources are made into a common uniform format that the rest of the OSI model can understand responsible for protocol conversion, character conversion, data encryption / decryption, expanding graphics commands, data compression sets standards for different systems to provide seamless communication from multiple protocol stacks not always implemented in a network protocol
Protocols
Network Components
DNS; FTP; TFTP; Gateway BOOTP; SNMP;RLOGIN; SMTP; MIME; NFS; FINGER; TELNET; NCP; APPC; AFP; SMB
Presentation
Translation
Gateway Redirector
Session
"syncs and sessions"
establishes, maintains and ends sessions across NetBIOS the network responsible for name recognition (identification) Names Pipes so only the designated parties can participate in the session Mail Slots provides synchronization services by planning check points in the data stream => if session fails, only data after the most recent checkpoint need RPC be transmitted manages who can transmit data at a certain time and for how long Examples are interactive login and file transfer connections, the session would connect and reconnect if there was an interruption; recognize names in sessions and register names in history additional connection below the session layer manages the flow control of data between parties across the network divides streams of data into chunks or packets; the transport layer of the receiving computer reassembles the message from packets "train" is a good analogy => the data is divided into identical units
Gateway
Transport
packets; flow control & error-handling
TCP, ARP, RARP; Gateway SPX NWLink Brouter NetBIOS / Advanced Cable Tester
provides error-checking to guarantee error-free data delivery, with on losses or duplications provides acknowledgment of successful transmissions; requests retransmission if some packets dont arrive error-free provides flow control and error-handling translates logical network address and names to their physical address (e.g. computername ==> MAC address) responsible for o addressing o determining routes for sending o managing network problems such as packet switching, data congestion and routing if router cant send data frame as large as the source computer sends, the network layer compensates by breaking the data into smaller units. At the receiving end, the network layer reassembles the data
NetBEUI ATP
Network
addressing; routing
IP; ARP; RARP, Brouter ICMP; RIP; OSFP; Router IGMP; Frame Relay IPX Device NWLink NetBEUI OSI ATM Switch Advanced Cable Tester
think of this layer stamping the addresses on each DDP train car turns packets into raw bits 100101 and at the receiving end turns bits into packets. handles data frames between the Network and Physical layers the receiving end packages raw data from the Physical layer into data frames for delivery to the Network layer responsible for error-free transfer of frames to other computer via the Physical Layer
Data Link
data frames to bits
DECnet Logical Link Control
Bridge Switch
error correction and ISDN Router flow control manages link control and Intelligent Hub defines SAPs
this layer defines the methods used to transmit 802.1 OSI Model and receive data on the network. It consists of the wiring, the devices use to connect the NIC to the 802.2 Logical Link wiring, the signaling involved to transmit / Control receive data and the ability to detect signaling Media Access errors on the network media
NIC
Advanced Cable Tester
Control
communicates with the adapter card controls the type of media being used:
802.3 CSMA/CD (Ethernet) 802.4 Token Bus
(ARCnet) 802.5 Token Ring 802.12 Demand Priority IEEE 802
Physical
hardware; raw bit stream
