Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Could Be Advantageous in The Following Cases
Загружено:
prashant832Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Could Be Advantageous in The Following Cases
Загружено:
prashant832Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
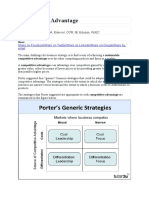
The Strategy Clock Strategies Likely to be Failure ( 6,7,8) Increased Price/Standard Value - - - When highermargins are realized if competitors
do not follow immediately; nut, risk losing market share Increased Price/Low Value - - - Only feasible inmonopoly situation Low Value/Standard Price - - - Risk Loosing of Market Share
No Frills Strategy Low priceLow perceived product/service benefitsFocus on price-sensitive market segment Low priceLow perceived product/servicebenefitsFocus on price-sensitive marketsegment For Commodity-like products or services For non-affording Price Sensitive Customers When buyer power is or when switching costsare low; generally, if customer loyalty is difficult When number of providers are small, and ifmarket shares & cost structures are almost same For low-price segment If major competitors areon non-prise basis Low Price Strategy - Lower price than competitors- Maintain similar product/service benefits Pitfalls of low price strategy Margin reduction (Competitor reaction) Inability to reinvest to develop the product,leading to loss of perceived benefit of product Hence, Low Cost Base is essential Low cost by itself may not be a basis foradvantage since it could be imitated. Hence, Low cost achieved in ways that competitorscannot match to give sustainable advantage
Differentiation Strategies 1. Offering benefits different from competitors2. Widely valued by buyers3. Better products/services at same/higher prices Success depends on Identification of StrategicCustomers and knowing what they value,And, on Knowing the Competitors- Adopt Focused differentiation if competitorbase is small/narrow- If competitor base is wide, address on whatparameters differentiate for value to customers Hybrid Strategy Simultaneously achieving differentiation & lower price Could be advantageous in the following cases If much greater greater volumes can be achieved thancompetitors, thus decreasing costs to enlarge margins If there is clarity about activities on whichdifferentiation can be built (core competences) And, be able to reduce costs on other activities Use the Hybrid Strategy to enter a market wherethere are already established competitors Focused Differentiation High perceived product/service benefits to nichemarket segments & Premium branded products
First, Choice to be made between focuseddifferentiation (5) and broad differentiation (4) Difficult when the focus strategy is applicable onlyfor part of an organizations overall strategy Possible conflicts with stakeholder expectations,when the focused benefits are not uniform New ventures usually start off this way, but it maybe difficult to grow with focused approach Market situation may change, making focusirrelevant, if differences in segments get reduced
Failure Strategies Results if perceived value-for-money doesnot get provided in terms of productfeatures or price, or both For example, Increase price withoutincreasing benefits in products orservices Or, Reduce benefits whilst maintainingprice