transmits raw bit stream over physical cable defines cables, cards, and physical aspects defines NIC attachments to hardware, how cable IEEE 802.2 is attached to NIC ISO 2110 defines techniques to transfer bit stream to cable ISDN
Repeater Multiplexer Hubs
Passive Active
TDR Oscilloscope Amplifier
Вам также может понравиться
- Networking Project ReportДокумент47 страницNetworking Project Reportmansha9933% (3)
- Cheat SheetДокумент2 страницыCheat SheetDevan TillyОценок пока нет
- User Manual JetWave 2212SДокумент89 страницUser Manual JetWave 2212SDurga Prasad SharmaОценок пока нет
- Technical Seminar Report On Wireless Application ProtocolДокумент25 страницTechnical Seminar Report On Wireless Application ProtocolPankaj Dubey100% (4)
- Provides Interface To End-Users Processes Provides Standardized Services To Applications FunctionДокумент8 страницProvides Interface To End-Users Processes Provides Standardized Services To Applications FunctionSushil SharmaОценок пока нет
- 98-366 MVA Slides Lesson 2Документ29 страниц98-366 MVA Slides Lesson 2cvigaОценок пока нет
- OSI Model Reference TableДокумент4 страницыOSI Model Reference Tablem_karthikeyan1118264Оценок пока нет
- OSI Model Reference TableДокумент4 страницыOSI Model Reference Tablem_karthikeyan1118264Оценок пока нет
- Defining Networks With The OSI ModelДокумент29 страницDefining Networks With The OSI ModelPradeep ManralОценок пока нет
- OSI FinalДокумент16 страницOSI FinalBMLIVEОценок пока нет
- CCNA 640-802 Study Guide: Tutorial Quick LinksДокумент14 страницCCNA 640-802 Study Guide: Tutorial Quick Linksahmad_naser12Оценок пока нет
- Types of NetworksДокумент13 страницTypes of NetworkssumitОценок пока нет
- NetworkingДокумент55 страницNetworkingRey Allen TenosoОценок пока нет
- Network Protocols: Lecturer SlidesДокумент33 страницыNetwork Protocols: Lecturer SlidesevhyajahОценок пока нет
- The OSI Model: Layer 1 - PhysicalДокумент7 страницThe OSI Model: Layer 1 - PhysicalJon FordОценок пока нет
- Network Protocol and TCPДокумент5 страницNetwork Protocol and TCPJoshua SantillanaОценок пока нет
- OSI Model Concepts: Layer 1 - PhysicalДокумент6 страницOSI Model Concepts: Layer 1 - PhysicalZarrish Marcel AsherОценок пока нет
- OSI Model:: Application CiscoДокумент16 страницOSI Model:: Application CiscoHAINHDT2Оценок пока нет
- "Please Do Not Throw Sausage Pizza Away": Layer 7: Application LayerДокумент3 страницы"Please Do Not Throw Sausage Pizza Away": Layer 7: Application LayerAndres GonzalezОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2Документ8 страницLecture 2jasmhmyd205Оценок пока нет
- OSI Model & Tcp/Ip ProtocolДокумент31 страницаOSI Model & Tcp/Ip ProtocolSauabh SrivastavaОценок пока нет
- CCNA 640-802 Study Guide: A P S T N D PДокумент8 страницCCNA 640-802 Study Guide: A P S T N D PPietersen VinothОценок пока нет
- Asics F Nternet: UNIT-4Документ26 страницAsics F Nternet: UNIT-4Gaurav TharejaОценок пока нет
- The Layers of TCPДокумент2 страницыThe Layers of TCPNaveen RecizОценок пока нет
- Company Profile: Centre For Electronic Governance (CEG)Документ32 страницыCompany Profile: Centre For Electronic Governance (CEG)jain21ankitОценок пока нет
- Computer CommunicationДокумент7 страницComputer Communicationsaravanamuthaly1397Оценок пока нет
- Introduction To 7 Layer OSI ModelДокумент35 страницIntroduction To 7 Layer OSI ModelMin Kwon100% (1)
- Cloud NetworkingДокумент26 страницCloud NetworkingHeliosОценок пока нет
- Sub Netting - Apjohns0 Ch01-Where We'Ve BeenДокумент50 страницSub Netting - Apjohns0 Ch01-Where We'Ve Beenpeterpan0420Оценок пока нет
- Computer Networks Set 2Документ19 страницComputer Networks Set 2madhavibandari609Оценок пока нет
- OSI Layers and ProtocolsДокумент5 страницOSI Layers and Protocolsapi-3805926Оценок пока нет