Sustaining Competitive Advantage When the Strategies are price based: Be ready to accept reduced margin ( either because higher volumes or by cross-subsidies ) Get ready to sustain and Win a Price War Reduce Costs through organization specificstrategic capabilities Focus on Specific Segments that value price Sustaining Competitive Advantage If the Strategies are differentiation-based: Create Difficulties of imitation Achieve imperfect mobility (of resources/competences e.g. key R & Dpersonnel) Many intangible assets such as brand, image orreputation are difficult for imitation Sustaining Competitive Advantage Derive sustenance by achieving Lock-in Status - - -- achieving proprietary position in the industry bycreating the industrys standard - - like what IBM,or Microsoft, Xerox, Intel had achieved By Achieving Size/Market Dominance By deriving First Mover Advantage Reinforcement Rigorous Enforcement thorough insistence onconformities to standards thus seeing off competitors
Вам также может понравиться
- Copy Trading Secrets GuideДокумент22 страницыCopy Trading Secrets Guidearies_teaОценок пока нет
- Porter's Five Forces: Understand competitive forces and stay ahead of the competitionОт EverandPorter's Five Forces: Understand competitive forces and stay ahead of the competitionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (10)
- Business Level StrategiesДокумент28 страницBusiness Level StrategiesAditi ChandraОценок пока нет
- Strategic Management Competitive AdvantageДокумент3 страницыStrategic Management Competitive AdvantageUpendra RaoОценок пока нет
- Castrol Oil - Consumer Behavior of in Pune CityДокумент47 страницCastrol Oil - Consumer Behavior of in Pune CitySohel Bangi100% (1)
- Housing Book One Web Single PDFДокумент194 страницыHousing Book One Web Single PDFAnton ŽakovičОценок пока нет
- Strategy and Competitive Advantage Chapter 6Документ7 страницStrategy and Competitive Advantage Chapter 6Drishtee DevianeeОценок пока нет
- Generic StrategiesДокумент7 страницGeneric StrategiesMagnus ColacoОценок пока нет
- On Competitive StrategiesДокумент33 страницыOn Competitive Strategiesmmjmmj100% (1)
- Porter's Generic StrategiesДокумент3 страницыPorter's Generic StrategiesAhmed ElGeoshyОценок пока нет
- Financial Accounting and Reporting - QUIZ 5Документ4 страницыFinancial Accounting and Reporting - QUIZ 5JINGLE FULGENCIOОценок пока нет
- Leadership, Differentiation, and Focus. These Strategies Are Applied at TheДокумент4 страницыLeadership, Differentiation, and Focus. These Strategies Are Applied at TheromirathiОценок пока нет
- Strategic Management Assignment 3Документ14 страницStrategic Management Assignment 3Djimajor Robert TettehОценок пока нет
- Competitive StrategyДокумент16 страницCompetitive Strategyaerogem100% (2)
- Competitive Advantage: Chapter 7 & 8 (Part One)Документ41 страницаCompetitive Advantage: Chapter 7 & 8 (Part One)Akash DhillonОценок пока нет
- Building Competitive Advantage Through Business-Level StrategyДокумент33 страницыBuilding Competitive Advantage Through Business-Level StrategyRizwan Sait100% (2)
- The Five Generic Competitive StrategiesДокумент11 страницThe Five Generic Competitive StrategiesMonoar HossainОценок пока нет
- Diversification & Porters Generic StategiesДокумент11 страницDiversification & Porters Generic StategiesvaryushОценок пока нет
- Porter's Generic StrategiesДокумент4 страницыPorter's Generic StrategiesAshish PereОценок пока нет
- PSI PlanningДокумент2 страницыPSI Planningferrymanuputty4147100% (1)
- Porter's Generic StrategiesДокумент4 страницыPorter's Generic StrategiesJayanta RakshitОценок пока нет
- Cafe Coffee Day PESTLE, Porter's Five ForcesДокумент15 страницCafe Coffee Day PESTLE, Porter's Five ForcesSpoorthi N Swamy0% (1)
- Chapter 5-Kapil DoshiДокумент50 страницChapter 5-Kapil DoshiRutika VyasОценок пока нет
- Business Management 3B Exam NotesДокумент39 страницBusiness Management 3B Exam NotesTashaОценок пока нет
- Competitive StrategyДокумент44 страницыCompetitive StrategyJH ITОценок пока нет
- Business Level StrategyДокумент36 страницBusiness Level StrategyEmranul Islam ShovonОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4: Business-Level Strategy: OverviewДокумент22 страницыChapter 4: Business-Level Strategy: OverviewTeerraОценок пока нет
- Porter Generic StrategiesДокумент4 страницыPorter Generic StrategiesDave DeОценок пока нет
- Strategy Formulation at Strategic Business Unit LevelДокумент20 страницStrategy Formulation at Strategic Business Unit Leveldulshan jeewanthaОценок пока нет
- SM 6Документ22 страницыSM 6Ayesha TariqОценок пока нет
- Business Level StrategiesДокумент4 страницыBusiness Level StrategiesSasi KumarОценок пока нет
- Porter's Generic Strategies: Cost Leadership DifferentiationДокумент5 страницPorter's Generic Strategies: Cost Leadership DifferentiationbiswasjoyОценок пока нет
- Competitive AdvantageДокумент41 страницаCompetitive AdvantageGurmeet KamraОценок пока нет
- Business Level Strategies-1Документ7 страницBusiness Level Strategies-1Øfficial AßhiОценок пока нет
- Business-Level StrategyДокумент22 страницыBusiness-Level StrategyVijay Singh Kumar VijayОценок пока нет
- Strategic PositioningДокумент13 страницStrategic PositioningleesadzebondeОценок пока нет
- GRP5 GCSДокумент42 страницыGRP5 GCSThilak AlvaОценок пока нет
- Business Level StrategyДокумент5 страницBusiness Level StrategyMahajuba JabinОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Resumen y CasoДокумент6 страницChapter 5 Resumen y CasoPolly GarcíaОценок пока нет
- 11 1204 Porter StrategyДокумент13 страниц11 1204 Porter Strategyanna rambuОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 - Global Business-Level Strategies - Choosing Competitive Strategies in A Single IndustryДокумент17 страницChapter 4 - Global Business-Level Strategies - Choosing Competitive Strategies in A Single IndustryHà Nhi LêОценок пока нет
- International StrategyДокумент23 страницыInternational StrategySumeet SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Strategic ManagementДокумент6 страницStrategic ManagementDhushor SalimОценок пока нет
- The Five Generic Competitive Strategies: Presentation by Omkar, Vijay and DilleshwarДокумент20 страницThe Five Generic Competitive Strategies: Presentation by Omkar, Vijay and DilleshwarEverton Snow MuberekwaОценок пока нет
- SM 11 PDFДокумент45 страницSM 11 PDFSamridh AgarwalОценок пока нет
- Stratma MaДокумент17 страницStratma MaMae TndnОценок пока нет
- S.M. (C-5) Mid (Arafat)Документ7 страницS.M. (C-5) Mid (Arafat)0012 Shah Md. Arafat [C]Оценок пока нет
- What Are Porter's Generic Strategies?Документ4 страницыWhat Are Porter's Generic Strategies?Farida KalufyaОценок пока нет
- PorterДокумент31 страницаPorterKashif Niaz Meo100% (1)
- Chapter 5Документ7 страницChapter 5ERICKA MAE NATOОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ7 страницChapter 2jalaja munirajuОценок пока нет
- Pricing StrategyДокумент15 страницPricing Strategy정마이Оценок пока нет
- Competitive AdvantageДокумент3 страницыCompetitive AdvantageAnonymous X8hNvFAyzОценок пока нет
- SM Mod 05Документ60 страницSM Mod 05Kavi_3788Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 6Документ1 страницаChapter 6Eika BorjaОценок пока нет
- Do You Have A Competitive StrategyДокумент12 страницDo You Have A Competitive StrategysvdangyeuОценок пока нет
- Group IVДокумент4 страницыGroup IVkaye zuluetaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Strategic ChoiceДокумент39 страницChapter 5 Strategic Choiceprasad guthiОценок пока нет
- Strategies: Unit - 3Документ28 страницStrategies: Unit - 3Mythili MaragathamОценок пока нет
- BLSДокумент21 страницаBLSArvind MehtaОценок пока нет
- The Five Generic Competitive Strategies: Chapter TitleДокумент24 страницыThe Five Generic Competitive Strategies: Chapter TitleKishor ParmarОценок пока нет
- Day 11Документ33 страницыDay 11Shailee MehtaОценок пока нет