- 5 Internet ProtocolsДокумент41 страница5 Internet Protocolsstephenhilario3434Оценок пока нет
- COEN 3193 (Data Communications) - Chapter 3Документ80 страницCOEN 3193 (Data Communications) - Chapter 3Joel ManacmulОценок пока нет
- NetworkДокумент82 страницыNetworkDavidoffОценок пока нет
- Jason Zandri : TCP/IP Protocol Within Windows XP ProfessionalДокумент29 страницJason Zandri : TCP/IP Protocol Within Windows XP ProfessionalruvinduОценок пока нет
- Network Models: Ambo University Woliso Campus Technology and Informatics School Department of Computer ScienceДокумент73 страницыNetwork Models: Ambo University Woliso Campus Technology and Informatics School Department of Computer ScienceNoel GirmaОценок пока нет
- The Open Systems InterconnectДокумент9 страницThe Open Systems InterconnectJay ShreeОценок пока нет
- Network Protocol ArchitecturesДокумент17 страницNetwork Protocol Architecturesamash.emillyОценок пока нет
- Week 3Документ5 страницWeek 3hiren_keepsmilingОценок пока нет
- 4.osi LayersДокумент48 страниц4.osi LayersSami AhmedОценок пока нет
- OSI MODEL AssДокумент16 страницOSI MODEL AssMatovu HerbertОценок пока нет
- 01 Networking ConceptsДокумент39 страниц01 Networking Concepts四月的奥德赛Оценок пока нет
- CCNA1 M2 Networking FundamentalsДокумент28 страницCCNA1 M2 Networking FundamentalsAko Si NonongОценок пока нет
- Seven Layers of OSI Reference ModelДокумент4 страницыSeven Layers of OSI Reference ModelpervezkanjuОценок пока нет
- Ccna Basic FinalДокумент273 страницыCcna Basic FinalTanuОценок пока нет
- 1.1: Networking Theory & Java Overview: Prepared By: Siti Nur Ain FTK 2016Документ38 страниц1.1: Networking Theory & Java Overview: Prepared By: Siti Nur Ain FTK 2016ainnОценок пока нет
- Cisco Three Layer Vs OSI LayersДокумент8 страницCisco Three Layer Vs OSI LayersDinesh LoitongbamОценок пока нет
- FAQ'sДокумент24 страницыFAQ'sduvvuruvitОценок пока нет
- Fundamental Network ModelsДокумент9 страницFundamental Network ModelsSailas Khulumani TshabanguОценок пока нет
- DCC Chapter 5 Notes - Ur Engineering Friend (1st) DsadДокумент15 страницDCC Chapter 5 Notes - Ur Engineering Friend (1st) DsadychokhatОценок пока нет
- Unit-4: Iot Architecture and ProtocolsДокумент22 страницыUnit-4: Iot Architecture and ProtocolsMahesh ChauhanОценок пока нет
- Datacom LectureДокумент15 страницDatacom LecturexharlylejahnОценок пока нет
- Open System Interconnection Model (OSI)Документ38 страницOpen System Interconnection Model (OSI)SvetlanaОценок пока нет
- Chapter TwoДокумент71 страницаChapter TwoyaОценок пока нет
- 1.0 The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) ModelДокумент5 страниц1.0 The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) Modelvickypatel_63873791100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Device Configuration PDFДокумент24 страницыChapter 1 Device Configuration PDFShambel WorkuОценок пока нет
- Osi Model CompleteДокумент4 страницыOsi Model Completebaraynavab100% (9)
- 7-Layer OSI MODELДокумент11 страниц7-Layer OSI MODELBabu CamОценок пока нет
- Hacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisОт EverandHacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisОценок пока нет
- Introduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyОт EverandIntroduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Cisco Network Administration Interview Questions: CISCO CCNA Certification ReviewОт EverandCisco Network Administration Interview Questions: CISCO CCNA Certification ReviewРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (6)
- DH-IPC-HDBW5231E-ZE-HDMI: 2MP WDR IR Dome Network CameraДокумент3 страницыDH-IPC-HDBW5231E-ZE-HDMI: 2MP WDR IR Dome Network CameraIP solutionОценок пока нет
- 8.1.2.8 Lab - Converting IPv4 Addresses To BinaryДокумент4 страницы8.1.2.8 Lab - Converting IPv4 Addresses To Binarynexus22387% (39)