- Competitive Advantage: Print Page Share On Facebook Share On Twitter Share On Linkedin Share On Google Share by EmailДокумент3 страницыCompetitive Advantage: Print Page Share On Facebook Share On Twitter Share On Linkedin Share On Google Share by EmailAarthi MuthusamiОценок пока нет
- The Five Generic Competing StrategiesДокумент30 страницThe Five Generic Competing StrategiesFarhana MituОценок пока нет
- Strategy Management Chp. 4-Business Level StrategyДокумент8 страницStrategy Management Chp. 4-Business Level StrategyNabilah UsmanОценок пока нет
- Value-based Intelligent Pricing: Marketing and Business, #1От EverandValue-based Intelligent Pricing: Marketing and Business, #1Оценок пока нет
- Business To Business MarketingДокумент5 страницBusiness To Business MarketingRicha Mittal100% (1)
- Klaus Uhlenbruck - Hochland CaseДокумент15 страницKlaus Uhlenbruck - Hochland CaseAvogadro's ConstantОценок пока нет
- 14Mkt Intervention Q&AДокумент14 страниц14Mkt Intervention Q&AJacquelyn ChungОценок пока нет
- UrbanGov GSDRCДокумент60 страницUrbanGov GSDRCHimgiri AuthorsОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4Документ12 страницChapter 4divaОценок пока нет
- Assignment 2 - Financial Statement AnalysisДокумент6 страницAssignment 2 - Financial Statement AnalysisGennia Mae MartinezОценок пока нет
- Electronic Payment Systems Development in A DeveloДокумент17 страницElectronic Payment Systems Development in A DeveloMinh ThưОценок пока нет
- Apple PresentationДокумент35 страницApple PresentationShihabAkhandОценок пока нет
- NI Approach MainДокумент9 страницNI Approach MainRevati ShindeОценок пока нет
- Actividad 8 Doing Business in The AmericasДокумент3 страницыActividad 8 Doing Business in The AmericasAntonio NaelsonОценок пока нет
- Bobs Coffee ShopДокумент1 страницаBobs Coffee Shopz zzzОценок пока нет
- WP Contentuploads201804ECONOMICS PDFДокумент9 страницWP Contentuploads201804ECONOMICS PDFGød's wïllОценок пока нет
- Marketing & Communications Objectives, Strategies, Tactics: Let's Start With The First Set of SlidesДокумент5 страницMarketing & Communications Objectives, Strategies, Tactics: Let's Start With The First Set of Slidesmuhammad arya tamaОценок пока нет
- Marketing Strategy and Consumer BehaviorДокумент6 страницMarketing Strategy and Consumer BehaviorSamuel MichaelОценок пока нет
- Barra China Equity Model (CNE5) FactsheetДокумент2 страницыBarra China Equity Model (CNE5) FactsheetDominic TsuiОценок пока нет
- Siemens Finance Case StudyДокумент9 страницSiemens Finance Case StudyJohnОценок пока нет
- Product Management and Its Interface With Other OrganizationalДокумент8 страницProduct Management and Its Interface With Other OrganizationalSamantha Rent To OwnОценок пока нет
- Acquisition Based LearningsДокумент32 страницыAcquisition Based LearningsVarun SharmaОценок пока нет
- Test-Bank-Accounting-Management-11e-Chapter-14-Cost-Allocation-Customer-Profitability-Analysis-And-Sales-Variance-Anaylsis (Документ17 страницTest-Bank-Accounting-Management-11e-Chapter-14-Cost-Allocation-Customer-Profitability-Analysis-And-Sales-Variance-Anaylsis (Jalil AhmedОценок пока нет
- Bcom Airtel Project CRMДокумент82 страницыBcom Airtel Project CRMChandini SehgalОценок пока нет
- Ch06 Solations Brigham 10th EДокумент32 страницыCh06 Solations Brigham 10th ERafay HussainОценок пока нет
- State Preference Theory ProblemsДокумент2 страницыState Preference Theory ProblemsGrim ReaperОценок пока нет
- Edit 2022-23 - Textes 1 - Assignments - Enjeux Mondialisation EUДокумент30 страницEdit 2022-23 - Textes 1 - Assignments - Enjeux Mondialisation EUirolines kolaplОценок пока нет
- Instructional Material Product Management Topic 1Документ10 страницInstructional Material Product Management Topic 1Rita DanielaОценок пока нет