- 2 Element SyncДокумент64 страницы2 Element SyncRyankirimiОценок пока нет
- 520CMD01 DS enДокумент4 страницы520CMD01 DS enDJ ThangОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4: Network Layer: Prof James KuroseДокумент145 страницChapter 4: Network Layer: Prof James KuroseKalyankar SachinОценок пока нет
- CCNA1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer 2017 (100%) - CCNA v6.0 Exam 2018 PDFДокумент1 страницаCCNA1 v6.0 Final Exam Answer 2017 (100%) - CCNA v6.0 Exam 2018 PDFNouhailaОценок пока нет
- Hirschmann Industrial Hivision 2021 10 Pb283 EN LowResДокумент3 страницыHirschmann Industrial Hivision 2021 10 Pb283 EN LowResMrFelippeRodriguesОценок пока нет
- Sockets and Network Programming - Java Lecture 24Документ20 страницSockets and Network Programming - Java Lecture 24HelloОценок пока нет
- LTE Open Source HackerHaltedДокумент50 страницLTE Open Source HackerHaltedErnesto VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- Exam Az 800 Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure Skills MeasuredДокумент5 страницExam Az 800 Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure Skills Measuredtewiya AKOSSI100% (2)
- Patch Panels - FL-PP-RJ45-SCC - 2901642: Product Description Your AdvantagesДокумент10 страницPatch Panels - FL-PP-RJ45-SCC - 2901642: Product Description Your Advantageshsouna nasfiОценок пока нет
- Suh ContentДокумент7 страницSuh ContentSuhara JabeenОценок пока нет
- Horizontal Comm GooseДокумент80 страницHorizontal Comm Gooseranjith kumarОценок пока нет
- Module 3 STP and RSTP: Lab 3-1 Configuring STP Learning ObjectivesДокумент28 страницModule 3 STP and RSTP: Lab 3-1 Configuring STP Learning ObjectivesSokhna Cambell DIENGОценок пока нет
- Newsletter: Hardware + Software + Tools + EngineeringДокумент48 страницNewsletter: Hardware + Software + Tools + EngineeringHữu ĐứcОценок пока нет
- RADWIN 2000 Alpha Point-to-Point Series: 500 Mbps Carrier Class SolutionДокумент2 страницыRADWIN 2000 Alpha Point-to-Point Series: 500 Mbps Carrier Class SolutionMayori Najhara Nava DenkerОценок пока нет
- Data Link Layer: Unit - IIIДокумент24 страницыData Link Layer: Unit - IIIFrancis Densil RajОценок пока нет
- Network TopologyДокумент40 страницNetwork TopologyRez HabloОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Data TransmissionДокумент20 страницChapter 2 Data TransmissionMuhammad AounОценок пока нет
- Behavior of RIP Version 1 in Contiguous and Discontiguous Networks PDFДокумент6 страницBehavior of RIP Version 1 in Contiguous and Discontiguous Networks PDFCynthia Indah FebriyantiОценок пока нет
- Dos and Don'ts of Deploying NVMe Over Fabrics BRKDCN-3912 2023Документ344 страницыDos and Don'ts of Deploying NVMe Over Fabrics BRKDCN-3912 2023James Zhang100% (1)
- 0a-Esp8285 Datasheet enДокумент31 страница0a-Esp8285 Datasheet enJose JaramilloОценок пока нет
- R - S Week 1Документ54 страницыR - S Week 1Rani ShamasОценок пока нет
- Admission and Congestion Control (eRAN7.0 - 01)Документ104 страницыAdmission and Congestion Control (eRAN7.0 - 01)dnzgnsОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of 5g Wireless Communications Sachan Book 82 - CompressДокумент171 страницаFundamentals of 5g Wireless Communications Sachan Book 82 - CompressBijoy BanerjeeОценок пока нет
- D Link Lan Card Driver Dl10028a PDFДокумент3 страницыD Link Lan Card Driver Dl10028a PDFjiban chatterjeeОценок пока нет
- Connecting Arduino Programming and Networking With The Ethernet Shield - Bob HammellДокумент226 страницConnecting Arduino Programming and Networking With The Ethernet Shield - Bob HammellBaciu Vlad-Eusebiu92% (13)
- CN - Unit4.2-1Документ23 страницыCN - Unit4.2-1Kanika TyagiОценок пока нет